Tạp chí Nghề cá sông Cửu Long - Số 07/2016
TÓM TẮT
Nghiên cứu được thực hiện tại vùng rừng ngập mặn Thạnh Phong, Thạnh Hải, huyện Thạnh Phú,
tỉnh Bến Tre qua 5 đợt khảo sát từ tháng 4 đến tháng 8 năm 2014 với 330 mẫu nghêu giống, 60 mẫu
thức ăn trong ruột nghêu, 60 mẫu đất nền đáy đã được thu và đo một số chỉ tiêu chất lượng nước
tại 33 điểm bao gồm: 13 điểm vùng ven biển (lớp biển), 11 điểm vùng kênh rạch sát biển (lớp giữa)
và 9 điểm vùng rừng ngập mặn (lớp rừng). Mẫu nước được đo tại hiện trường các chỉ tiêu nhiệt
độ, độ muối, độ trong và pH. Mẫu đất được thu bằng khoan đất và gàu đáy chuyên dùng. Mẫu ấu
trùng nghêu phù du và nghêu giống được thu bằng lưới có kích thước mắt lưới tương ứng 30μm
và 1mm và được cố định bằng cồn. Mẫu phân tích thức ăn trong ruột nghêu và độ béo được tiến
hành bằng cách đo chiều cao, khối lượng nghêu không có vỏ, cố định ruột bằng dung dịch formol.
Mẫu được phân tích tại phòng thí nghiệm Viện Nghiên cứu Nuôi trồng Thủy sản II. Kết quả nghiên
cứu cho thấy, các yếu tố chất lượng nước có giá trị nằm trong giới hạn bình thường cho thủy sinh
vật và nghêu phát triển. Ở vùng ven biển, nhóm đất cát chiếm 94,28%, có tính chất rời rạc, thấm
nước dễ và cũng khó giữ nước. Ở vùng kênh rạch sát biển, có lượng bùn cát trung bình (41,20%
thịt và 2,77% sét). Ở vùng trong rừng ngập mặn, nền đáy chủ yếu là bùn có hàm lượng thịt và sét
cao. Nghêu giống chỉ phân bố ở vùng ven biển Thạnh Phong, Thạnh Hải nơi có nền đáy là cát bùn,
thành phần cát trung bình chiếm 94,28 ± 2,14% và nghiên cứu không xác định nghêu giống phân
bố ở vùng kênh rạch và trong rừng ngập mặn. Độ béo của nghêu vào tháng 6/2014 cao hơn tháng
7/2014. Thành phần thức ăn trong ruột nghêu đa số là mùn bã hữu cơ, chiếm từ 73,68%-91,67% và
tảo từ 8,33%-26,14% số lượng thức ăn trong ruột nghêu.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
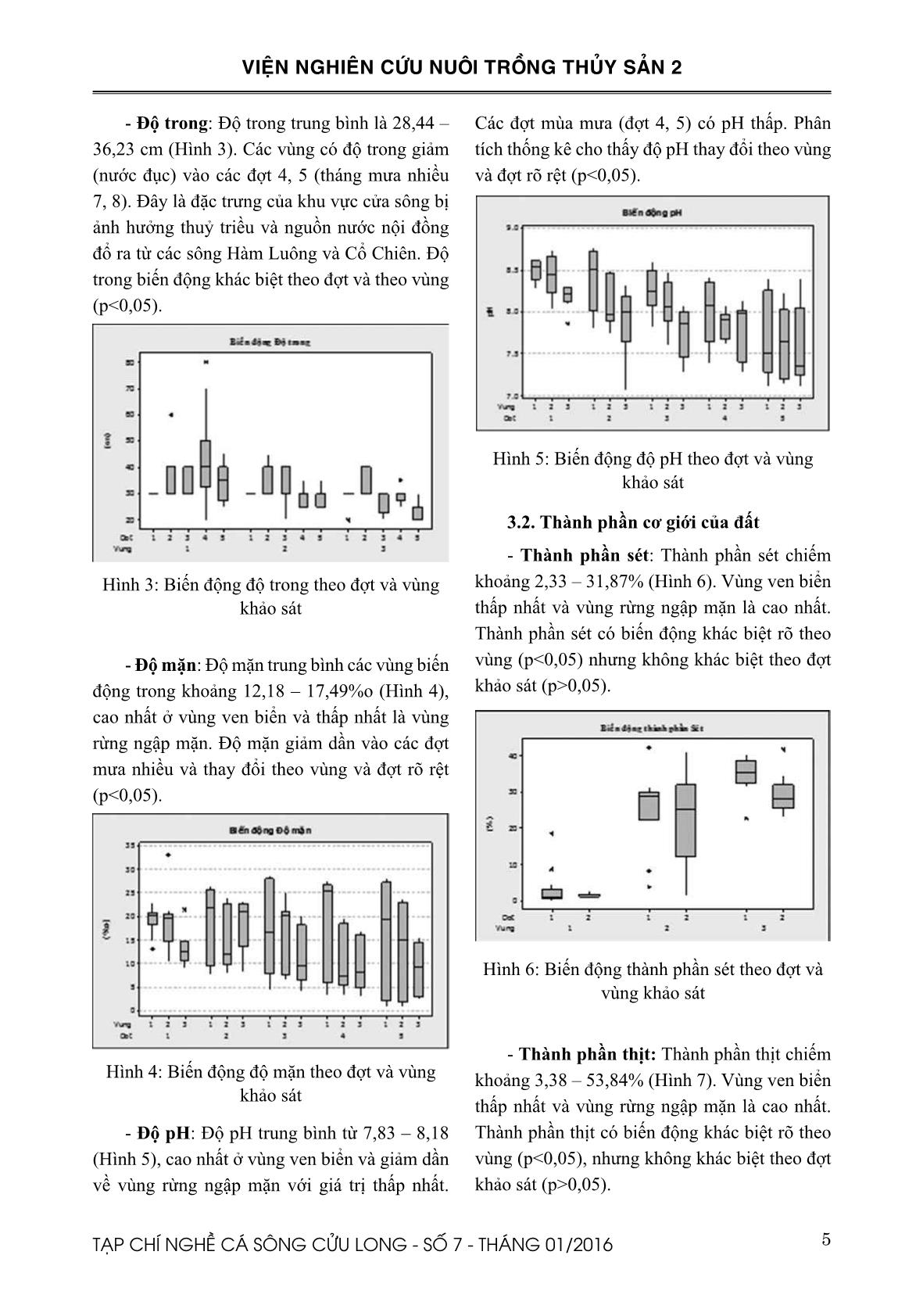
Trang 5
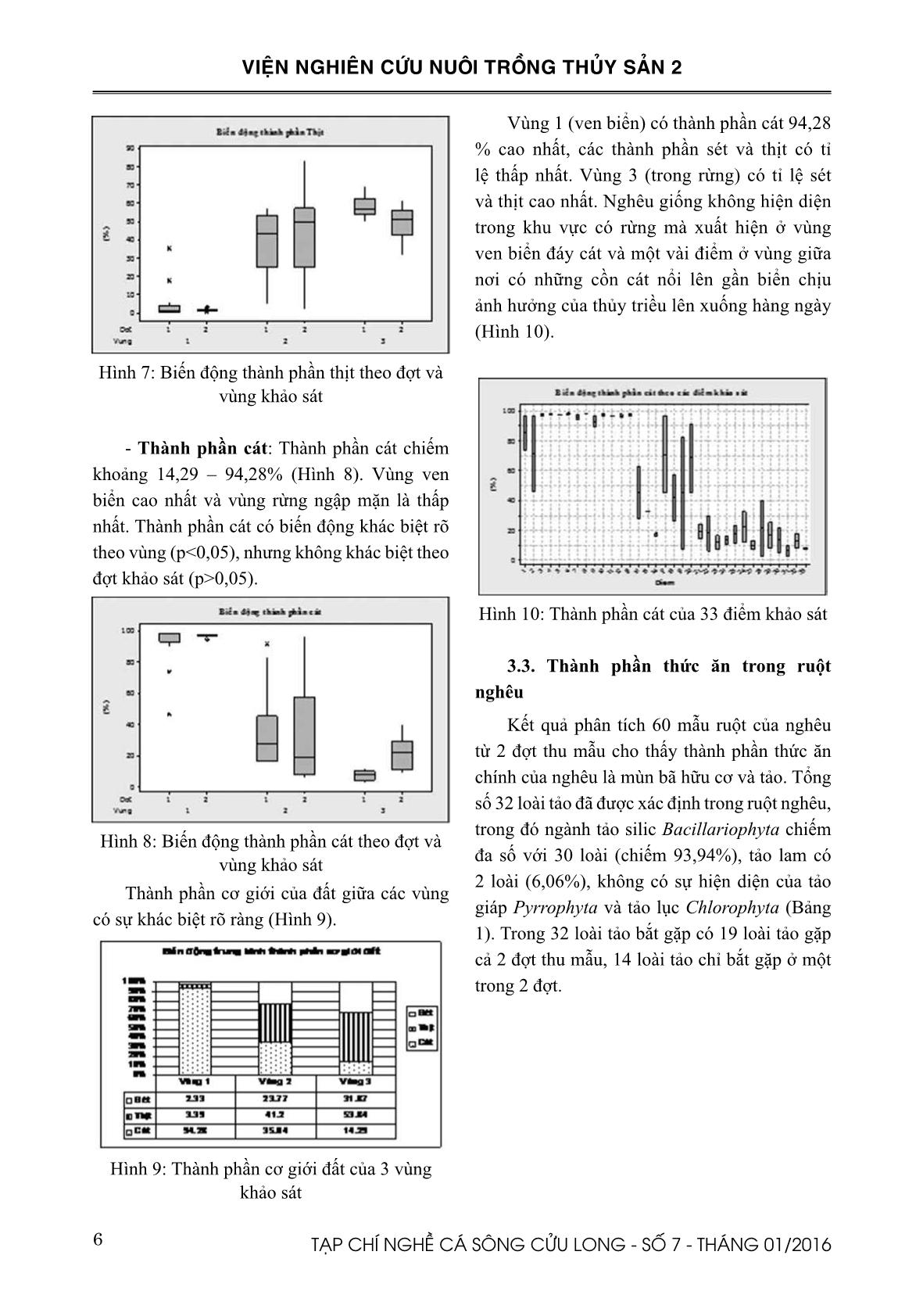
Trang 6
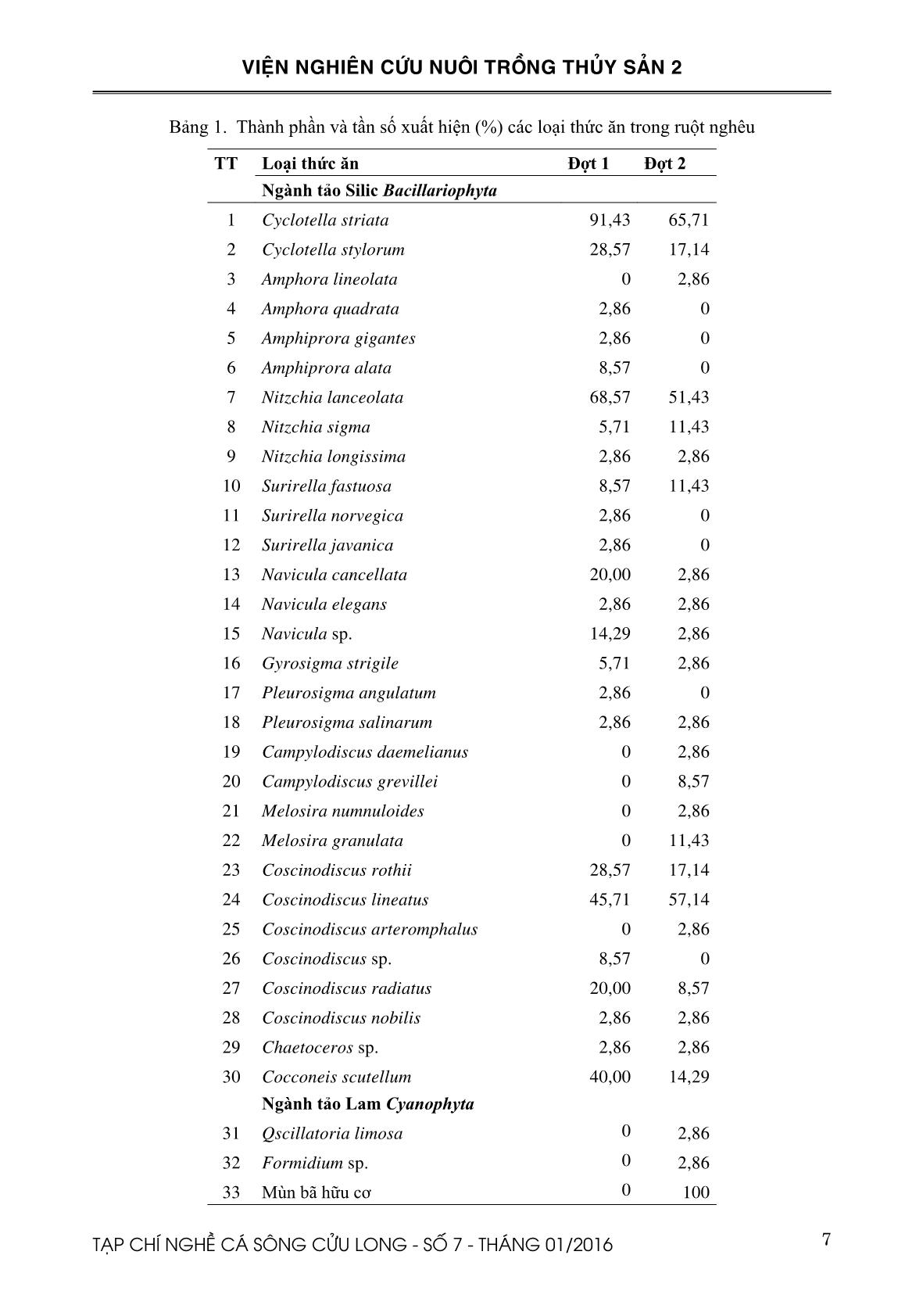
Trang 7
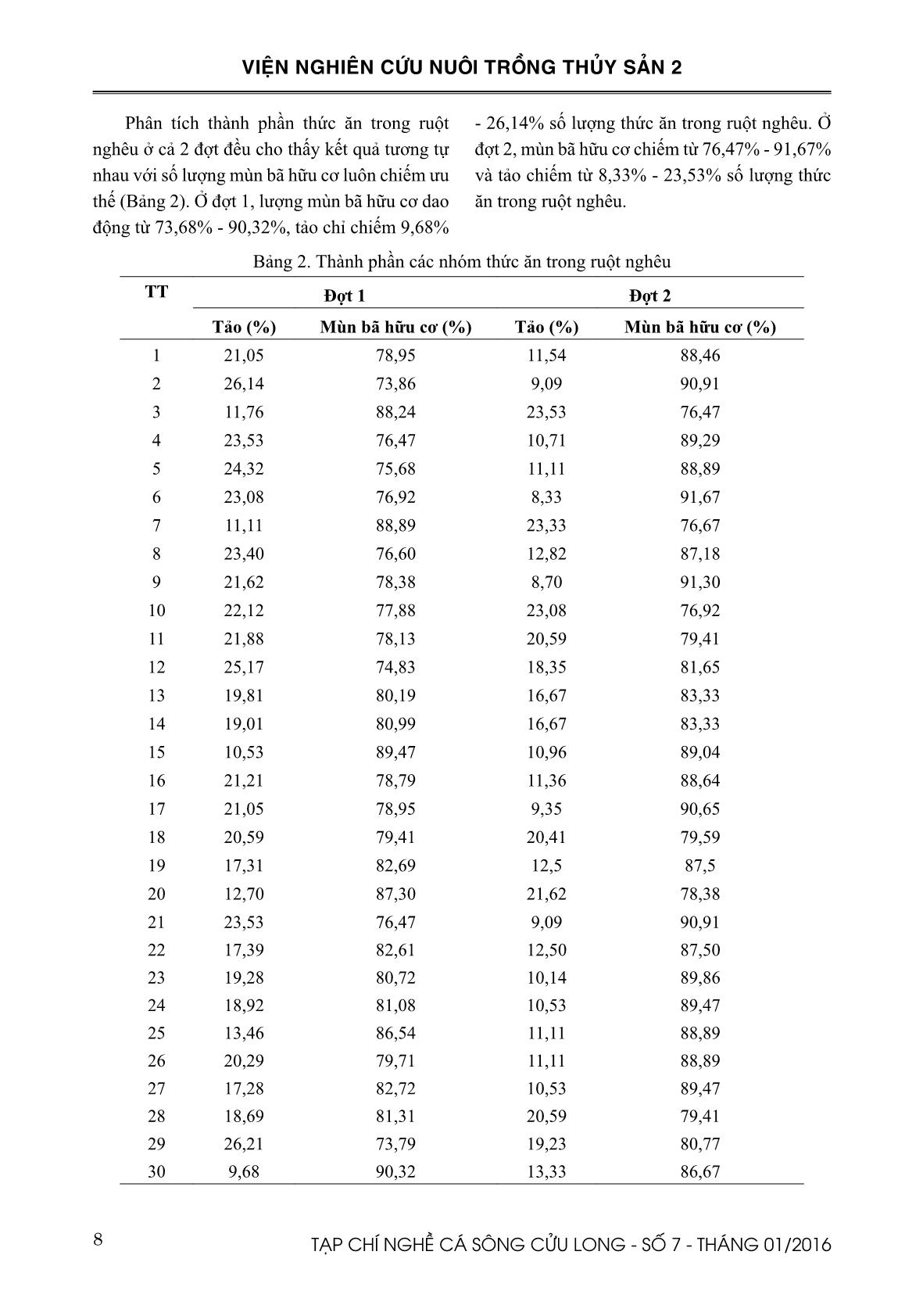
Trang 8
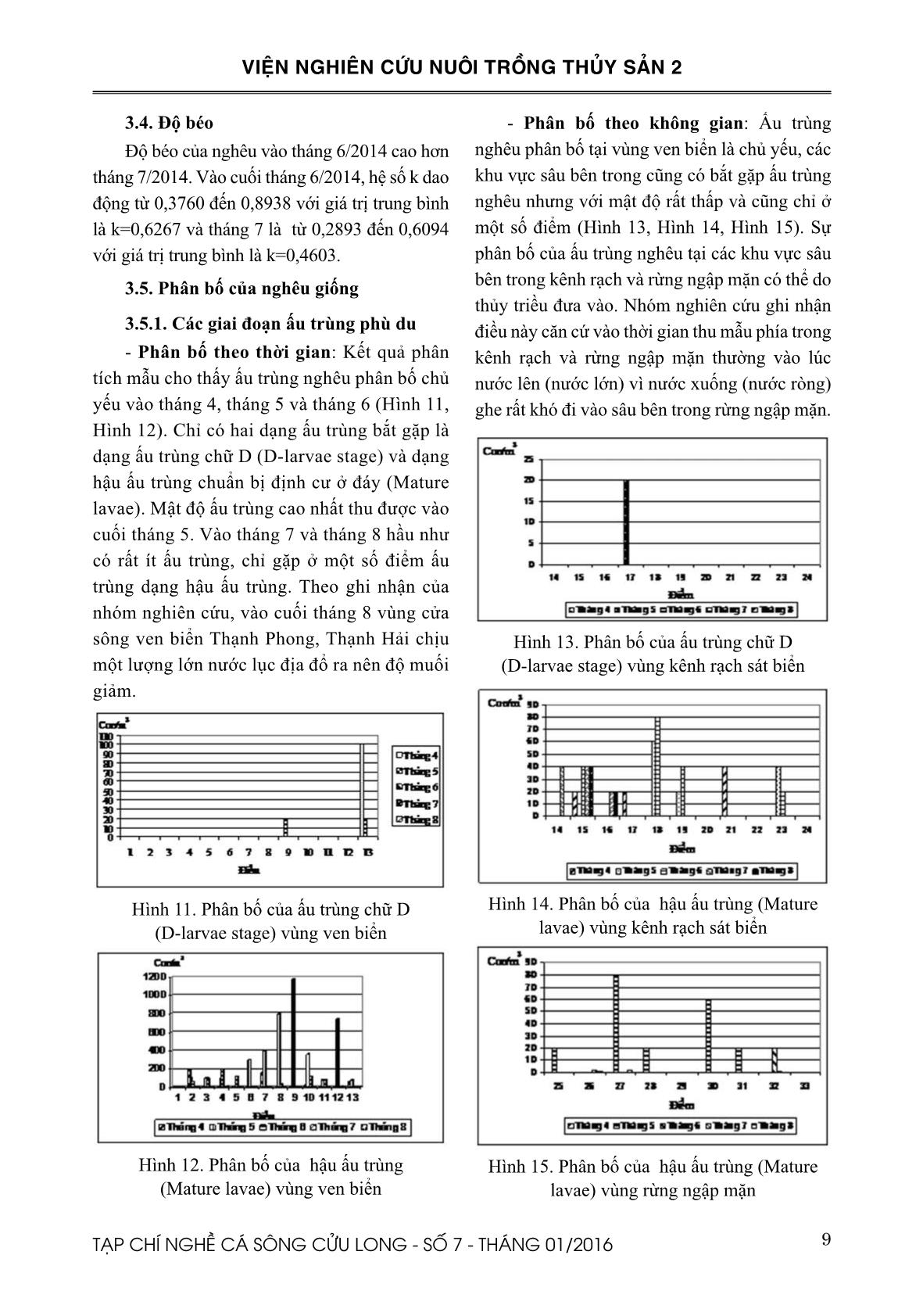
Trang 9
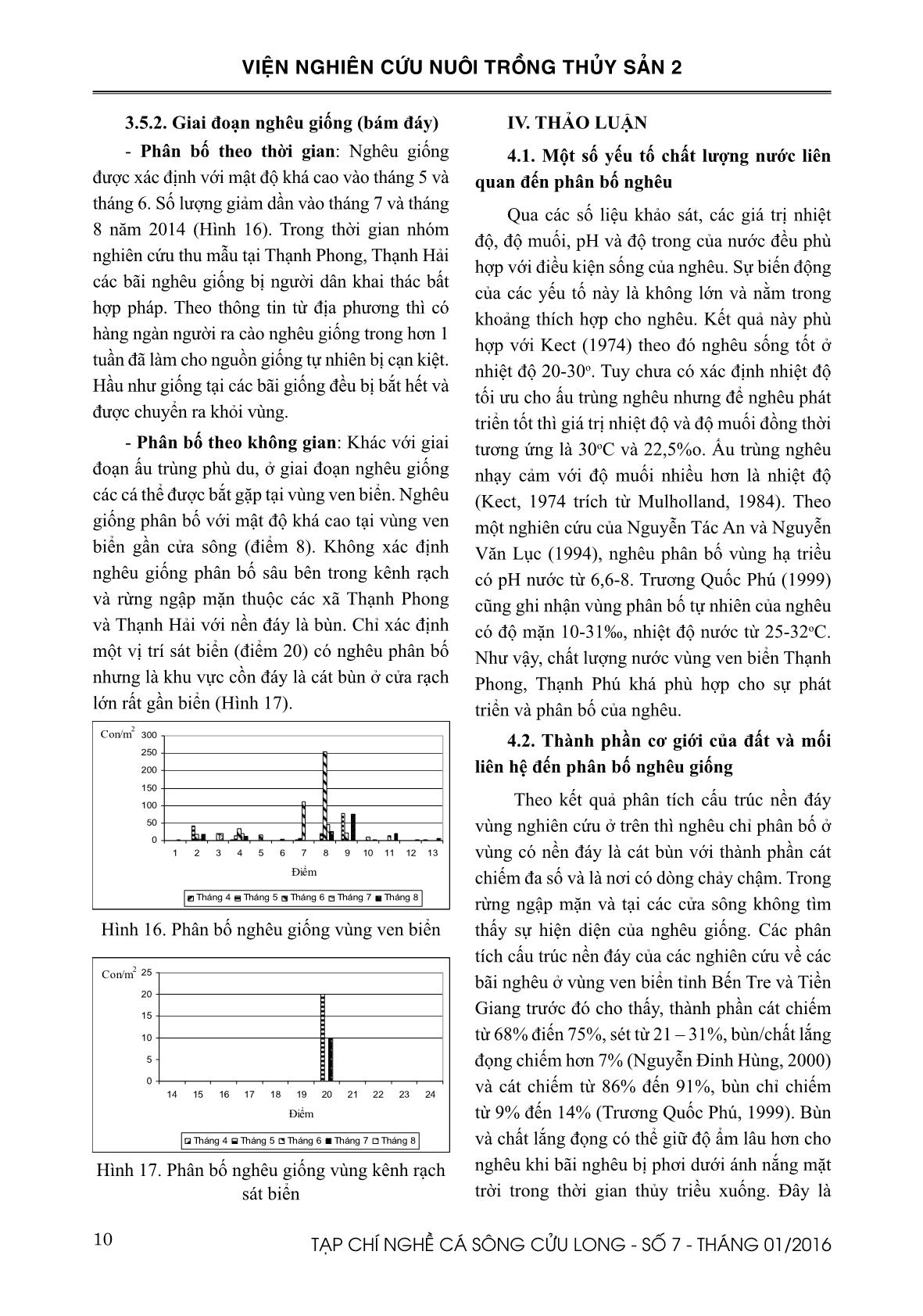
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Tạp chí Nghề cá sông Cửu Long - Số 07/2016

hfuzuddin Ahmed., 2005. Aquaculture—Food and Livelihoods for the Poor in Asia: A Brief Overview of the Issues. Aquaculture Economics & Management 9(1- 2):1–10. Fisheries Directorate, 2012. Report on the Vietnam Shrimp Production and Consumption in 2012 and Plan of 2013 (in Vietnamese). Ministry of Agriculture & Rural Development. Ha Noi. Fisheries Directorate, 2013. Review on the Achievements of 2012 Plan and Implementation of 2013 Plan (in Vietnamese), Ministry of Agriculture & Rural Developemnt. Ha Noi. Francesconi, G. N., 2009. Cooperation for Competition- Linking Ethiopian Farmers to Markets. Wageningen University, the Netherlands. GAA, 2009. Aquaculture Facility Certification: Shrimp Farms. Best Aquaculture Practices Certification Standards, Guidelines. Global Aquaculture Alliance (GAA). GAA, 2010. Aquaculture Facility Certification: Pangasius Farms. Best Aquaculture Practices Certification Standards, Guidelines. Global Aquaculture Alliance (GAA). Gereffi, G., J. Humphrey, and T. J. Sturgeon, 2005. The Governance of Global Value Chains. Review of International Political Economy 12(1):78–104. GlobalGAP, 2011. Control Points and Compliance Criteria: All Farm Base. Code Ref: IFA V4.0 March11; Edition AF 4.0-1; English Version. Grunert, Klaus G. et al, 2005. “Market Orientation of Value Chains: A Conceptual Framework Based on Four Case Studies from the Food Industry.” European Journal of Marketing 39(5/6):428–55. Han, Han and Anton Immink, 2013. “A Zonal Approach for Aquaculture Sustainability.” INFOFISH International 26–28. Retrieved ( s3.amazonaws.com/2013/11/26/26 - 28 _ Han Han - A zonal approach for aquaculture-2- bdfaec03.pdf). Haugen, A. S., S. Bremer, and M. Kaiser, 2013. Assessment of Costs and Benefits of Mandatory and Voluntary Certification Schemes Applied to Asian Producers. SEAT Deliverable 8.5,Centre for the Study of the Sciences and Humanities, University of Bergen. Bergen. Henson, S., S. Jaffee, J. Cranfield, and P. Siegel, 2008. Linking African Smallholders to High-Value Markets: Practitioner Perspectives on Benefits, Constrains, and Interventions. Policy Research Working Paper, the World Bank. Hoa, Tran Thi Tuyet, Mark P. Zwart, Nguyen Thanh, Just M. Vlak, and Mart C. M. De Jong, 2011. “Transmission of White Spot Syndrome Virus in Improved-Extensive and Semi-Intensive Shrimp Production Systems : A Molecular Epidemiology Study.” Aquaculture 313(1-4):7–14. 134 TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 7 - THÁNG 01/2016 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN 2 Irz, Xavier, James R. Stevenson, Arnold Tanoy, and Pierre Morissens, 2007. “The Equyty and Poverty Impacts of Aquaculture: Insights from the Philippines.” Development Policy Review 25(April 2004):495–516. Jespersen, Karen Sau, Ingrid Kelling, Stefano Ponte, and Froukje Kruijssen, 2014. “Institutional Frameworks and the Governance of Aquaculture Value Chains: Lessons from Asia.” Food Policy in press. Kambewa, E. V., 2007. “Balancing the People, Profit and Planet Dimensions in International Marketing Channels - A Study on Coordinating Mechanisms in the Nile Perch Channel from Lake Victoria.” Wageningen University, the Netherlands. Kariuki, L., 2006. “Participation of Smallholders in International Trade.” Agro-food Chains and Network for Development 14:41–48. Kelling, Ingrid, 2012. “Knowledge Is Power? A Market Orientation Approach to the Global Value Chain Analysis of Aquaculture: Two Cases Linking Southeast Asia and the EU.” The University of Stirling. Kelling, Ingrid, Froukje Kruijssen, and Chen Oai Li, 2010. Review of Trade, Regulation and Certification Issues Related to Farmed Aquatic Animals. SEAT Deliverable 2.7, The WorldFish Center. Penang. Key, N. and D. Runsten, 1999. “Contract Farming, Smallholders, and Rural Development in Latin America: The Organization of Agro-Processing Firms and the Scale of out Grower Production.” World Development 27(2):381–401. Khiem, Nguyen T., Simon R. Bush, Chau M. Nguyen, and Loc T. T. Vo, 2010. Upgrading Small-Holders in the Vietnamese Pangasius Value Chain. Final Report, ODI grant number RO334, An Giang. Khoi, Le Doan Nguyen, 2011. “Quality Management in the Pangasius Export Supply Chain in Vietnam: The Case of Small-Scale Pangasius Farming in the Mekong River Delta.” University of Groningen. Lam, X. T. and M. H. Truong, 2010. Current Status of Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP) Certification Apply for the Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus Monodon) Culture in the Mekong River Delta. College of Aquaculture & Fisheries, Can Tho University, Can Tho. Le, Sinh Xuan, 2009. “Social Impacts of Coastal Aquaculture in the Mekong Delta.” Pp. 95–107 in Measuring the contribution of small-scale aquaculture: an assessment. FAO Tecnical paper 534, edited by M. Bondad-Reantaso M.G.; Prein. Rome: FAO. Mohan, C. V., 2013. “Aquaculture Certification: Producer Compliance Constraints.” in VIETFISH 2013: Trade Show and Conference in Vietnam, Vietnam Association of Seafood Exporters and Producers. Ho Chi Minh. Murray, F. J. et al., 2011. Report on Boundary Issues. SEAT Deliverable 2.8. SEAT project, Institute of Aquaculture, The University of Stirling, Stirling. Naturland, 2012. Naturland Standards for Organic Aquaculture. Naturland - Association for Organic Agriculture, Registered Association. Gräfelfing, Germany. Nguyen, Phuong T. and Oanh T. H. Dang, 2009. “Striped Catfish Aquaculture in Viet Nam: A Decade of Unprecedented Development.” Pp. 133–50 in Success Stories in Asian Aquaculture, edited by S. S. De Silva and F. B. Davy. Springer and IDRC, Canada, Drodecht, The Netherlands. Nguyen, T. T. et al., 2009. Project on Development Planning for Aquaculture Sector in the Mekong Delta up to 2015 and Strategic Planning up to 2020 (in Vietnamese). Ministry of Agriculrue & Rural Development. Ho Chi Minh. Nhuong, Tran V. et al., 2003. The Shrimp Industry in Vietnam: Status, Opportunities and Challenges. Research Institute for Aquaculture No.1, Ha Noi. Nietes-Satapornvanit, Arlene, 2014. “Sustainable Development of Export-Orientated Farmed Seafood in Thailand.” The University of Stirling. Oanh, Dang Thi Hoang and Nguyen Thanh Phuong, 2012. “Serious Diseases in Marine Shrimp and Freshwater Prawn Farming in the Mekong River Delta.” Science Journal of Can Tho University 22c:106–18. Oosterveer, Peter. 2006, “Globalization and Sustainable Consumption of Shrimp: Consumers and Governance in the Global Space of Flows.” International Journal of Consumer Studies (September):465–76. Page, S. and R. Slater. 2003, “Small Producer Participation in Global Food Systems: Policy Opportunities and Constraints.” Development Policy Review 21(5-6):641–54. Pham, Anh T., Simon R. Bus, Arthur P. J. Mol, and Carolien Kroeze, 2011. “The Multi-Level Environmental Governance of Vietnamese Aquaculture: Global Certification , National Standards , Local Cooperatives.” Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning 13(4):373–97. Phan, Lam T. et al. 2009. “Current Status of Farming Practices of Striped Catfish, Pangasianodon Hypophthalmus in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam.” Aquaculture 296(3-4):227–36. Phan, Lam T., Phuong T. Nguyen, Francis J. Murray, and David C. Little. 2011. Development Trends and Local Sustainability Perceptions for the International Trade in Seafood Farmed in Vietnam. SEAT Deliverable 2.1, The University of Stirling. Stirling. Ponte, Stefano, Ingrid Kelling, Karen Sau Jespersen, 135TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 7 - THÁNG 01/2016 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN 2 and Froukje Kruijssen. 2014. “The Blue Revolution in Asia: Upgrading and Governance in Aquaculture Value Chains.” World Development 64:52–64. Reardon, T. and C. P. Timmer. 2006. “Transformation of Markets for Agricultural Output in Developing Countries Since 1950: How Has Thinking Changed?” in Handbook of Agricultural Economics, edited by T. Reardon and C. P. Timmer. Elsevier. Reilly, Alan. 2007. “From Farm to Fork – New European Food Hygiene Regulations.” Pp. 47– 57 in International seafood trade: challenges and opportunities, edited by W. Einarsson, H.; Emerson. Akureyri, Iceland: FAO Fisheries & Aquaculture proceeding 13. FAO. Ruben, R., A. V. Tilburg, J. Trinekens, and M. V. Boekel. 2007. “Linking Market Integration, Supply Chain Governance, Quality and Value Added.” Pp. 13–46 in In Tropical Food Chains: Governance Regimes for Quality Management, edited by R. Ruben, A. V. Tilburg, J. Trinekens, and M. V. Boekel. Wageningen: Wageningen Academic Publishers. Segura, S. F. 2006. “Contract Farming in Costa Rica. Opportunities for Smallholders?” Wageningen University, the Netherlands. SFP. 2013. “Vietnamese Pangasius Aquaculture Improvement Project.” Sustainable Fisheries Partnership. Retrieved ( sustainablefish.org/aquaculture-improvement/ pangasius/pangasius-aquaculture-improvement- partnership). Siar, Susana V. and Percy E. Sajise. 2009. “Access Rights for Sustainable Small-Scale Aquaculture and Rural Development.” Pp. 87–95 in Measuring the contribution of small-scale aquaculture: an assessment. FAO Tecnical paper 534, edited by M. Bondad-Reantaso M.G.; Prein. Rome: FAO. De Silva, Sena S. and Phuong T. Nguyen. 2011. “Striped Catfish Farming in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam: A Tumultuous Path to a Global Success.” Reviews in Aquaculture 3(2):45–73. Sriwichailamphan, T., 2007. “Global Food Chains and Environment: Agro-Food Production and Processing in Thailand.” Wageningen University, the Netherlands. Subasinghe, Rohana, Doris Soto, and Jiansan Jia, 2009. Global Aquaculture and Its Role in Sustainable Development. Reviews in Aquaculture 1(1):2–9. Tran, Nhuong, Conner Bailey, Norbert Wilson, and Michael Phillips, 2013. Governance of Global Value Chains in Response to Food Safety and Certification Standards: The Case of Shrimp from Vietnam. World Development 45(202374):325–36. Trifković, Neda, 2013. The Role of Food Standards in Development: An Empirical Perspective. University of Copenhagen. Umesh, N. R. et al., 2009. Shrimp Farmer in India: Empowering Small Scale Farmer through a Cluster-Based Approach. Pp. 43–65 in Success Stories in Asian Aquaculture, edited by S. S. De Silva and F. B. Davy. Springer and IDRC, Canada, Drodecht, The Netherlands. VASEP. 2014, Report on Vietnam Seafood Export in 2013 (in Vietnamese). Vietnam Association of Seafood Exporters and Producers. Ha Noi. VIFEP, 2009. Project on Development Planning for Crustacean Production and Consumption of Vietnam Upto 2020 (in Vietnamese). Vietnam Institute of Fisheries & Economic Plan. Ha Noi. VIFEP, 2015. Project on Development Planning for Crustacean Production and Consumption of Vietnam Upto 2020 (in Vietnamese). Vietnam Institute of Fisheries & Economic Plan. Ha Noi. Vo, L. T. T., S. R. Bush, and S. X. Le., 2009. Assessment of Value Chains for Promoting Sustainable Fisheries Development in the Mekong Basin: Cases of Pangasius in Vietnam and Cambodia. Vietnam Economic Management Review 26(5-6):32–42. Vu, An V. and Lam T. Phan, 2008. Inland Fisheries and Aquaculture in the Mekong Delta: A Review. Research Institute for Aquaculture No.2, Ho Chi Minh. Vu, T. A. et al., 2013. Status of Small-Scale Environmentall Friendly Shrimp Production in the Ca Mau Province, the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. GIZ Vietnam, Ca Mau. Washington, S. and L. Ababouch, 2011. Private Standards and Certification in Fisheries and Aquaculture: Current Practice and Emerging Issues. Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome. Washington, Sally and Lahsen Ababouch, 2011. Private Standards and Certification in Fisheries and Aquaculture: Current Practice and Emerging Issues. FAO Fisher. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations. WWF, 2011. Draft Stabdards for Responsible Shrimp Aquaculture. Version 3.0 for Guidance Development and Field Testing, ShAD. Yamprayoon, Jirawan and Krissana Sukhumparnich. 2010, Thai Aquaculture: Achieving Quality and Safety through Management and Sustainability. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society 41(2):274–80. Young, James A., Ian Goulding, and Roderick L. Stirrat. 2011,Post-Harvest to Consumer Driver Review of the Aquatic Supply Chain. Driver Review-DR17/ Foresight Project on Global Food and Farming Futures. London. 136 TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 7 - THÁNG 01/2016 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN 2 FARMING PRACTICES AND CHALLENGES TO REACH FOOD STANDARDS OF SMALL-SCALE SHRIMP FARMS IN THE MEKONG DELTA Phan Thanh Lam1* ABSTRACT Shrimp culture becomes main occupation of many farmers in the coastal areas of the Mekong River Delta (MKD); however, shrimp farming has not really sustainable. This study is to assess the current farming practices and challenges to reach international food standards of small-scale shrimp farms. This study was carried-out in four coastal provinces in the MKD,A randomized stratified sampling method was used to select survey-sites and survey-farms for interview. The 230 belongings to five typical shrimp farming systems in the MKD were selected for face-to-face interviewing. The findings show that many shrimp farms were likely to reach several standard criteria such eFCR (≤1.8 in Black Tiger Shrimp culture, and ≤1.5 in White-legged Shrimp culture), stocking density (≤15PL/m2 in the lower investment shrimp system), survival rate (>25% in the lower investment shrimp system, and >60% in the higher investment shrimp system), no banned chemical/drug and wild-seed source use, community relationships, property rights, and biodiversity protection. However, there are still many standard criteria that farms could not meet such as criteria for effluent management (most farms release their waste water without any treatment and had no sediment basins), registration of farms (many farms were not legally registered), shrimp mortality management (lack of proper methods), labor arrangements (verbal contracts), farm hygiene, and recordkeeping requirements.With these current shrimp farming practices, it is still far behind to reach criteria of the food standards; therefore, the shrimp farms, especially small-scale farms need to be strengthened and to improved their infrastructure conditions and farming techniques to promote the adoption of international food standards. Keywords: farming practices, small-scale farm, food standards. Người phản biện: TS. Vũ Anh Tuấn Ngày nhận bài: 18/11/2015 Ngày thông qua phản biện: 18/12/2015 Ngày duyệt đăng: 25/12/2015 1. Department of Fisheries Ecology &Aquatic Resources, Research Institute for Aquaculture No.2 * Email: pthanhlam@yahoo.com
File đính kèm:
 tap_chi_nghe_ca_song_cuu_long_so_072016.pdf
tap_chi_nghe_ca_song_cuu_long_so_072016.pdf

