Đánh giá ảnh hưởng của ba loại chiết xuất thảo dược đến sự biểu hiện gen của tế bào cá mú Epinephelus coioides
TÓM TẮT
Trong nghiên cứu thử nghiệm đối với ba loại chiết xuất từ thảo dược (Houttuynia cordata, Polygonum
cuspidatum và Astragalus spp.) nhằm khảo sát khả năng ảnh hưởng đến sự biểu hiện gen trên tế
bào GK của cá mú bông. Thí nghiệm được tiến hành với 3 nồng khác nhau ở thảo dược Houttuynia
cordata và Polygonum cuspidatum (1μL; 5μL và 10μL), 2 nồng độ với Astragalus spp. Kết quả biểu
hiện các gen IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α, MHC-I, C3 và IL6 của tế bào GK có sự khác
nhau đối với từng loại thảo dược ở các nồng độ khác nhau. Đối với hai loại thảo dược Huottuynia
cordata và Polygonum cuspidatum, các gen được phân tích khả năng biểu hiện sau 24 giờ thí
nghiệm cho kết quả tương đương nhau chủ yếu với các gen IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, và TNF
α gene. Ở thí nghiệm đối với Astragalus spp, kết quả miêu tả rằng có 5 loại gen được biểu hiện là
IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β và Mx. Trong các gen biểu hiện thì IgD là cao nhất so với các gen khác.

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Đánh giá ảnh hưởng của ba loại chiết xuất thảo dược đến sự biểu hiện gen của tế bào cá mú Epinephelus coioides

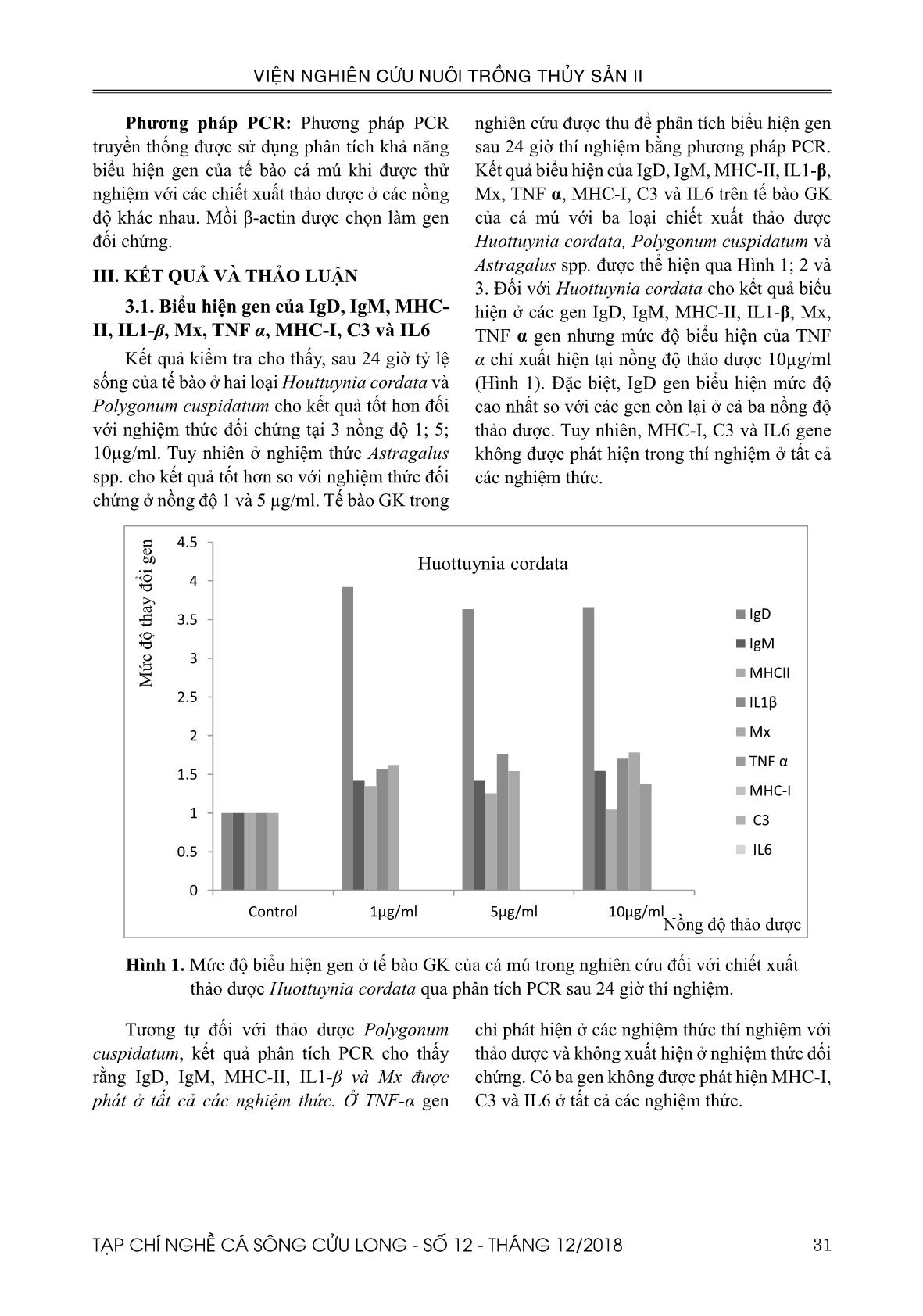
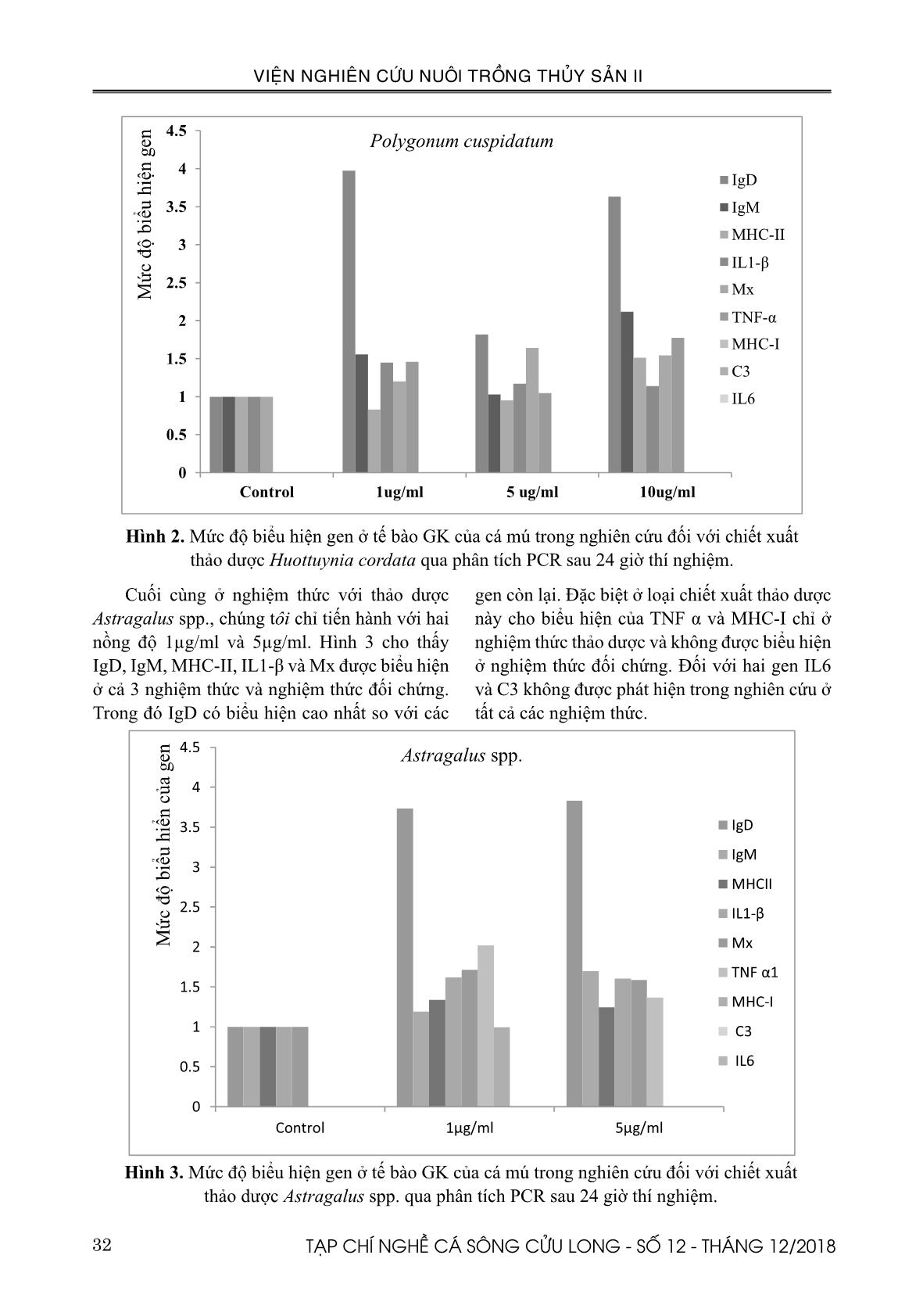
Đối với từng loại thảo dược, thử nghiệm 4 nồng độ nhằm kiểm tra độc tố của thảo dược lên tế bào là 1; 5; 10 và 50μg/ml. Các loại mồi được tiến hành nghiên cứu trên biểu hiện gen của tế bào cá mú khi thử nghiệm với các nồng độ khác nhau của 3 loại thảo dược. Có 9 loại mồi được tiến hành trong thí nghiệm IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α, MHC-I, C3 và IL6, trình tự mồi được thể hiện ở Bảng 1. Bảng 1: Các loại mồi được sử dụng trong nghiên cứu biểu hiện gen ở tế bào cá mú khi thử nghiệm với các loại thảo dược. Tên mồi Mồi xuôi Mồi ngược IL-1β AgCTCTgCCTCCACAgAgA CTCAAgCTgTgCCAgAACCT IL-6 CCTCCAACTTCAgCAAggAg CCTAGACAgCCAGgACTTCCTC TNF-α gAATggAggAgTCAggTggA CTCCTCACAAggCAAACACA Mx gCTgCgAgAAggAgCTAgAA TCTCTCCATCAggATCCACC C3 gCTggAgAAAgTCgTCTTgg gTgggTTgCTgTggAACTTT IgD ATTTTgACgCCAAgTTgACC TgCCAgCTTgAAAAgTgATg IgM CTATCTgCTgggCAggTgTT gCAgCAgAATCTTCAgTCTTCA MHC Iα ACCACgATggATCCTTTCAg TgCgCCTACAATCACAgAAg MHC IIα ggAgAAgACTCAgCCCAgTg CTgAAgCCTgACCAACACAA β-actin gTTgCACTggACTTTgAgCA ACATCTgCTggAAggTggAC 31TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 12 - THÁNG 12/2018 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN II Phương pháp PCR: Phương pháp PCR truyền thống được sử dụng phân tích khả năng biểu hiện gen của tế bào cá mú khi được thử nghiệm với các chiết xuất thảo dược ở các nồng độ khác nhau. Mồi β-actin được chọn làm gen đối chứng. III. KẾT QUẢ VÀ THẢO LUẬN 3.1. Biểu hiện gen của IgD, IgM, MHC- II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α, MHC-I, C3 và IL6 Kết quả kiểm tra cho thấy, sau 24 giờ tỷ lệ sống của tế bào ở hai loại Houttuynia cordata và Polygonum cuspidatum cho kết quả tốt hơn đối với nghiệm thức đối chứng tại 3 nồng độ 1; 5; 10µg/ml. Tuy nhiên ở nghiệm thức Astragalus spp. cho kết quả tốt hơn so với nghiệm thức đối chứng ở nồng độ 1 và 5 µg/ml. Tế bào GK trong nghiên cứu được thu để phân tích biểu hiện gen sau 24 giờ thí nghiệm bằng phương pháp PCR. Kết quả biểu hiện của IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α, MHC-I, C3 và IL6 trên tế bào GK của cá mú với ba loại chiết xuất thảo dược Huottuynia cordata, Polygonum cuspidatum và Astragalus spp. được thể hiện qua Hình 1; 2 và 3. Đối với Huottuynia cordata cho kết quả biểu hiện ở các gen IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α gen nhưng mức độ biểu hiện của TNF α chỉ xuất hiện tại nồng độ thảo dược 10µg/ml (Hình 1). Đặc biệt, IgD gen biểu hiện mức độ cao nhất so với các gen còn lại ở cả ba nồng độ thảo dược. Tuy nhiên, MHC-I, C3 và IL6 gene không được phát hiện trong thí nghiệm ở tất cả các nghiệm thức. Hình 1. Mức độ biểu hiện gen ở tế bào GK của cá mú trong nghiên cứu đối với chiết xuất thảo dược Huottuynia cordata qua phân tích PCR sau 24 giờ thí nghiệm. Tương tự đối với thảo dược Polygonum cuspidatum, kết quả phân tích PCR cho thấy rằng IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β và Mx được phát ở tất cả các nghiệm thức. Ở TNF-α gen chỉ phát hiện ở các nghiệm thức thí nghiệm với thảo dược và không xuất hiện ở nghiệm thức đối chứng. Có ba gen không được phát hiện MHC-I, C3 và IL6 ở tất cả các nghiệm thức. 32 TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 12 - THÁNG 12/2018 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN II Hình 2. Mức độ biểu hiện gen ở tế bào GK của cá mú trong nghiên cứu đối với chiết xuất thảo dược Huottuynia cordata qua phân tích PCR sau 24 giờ thí nghiệm. gen còn lại. Đặc biệt ở loại chiết xuất thảo dược này cho biểu hiện của TNF α và MHC-I chỉ ở nghiệm thức thảo dược và không được biểu hiện ở nghiệm thức đối chứng. Đối với hai gen IL6 và C3 không được phát hiện trong nghiên cứu ở tất cả các nghiệm thức. Cuối cùng ở nghiệm thức với thảo dược Astragalus spp., chúng tôi chỉ tiến hành với hai nồng độ 1µg/ml và 5µg/ml. Hình 3 cho thấy IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β và Mx được biểu hiện ở cả 3 nghiệm thức và nghiệm thức đối chứng. Trong đó IgD có biểu hiện cao nhất so với các Hình 3. Mức độ biểu hiện gen ở tế bào GK của cá mú trong nghiên cứu đối với chiết xuất thảo dược Astragalus spp. qua phân tích PCR sau 24 giờ thí nghiệm. 33TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 12 - THÁNG 12/2018 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN II IV. KẾT LUẬN Kết quả nghiên cứu biểu hiện gen của tế bào GK cá mú cho kết quả tương ứng với từng loại gen và từng nồng độ thảo dược khác nhau. Đối với Houttuynia cordata cho kết quả biểu hiện ở 5 loại gen IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, và Mx. Trong khi đó ở thí nghiệm với thảo dược Polygonum cuspidatum cho kết quả biểu hiện trên 6 loại IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx và TNF α. Riêng đối với thảo dược Astragalus spp. cho kết quả biểu hiện trên 6 loại gen ở nồng độ 1 µg/ml và 7 loại gen biểu hiện ở nồng độ 5 µg/ml. TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO Brown, D. L., Dorling, K., 2006. Encyclopedia of herbs and their uses. Chakraborti, S., Sinha, S., Sinha, R.K, 2006. High- frequency induction of multiple shoots and clonal propagation from rhizomatous nodal segments of Houttuynia Cordata Thunb. An ethnomedicinal herb of India. In vitro cellular & developmental biology - plant 42:394–8. Chao, C.B., Yang, C.S., Tsai, Y.H., Chen, C.Y., Lin, C.S., Huang, H.T., 2016. A nested PCR for the detection of grouper iridovirus in Taiwan (TGIV) in cultured Hybrid grouper, Giant seaperch, and Largemouth bass. Journal of aquatic animal health 14: 104-113. Chen, X., Wang, Z., Yang, Z., Wang, J., Xu, Y., Tan, R.X., 2011. Houttuynia cordata blocks HSV infection through inhibition of NF-κB activation. Antiviral Res. 92: 341–5. Chen, Y.M., Kuo, C.E., Chen, G.R., Kao, Y.T., Zou, J., Secombes, C.J., Chen, T.Y., 2014. Functional analysis of an orange-spotted grouper (Epiephelus coioides) interferon gene and characterization of its expression in response to nodavirus infection. Developmental and comparative immunology 46: 117-128. Chen, L.M., Wang, F., Song, W., Hew, C.L., 2006. Temporal and differential gene expression of Singapore grouper iridovirus. Journal of general virology 87: 2907-2915. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2015. Chinese Pharmacopoeia, Section on Chinese medicine, Notes for clinicians. China Medical Science Press, Beijing, pp. 302-303. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission: Part I. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2010. Choi, H.J, Song, J.H., Park, K.S., Kwon, D.H., 2009b. Inhibitory effects of quercetin 3-rhamnoside on influenza A virus replication. Eur J Pharm Sci. 37: 329–33. Chou, S.C., Su, C.R., Ku, Y.C., Wu, T.S., 2009. The constituents and their bioactivities of Houttuynia cordata. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 57: 1227–30. Editorial Committee of Chinese Materia Medica, 1998. Chinese Materia Medica. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Science and Technology Press. Fu, J., Wang, Z., Huang, L., Zheng, S., Wang, D., Chen, S., Zhang, H., Yang, S., 2014. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res. 28: 1275-1283. Goshi, K., Hidehiro, K., Takashi, A., Ikuo, H., 2010. BBC vaccine confers adaptive immunity against Mycobacterium sp. Infection in fish. Developmental and comparative immunology 34: 133-140. Harley, C. B., Liu, W., Blasco, M., Vera, E., Andrews, W. H., Briggs, L. A., Raffaele, J. M., 2011. A Natural Product Telomerase Activator as Part of a Health Maintenance Program. Rejuvenation Research 14 (1): 45-56. Hynniewta, S.R. and Kumar, Y., 2008. Herbal remedies among the Khasi traditional healers and village folks in Meghalaya. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 7: 581-6. Infante, F., Garcıa, A., Moyano, R., 1991. Toxicolog´ıa del g´enero Astragalus. In Libro homenaje al Profesor Doctor Don Rodrigo Pozo Lara, ed. by A. Rodero and R. Jordano, pp. 21- 57. Ed. Universidad de Co´ rdoba, Spain. James, J.E., Molyneux, R.J., and Panter, K.E., 1990. The potential for the toxic principles of Astragalus and related plants to appear in meat and milk. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 32 (suppl.): 104-109. Kai, Y.H., Wu, Y.C., Chi, S.C., 2014. Immune gene expressions in grouper larvae (Epinephelus coioides) induced by bath and vaccinations with inactivated betanodavirus. Fish & shellfish immunology 40: 563-569. Kanjilal, P.C., Dev, R.N., 1937. III. New Delhi: Omsons Publishers. Flora of Assam: 113. 34 TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 12 - THÁNG 12/2018 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN II Ketut, M., Haryanti, A.M., Teruo, M., 2008. Histopathological and ultrastructural features of enlarged cells of humpback grouper Cromileptes altivelis challenged with Megalocytivirus (family Iridovidae) after vaccination. Diseases of aquatic organisms 79: 163-168. Kim, G.S., Kim, D.H., Lim, J.J., Lee, J.J., Han, D.Y., Lee, W.M., 2008. Biological and antibacterial activities of the natural herb Houttuynia cordata water extract against the intracellular bacterial pathogen Salmonella within the RAW 264.7 macrophage. Biol Pharm Bull. 31: 2012–7. Lau, K.M., Lee, K.M., Koon, C.M., Cheung, C.S., Lau, C.P., Ho, H.M., 2008. Immunomodulatory and anti-SARS activities of Houttuynia cordata. J Ethnopharmacol. 118: 79–85. Leardkamolkarn, V., Sirigulpanit, W., Phurimsak, C., Kumkate, S., Himakoun, L., Sripanidkulchai, B., 2012. The inhibitory actions of Houttuynia cordata aqueous extract on dengue virus and dengue-infected cell. J Food Biochem 36: 86-92. Leu, Y.L., Hwang, T.L., Hu, J.W., Fang, J.Y., 2008. Anthraquinones from Polygonum cuspidatum as tyrosinase inhibitors for dermal use. Phytother Res. 22(4): 552-6. Lin, L.Z., He, X.G., Lindenmaier, M., Nolan, G., Yang, J., Cleary, M., Qiu, S. X., Cordell, G.A., 2000. “Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Study of the Flavonoids of the Roots of Astragalus mongholicus and A. membranaceus”. Journal of Chromatography A 876 (1–2): 87-95. Lu, H.M., Liang, Y.Z., Yi, L.Z., Wu, X.J., 2006. Anti-inflammatory effect of Houttuynia cordata injection. J Ethnopharmacol. 104: 245-9. Lu, L., Zhou, S.Y., Chen, C., Weng, S.P., Chan, S.M., He, J.G., 2005. Complete genome sequence analysis of an iridovirus isolated from the orange-spotted grouper, Epiephelus coioides. Virology. 339: 81-100. Matsuda, H., Shimoda, H., Morikawa, T., Yoshikawa, M., 2001. Phytoestrogens from the roots of Polygonum cuspidatum (Polygonaceae): structure-requirement of hydroxyanthraquinones for estrogenic activity. Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry Letters 11(14): 39-42. Mei, J., 2012. Analysis on medication rule in diabetes Ⅱ patients treated with Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhongguo Shi yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi v.18: 290-291. Ren, X., Sui, X., Yin, J., 2011. The effect of Houttuynia cordata injection on pseudorabies herpesvirus (PrV) infection in vitro. Pharm Biol. 49: 161-6. Shangliang, T., Hetrick, F.M, Roberson, B.S Baya, A., 1990. The antibacterial and antiviral activity of herbal extracts for fish pathogens. J Ocean Univ Qingdao 20: 53-60. Sivasankar, P., Anix, V., Santhiya, A., Kanaga, V.A., 2015. Review on plants and herbal extracts against viral diseases in aquaculture. JMPS 3(2): 75-79. Tutupalli, L.V., Chaubal, M.G., Saururaceae, V., 1975. Composition of essential oil from foliage of Houttuynia cordata and chemo systematics of Saururaceae. Lloydia. 38: 92-106. Uphof, J.C.T., 1968. Dictionary of Economic Plants, p. 591. J. Cramer, Lehre (Germany). Xu, D., Wei, J., Cui, H., Gong, J., Yan, Y., Lai, R., Qin, Q., 2010. Differential profile of gene expression in grouper Epiephelus coioides, infected with Singapore grouper iridovirus, revealed by suppression subtractive hybridization and DNA microarray. Journal of fish biology 77: 341-360. Xu, Q., Ma, X., Liang, X., 2007. “Determination of Astragalosides in the Roots of Astragalus spp. Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry”. Phytochemical Analysis 18 (5): 419-427. Yeh, C.H., Chen, Y.S., Wu, M.S., Chen, C.W., Yuan, C.H., Pan, K.W., Chang, Y.N., Chuang, N.N., Chang, C.Y., 2008. Differential display of grouper iridovirus-infected grouper cells by immunostaining. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 372: 674-680. Zhang, C., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Xiao, H., Liang, X., 2009. Bioassay-guided separation of citreorosein and other oestrogenic compounds from Polygonum cuspidatum. Phytother Res. 23(5): 740-751. Zhang, H., Zhang, Q.W., Wang, L., Zhang, X.Q., Ye, W.C., Wang, Y.T., 2012. Two new anthraquinone malonylglucosides from Polygonum cuspidatum. Nat Prod Res. 26 (14): 23-27. Zhang, K., Pugliese, M., Pugliese, A., Passantino, A., 2015. Biological active ingredients of traditional Chinese herb Astragalus membranaceus on treatment of diabetes: a systematic review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem 15: 315-329. 35TẠP CHÍ NGHỀ CÁ SÔNG CỬU LONG - SỐ 12 - THÁNG 12/2018 VIỆN NGHIÊN CỨU NUÔI TRỒNG THỦY SẢN II EVALUATION OF FUNCTION OF THREE DIFFERENT HERBS ON GENE EXPRESSION IN GROUPER Epinephelus coioides Vo Bich Xoan1*, Ming Wei-Lu ABTRACT In this study, we examined the effect of three Chinese herbal extracts (Houttuynia cordata, Polygonum cuspidatum and Astragalus spp.) applied on GK cells of orange-spotted grouper to evaluate gene expression. The experiment was conducted at 3 concentrations (1 µg/ml, 5µg/ml and 10µg/ml) for Houttuynia cordata, Polygonum cuspidatum and two concentration (1μL; μL 5 ) for Astragalus spp. In this experiment, the result of gene expression of IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α, MHC-I, C3 and IL6 in GK cells infected with three Chinese herbs namely Huottuynia cordata, Polygonum cuspidatum and Astragalus spp were different at three concentrations. IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β, Mx, TNF α gene expression were observed GK cells infected with Huottuynia cordata and Polygonum cuspidatum after 24 hours of herb treatment. At Astragalus spp treatment, the result indicated that five genes namely IgD, IgM, MHC-II, IL1-β and Mx were detected and the expression of IgD was highest compared to others. Keywords: orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, herbal extracts, iridovirus. Người phản biện: TS. Lê Hồng Phước Ngày nhận bài: 20/12/2018 Ngày thông qua phản biện: 27/12/2018 Ngày duyệt đăng: 31/12/2018 1 Research sub-Institute for Southern Hau River Fisheries, Research Institute for Aquaculture No. 2 * Email:xoangiang@gmail.com
File đính kèm:
 danh_gia_anh_huong_cua_ba_loai_chiet_xuat_thao_duoc_den_su_b.pdf
danh_gia_anh_huong_cua_ba_loai_chiet_xuat_thao_duoc_den_su_b.pdf

