Factors affecting the application of social responsibility accounting
Vietnam is facing a lot of social problems such as excessive resources exploitation, social imbalance,
threatened natural environment, etc. The majority of enterprises in Vietnam care about profits and they
are blamed for harmful effects on the environment and society. Social responsibility accounting is
applied as a tool which evaluates efforts to protect the environment and ensure the social stability of
the businesses. Therefore, social responsibility accounting is essential to help administrators propose
business strategies combining with environment conservation most appropriately. This research
focuses on four factors affecting the application of the social responsibility accounting in Vietnamese
enterprises. In this paper, SPSS 20 was used to collect and analysis data from Vietnamese enterprises.
From this, recommendations can be given so that the enterprises can apply social responsibility
accounting and promote it widely in Vietnam.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Factors affecting the application of social responsibility accounting

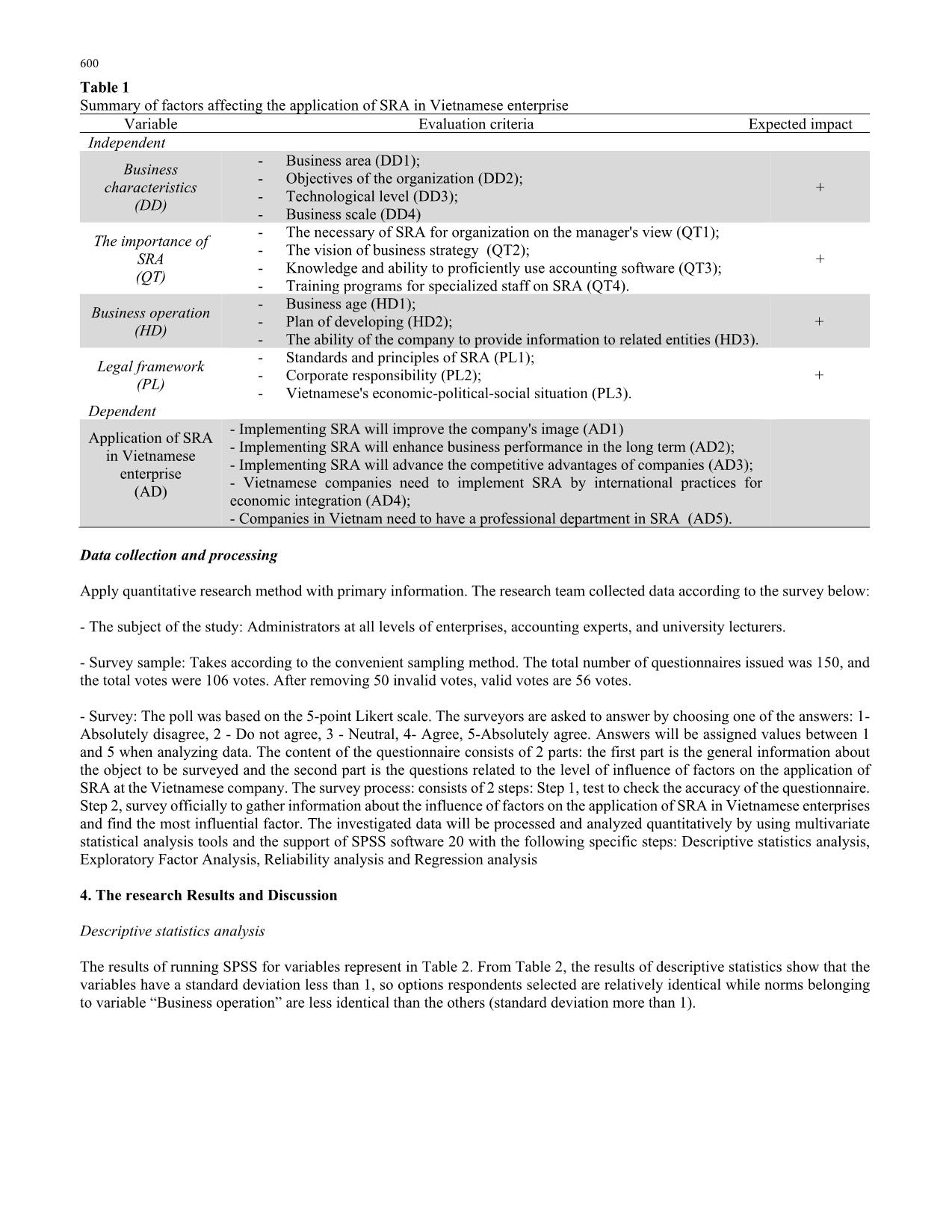
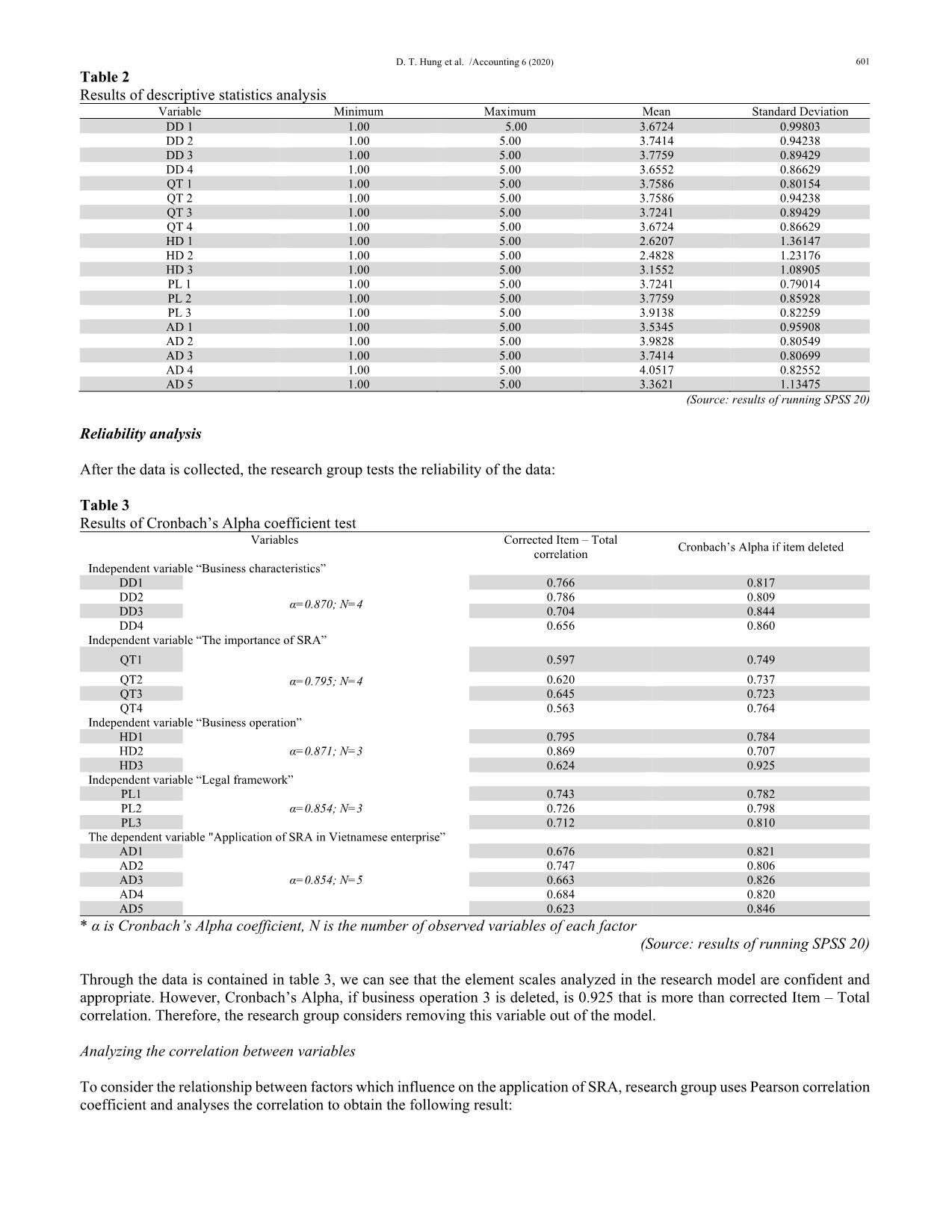
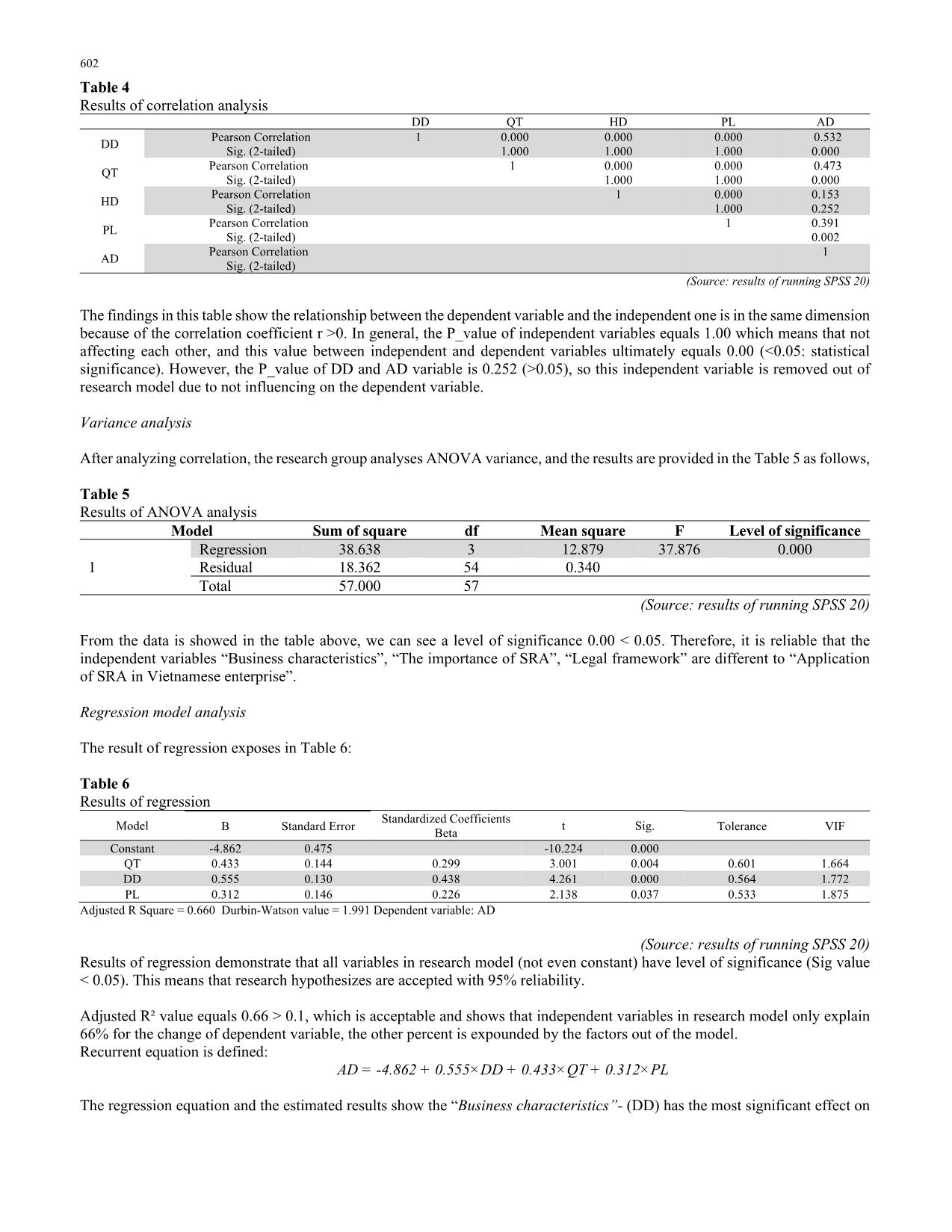
d impact Independent Business characteristics (DD) - Business area (DD1); - Objectives of the organization (DD2); - Technological level (DD3); - Business scale (DD4) + The importance of SRA (QT) - The necessary of SRA for organization on the manager's view (QT1); - The vision of business strategy (QT2); - Knowledge and ability to proficiently use accounting software (QT3); - Training programs for specialized staff on SRA (QT4). + Business operation (HD) - Business age (HD1); - Plan of developing (HD2); - The ability of the company to provide information to related entities (HD3). + Legal framework (PL) - Standards and principles of SRA (PL1); - Corporate responsibility (PL2); - Vietnamese's economic-political-social situation (PL3). + Dependent Application of SRA in Vietnamese enterprise (AD) - Implementing SRA will improve the company's image (AD1) - Implementing SRA will enhance business performance in the long term (AD2); - Implementing SRA will advance the competitive advantages of companies (AD3); - Vietnamese companies need to implement SRA by international practices for economic integration (AD4); - Companies in Vietnam need to have a professional department in SRA (AD5). Data collection and processing Apply quantitative research method with primary information. The research team collected data according to the survey below: - The subject of the study: Administrators at all levels of enterprises, accounting experts, and university lecturers. - Survey sample: Takes according to the convenient sampling method. The total number of questionnaires issued was 150, and the total votes were 106 votes. After removing 50 invalid votes, valid votes are 56 votes. - Survey: The poll was based on the 5-point Likert scale. The surveyors are asked to answer by choosing one of the answers: 1- Absolutely disagree, 2 - Do not agree, 3 - Neutral, 4- Agree, 5-Absolutely agree. Answers will be assigned values between 1 and 5 when analyzing data. The content of the questionnaire consists of 2 parts: the first part is the general information about the object to be surveyed and the second part is the questions related to the level of influence of factors on the application of SRA at the Vietnamese company. The survey process: consists of 2 steps: Step 1, test to check the accuracy of the questionnaire. Step 2, survey officially to gather information about the influence of factors on the application of SRA in Vietnamese enterprises and find the most influential factor. The investigated data will be processed and analyzed quantitatively by using multivariate statistical analysis tools and the support of SPSS software 20 with the following specific steps: Descriptive statistics analysis, Exploratory Factor Analysis, Reliability analysis and Regression analysis 4. The research Results and Discussion Descriptive statistics analysis The results of running SPSS for variables represent in Table 2. From Table 2, the results of descriptive statistics show that the variables have a standard deviation less than 1, so options respondents selected are relatively identical while norms belonging to variable “Business operation” are less identical than the others (standard deviation more than 1). D. T. Hung et al. /Accounting 6 (2020) 601 Table 2 Results of descriptive statistics analysis Variable Minimum Maximum Mean Standard Deviation DD 1 1.00 5.00 3.6724 0.99803 DD 2 1.00 5.00 3.7414 0.94238 DD 3 1.00 5.00 3.7759 0.89429 DD 4 1.00 5.00 3.6552 0.86629 QT 1 1.00 5.00 3.7586 0.80154 QT 2 1.00 5.00 3.7586 0.94238 QT 3 1.00 5.00 3.7241 0.89429 QT 4 1.00 5.00 3.6724 0.86629 HD 1 1.00 5.00 2.6207 1.36147 HD 2 1.00 5.00 2.4828 1.23176 HD 3 1.00 5.00 3.1552 1.08905 PL 1 1.00 5.00 3.7241 0.79014 PL 2 1.00 5.00 3.7759 0.85928 PL 3 1.00 5.00 3.9138 0.82259 AD 1 1.00 5.00 3.5345 0.95908 AD 2 1.00 5.00 3.9828 0.80549 AD 3 1.00 5.00 3.7414 0.80699 AD 4 1.00 5.00 4.0517 0.82552 AD 5 1.00 5.00 3.3621 1.13475 (Source: results of running SPSS 20) Reliability analysis After the data is collected, the research group tests the reliability of the data: Table 3 Results of Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient test Variables Corrected Item – Total correlation Cronbach’s Alpha if item deleted Independent variable “Business characteristics” DD1 α=0.870; N=4 0.766 0.817 DD2 0.786 0.809 DD3 0.704 0.844 DD4 0.656 0.860 Independent variable “The importance of SRA” QT1 α=0.795; N=4 0.597 0.749 QT2 0.620 0.737 QT3 0.645 0.723 QT4 0.563 0.764 Independent variable “Business operation” HD1 α=0.871; N=3 0.795 0.784 HD2 0.869 0.707 HD3 0.624 0.925 Independent variable “Legal framework” PL1 α=0.854; N=3 0.743 0.782 PL2 0.726 0.798 PL3 0.712 0.810 The dependent variable "Application of SRA in Vietnamese enterprise” AD1 α=0.854; N=5 0.676 0.821 AD2 0.747 0.806 AD3 0.663 0.826 AD4 0.684 0.820 AD5 0.623 0.846 * α is Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient, N is the number of observed variables of each factor (Source: results of running SPSS 20) Through the data is contained in table 3, we can see that the element scales analyzed in the research model are confident and appropriate. However, Cronbach’s Alpha, if business operation 3 is deleted, is 0.925 that is more than corrected Item – Total correlation. Therefore, the research group considers removing this variable out of the model. Analyzing the correlation between variables To consider the relationship between factors which influence on the application of SRA, research group uses Pearson correlation coefficient and analyses the correlation to obtain the following result: 602 Table 4 Results of correlation analysis DD QT HD PL AD DD Pearson Correlation 1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.532 Sig. (2-tailed) 1.000 1.000 1.000 0.000 QT Pearson Correlation 1 0.000 0.000 0.473 Sig. (2-tailed) 1.000 1.000 0.000 HD Pearson Correlation 1 0.000 0.153 Sig. (2-tailed) 1.000 0.252 PL Pearson Correlation 1 0.391 Sig. (2-tailed) 0.002 AD Pearson Correlation 1 Sig. (2-tailed) (Source: results of running SPSS 20) The findings in this table show the relationship between the dependent variable and the independent one is in the same dimension because of the correlation coefficient r >0. In general, the P_value of independent variables equals 1.00 which means that not affecting each other, and this value between independent and dependent variables ultimately equals 0.00 (<0.05: statistical significance). However, the P_value of DD and AD variable is 0.252 (>0.05), so this independent variable is removed out of research model due to not influencing on the dependent variable. Variance analysis After analyzing correlation, the research group analyses ANOVA variance, and the results are provided in the Table 5 as follows, Table 5 Results of ANOVA analysis Model Sum of square df Mean square F Level of significance 1 Regression 38.638 3 12.879 37.876 0.000 Residual 18.362 54 0.340 Total 57.000 57 (Source: results of running SPSS 20) From the data is showed in the table above, we can see a level of significance 0.00 < 0.05. Therefore, it is reliable that the independent variables “Business characteristics”, “The importance of SRA”, “Legal framework” are different to “Application of SRA in Vietnamese enterprise”. Regression model analysis The result of regression exposes in Table 6: Table 6 Results of regression Model Standardized Coefficients Beta t Sig. B Standard Error Tolerance VIF Constant -4.862 0.475 -10.224 0.000 QT 0.433 0.144 0.299 3.001 0.004 0.601 1.664 DD 0.555 0.130 0.438 4.261 0.000 0.564 1.772 PL 0.312 0.146 0.226 2.138 0.037 0.533 1.875 Adjusted R Square = 0.660 Durbin-Watson value = 1.991 Dependent variable: AD (Source: results of running SPSS 20) Results of regression demonstrate that all variables in research model (not even constant) have level of significance (Sig value < 0.05). This means that research hypothesizes are accepted with 95% reliability. Adjusted R² value equals 0.66 > 0.1, which is acceptable and shows that independent variables in research model only explain 66% for the change of dependent variable, the other percent is expounded by the factors out of the model. Recurrent equation is defined: AD = -4.862 + 0.555×DD + 0.433×QT + 0.312×PL The regression equation and the estimated results show the “Business characteristics”- (DD) has the most significant effect on D. T. Hung et al. /Accounting 6 (2020) 603 using SRA with the regression coefficient is 0.555. That also means the features of the organization has the most positive effects on using SRA. Depending on the characteristics of each corporation, the level of applying SRA is different to ensure the sustainable development goals of corporation. The second factor is “The Importance of SRA” - QT whose regression coefficient is 0.433. It shows that the role of SRA has a positive influence on using SRA in enterprises. If the management is more aware of the importance of SRA, implement SRA in enterprises is more necessary. Lastly, the “Legal framework” - PL, the regression coefficient is 0.312 has the least effect. If the legal system and judicial administration are more stringent, the user level will increase. However, this is forced by the provisions of the law, so it is not highly effective (regression coefficient is the smallest). Therefore, it can be said that to increase the level of application of SRA, the impact of enterprise features brings the highest efficiency. Conclusion for hypothesis: Business characteristics, The Importance of SRA, and the Legal framework has a positive impact on applying SRA in Vietnamese enterprises. According to the correlation analysis between independent variables and dependent variables, Business operation does not affect the application of SRA, and it was removed from the regression model. Thus, H3 is rejected. 5. Conclusion During the past two decades, there have been tremendous efforts to take care of environment through SRA efforts. Managers need to change their perception of SRA, improve their knowledge of SRA to meet the requirements of providing information not only quickly but also accurately on SRA. Understanding that, managers will be more proactive in applying SRA to the company's operations. It is necessary to clearly define the responsibilities of state management agencies and related entities, generally in policy making, information, propaganda, inspection, and handling of violations of enterprises, which are related to social responsibility and responsibility for the market, consumers and environmental protection in particular. Coordination between state management agencies and other related entities also plays an essential role since SRA only becomes urgent when there is a synchronous monitoring mechanism, a combination of government and local forces in society, especially associations, the media and newspapers. Government agencies and organizations should have a close combination. The government should provide regulations on SRA, social information, and environmental information to ensure consistency in the management of social responsibility. Besides, it must be stronger in the introduction of SRA to increase awareness, actions of organizations, parties involved in social and environmental issues in each enterprise, and the entire economy. References Bebbington, J., Gray, R., Thomson, I., & Walters, D. (1994). Accountants' attitudes and environmentally-sensitive accounting. Accounting and business research, 24(94), 109-120. Gray, R., Owen, D., & Adams, C. (1996). Accounting & accountability: changes and challenges in corporate social and environmental reporting. Prentice Hall. Gray, R., Owen, D., & Maunders, K. (1987). Corporate social reporting: Accounting and accountability. Prentice-Hall International. Kuasirikun, N. (2005). Attitudes to the development and implementation of social and environmental accounting in Thailand. Critical Perspectives on Accounting, 16(8), 1035-1057. Gholami, S., Parvizi, M., TamriNeia, A., Nemati, S., Abgineh, M., & Emami, M. (2012). Social Responsibility Accounting: From Theory to Practice. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 2(10), 10111-10117. Le Kim Ngoc (2016). Accounting of corporate social responsibility. Journal of Accounting & Auditing, 4, 151. Mathews, M. R. (1993). Socially responsible accounting. CRC Press. Mathews, M. R. (1997). Twenty‐five years of social and environmental accounting research. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 10(4), 481-531. Ministry of the Environment (1999). Environmental Accounting Guidelines. Nguyen Huu Phu (2014). Organize responsibility accounting in the construction corporations under the Ministry of Transport. Phd Thesis. Academy of Financial. Nguyen Thi Bich Lien (2017). Small and medium-sized enterprises development in supporting industry”, PhD thesis, Graduate Academy of Social Sciences, Vietnam Academy of Social Sciences Pal, N., Sundaresan, S., Ray, J., Bhargava, H., Glantz, E., & McHugh, M. W. (2004). Knowledge Quotient™(KQ): A Way to Measure the Knowledge Intensity of Your Team. O’Dwyer, B. (2006). Theoretical and practical contributions of social accounting to corporate social responsibility. Corporate social responsibility, 1, 123-148. Pham Duc Hieu (2018). Factors affecting the implementation and reporting of corporate social responsibility of Vietnamese enterprises. Journal of Economic Development, 246. Pham Van Duoc (2010). Organize the accounting reporting system to assess the division of responsibilities in commercial enterprises in Vietnam, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh city. 604 Sabha, S. A., & Shoubaki, Y. (2013). The importance of implementing Social Responsibility Accounting (SRA) in public shareholding companiesin Jordanand its impacton their sustainability. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 4(6). Tran Minh Phuong (2017). Factors affecting the implementation of Social Responsibility Accounting in enterprises in Vietnam. Master Thesis, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh city. Trotman, K. T., & Bradley, G. W. (1981). Associations between social responsibility disclosure and characteristics of companies. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 6(4), 355-362. Zulkifli, N., Telford, B., & Marriott, N. (2009). Social and environmental accounting in Malaysia: practitioners’ views.'. Research in Accounting in Emerging Economies, 9, 145-167. © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science, Canada. This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (
File đính kèm:
 factors_affecting_the_application_of_social_responsibility_a.pdf
factors_affecting_the_application_of_social_responsibility_a.pdf

