Solutions to attract investment capital for tourism development: Evidence from Vietnam economy
The objective of this study is to propose solutions to attract investment capital for tourism
development in Thanh Hoa province, Vietnam. Based on the theoretical framework following
eclectic or “OLI model” developed by Dunning and Narula (1996) [Dunning, J., & Narula, R.
(2003). Foreign direct investment and governments: catalysts for economic restructuring.
Routledge.] and data of 660 questionnaires collected from a survey of tourism investors in Thanh
Hoa provinces, we found some important influential factors affecting the attraction of investment
for tourism development in Thanh Hoa province. In particular, the local government’s policy of
attracting capital appears to have the highest level of importance. The study has some policy
implications to increase the attractiveness of investment capital in tourism development in the
area.

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Solutions to attract investment capital for tourism development: Evidence from Vietnam economy

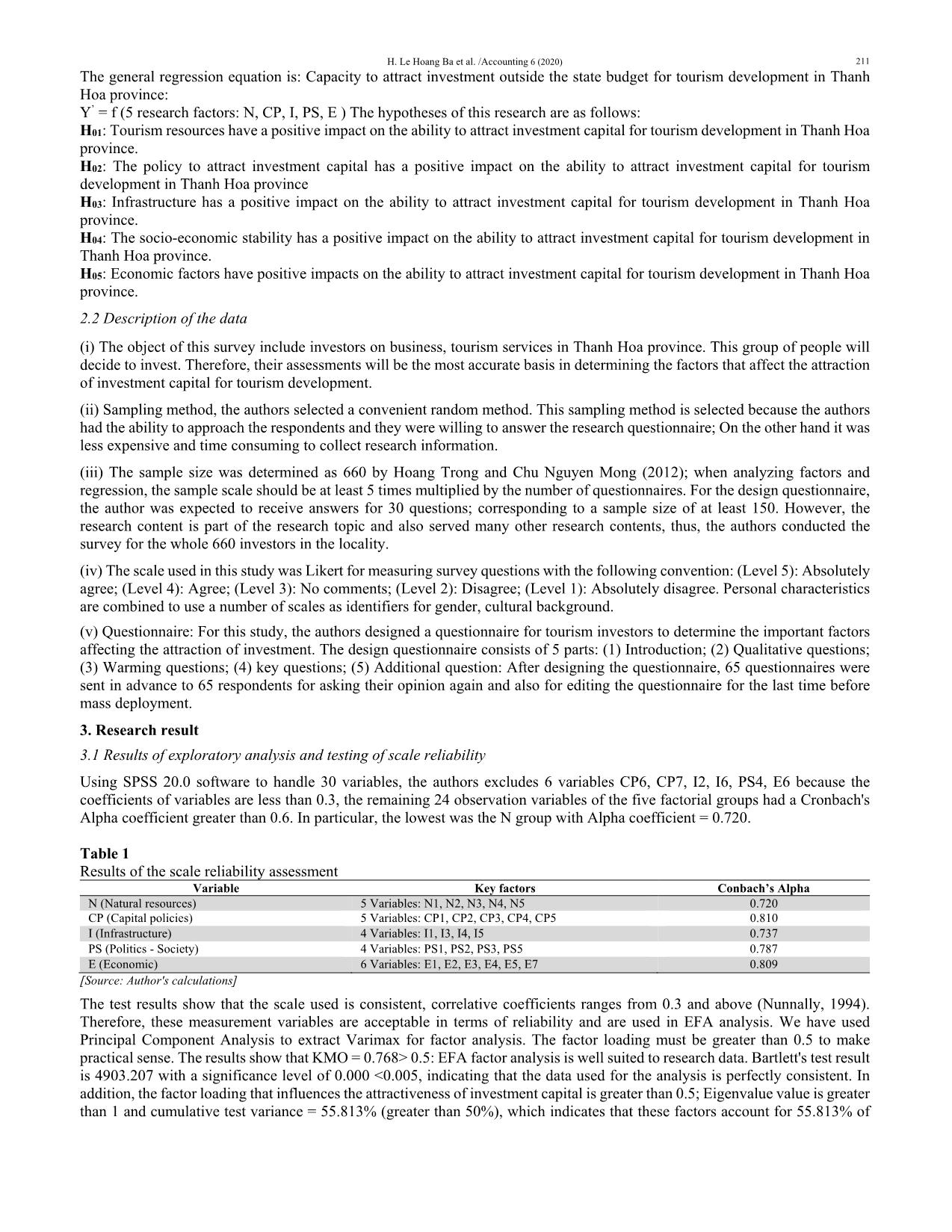
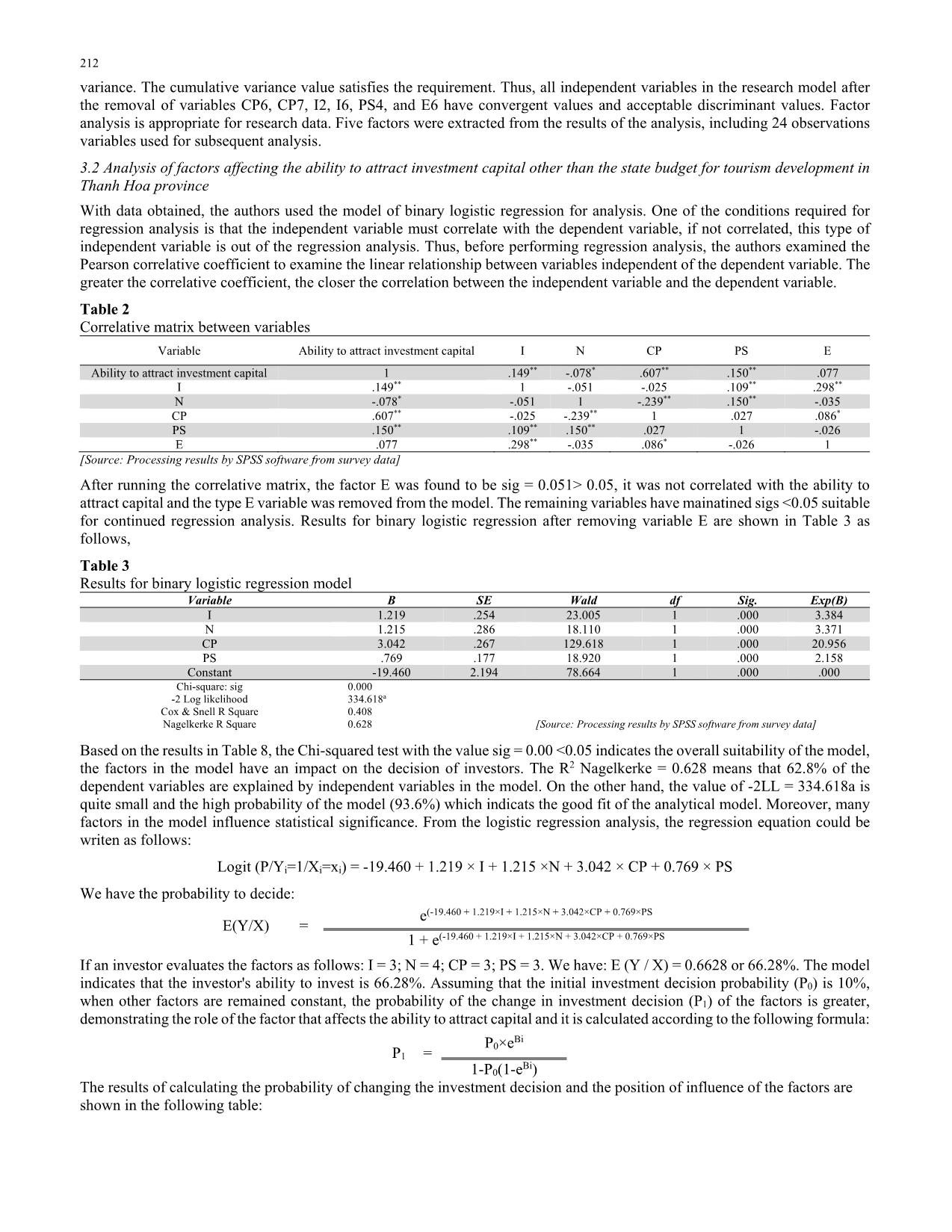
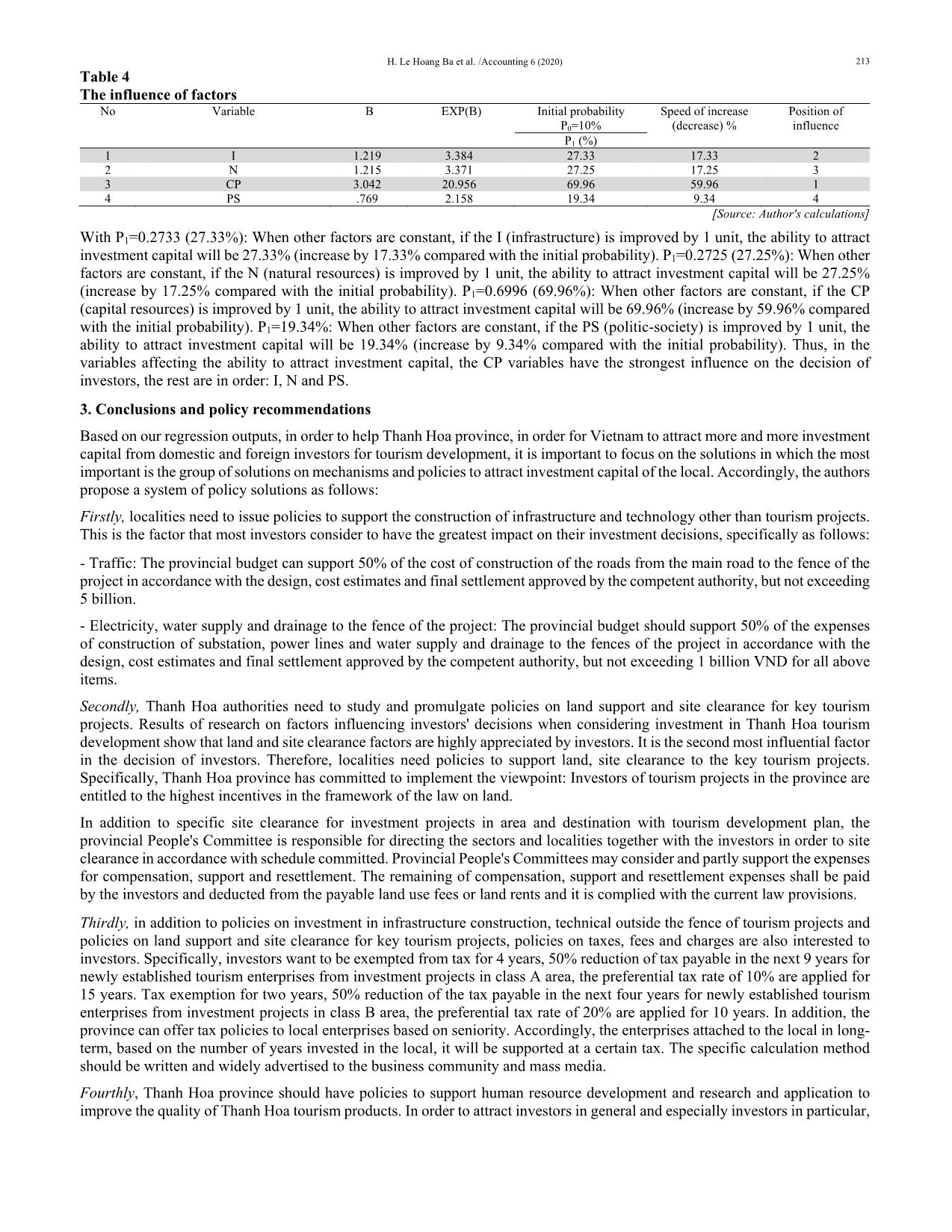
ffecting the ability to attract investment capital other than the state budget for tourism development in Thanh Hoa province With data obtained, the authors used the model of binary logistic regression for analysis. One of the conditions required for regression analysis is that the independent variable must correlate with the dependent variable, if not correlated, this type of independent variable is out of the regression analysis. Thus, before performing regression analysis, the authors examined the Pearson correlative coefficient to examine the linear relationship between variables independent of the dependent variable. The greater the correlative coefficient, the closer the correlation between the independent variable and the dependent variable. Table 2 Correlative matrix between variables Variable Ability to attract investment capital I N CP PS E Ability to attract investment capital 1 .149** -.078* .607** .150** .077 I .149** 1 -.051 -.025 .109** .298** N -.078* -.051 1 -.239** .150** -.035 CP .607** -.025 -.239** 1 .027 .086* PS .150** .109** .150** .027 1 -.026 E .077 .298** -.035 .086* -.026 1 [Source: Processing results by SPSS software from survey data] After running the correlative matrix, the factor E was found to be sig = 0.051> 0.05, it was not correlated with the ability to attract capital and the type E variable was removed from the model. The remaining variables have mainatined sigs <0.05 suitable for continued regression analysis. Results for binary logistic regression after removing variable E are shown in Table 3 as follows, Table 3 Results for binary logistic regression model Variable B SE Wald df Sig. Exp(B) I 1.219 .254 23.005 1 .000 3.384 N 1.215 .286 18.110 1 .000 3.371 CP 3.042 .267 129.618 1 .000 20.956 PS .769 .177 18.920 1 .000 2.158 Constant -19.460 2.194 78.664 1 .000 .000 Chi-square: sig 0.000 -2 Log likelihood 334.618a Cox & Snell R Square 0.408 Nagelkerke R Square 0.628 [Source: Processing results by SPSS software from survey data] Based on the results in Table 8, the Chi-squared test with the value sig = 0.00 <0.05 indicates the overall suitability of the model, the factors in the model have an impact on the decision of investors. The R2 Nagelkerke = 0.628 means that 62.8% of the dependent variables are explained by independent variables in the model. On the other hand, the value of -2LL = 334.618a is quite small and the high probability of the model (93.6%) which indicats the good fit of the analytical model. Moreover, many factors in the model influence statistical significance. From the logistic regression analysis, the regression equation could be writen as follows: Logit (P/Yi=1/Xi=xi) = -19.460 + 1.219 × I + 1.215 ×N + 3.042 × CP + 0.769 × PS We have the probability to decide: E(Y/X) = e (-19.460 + 1.219×I + 1.215×N + 3.042×CP + 0.769×PS 1 + e(-19.460 + 1.219×I + 1.215×N + 3.042×CP + 0.769×PS If an investor evaluates the factors as follows: I = 3; N = 4; CP = 3; PS = 3. We have: E (Y / X) = 0.6628 or 66.28%. The model indicates that the investor's ability to invest is 66.28%. Assuming that the initial investment decision probability (P0) is 10%, when other factors are remained constant, the probability of the change in investment decision (P1) of the factors is greater, demonstrating the role of the factor that affects the ability to attract capital and it is calculated according to the following formula: P1 = P0×eBi 1-P0(1-eBi) The results of calculating the probability of changing the investment decision and the position of influence of the factors are shown in the following table: H. Le Hoang Ba et al. /Accounting 6 (2020) 213 Table 4 The influence of factors No Variable B EXP(B) Initial probability P0=10% Speed of increase (decrease) % Position of influence P1 (%) 1 I 1.219 3.384 27.33 17.33 2 2 N 1.215 3.371 27.25 17.25 3 3 CP 3.042 20.956 69.96 59.96 1 4 PS .769 2.158 19.34 9.34 4 [Source: Author's calculations] With P1=0.2733 (27.33%): When other factors are constant, if the I (infrastructure) is improved by 1 unit, the ability to attract investment capital will be 27.33% (increase by 17.33% compared with the initial probability). P1=0.2725 (27.25%): When other factors are constant, if the N (natural resources) is improved by 1 unit, the ability to attract investment capital will be 27.25% (increase by 17.25% compared with the initial probability). P1=0.6996 (69.96%): When other factors are constant, if the CP (capital resources) is improved by 1 unit, the ability to attract investment capital will be 69.96% (increase by 59.96% compared with the initial probability). P1=19.34%: When other factors are constant, if the PS (politic-society) is improved by 1 unit, the ability to attract investment capital will be 19.34% (increase by 9.34% compared with the initial probability). Thus, in the variables affecting the ability to attract investment capital, the CP variables have the strongest influence on the decision of investors, the rest are in order: I, N and PS. 3. Conclusions and policy recommendations Based on our regression outputs, in order to help Thanh Hoa province, in order for Vietnam to attract more and more investment capital from domestic and foreign investors for tourism development, it is important to focus on the solutions in which the most important is the group of solutions on mechanisms and policies to attract investment capital of the local. Accordingly, the authors propose a system of policy solutions as follows: Firstly, localities need to issue policies to support the construction of infrastructure and technology other than tourism projects. This is the factor that most investors consider to have the greatest impact on their investment decisions, specifically as follows: - Traffic: The provincial budget can support 50% of the cost of construction of the roads from the main road to the fence of the project in accordance with the design, cost estimates and final settlement approved by the competent authority, but not exceeding 5 billion. - Electricity, water supply and drainage to the fence of the project: The provincial budget should support 50% of the expenses of construction of substation, power lines and water supply and drainage to the fences of the project in accordance with the design, cost estimates and final settlement approved by the competent authority, but not exceeding 1 billion VND for all above items. Secondly, Thanh Hoa authorities need to study and promulgate policies on land support and site clearance for key tourism projects. Results of research on factors influencing investors' decisions when considering investment in Thanh Hoa tourism development show that land and site clearance factors are highly appreciated by investors. It is the second most influential factor in the decision of investors. Therefore, localities need policies to support land, site clearance to the key tourism projects. Specifically, Thanh Hoa province has committed to implement the viewpoint: Investors of tourism projects in the province are entitled to the highest incentives in the framework of the law on land. In addition to specific site clearance for investment projects in area and destination with tourism development plan, the provincial People's Committee is responsible for directing the sectors and localities together with the investors in order to site clearance in accordance with schedule committed. Provincial People's Committees may consider and partly support the expenses for compensation, support and resettlement. The remaining of compensation, support and resettlement expenses shall be paid by the investors and deducted from the payable land use fees or land rents and it is complied with the current law provisions. Thirdly, in addition to policies on investment in infrastructure construction, technical outside the fence of tourism projects and policies on land support and site clearance for key tourism projects, policies on taxes, fees and charges are also interested to investors. Specifically, investors want to be exempted from tax for 4 years, 50% reduction of tax payable in the next 9 years for newly established tourism enterprises from investment projects in class A area, the preferential tax rate of 10% are applied for 15 years. Tax exemption for two years, 50% reduction of the tax payable in the next four years for newly established tourism enterprises from investment projects in class B area, the preferential tax rate of 20% are applied for 10 years. In addition, the province can offer tax policies to local enterprises based on seniority. Accordingly, the enterprises attached to the local in long- term, based on the number of years invested in the local, it will be supported at a certain tax. The specific calculation method should be written and widely advertised to the business community and mass media. Fourthly, Thanh Hoa province should have policies to support human resource development and research and application to improve the quality of Thanh Hoa tourism products. In order to attract investors in general and especially investors in particular, 214 in the future, Thanh Hoa needs to effectively implement human resource training program to meet the development requirements of socio-economic situation and the demand of the local labor market. Fifthly, localities should also pay attention to the issuance of credit policies to support local tourism development projects because they are always important factors for investors in general as well as investors in the tourism sector in particular. Therefore, an important content that local government needs to support investors in Thanh Hoa is to have a specific policy on credit for tourism projects. Specifically, projects on investing ships and boats to transport tourists by water: investment, procurement of new ships with a capacity of installing 150 seats or more are facilitated to borrow capital with preferential interest rates; In case of inability to borrow preferential capital and having to borrow capital from commercial banks, the provincial budget shall support 3% of the loan interest rate within 36 months from the date of repayment under the credit contract. The maximum support level must not exceed VND 200 million/project. Moreover, investment projects in the tourism sectors under this regulation are given priority by the Development Bank and the Social Policy Bank to provide loans for investment in accordance with the regulations. Sixthly, in addition to the proposed price policies, Thanh Hoa province should consider implementing the social value strategy. Local authorities should also have policies to support organizations and individuals who have achievements in mobilizing investment projects in the field of tourism. Apart from being rewarded according to the current regulations of the State, provincial budgets will be rewarded from 100 million VND to 500 million VND depending on the scale of the project (Not applicable to the following subjects: state agencies, socio-political organizations and public non-business units using the state budget for operation. According to the policies to attract tourism investment in Thanh Hoa province as above, Thanh Hoa province will use price means to attract investment and take the criteria for social benefits to send messages to investors. Investors who benefit from this price strategy will have to be able to bring many social benefits to Thanh Hoa province, in which employment and reinvestment for urban upgrade are improved. That is the number one priority. References Anh, T., Hanh, P., Cam, L., Van, K., & Dinh, L. (2019). A study of the factors affecting the content created by international travellers in Vietnam. Management Science Letters, 9(12), 2051-2062. Anh, T., Diem, C., Cam, L., & Viet, T. (2020). Exploring factors influencing on organizational repurchases intention in B2B tourism context. Management Science Letters, 10(3), 531-542. Donwa, P., & Odia, J. (2010). An empirical analysis of the impact of the Nigerian capital market on her socio-economic development. Journal of Social Sciences, 24(2), 135-142. Dunning, J. H. (1997). A business analytic approach to governments and globalization. Governments, globalization, and international business, 114-131. Ewah, S. O., Esang, A. E., & Bassey, J. U. (2009). Appraisal of capital market efficiency on economic growth in Nigeria. International Journal of Business and Management, 4(12), 219-225. Gilmore, A., O'Donnell, A., Carson, D., & Cummins, D. (2003). Factors influencing foreign direct investment and international joint ventures: A comparative study of Northern Ireland and Bahrain. International Marketing Review, 20(2), 195-215. Gupta, A. K., Sinha, R., Koradia, D., Patel, R., Parmar, M., Rohit, P., ... & Chandan, A. (2003). Mobilizing grassroots’ technological innovations and traditional knowledge, values and institutions: articulating social and ethical capital. Futures, 35(9), 975-987. Ha, N. K. G., Le, Q. H., & Nguyen, T. C. H. (2013). Survey on the factors that attract investment capital in Quang Tri province. Journal of Science, Dong Thap University, 3(6), 19-30. Le, H.B.H., Nguyen, T.H. (2017). Determination of factors affecting the attraction of investment capital beyond the state budget for tourism development in Thanh Hoa province. Journal of Economics and Development, 242(2). Nguyen, M. T. (2010). Factors influencing the attraction of foreign direct investment into one locality of Vietnam. Journal of Science & Technology, University of Da Nang, 5(40) , 270-276. Nguyen, T., Nguyen, N., & Nguyen, V. (2019a). Identifying factors influencing on the profitability of tourist enterprises: Evidence from Vietnam. Management Science Letters, 9(11), 1933-1940. Nguyen, V., Nguyen, T., Tran, T., & Nghiem, T. (2019b). The impact of financial leverage on the profitability of real estate companies: A study from Vietnam stock exchange. Management Science Letters, 9(13), 2315-2326. Nunnally, J. C. (1994). Psychometric theory 3E. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. Rankin, K. N. (2002). Social capital, microfinance, and the politics of development. Feminist economics, 8(1), 1-24. Tran, T., Phi, T., Tran, M., & Hoang, V. (2019). Economic linkage in key economic zones: The case of Vietnam. Management Science Letters, 9(3), 443-456. Tung, L. (2019). Does exchange rate affect the foreign tourist arrivals? Evidence in an emerging tourist market. Management Science Letters, 9(8), 1141-1152. © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science, Canada. This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (
File đính kèm:
 solutions_to_attract_investment_capital_for_tourism_developm.pdf
solutions_to_attract_investment_capital_for_tourism_developm.pdf

