Bài giảng Quản lý công - Bài 14: Tiếp cận hệ thống và phức hợp trong quản lý công
• Từ đầu thế kỷ 21 đến nay, nhiều nhà lý
thuyết và thực hành quản lý công đã
bắt đầu nhìn nhận nhiều vấn đề công
(kinh tế, quy hoạch, giao thông, y tế,
môi trường), theo góc độ hệ thống,
liên ngành, biến động và khó lường
thay vì cục bộ, đơn ngành, ổn định và
tiên lượng.
• “Stop pretending that an economy can
be controlled”, Angel Gurría, OECD
Secretary-General
• Tư duy/ tiếp cận hệ thống (systems
thinking/approach) và lý thuyết phức
hợp (complexity theory): cách tiếp cận
mới trong chính sách và quản lý công
hiện đại để giải quyết những vấn đề
trên.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Quản lý công - Bài 14: Tiếp cận hệ thống và phức hợp trong quản lý công", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Quản lý công - Bài 14: Tiếp cận hệ thống và phức hợp trong quản lý công

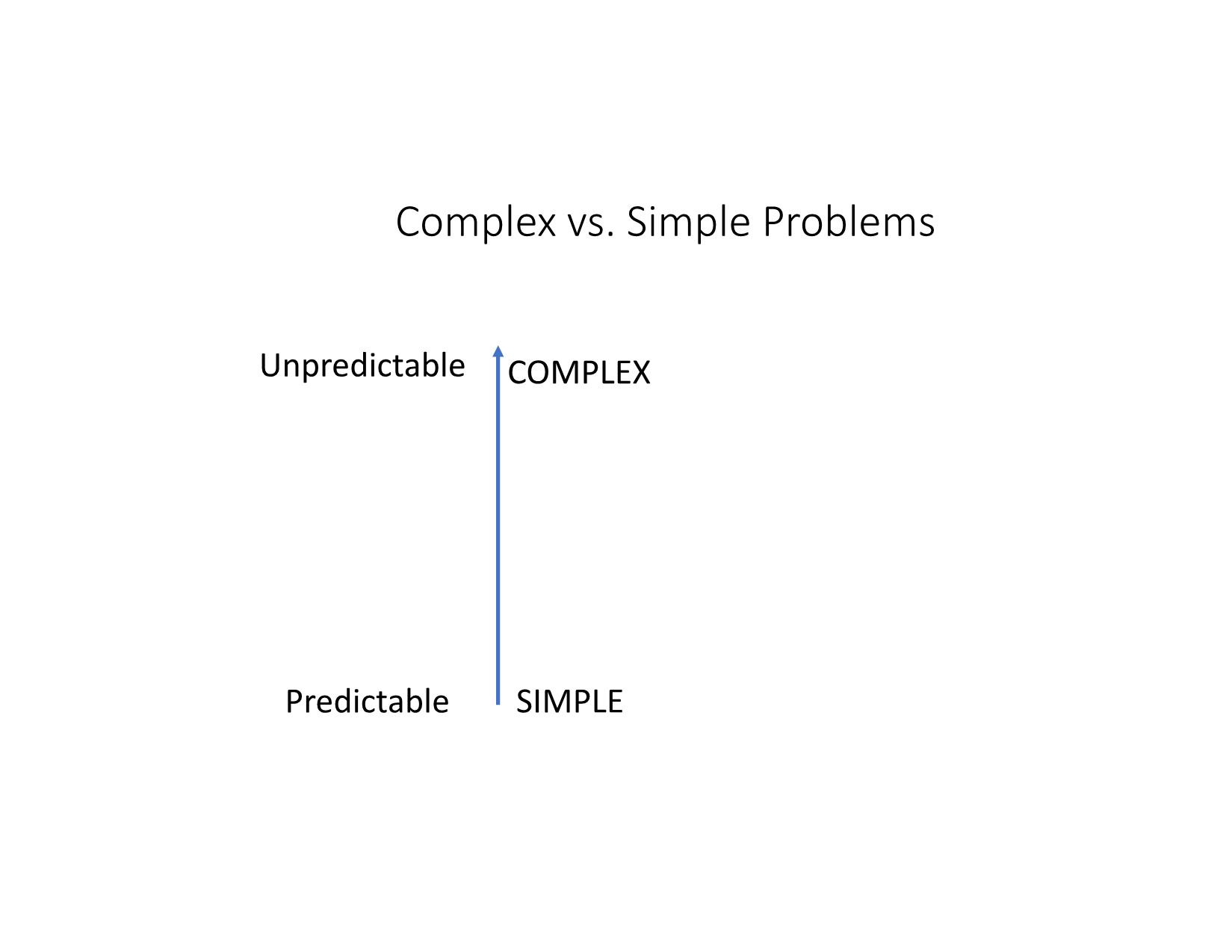
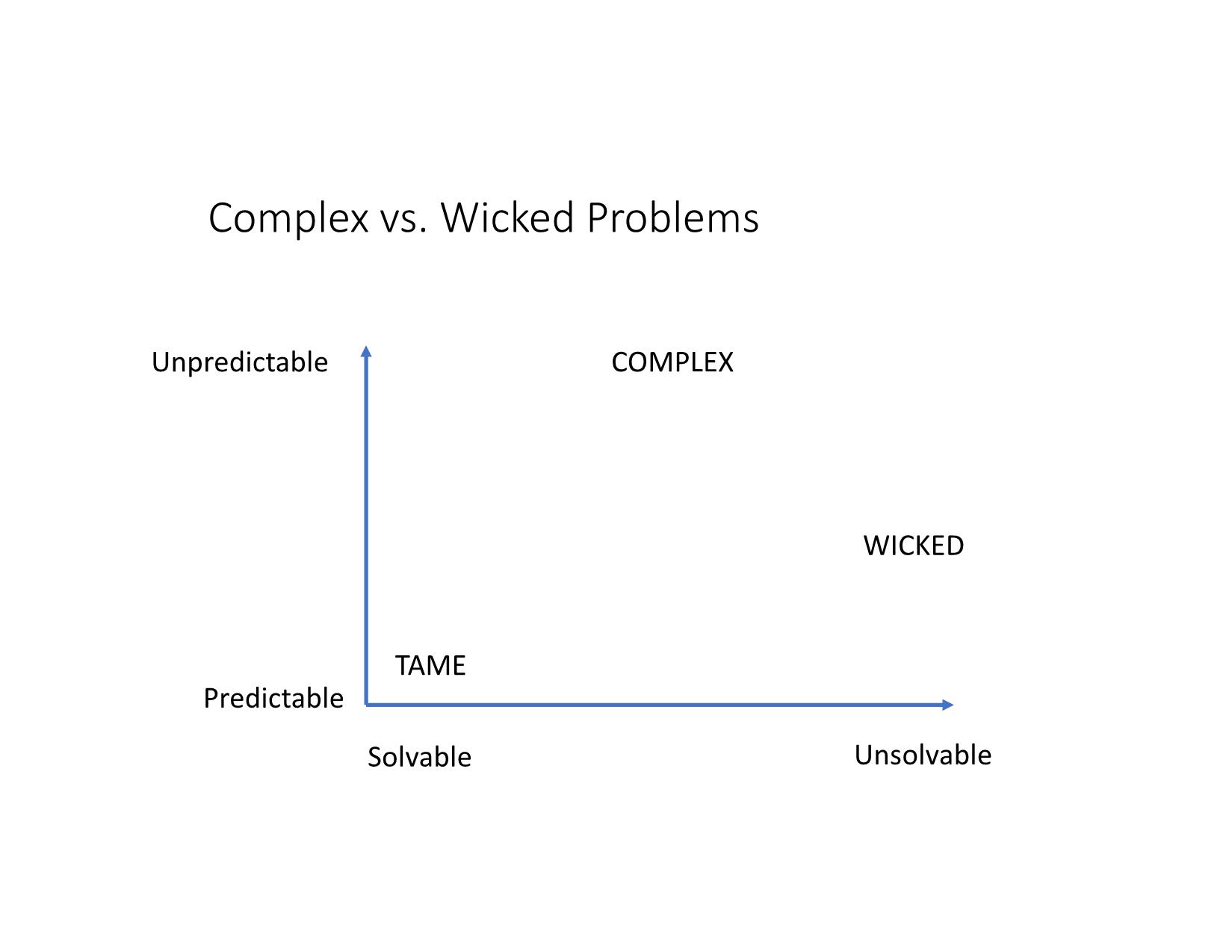
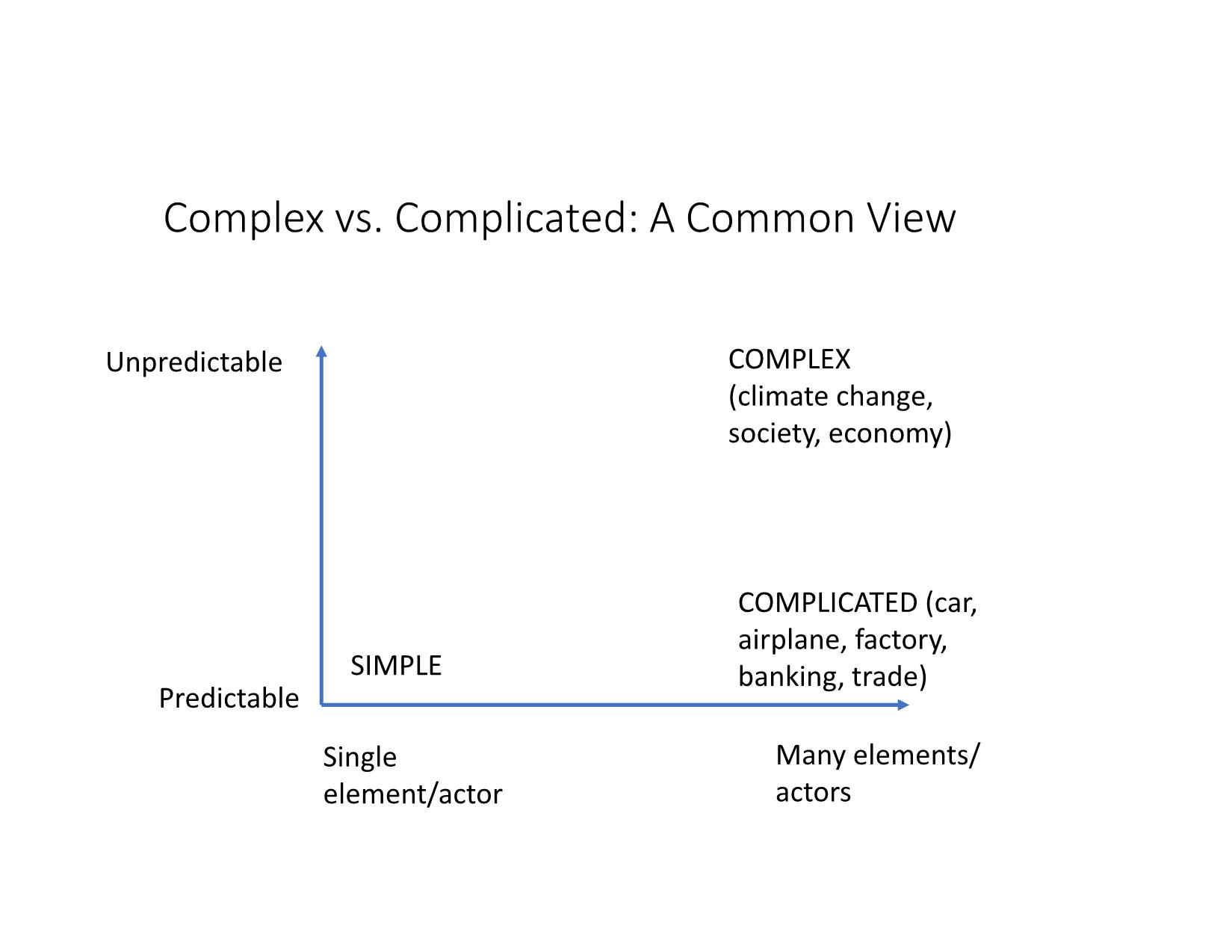
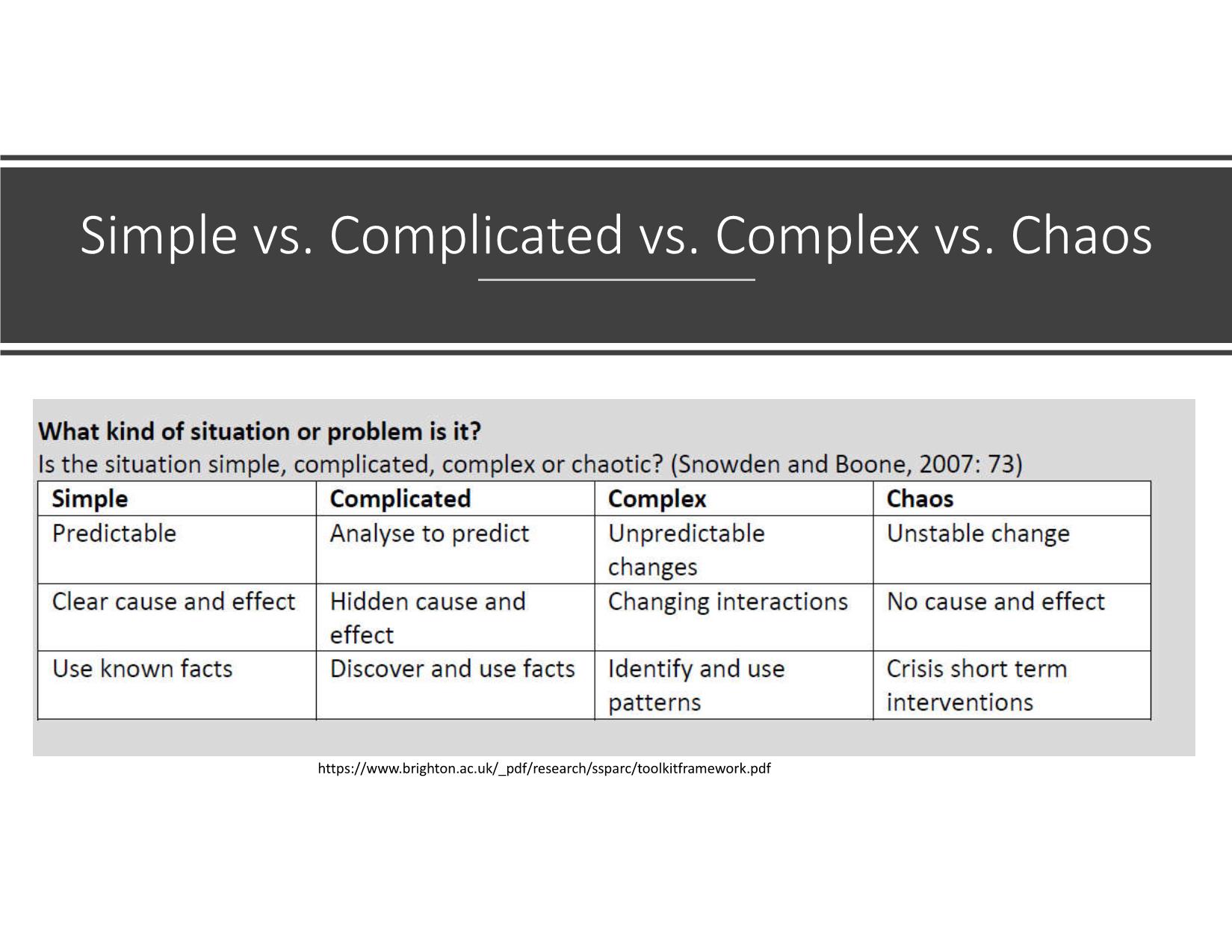
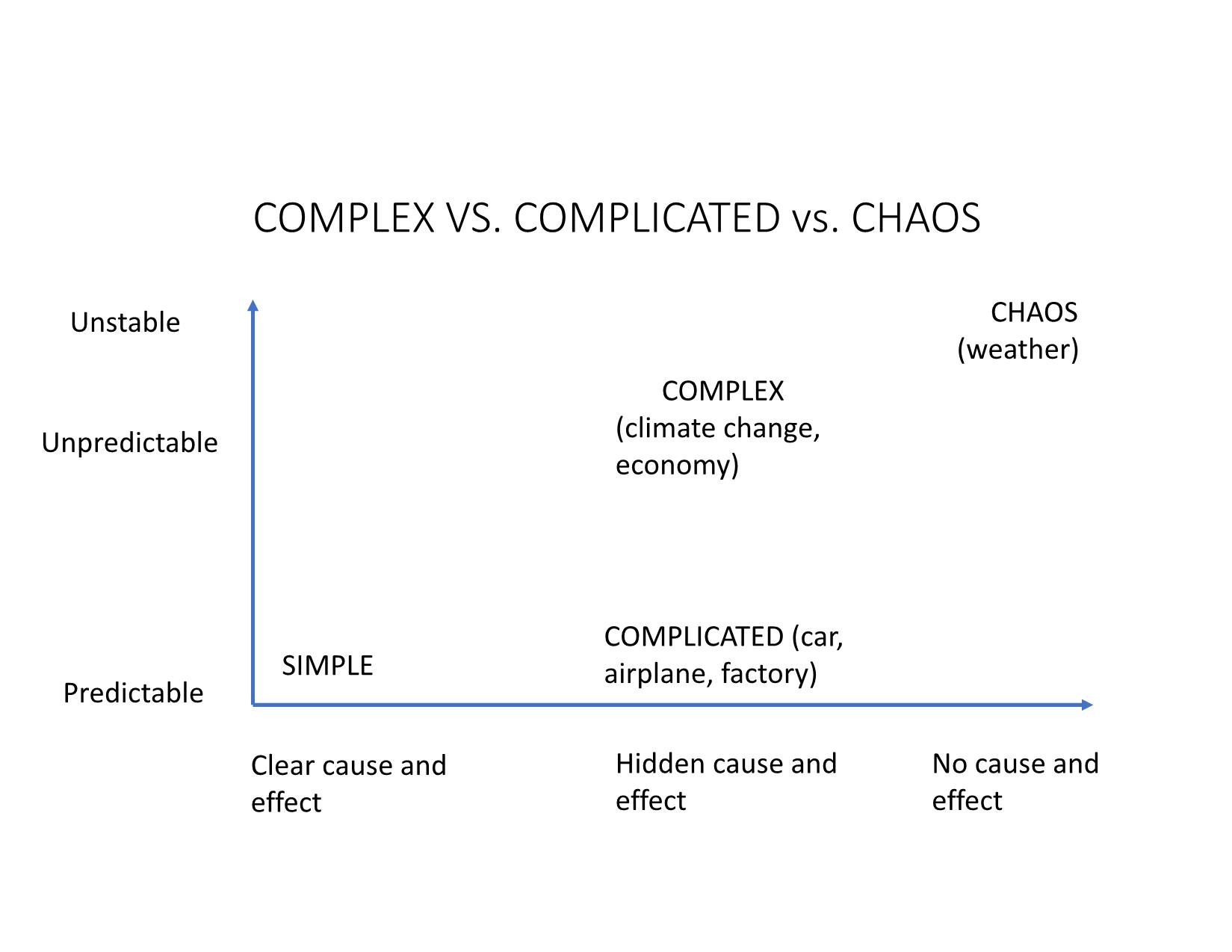
Quản Lý Công Bài 14: Tiếp cận Hệ thống và Phức hợp trong Quản lý công Nội dung Những vấn đề phức hợp (complex) trong quản lý công Tiếp cận hệ thống và phức hợp trong giải quyết những vấn đề công Thảo luận: Phòng, tránh sạt lở, lũ quét – cuộc chiến cấp bách Những vấn đề phức hợp trong quản lý công Khái niệm vấn đề phức hợp (complex) So sánh với vấn đề phức tạp (complicated) và nan giải (wicked) So sánh với hỗn loạn (chaos) Giới thiệu • Từ đầu thế kỷ 21 đến nay, nhiều nhà lý thuyết và thực hành quản lý công đã bắt đầu nhìn nhận nhiều vấn đề công (kinh tế, quy hoạch, giao thông, y tế, môi trường), theo góc độ hệ thống, liên ngành, biến động và khó lường thay vì cục bộ, đơn ngành, ổn định và tiên lượng. • “Stop pretending that an economy can be controlled”, Angel Gurría, OECD Secretary-General • Tư duy/ tiếp cận hệ thống (systems thinking/approach) và lý thuyết phức hợp (complexity theory): cách tiếp cận mới trong chính sách và quản lý công hiện đại để giải quyết những vấn đề trên. Complex issues • Newton world: predictable, deterministic, stable, order, rules, principles E.g. factory, bureaucracy, engineering, transportation, machinery, mechanics, construction • Complicated world: ultimately predictable with sufficient analysis and modelling E.g. banking regulation, trade treaties and healthcare systems • Complex world: unpredictable, uncertain, unstable, emergent, interactive, adaptive E.g. society, economy, urban development, traffic, biology, jungle, weather; COVID pandemic https://laodong.vn/dien-dan/tphcm-de-xuat-thu-phi-xe-oto-vao-trung-tam-de-giai-quyet- ket-xe-coi-chung-pha-san-565774.ldo https://tuoitre.vn/ket-xe-tai-tphcm-se-ngay-cang-tram-trong-968832.htm Complex vs. Simple Problems Predictable SIMPLE COMPLEXUnpredictable Complex vs. Wicked Problems Unsolvable Predictable TAME WICKED COMPLEX Solvable Unpredictable Complex vs. Complicated: A Common View Many elements/ actors Predictable SIMPLE COMPLICATED (car, airplane, factory, banking, trade) COMPLEX (climate change, society, economy) Single element/actor Unpredictable Simple vs. Complicated vs. Complex vs. Chaos https://www.brighton.ac.uk/_pdf/research/ssparc/toolkitframework.pdf COMPLEX VS. COMPLICATED vs. CHAOS Clear cause and effect Predictable SIMPLE COMPLICATED (car, airplane, factory) COMPLEX (climate change, economy) Hidden cause and effect No cause and effect CHAOS (weather) Unpredictable Unstable From complexity to chaos: Edward Lorenz’s “The Butterfly’s Effect” Tiếp cận hệ thống và phức hợp trong giải quyết những vấn đề công Tư duy/tiếp cận hệ thống Tiếp cận vấn đề công: truyền thống - hệ thống - phức hợp Giải quyết vấn đề nan giải và phức hợp Tư duy/tiếp cận hệ thống (systems approaches/thi nking) • System: • elements joined together by dynamics that produce an effect, create a whole or influence other elements and systems. • Systems exist on a spectrum of comprehensibility – from those easily observed and analysed to those that are highly complex or novel requiring postulation. • A system always exceeds the sum of its parts.” (OECD, 2017) • Complex adaptive system: “a system often involving human activities and dynamics that make it continuously emergent and with only limited predictability.” (OECD, 2017) Tư duy/tiếp cận hệ thống Traditional • “ceteris paribus” • Dependent, independent, controlled variables System • All other things change • Interdependent actors Tiếp cận vấn đề công: Truyền thống - hệ thống - phức hợp Truyền thống Hệ thống Phức hợp So sánh các cách tiếp cận vấn đề công Tr ad it io n al • Discipline • Vertical • Stable • Goals-based • Effective • Linear • Reductionist • Process/cycle Sy st em a p p ro ac h • Complicated • Predictable • Connection • Rules-based • Optimal/efficient • Rational choice • System analysis • Governance Networks C o m p le xi ty • Complex • Unpredictable • Interactive • Emergent • Adaptive • Dynamic • Evolving • Complex Adaptive System Four patterns and responses https://txm.com/making-sense-problems-cynefin-framework/ Giải quyết vấn đề nan giải và phức hợp • Solving wicked/complex problems by • complexity theory and governance networks as useful analytical tools • “situational awareness” for negotiating the complex systems (B&L). • Public Private Partnership (PPP) • Collaborative governance: multiple stakeholders (resources, sources of knowledge) • Complex networks of actors: complex adaptive system (CAS) https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/social-sustainability-past-and-future/role-of-the-complex- adaptive-systems-approach/F6F59CA8879515E3178770111717455A/core-reader Types of complexity (B&L) Substantive complexity Information shortage Ambiguity Strategic complexity: The complex set of actors With their different perceptions and interests. Institutional complexity •Network actors: from different cultures and diverse backgrounds. •Collaboration between actors from public and private domains may be problematic. •Networks embedded in a larger environment with many other networks: actors in various networks at different levels. How to respond to complexity Managing substantive complexity within governance networks • Learning about “frames” and consensus building • Win–win situations and enhancing variety • Enhancing the authoritativeness of experts and research Managing strategic complexity • Bonding through facilitation • Bonding through negotiation Managing institutional complexity • Network formation and change by boundary spanning • Enhancing and changing institutional rules • Managing internal and external feedback mechanisms. Complex Adaptive System (CAS) • Complexity theory: economics, weather, computer science, biology, society • CAS: “systems that have a large number of components, often called agents, that interact and adapt or learn” (Holland, in B &L); “robust patterns of organization and activity in systems that have no central control or authority.” • CAS: used to analyze social, biological and natural systems. • CAS characteristics: • Emergent • Dynamic • Interactive • Interdependent Source: Vietnam (exemplars.health) Thảo luận: “Phòng, tránh sạt lở, lũ quét” 1. Ưu/nhược điểm của tư duy hệ thống và phức hợp trong quản lý công. 2. Có áp dụng cách tiếp cận hệ thống và phức hợp với những vấn đề công ở Việt Nam được không? Nếu không, tại sao? Nếu được, như thế nào? 3. Tình trạng sạt lở, lũ quét ở miền Trung năm 2020 là vấn đề đơn giản, phức tạp, nan giải, phức hợp? Tại sao? Thử áp dụng tư duy hệ thống và phức hợp để nhìn nhận và phân tích vấn đề này.
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_quan_ly_cong_bai_14_tiep_can_he_thong_va_phuc_hop.pdf
bai_giang_quan_ly_cong_bai_14_tiep_can_he_thong_va_phuc_hop.pdf

