Study on the removal of interferences for the determination of ⁸⁷Sr/⁸⁶Sr isotopic ratio in petroleum drill-Hole water samples using isotope dilution – inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ID-ICP-MS)
87Sr/86Sr isotopic ratio is one of the useful tools that can authenticate the original source of
the natural products from the earth-created and/or geological processes. However, the effect of
interferences in petroleum drill-holes water sample such as thickness of sample matrix or isotopic
signal of 87Rb might cause the low precision of 87Sr/86Sr determination using quadrupole inductively
coupled plasma spectrometry (ICP-MS). The elimination of these mentioned effects was thus studied
by using the ion - exchange chromatography. Calcium in sample matrix was separated on anionite
column (Bio-Rad AG1-X8 resin) in methanol medium with the high efficiency while rubidium was
removed from strontium on cation exchange resin (Bio-Rad AG50-X8) with strontium recovery over
99%. The isotope dilution technique with 86Sr - enriched isotopic standard solution was used for the
control of separation process. The 87Sr/86Sr isotopic ratio was thus determined using ICP-MS with the
signal correction by a strontium isotopic ratio standard reference material (NIST SRM 987).

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8

Trang 9

Trang 10
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Study on the removal of interferences for the determination of ⁸⁷Sr/⁸⁶Sr isotopic ratio in petroleum drill-Hole water samples using isotope dilution – inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ID-ICP-MS)

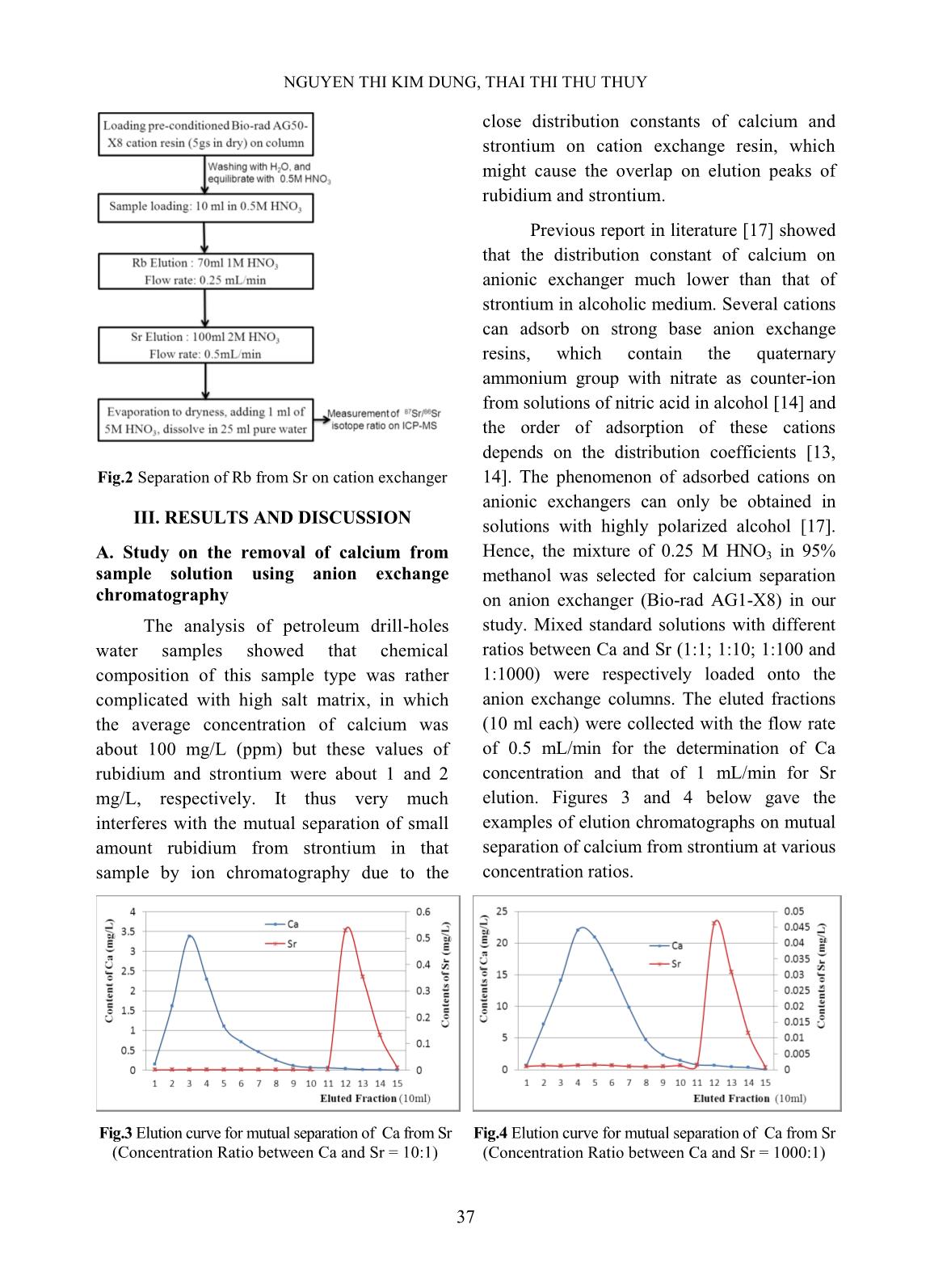
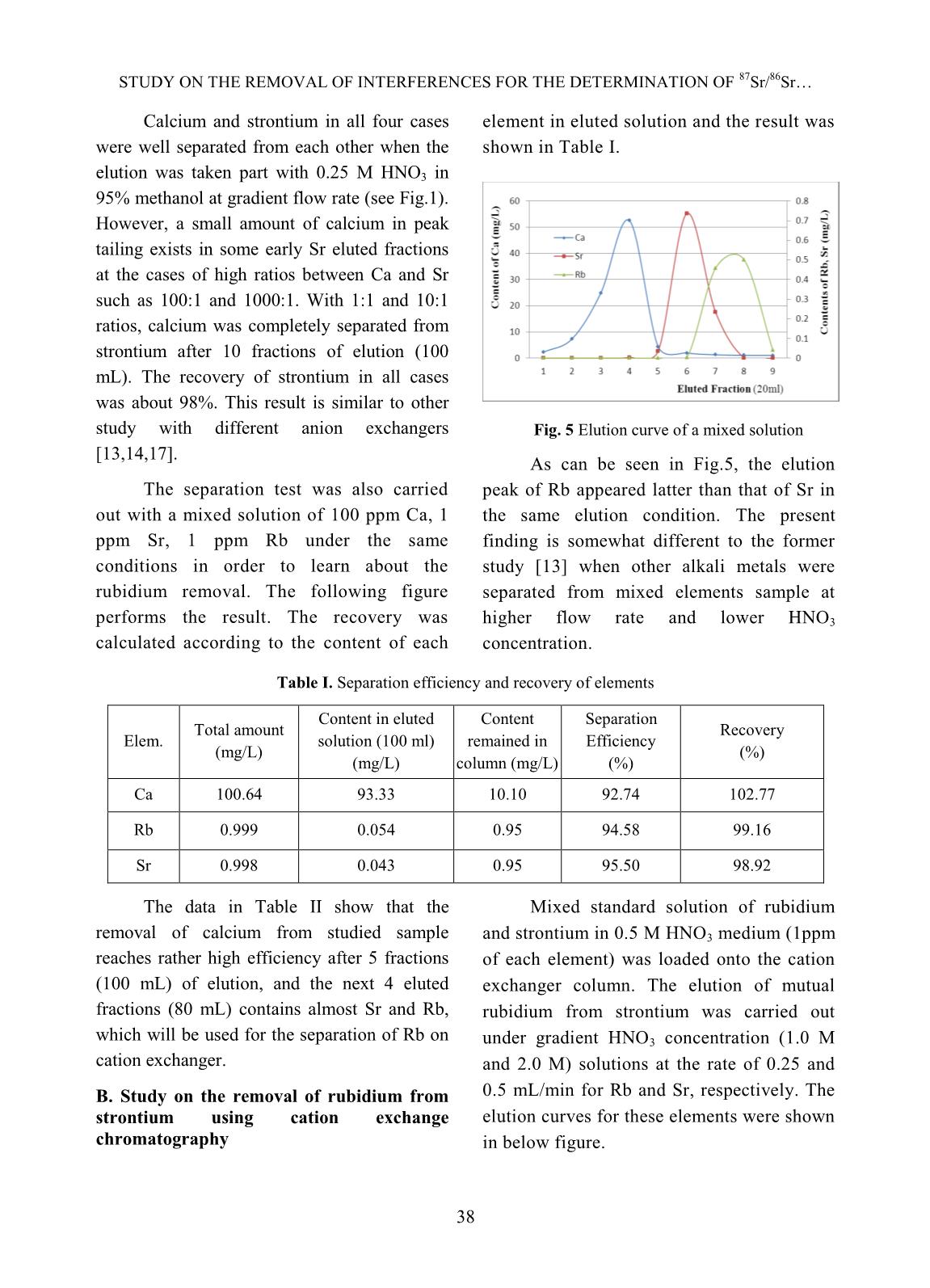
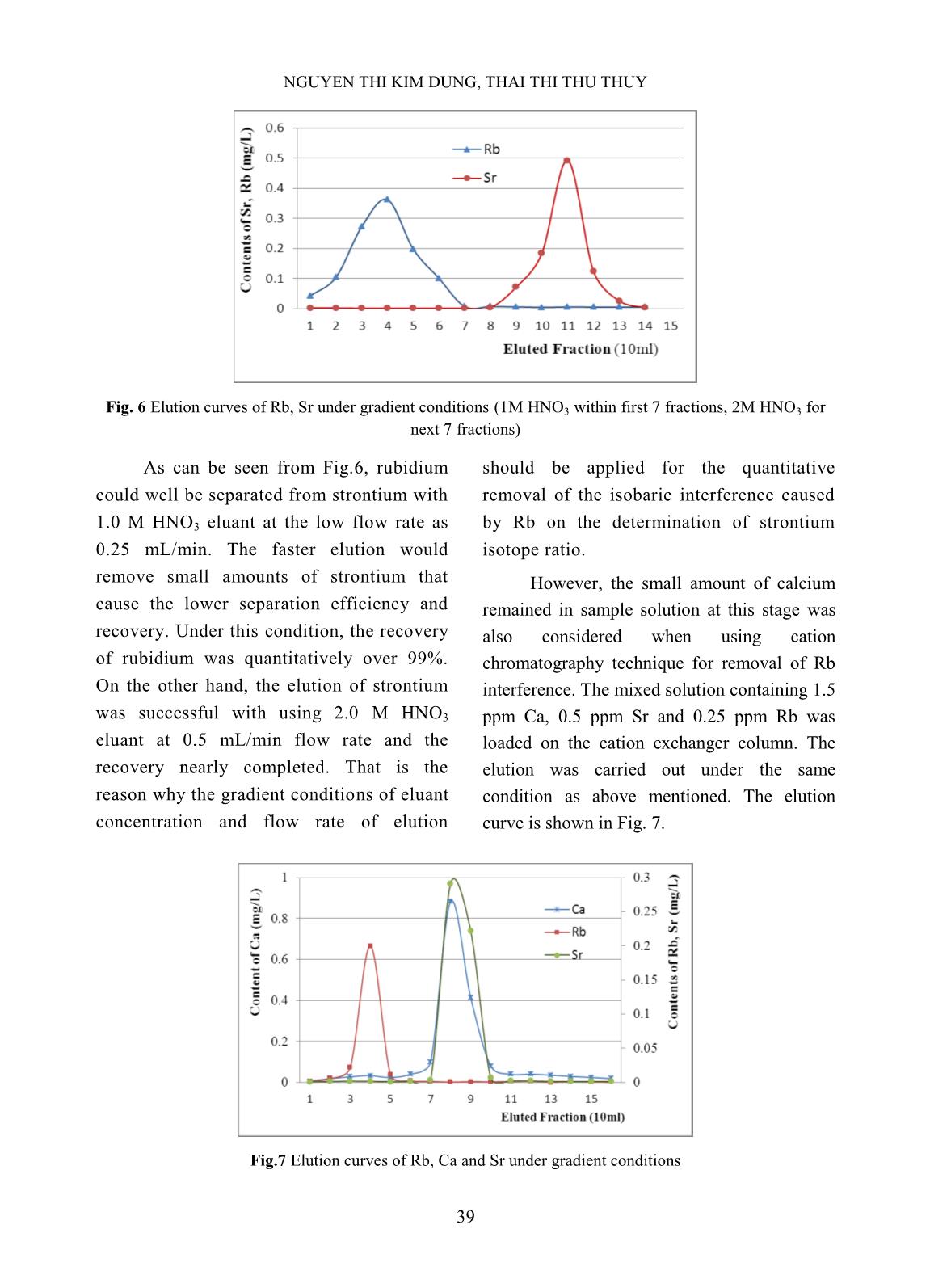
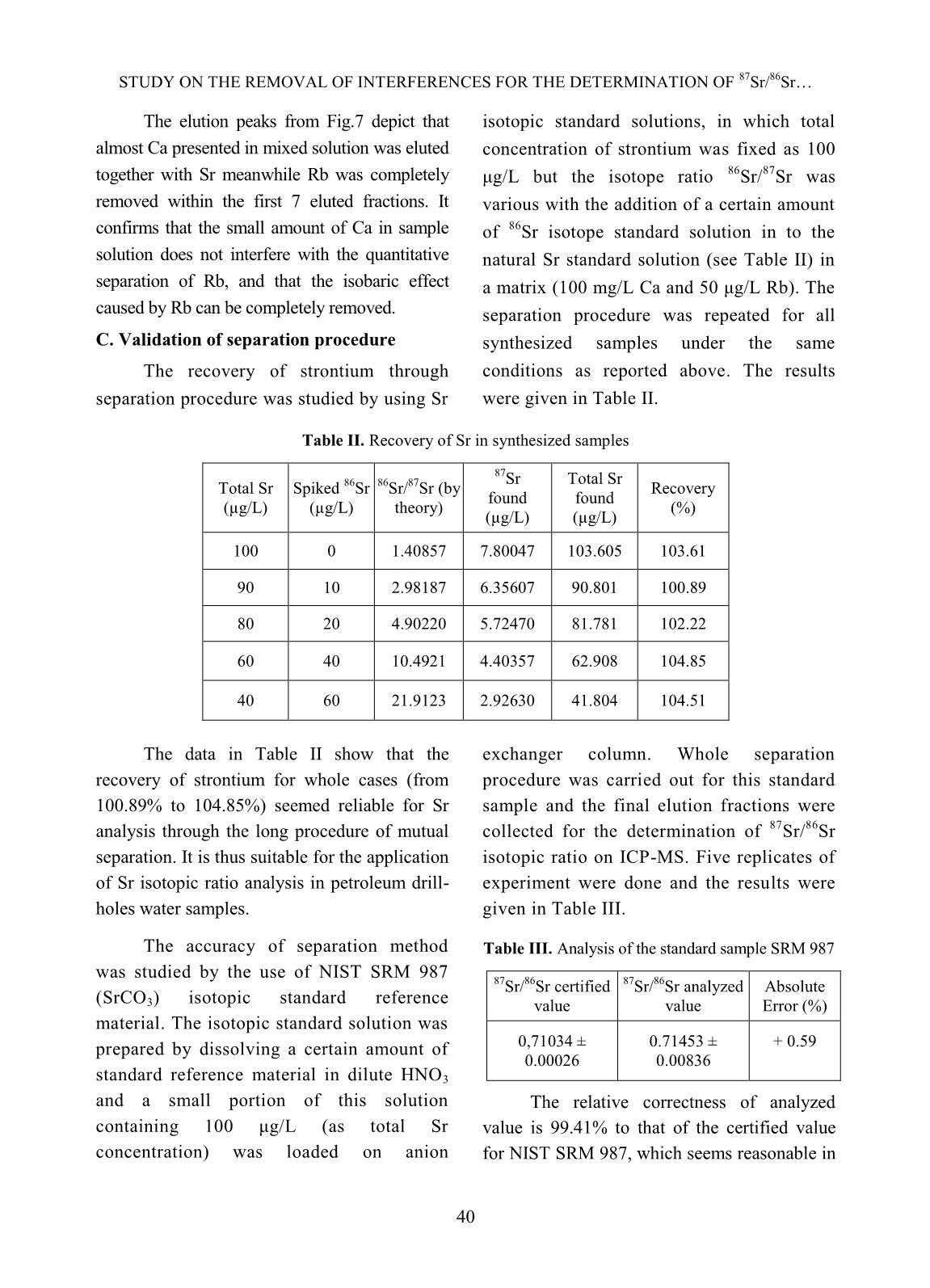
t matrix, in which anion exchange columns. The eluted fractions the average concentration of calcium was (10 ml each) were collected with the flow rate about 100 mg/L (ppm) but these values of of 0.5 mL/min for the determination of Ca rubidium and strontium were about 1 and 2 concentration and that of 1 mL/min for Sr mg/L, respectively. It thus very much elution. Figures 3 and 4 below gave the interferes with the mutual separation of small examples of elution chromatographs on mutual amount rubidium from strontium in that separation of calcium from strontium at various sample by ion chromatography due to the concentration ratios. Fig.3 Elution curve for mutual separation of Ca from Sr Fig.4 Elution curve for mutual separation of Ca from Sr (Concentration Ratio between Ca and Sr = 10:1) (Concentration Ratio between Ca and Sr = 1000:1) 37 STUDY ON THE REMOVAL OF INTERFERENCES FOR THE DETERMINATION OF 87Sr/86Sr Calcium and strontium in all four cases element in eluted solution and the result was were well separated from each other when the shown in Table I. elution was taken part with 0.25 M HNO3 in 95% methanol at gradient flow rate (see Fig.1). However, a small amount of calcium in peak tailing exists in some early Sr eluted fractions at the cases of high ratios between Ca and Sr such as 100:1 and 1000:1. With 1:1 and 10:1 ratios, calcium was completely separated from strontium after 10 fractions of elution (100 mL). The recovery of strontium in all cases was about 98%. This result is similar to other study with different anion exchangers Fig. 5 Elution curve of a mixed solution [13,14,17]. As can be seen in Fig.5, the elution The separation test was also carried peak of Rb appeared latter than that of Sr in out with a mixed solution of 100 ppm Ca, 1 the same elution condition. The present ppm Sr, 1 ppm Rb under the same finding is somewhat different to the former conditions in order to learn about the study [13] when other alkali metals were rubidium removal. The following figure separated from mixed elements sample at performs the result. The recovery was higher flow rate and lower HNO3 calculated according to the content of each concentration. Table I. Separation efficiency and recovery of elements Content in eluted Content Separation Total amount Recovery Elem. solution (100 ml) remained in Efficiency (mg/L) (%) (mg/L) column (mg/L) (%) Ca 100.64 93.33 10.10 92.74 102.77 Rb 0.999 0.054 0.95 94.58 99.16 Sr 0.998 0.043 0.95 95.50 98.92 The data in Table II show that the Mixed standard solution of rubidium removal of calcium from studied sample and strontium in 0.5 M HNO3 medium (1ppm reaches rather high efficiency after 5 fractions of each element) was loaded onto the cation (100 mL) of elution, and the next 4 eluted exchanger column. The elution of mutual fractions (80 mL) contains almost Sr and Rb, rubidium from strontium was carried out which will be used for the separation of Rb on under gradient HNO3 concentration (1.0 M cation exchanger. and 2.0 M) solutions at the rate of 0.25 and B. Study on the removal of rubidium from 0.5 mL/min for Rb and Sr, respectively. The strontium using cation exchange elution curves for these elements were shown chromatography in below figure. 38 NGUYEN THI KIM DUNG, THAI THI THU THUY Fig. 6 Elution curves of Rb, Sr under gradient conditions (1M HNO3 within first 7 fractions, 2M HNO3 for next 7 fractions) As can be seen from Fig.6, rubidium should be applied for the quantitative could well be separated from strontium with removal of the isobaric interference caused 1.0 M HNO3 eluant at the low flow rate as by Rb on the determination of strontium 0.25 mL/min. The faster elution would isotope ratio. remove small amounts of strontium that However, the small amount of calcium cause the lower separation efficiency and remained in sample solution at this stage was recovery. Under this condition, the recovery also considered when using cation of rubidium was quantitatively over 99%. chromatography technique for removal of Rb On the other hand, the elution of strontium interference. The mixed solution containing 1.5 was successful with using 2.0 M HNO3 ppm Ca, 0.5 ppm Sr and 0.25 ppm Rb was eluant at 0.5 mL/min flow rate and the loaded on the cation exchanger column. The recovery nearly completed. That is the elution was carried out under the same reason why the gradient conditions of eluant condition as above mentioned. The elution concentration and flow rate of elution curve is shown in Fig. 7. Fig.7 Elution curves of Rb, Ca and Sr under gradient conditions 39 STUDY ON THE REMOVAL OF INTERFERENCES FOR THE DETERMINATION OF 87Sr/86Sr The elution peaks from Fig.7 depict that isotopic standard solutions, in which total almost Ca presented in mixed solution was eluted concentration of strontium was fixed as 100 together with Sr meanwhile Rb was completely μg/L but the isotope ratio 86Sr/87Sr was removed within the first 7 eluted fractions. It various with the addition of a certain amount confirms that the small amount of Ca in sample of 86Sr isotope standard solution in to the solution does not interfere with the quantitative natural Sr standard solution (see Table II) in separation of Rb, and that the isobaric effect a matrix (100 mg/L Ca and 50 μg/L Rb). The caused by Rb can be completely removed. separation procedure was repeated for all C. Validation of separation procedure synthesized samples under the same The recovery of strontium through conditions as reported above. The results separation procedure was studied by using Sr were given in Table II. Table II. Recovery of Sr in synthesized samples 87Sr Total Sr Total Sr Spiked 86Sr 86Sr/87Sr (by Recovery found found (µg/L) (µg/L) theory) (%) (µg/L) (µg/L) 100 0 1.40857 7.80047 103.605 103.61 90 10 2.98187 6.35607 90.801 100.89 80 20 4.90220 5.72470 81.781 102.22 60 40 10.4921 4.40357 62.908 104.85 40 60 21.9123 2.92630 41.804 104.51 The data in Table II show that the exchanger column. Whole separation recovery of strontium for whole cases (from procedure was carried out for this standard 100.89% to 104.85%) seemed reliable for Sr sample and the final elution fractions were analysis through the long procedure of mutual collected for the determination of 87Sr/86Sr separation. It is thus suitable for the application isotopic ratio on ICP-MS. Five replicates of of Sr isotopic ratio analysis in petroleum drill- experiment were done and the results were holes water samples. given in Table III. The accuracy of separation method Table III. Analysis of the standard sample SRM 987 was studied by the use of NIST SRM 987 87Sr/86Sr certified 87Sr/86Sr analyzed Absolute (SrCO3) isotopic standard reference value value Error (%) material. The isotopic standard solution was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of 0,71034 ± 0.71453 ± + 0.59 0.00026 0.00836 standard reference material in dilute HNO3 and a small portion of this solution The relative correctness of analyzed containing 100 μg/L (as total Sr value is 99.41% to that of the certified value concentration) was loaded on anion for NIST SRM 987, which seems reasonable in 40 NGUYEN THI KIM DUNG, THAI THI THU THUY this study due to the contribution of signal procedure. The chemical composition of measurement deviation of instrument to the sample was analyzed using ICP-MS in order to error. That is also the reason why the more preliminary classification of the solution precision of the isotopic analysis can be matrix. The sample solution was diluted with obtained from MC-ICPMS [1]. pure water as needed before applying the separation procedure, followed by the isotopic D. Analysis of petroleum drill-holes water ratio measurement on ICP-MS. The analytical samples data were given in Table IV together with total Petroleum drill-holes water samples concentrations of Rb and Sr and relative were pretreated to remove the oil and standard deviation (RSD) of 87Sr/86Sr isotopic suspended solid particles as denoted in ratio measurement. Table IV. Analysis of petroleum drill-holes water samples Sample Total Rb 87Sr/86Sr Isotopic ratio Total Sr (µg/L) Code (µg/L) Value RSD (%) EW02 36.6 989.8 0.70715 1.17 EW05 45.3 3502.5 0.70734 2.78 EW17 34.5 1240.1 0.70699 1.52 PW03 80.0 824.0 0.70686 1.45 PW04 60.2 423.5 0.70639 1.63 PW14 120.0 1980.0 0.70674 2.46 Analytical results showed that, 87Sr/86Sr exchange chromatography. The anion isotopic ratio of petroleum drill-holes water exchange resin (Bio-Rad AG1X8 200-400 samples was various with different sample mesh) was employed for the separation of matrix. These data relatively agreed with those, major calcium by 0.25 M HNO3 in 95% which were obtained from similar study [4] of methanol with Sr recovery over 99%. The drill-holes water in Vietnam Petroleum mutual separation of rubidium and strontium Institute, where the water samples were by gradient conditions of HNO3 concentration 87 86 pretreated and the analysis of Sr/ Sr isotopic and flow rate on cation exchanger (Bio-Rad was carried out by TIMS in over-sea AG50X8 200-400 mesh) was taken part with laboratory. nearly complete Sr recovery. The validation of method was also studied using isotopic IV. CONCLUSIONS standard solution and standard reference The removal of calcium in matrix from material with relative correctness of the petroleum drill-holes water samples and the analyzed value about 99.41% to the certified elimination of rubidium isobaric interference value of NIST SRM 987 reference material. with strontium isotopic ratio determination The analytical procedure was then applied for were successfully achieved by using ion the determination of 87Sr/86Sr isotopic ratio in 41 STUDY ON THE REMOVAL OF INTERFERENCES FOR THE DETERMINATION OF 87Sr/86Sr petroleum drill-holes water samples using ICP- Table for Derivation of Numeric Age”, The MS, which would contribute to the Journal of Geology, Volume 105, p. 441–456, development of an analytical method to supply 1997. the demand of petroleum research and [6]. K. Notsu, H. Wakita, and Y. Nakamura, exploitation in Vietnam. “Strontium isotopic composition of oil-field and gas-field waters, Japan”, Appl. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Geochemistry, Vol. 3, No.2, 173–176, 1988. The authors are thankful to the [7]. Toshiro Takahashi, Yuka hirahara, Takashi assistance of M.Sc. Ngo Quang Huy on Miyazaki, Bogdan stefanov Vaglarov, Qing Chang, Jun-ichi Kimura, Yoshiyuki Tatsumi, carrying out some preliminary experiments. “Precise determination of Sr isotope ratios in The financial support under framework of a igneous rock samples ans application to micro- VINATOM project encoded analysis of plagioclase phenocrysts”, DTCB.09/18/VCNXH was highly appreciated. JAMSTEC-R IFREE Special Issue, 59-64, Nov. 2009. REFERENCES [8]. K. Ariyama, M. Shinozaki, and A. Kawasaki, [1]. S.Garcia-Ruiz, M.Moldovan and J.I.G.Alonso, “Determination of the geographic origin of rice "Measurement of strontium isotope ratios by by chemometrics with strontium and lead MC-ICP-MS after online Rb-Sr ion isotope ratios and multielement chromatography separation", concentrations”, J. Agric. Food Chem., Vol. J.Anal.At.Spectrom., 23, 84-93, 2008. 60, No.7, 1628–1634, 2012. [2]. S. Chassery, F. E. Grousset, G. Lavaux, and C. [9]. H. Oda, A. Kawasaki, and T. Hirata, R. Quetel, “87Sr/86Sr measurements on marine “Determination of the geographic origin of brown- sediments by inductively coupled plasma-mass rice with isotope ratios of 11B/10B and 87Sr/86Sr”, spectrometry,” Fresenius J. Anal. Chem., Vol. Anal. Sci., Vol. 17, pp. i1627–i1630, 2001. 360, 230–234, 1998. [10]. P.Martin, M.Madeira, F.Monteiro, R.Bruno de [3]. M. E. dos Santos, H. E. L. Palmieri, and R. M. Sousa, A.S.Curvelo-Garcia and S.Catarino, Moreira, “Testing the 87Sr/ 86Sr isotopic ratio “87Sr/86Sr ratio in vineyard soils from measured by ICP-MS as a tracer for inter-well portuguese denominations of origin and its investigation in oil reservoirs,” EPJ Web of potential from origin authentication”, J. Int. Conferences, 50, p. 02004, 2013. Sci. Vigne Vin, 48, No 1, 21-29, 2014. [4]. Luong Van Huan, Le Thi Thu Huong, Hoang [11]. C.M.Almeida and M.T.S.D. Vasconcelos, Long, Nguyen Minh Quy, Vo Thi Tuong “ICP-MS determination of strontium isotope Hanh, “Application of stable isotope (δ18O ratio in wine in order to be used as a and δ2H) analysis and 87Sr/86Sr equilibrium fingerprint of its regional origin”, J.Anal. At. to determine the source of produced water in Spectrom., 16, 607-611, 2001. the oil field”, Petrovietnam Journal, No.4, [12]. C.Vorster, T.N. van der Walt, P.P. Coetzee, pp. 24-31 (in Vietnamese), 2014. “Ion exchange separation of strontium and [5]. Richard J. Howarth and John M. McArthur, rubidium on Dowex 50W-X8, using the “Statistics for Strontium Isotope Stratigraphy: complexation properties of EDTA and A Robust LOWESS Fit to the Marine Sr- DCTA”, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 392, 287-296, Isotope Curve for 0 to 206 Ma, with Look-up 2008. 42 NGUYEN THI KIM DUNG, THAI THI THU THUY [13]. Ţ. Grahek, K. Košutić, and S. Lulić, [16]. E.P. Horwitz, m.L. Dietz, and D. E. Fisher, “Improved method for the separation of “Separation and preconcentration of strontium radioactive strontium from various samples from biological, environmental, and nuclear waste by mixed solvent anion exchange”, J. samples by extraction chromatography using Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., vol. 242, No.1, pp. crown ether”, Anal.Chem., 63, 522-525, 1991. 33–40, 1999. [17]. Ţ. Grahek, I. Eškinja, Š. Cerjan, K. Kvastek, [14]. Ţ. Grahek, I. Eškinja, K. Košutic, S. Lulic, and S. Lulić, “Separation of Strontium from K. Kvastek, “Isolation of radioactive strontium Calcium by means of Anion Exchanger and Alcoholic solution of Nitric acid”, J. from natural samples: Separation of strontium Radioanal. & Nucl. Chem., Vol.182, No2, 401- from alkaline and alkaline earth elements by 410, 1994. means of mixed solvent anion exchange”, Anal. Chim. Acta, vol. 379, no. 1–2, pp. 107– [18]. M.V. Zoriy, A. Rashad, C. Pickhardt, H.T. 119, 1999. Mohsen, H. Foerstel, A.I. Helal, N.F. Zahran, and J.S. Becker, “Routine method for [15]. V.E. Noshkin and N.S. Mott, “Separation of 87Sr/86Sr isotope ratio measurement in strontium from large amounts of calcium, with biological and geological samples after matrix application to radiostrontium analysis”, separation by ICP-MS”, Atomic Spectroscopy, Talanta, Vol.14, pp. 45 to 51, 1967. Vol. 24(6), pp. 195-199, 2003. 43
File đính kèm:
 study_on_the_removal_of_interferences_for_the_determination.pdf
study_on_the_removal_of_interferences_for_the_determination.pdf

