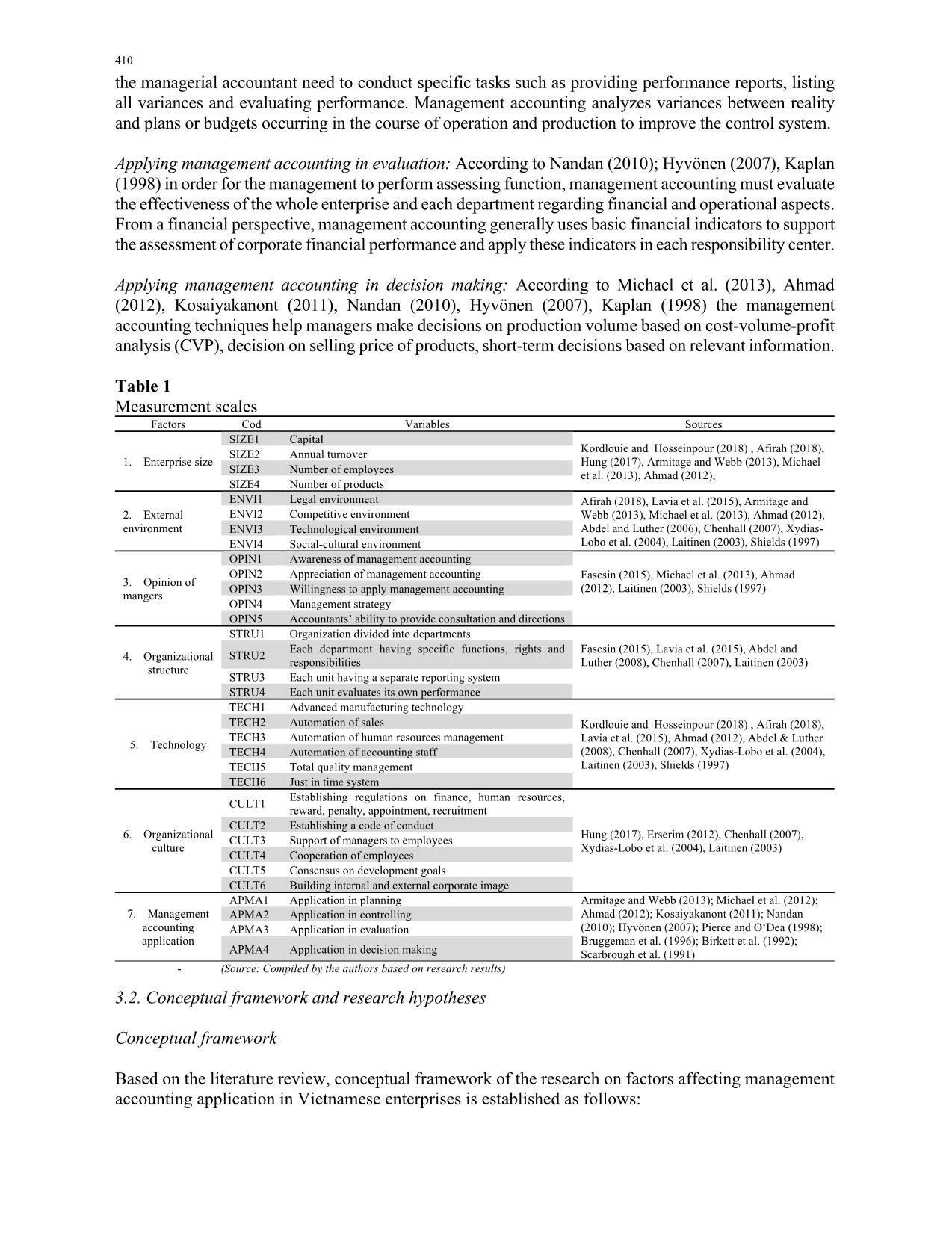
Factors affecting the application of management accounting in Vietnamese enterprises
This paper aims to investigate factors affecting the application of management accounting in
Vietnamese enterprises. Quantitative research was conducted and data was collected by
sending questionnaires to 120 companies in the manufacturing, trading and service sectors in
Vietnam. 6 factors were selected to measure the application of management accounting in
enterprises through correlation and regression analysis. The results showed that 5 out of 6
factors positively associated with the level of management accounting application; including
firm size, organizational culture, organizational structure, technology and human resources
operations. In particular, corporate culture has the highest impact and opinion of managers has
the lowest impact on management accounting application. Business environment has a
negative impact on management accounting application in enterprises. Based on the research
results, suggestions and recommendations are proposed for enterprises regarding application
of management accounting. The research provided an overview of management accounting
application and its benefits to enterprises. Whereby, it helps managers have a better
understanding of management accounting and future directions for application. Moreover, the
research results will be useful for managers to identify factors influencing their management
accounting practices and improve the current management process applied in organizations.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Factors affecting the application of management accounting in Vietnamese enterprises

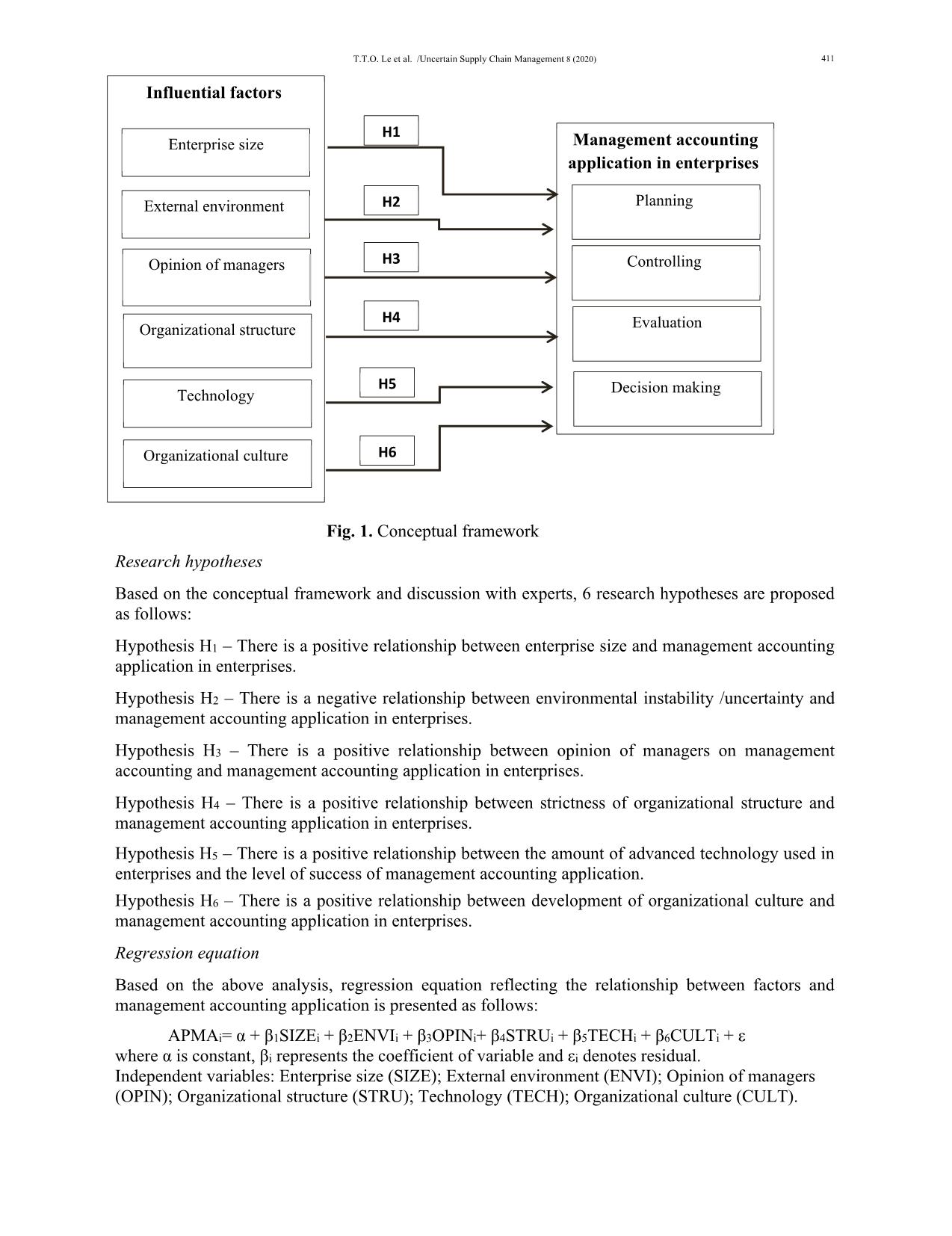
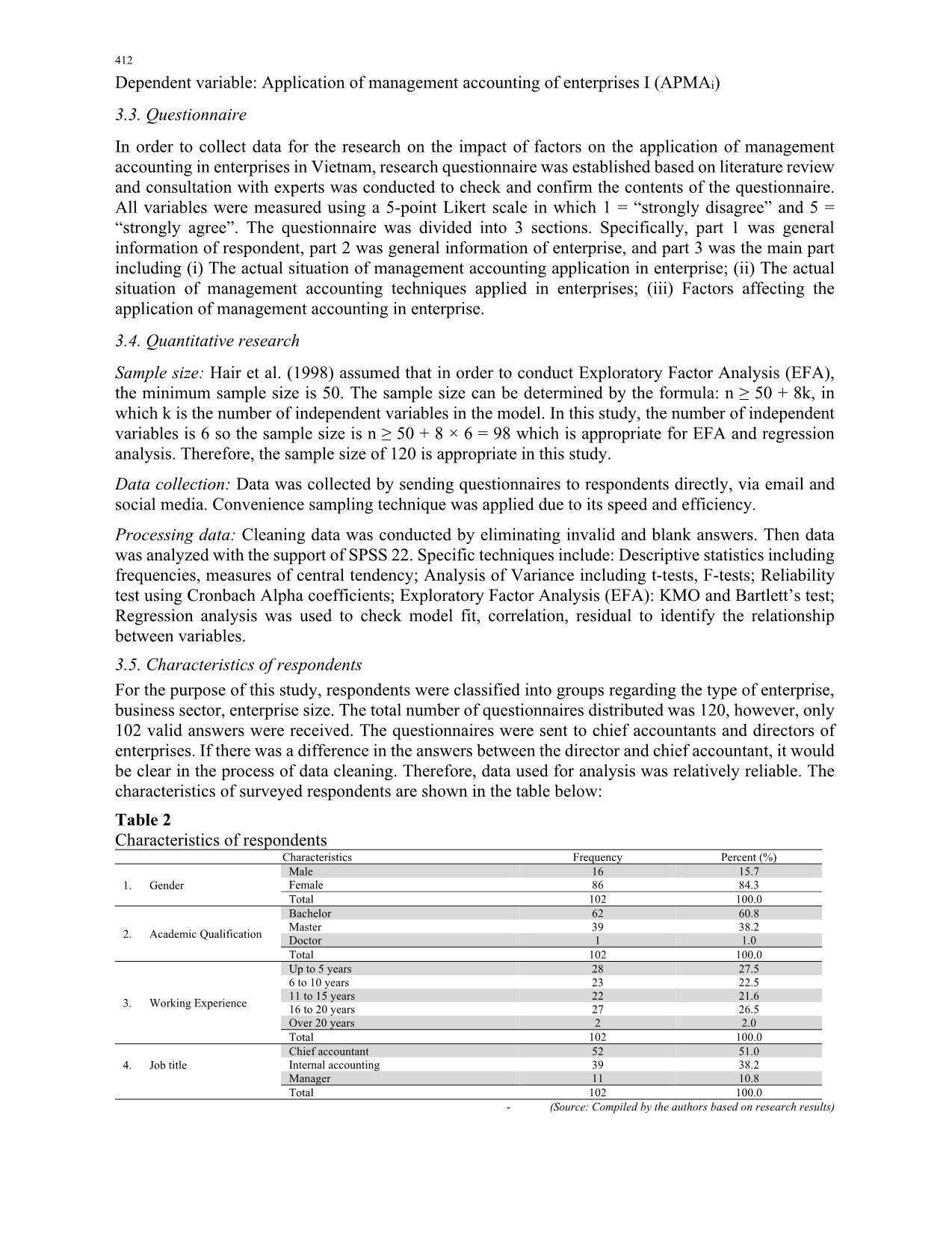
enterprises and large enterprises regarding the application of management accounting. Specifically, large-scale enterprises with strong financial capacity, diverse products, and large market share, with complex management systems require highly sophisticated management accounting techniques. In small enterprises, it is not necessary to design a management accounting system. However, it is possible to apply management accounting in small companies especially at high level management. The owners/ managers of enterprises or the chief accountants must equip themselves with knowledge and application of management accounting. The application of management accounting in small businesses can help them reduce risks through budgeting tools, create better business plan or take advantages of business opportunities. 5.3 Organizational culture In this study, the organizational culture has the highest impact on the application of management accounting in enterprises, with the coefficient of 0.375. Research results show that support from managers to employees, consensus on development goals, and cooperation of employees in departments increase the feasibility of management accounting application. This result confirms hypothesis H6, and is consistent with previous studies of Erserim (2012), Chenhall (2007), Xydias- Lobo et al. (2004), Laitinen (2003). In Vietnam, the majority of enterprises are small enterprises with personal and family relationships. Therefore, the consistency and conformity are relatively high which can facilitate the application of management accounting such as developing standard costing; decision making tools; budgeting and control; performance measurement can reach high consensus from business departments, and the Board of Directors. 420 5.4 Organizational structure The results of regression analysis show that organizational structure has a positive effect on the application of management accounting in enterprises, with the coefficient of 0.269. This factor has the highest impact on the dependent variable. This result confirms hypothesis H4 that, and is consistent with previous studies of Fasesin (2015), Lavia et al. (2015), Abdel and Luther (2008). Enterprises in Vietnam operate under the Vietnamese Enterprise Law and often have line and functional organizational structure. Specifically, clear structure of enterprises is reflected in the division of the organization into small units such as departments, units, teams with specific tasks, and performance of each unit is periodically evaluated. Therefore, clear organizational structure facilitates the application of management accounting in Vietnamese enterprises. 5.5 Technology This study proved that technology has a positive impact on the application of management accounting (coefficient = 0.203). This result confirms hypothesis H5, and is consistent with previous studies of Kordlouie and Hosseinpour (2018) , Afirah (2018), Lavia et al. (2015), Ahmad (2012). In the era of industrial revolution 4.0, technology has a great influence on business activities. New technology allows high-level automation in producing and manufacturing as well as communication and cooperation between machines and humans in a real-time. Specifically, technology is represented by the degree of automation in the processes of production, sales, personnel, business, management. It enables rapid production and standardized quality. This study also showed that technology factors and firm size (the amount of capital and the number of product) have a positive impact on the application of management accounting. Hardware and software technologies are applied and enhance efficiency in foreign-invested companies (joint ventures). Companies with a capital of more than 200 billion VND, revenues of more than 200 billion VND, and more than 200 products such as Samsung, Toyota, Canon, apart from machinery and equipment, they also apply technology such as management process, automatic production, employee work trackers, controlling inventory, materials. The automation level may reach 52%. In State-owned companies, technology is not advanced and includes mainly machinery and equipment with poor operation and management processes. The amount of investment in technology in the private sector (limited liability companies and joint stock companies) is smaller than that in stated-owned enterprises, but higher efficiency. 5.6 Human resources management The factor of human resources management has a positive influence on the application of management accounting, however the level of impact is small (0.046). The management of human resources depends greatly on the perspectives and strategies of the managers. With highly flexible management strategy, companies need to apply complex management accounting techniques to collect relevant information for making decisions in diverse business contexts. 6. Summary and Conclusion Management accounting is considered a component of management system in enterprises. Managers at all levels can use management accounting information to perform management functions and achieve business objectives. However, application of management accounting is affected by many factors, so investigating influential factors is essential. This study using quantitative research method proved that organizational culture has the highest impact of management accounting application, followed by organizational structure and technology. Therefore, potential solutions for enterprises are proposed as follows: Solutions regarding organizational culture: Organizational culture is one of the most valuable assets of an organization which should be preserved and promoted by its members. Companies with strong cultures have a high consensus among members toward common objectives which is a critical factor for long-term success. Potential solutions for companies to promote and strengthen their culture include T.T.O. Le et al. /Uncertain Supply Chain Management 8 (2020) 421 (i) Developing an investment strategy to explore and promote strengths and talents of each employee in the organization; (ii) Regularly evaluating strengths and weaknesses of corporate culture to communicate and remind responsibilities and obligations of each individual in enterprises; (iii) Organizing events to enhance teambuilding, contests, programs to enhance cooperation and help employees understand corporate culture as well as the importance and benefits of the development of the enterprises and its members. Solutions regarding enterprise size: There are many different ways to increase enterprise size such as mergers, integrations, alliances. With larger size, companies can have sufficient financial capacity to access capital from banks. It is recommendable to diversify business activities, products. Furthermore, in order to apply management accounting effectively, appropriate data collection should be emphasized which allows better processing of data and making reports for managers at all levels. In other words, it is critical to maintain high consistency from data collection to data analysis Solutions regarding business environment: Business environment is an external factor which has a negative impact on the application of management accounting in Vietnamese enterprises. Since it is impossible to restrain or reduce the impact of external environment, an effective solution is to adapt to the environment and take control of enterprises’ production and business activities. Particularly, enterprises should select appropriate management accounting techniques to help managers make right decisions to tackle environmental instability. Solutions regarding organizational structures: Enterprises should select suitable management structures, adapt the management structures in relation to organizational cultures. Furthermore, management structures should be established based on responsibility center. References Abdel-Kader, M., & Luther, R. (2006). Management accounting practices in the British food and drinks industry. British Food Journal, 108(5), 336-357. Abdel-Kader, M., & Luther, R. (2008). The impact of firm characteristics on management accounting practices: A UK-based empirical analysis. The British Accounting Review, 40(1), 2-27. Abdel-Maksoud, A. B. (2004). Manufacturing in the UK: contemporary characteristics and performance indicators. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 15(2), 155-171. Azudin, A., & Mansor, N. (2018). Management accounting practices of SMEs: The impact of organizational DNA, business potential and operational technology. Asia Pacific Management Review, 23(3), 222-226. Ahmad, K. (2012). The use of management accounting practices in Malaysia SMEs. PhD thesis. University of Exeter. Amat, J., Carmona, S., & Chenhalls, H. (1994). Context and change in management accounting systems: a Spanish case study. Management Accounting Research, 5(2), 107-122. Armitage, H. M., & Webb, A. (2013). The Use of Management Accounting Techniques by Canadian Small and Medium Sized Enterprises: A Field Study. In CAAA Annual Conference. Atkinson, A. (2012). Management accounting: information for decision-making and strategy executive. 6th ed., Pearson Prentice Hall. Bhimani, A. (2002). Management Accounting and Organizational Excellence. Management Press International LTD, United Kingdom. Birkett, W. P., Barbera, M. R., Chua, W. F., Fatseas, V. A., Luckett, P. F., & Macmullen, J. S. (1992). Cost management in small manufacturing enterprises. Australian Centre for Management Accounting Development, UNSW, Sydney. Chenhall, R. H. (2006). Theorizing contingencies in management control systems research. Handbooks of Management Accounting Research, 1, 163-205. Collis, J., & Jarvis, R. (2002). Financial information and the management of small private companies. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 9(2), 100-110. Dehejia, R. H., & Wahba, S. (2002). Propensity score-matching methods for nonexperimental causal studies. Review of Economics and statistics, 84(1), 151-161. Erserim, A. (2012). and external environment of firms on management accounting practices: an empirical research on industrial firms in Turkey. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 62, 372-376. Fasesin, O. O., Salman, A. Y., & Dunsin, A. T. (2015). Influence of management accounting system on 422 performance of small and medium enterprises in Nigeria. International Journal in Management and Social Science, 3(4), 435-446. Hair, J. F. J., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L.,& Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate Date Analysis. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Kordlouie, H. R., & Hosseinpour, A. (2018). Management accounting practices in small and medium-sized enterprises regarding the impact of organizational and, commercial potential and operational technology, International Journal of Business quantitative economic and applied management research, 4(8), January- 2018 Hiebl, M. R., Feldbauer-Durstmüller, B., & Duller, C. (2013). The changing role of management accounting in the transition from a family business to a non-family business. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change, 9(2), 119-154. Hung, N. T. (2016). Factors affecting management accounting application in small and medium-sized enterprises in Vietnam. Ph.D thesis, University of Economics, Ho Chi Minh City. Hyvönen, J. (2007). Strategy, performance measurement techniques and information technology of the firm and their links to organizational performance. Management Accounting Research, 18(3), 343-366. Kaplan, R., & Atkinson, A. (1998). Advanced Management Accounting. 3rd edition. USA, Hall Inc. Prentice International. Kosaiyakanont A. (2011). SME Entrepreneurs in Northern Thailand: Their Perception of and Need for Management Accounting. Journal of Business and Policy Research, 6, 143-155. Laitinen, E. K. (2003). Future-based management accounting: a new approach with survey evidence. Critical Perspectives on Accounting, 14(3), 293-323. Langfield-Smith, K., Smith, D., Andon, P., Hilton, R., & Thorne, H. (2017). Management accounting: Information for creating and managing value. McGraw-Hill Education Australia. Lavia L_opez, O., & Hiebl, M. R. W. (2015). Management accounting in small and medium-sized enterprises e current knowledge and avenues for further research. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 27(1), 81-119. Messner, M. (2016). Does industry matter? How industry context shapes management accounting practice. Management Accounting Research, 31, 103-111. Michael, L., Malcolm, P. and Glynn, L. (2013). Management Accounting Practices of (UK) Small - Medium - Sized Enterprises. Improving SME performance through Management Accounting Education. CIMA. 9:4. Mitchell, F., & Reid, G. C. (2000). Problems, challenges and opportunities: the small business as a setting for management accounting research. Management Accounting Research, 11(4), 385-390. Nandan, R. (2010). Management Accounting Needs of SMEs and the Role of Professional Accountants: A Renewed Research Agenda. Journal of applied management accounting research, 8(1). Nishimura, A. (2003). Management Accounting: Feed forward and Asian perspectives. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan. Pierce, B., & O'Dea, T. (1998). Management accounting practices in Ireland–the preparers' perspective. Scarbrough, P., Nanni Jr, A. J., & Sakurai, M. (1991). Japanese management accounting practices and the effects of assembly and process automation. Management Accounting Research, 2(1), 27-46. Senftlechner, D., & Hiebl, M. R. (2015). Management accounting and management control in family businesses: Past accomplishments and future opportunities. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change, 11(4), 573- 606. Shields, M. D. (1997). Research in management accounting by North Americans in the 1990s. Journal of management accounting research, 9, 3-62. Valančienė, L., & Gimžauskienė, E. (2007). Changing role of management accounting: Lithuanian Experience case studies. Inžinerinė ekonomika, (5), 16-23. Yen, T. T. (2017). Factors affecting management accounting application in small and medium-sized enterprises in Binh Dinh province. Industry and Trade Magazine. < anh-huong-den-viec-van-dung-ke-toan-quan-tri-trong-cac-doanh-nghiep-tai-tinh-binh-dinh-27201.htm> Xydias-Lobo, M., Tilt, C., & Forsaith, D. (2004). The future of management accounting: a South Australian perspective. Journal of Applied Management Accounting Research, 2(1), 55. © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science, Canada. This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (
File đính kèm:
 factors_affecting_the_application_of_management_accounting_i.pdf
factors_affecting_the_application_of_management_accounting_i.pdf

