Designing a competencies framework for STEM teaching for pre-Teachers of chemistry in the University of Education for meeting the new demands of current teacher training
The STEM education teaching approach (STEM teaching) has been one of the important orientations of the Vietnamese general education program. However, thus far there has been no competency framework for STEM teaching in our country. A competency framework for STEM teaching would include two important things. With this framework, learners would have complete control when setting up their plan, finding information, defining the learning content methodologies and providing multi-Subject knowledge at the beginning of a procedure. Furthermore, it can be orientated to evaluate the expression level of each student. This paper presents the process of designing a competency framework for a STEM teaching and suggests the ways to use this framework at the University of Education

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Designing a competencies framework for STEM teaching for pre-Teachers of chemistry in the University of Education for meeting the new demands of current teacher training

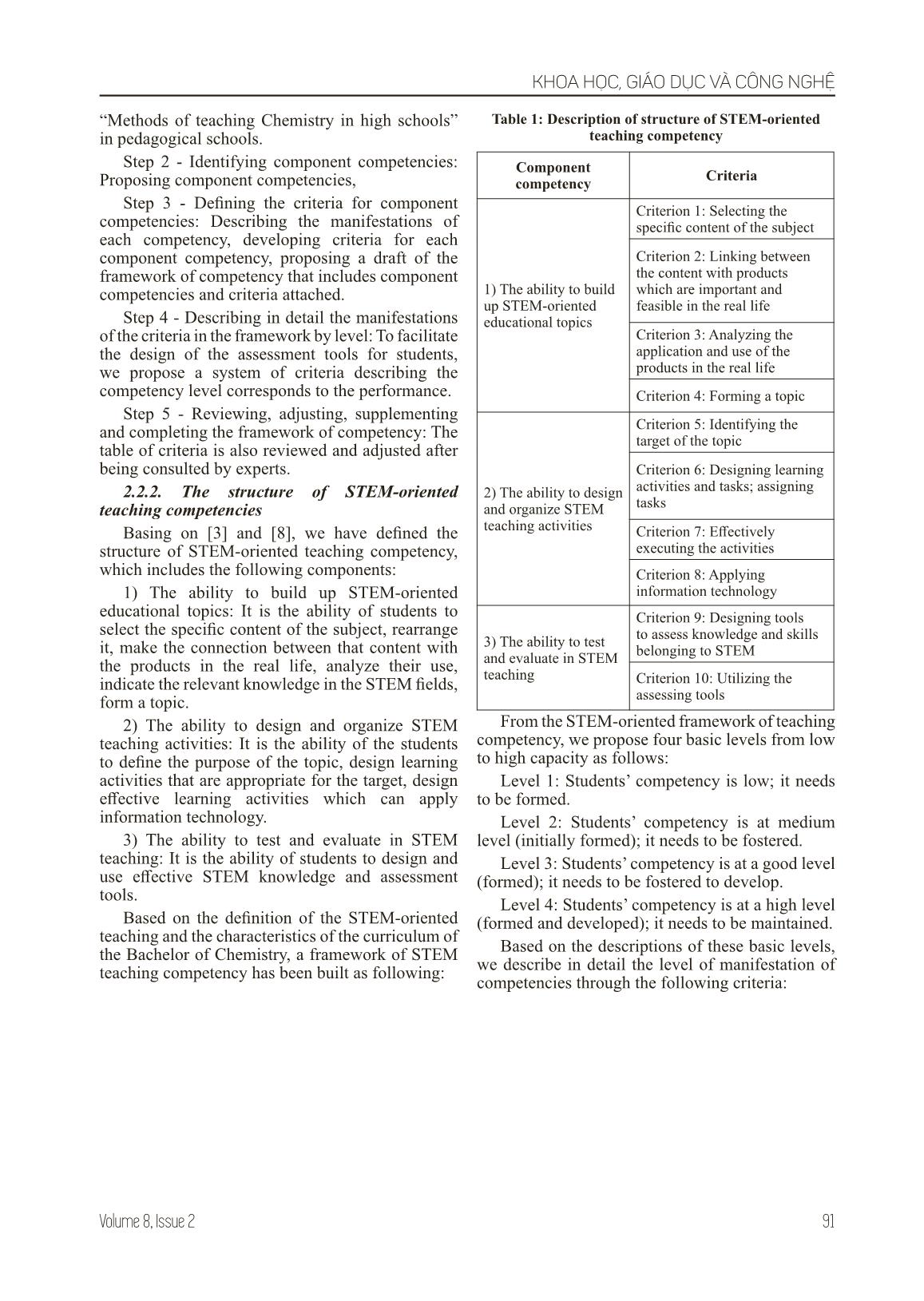
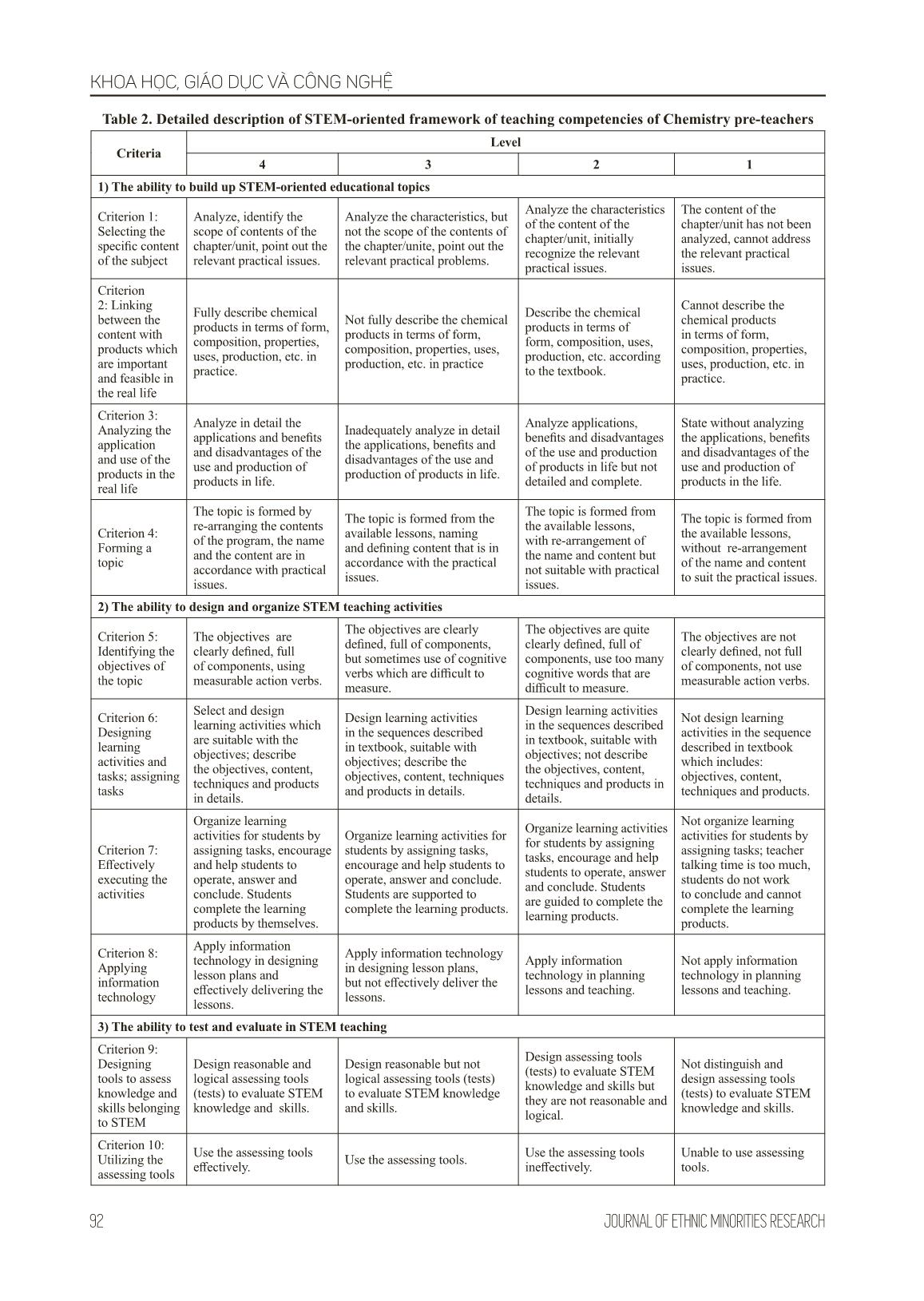
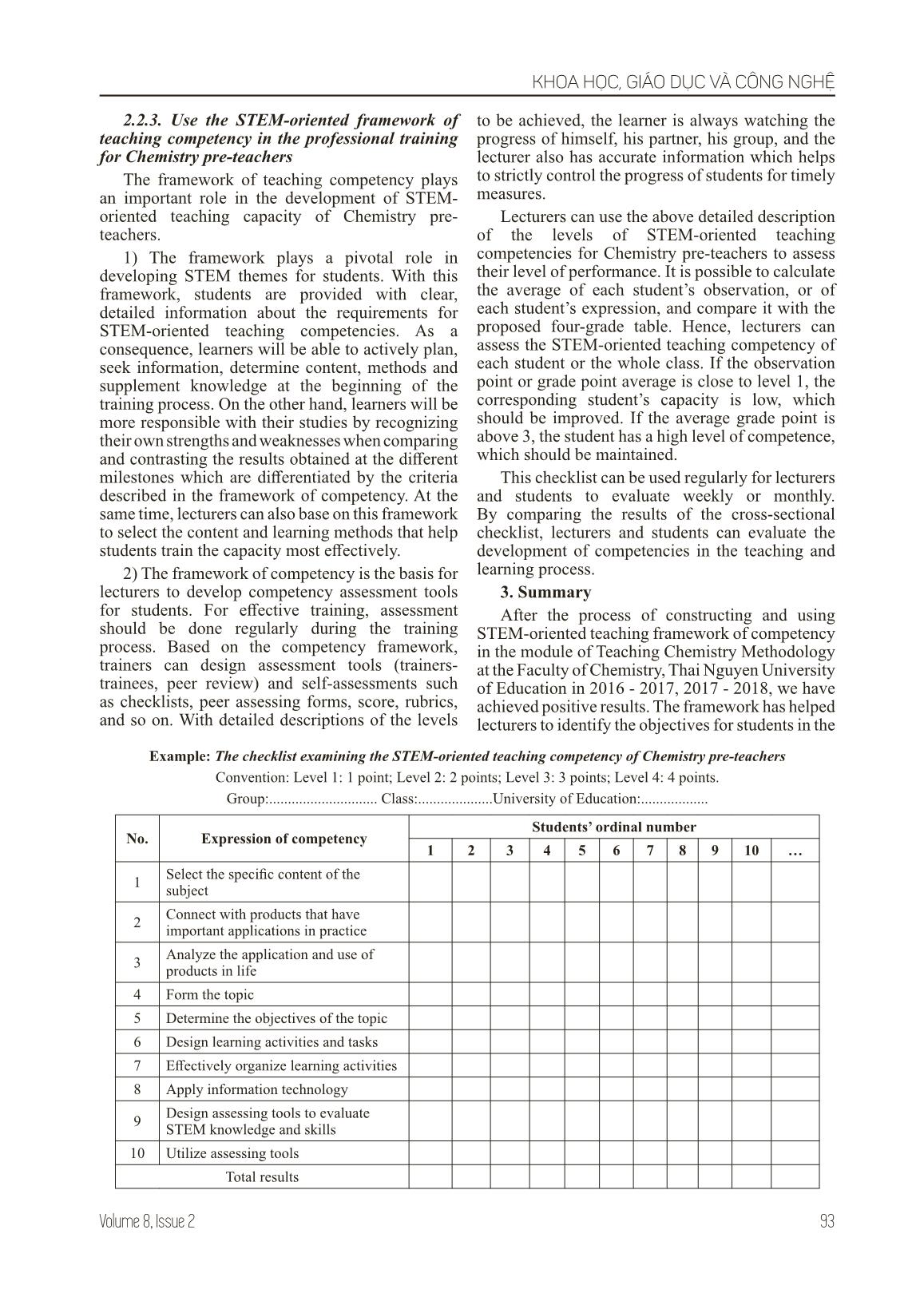
n and use effective STEM knowledge and assessment tools. Based on the definition of the STEM-oriented teaching and the characteristics of the curriculum of the Bachelor of Chemistry, a framework of STEM teaching competency has been built as following: Table 1: Description of structure of STEM-oriented teaching competency Component competency Criteria 1) The ability to build up STEM-oriented educational topics Criterion 1: Selecting the specific content of the subject Criterion 2: Linking between the content with products which are important and feasible in the real life Criterion 3: Analyzing the application and use of the products in the real life Criterion 4: Forming a topic 2) The ability to design and organize STEM teaching activities Criterion 5: Identifying the target of the topic Criterion 6: Designing learning activities and tasks; assigning tasks Criterion 7: Effectively executing the activities Criterion 8: Applying information technology 3) The ability to test and evaluate in STEM teaching Criterion 9: Designing tools to assess knowledge and skills belonging to STEM Criterion 10: Utilizing the assessing tools From the STEM-oriented framework of teaching competency, we propose four basic levels from low to high capacity as follows: Level 1: Students’ competency is low; it needs to be formed. Level 2: Students’ competency is at medium level (initially formed); it needs to be fostered. Level 3: Students’ competency is at a good level (formed); it needs to be fostered to develop. Level 4: Students’ competency is at a high level (formed and developed); it needs to be maintained. Based on the descriptions of these basic levels, we describe in detail the level of manifestation of competencies through the following criteria: KHOA HỌC, GIÁO DỤC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ 92 JOURNAL OF ETHNIC MINORITIES RESEARCH Table 2. Detailed description of STEM-oriented framework of teaching competencies of Chemistry pre-teachers Criteria Level 4 3 2 1 1) The ability to build up STEM-oriented educational topics Criterion 1: Selecting the specific content of the subject Analyze, identify the scope of contents of the chapter/unit, point out the relevant practical issues. Analyze the characteristics, but not the scope of the contents of the chapter/unite, point out the relevant practical problems. Analyze the characteristics of the content of the chapter/unit, initially recognize the relevant practical issues. The content of the chapter/unit has not been analyzed, cannot address the relevant practical issues. Criterion 2: Linking between the content with products which are important and feasible in the real life Fully describe chemical products in terms of form, composition, properties, uses, production, etc. in practice. Not fully describe the chemical products in terms of form, composition, properties, uses, production, etc. in practice Describe the chemical products in terms of form, composition, uses, production, etc. according to the textbook. Cannot describe the chemical products in terms of form, composition, properties, uses, production, etc. in practice. Criterion 3: Analyzing the application and use of the products in the real life Analyze in detail the applications and benefits and disadvantages of the use and production of products in life. Inadequately analyze in detail the applications, benefits and disadvantages of the use and production of products in life. Analyze applications, benefits and disadvantages of the use and production of products in life but not detailed and complete. State without analyzing the applications, benefits and disadvantages of the use and production of products in the life. Criterion 4: Forming a topic The topic is formed by re-arranging the contents of the program, the name and the content are in accordance with practical issues. The topic is formed from the available lessons, naming and defining content that is in accordance with the practical issues. The topic is formed from the available lessons, with re-arrangement of the name and content but not suitable with practical issues. The topic is formed from the available lessons, without re-arrangement of the name and content to suit the practical issues. 2) The ability to design and organize STEM teaching activities Criterion 5: Identifying the objectives of the topic The objectives are clearly defined, full of components, using measurable action verbs. The objectives are clearly defined, full of components, but sometimes use of cognitive verbs which are difficult to measure. The objectives are quite clearly defined, full of components, use too many cognitive words that are difficult to measure. The objectives are not clearly defined, not full of components, not use measurable action verbs. Criterion 6: Designing learning activities and tasks; assigning tasks Select and design learning activities which are suitable with the objectives; describe the objectives, content, techniques and products in details. Design learning activities in the sequences described in textbook, suitable with objectives; describe the objectives, content, techniques and products in details. Design learning activities in the sequences described in textbook, suitable with objectives; not describe the objectives, content, techniques and products in details. Not design learning activities in the sequence described in textbook which includes: objectives, content, techniques and products. Criterion 7: Effectively executing the activities Organize learning activities for students by assigning tasks, encourage and help students to operate, answer and conclude. Students complete the learning products by themselves. Organize learning activities for students by assigning tasks, encourage and help students to operate, answer and conclude. Students are supported to complete the learning products. Organize learning activities for students by assigning tasks, encourage and help students to operate, answer and conclude. Students are guided to complete the learning products. Not organize learning activities for students by assigning tasks; teacher talking time is too much, students do not work to conclude and cannot complete the learning products. Criterion 8: Applying information technology Apply information technology in designing lesson plans and effectively delivering the lessons. Apply information technology in designing lesson plans, but not effectively deliver the lessons. Apply information technology in planning lessons and teaching. Not apply information technology in planning lessons and teaching. 3) The ability to test and evaluate in STEM teaching Criterion 9: Designing tools to assess knowledge and skills belonging to STEM Design reasonable and logical assessing tools (tests) to evaluate STEM knowledge and skills. Design reasonable but not logical assessing tools (tests) to evaluate STEM knowledge and skills. Design assessing tools (tests) to evaluate STEM knowledge and skills but they are not reasonable and logical. Not distinguish and design assessing tools (tests) to evaluate STEM knowledge and skills. Criterion 10: Utilizing the assessing tools Use the assessing tools effectively. Use the assessing tools. Use the assessing tools ineffectively. Unable to use assessing tools. KHOA HỌC, GIÁO DỤC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ 93Volume 8, Issue 2 2.2.3. Use the STEM-oriented framework of teaching competency in the professional training for Chemistry pre-teachers The framework of teaching competency plays an important role in the development of STEM- oriented teaching capacity of Chemistry pre- teachers. 1) The framework plays a pivotal role in developing STEM themes for students. With this framework, students are provided with clear, detailed information about the requirements for STEM-oriented teaching competencies. As a consequence, learners will be able to actively plan, seek information, determine content, methods and supplement knowledge at the beginning of the training process. On the other hand, learners will be more responsible with their studies by recognizing their own strengths and weaknesses when comparing and contrasting the results obtained at the different milestones which are differentiated by the criteria described in the framework of competency. At the same time, lecturers can also base on this framework to select the content and learning methods that help students train the capacity most effectively. 2) The framework of competency is the basis for lecturers to develop competency assessment tools for students. For effective training, assessment should be done regularly during the training process. Based on the competency framework, trainers can design assessment tools (trainers- trainees, peer review) and self-assessments such as checklists, peer assessing forms, score, rubrics, and so on. With detailed descriptions of the levels to be achieved, the learner is always watching the progress of himself, his partner, his group, and the lecturer also has accurate information which helps to strictly control the progress of students for timely measures. Lecturers can use the above detailed description of the levels of STEM-oriented teaching competencies for Chemistry pre-teachers to assess their level of performance. It is possible to calculate the average of each student’s observation, or of each student’s expression, and compare it with the proposed four-grade table. Hence, lecturers can assess the STEM-oriented teaching competency of each student or the whole class. If the observation point or grade point average is close to level 1, the corresponding student’s capacity is low, which should be improved. If the average grade point is above 3, the student has a high level of competence, which should be maintained. This checklist can be used regularly for lecturers and students to evaluate weekly or monthly. By comparing the results of the cross-sectional checklist, lecturers and students can evaluate the development of competencies in the teaching and learning process. 3. Summary After the process of constructing and using STEM-oriented teaching framework of competency in the module of Teaching Chemistry Methodology at the Faculty of Chemistry, Thai Nguyen University of Education in 2016 - 2017, 2017 - 2018, we have achieved positive results. The framework has helped lecturers to identify the objectives for students in the Example: The checklist examining the STEM-oriented teaching competency of Chemistry pre-teachers Convention: Level 1: 1 point; Level 2: 2 points; Level 3: 3 points; Level 4: 4 points. Group:............................. Class:....................University of Education:.................. No. Expression of competency Students’ ordinal number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 Select the specific content of the subject 2 Connect with products that have important applications in practice 3 Analyze the application and use of products in life 4 Form the topic 5 Determine the objectives of the topic 6 Design learning activities and tasks 7 Effectively organize learning activities 8 Apply information technology 9 Design assessing tools to evaluate STEM knowledge and skills 10 Utilize assessing tools Total results KHOA HỌC, GIÁO DỤC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ 94 JOURNAL OF ETHNIC MINORITIES RESEARCH module, thereby developing the content of teaching and choosing more appropriate method of teaching. At the same time, more opportunities have been created for students to participate and evaluate the process, which, consequently, helps them to know what to do and to improve for the best results. This approach is perfectly suited to the requirements of learner-developing-oriented teaching method. References [1] content/Doc-String-in-chong-trinh-giao-duc-pho-thong-moi, accessed on 10/Oct/2018 [2] Ministry of Education and Training, Education Curriculum - General Program, 2017. [3] Le Xuan Quang, Teaching Technology in the orientation of STEM teaching, Ph.D thesis, Hanoi University of Education, 2017. [4] Ministry of Education and Training, Official Letter No. 4612 / MOET-SSE, dated 03/10/2017, Guiding the implementation of the current general education curriculum in the orientation of capacity and quality development for students starting at the academic years 2017-2018. [5] http // www.britishcouncil.vn / sites / default / files / tong_hop_link_tai_lieu_tap_huan_stem_ thang_8_0.pdf / Training on STEM-oriented teaching methods - accessed on 15/Oct/2018 [6] STEM Education in Schools: Not Just Theory - 6/May/2017. [7] Ministry of Education and Training, OL 1891 /MOET-UE 5/May/2017: Promoting and developing STEM education (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics), applying interdisciplinary knowledge to solve problems in life and production. [8] Assoc. Nguyen Xuan Thanh, Organizing teaching procedure in association with production and business in the general education curriculum, Core Teacher Training Lecture - Dec/2017. [9] Nguyen Thanh Hai, https://hocvienkhampha.edu.vn/mo-hinh-day-hoc-5e-trong-giao-duc-stem, accessed on 15/Oct/2018 [10] Boston Children Museum, STEM Sprouts Teaching Guide, 2013 XÂY DỰNG KHUNG NĂNG LỰC DẠY HỌC STEM CHO SINH VIÊN SƯ PHẠM HÓA HỌC ĐÁP ỨNG YÊU CẦU ĐỔI MỚI ĐÀO TẠO GIÁO VIÊN HIỆN NAY Hoàng Thị Chiên Đại học Sư phạm Thái Nguyên Email: hoangchien-khoahoa@dhsptn.edu.vn Ngày nhận bài: 27/5/2019 Ngày gửi phản biện: 3/6/2019 Ngày tác giả sửa: 7/6/2019 Ngày duyệt đăng: 12/6/2019 Ngày phát hành: 21/6/2019 DOI: https://doi.org/10.25073/0866-773X/306 Tóm tắt: Dạy học theo quan điểm giáo dục STEM (dạy học STEM) là một trong những định hướng quan trọng của đổi mới chương trình giáo dục phổ thông Việt Nam. Tuy nhiên, đến nay chưa có khung năng lực STEM trong dạy học ở nước ta. Khung năng lực dạy học STEM mang đồng thời hai ý nghĩa quan trọng. Một là: người học chủ động lập kế hoạch, tìm kiếm thông tin, xác định nội dung, phương pháp và bổ sung kiến thức liên môn từ khi bắt đầu quá trình rèn luyện. Hai là: định hướng cho việc đánh giá mức độ biểu hiện tương ứng cho từng sinh viên sư phạm. Bài viết trình bày quy trình xây dựng khung năng lực dạy học STEM đồng thời đề xuất một số cách sử dụng chúng trong quá trình đào tạo tại các trường Đại học Sư phạm. Từ khóa: Khung năng lực; Dạy học STEM; Đại học sư phạm; Sinh viên sư phạm hóa học.
File đính kèm:
 designing_a_competencies_framework_for_stem_teaching_for_pre.pdf
designing_a_competencies_framework_for_stem_teaching_for_pre.pdf

