Decays of higgs in randall - Sundrum model
In this paper, the decay widths of the Higgs under different channels in Randall -
Sundrum model are studied in detail. The results showed that the decay width depends
strongly on the mass of radion. This suggests that the existence of radion in the Randall -
Sundrum model is necessary.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4

Trang 5
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Decays of higgs in randall - Sundrum model", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Decays of higgs in randall - Sundrum model

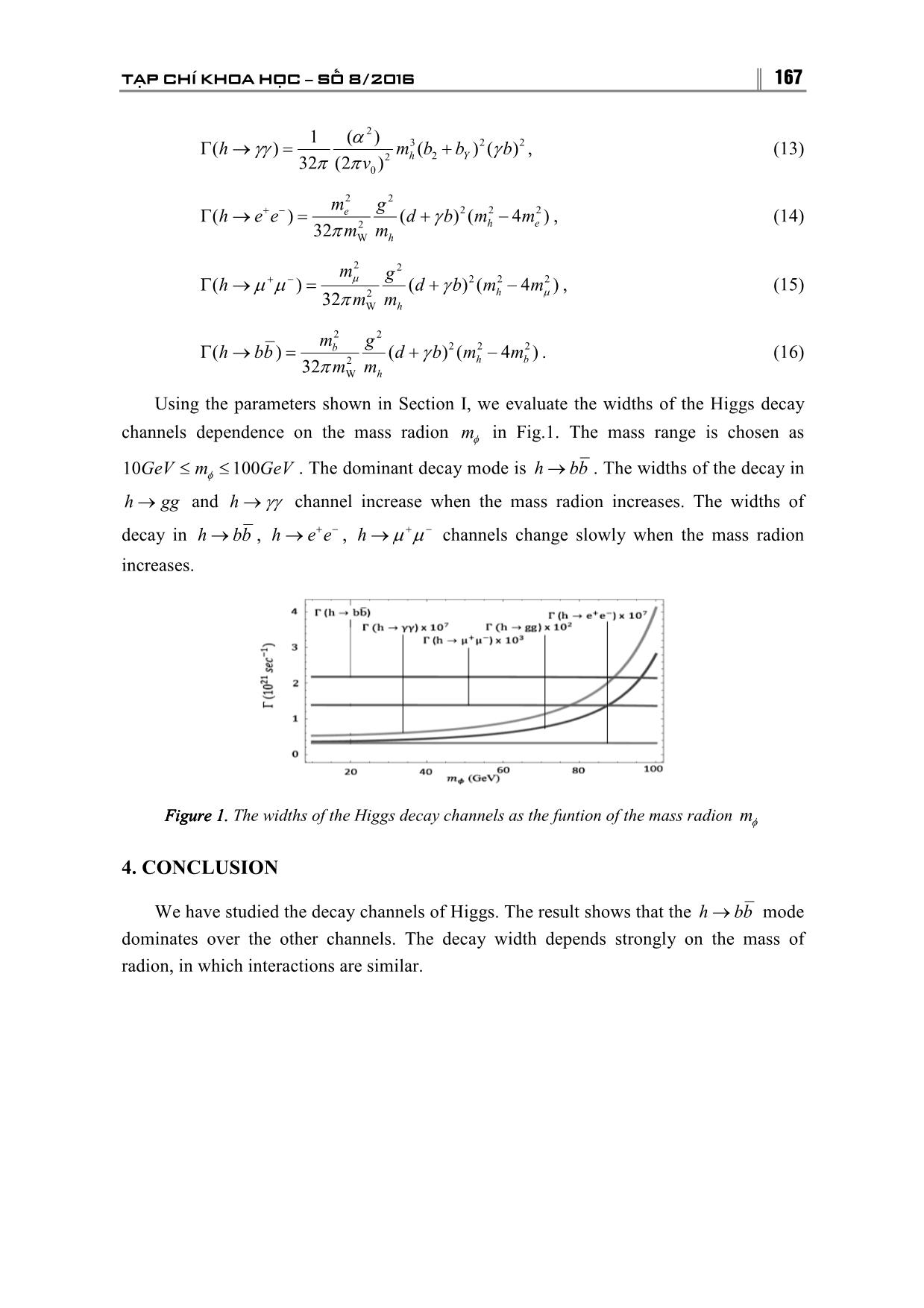
164 TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC THỦ ĐÔ H� NỘI DECAYS OF HIGGS IN RANDALL ��� SUNDRUM MODEL Dang Van Soa 1( 1), Dao Thi Le Thuy 2, Bui Thi Ha Giang 2 1Hanoi Metropolitan University 2Hanoi National University of Education Abstract : In this paper, the decay widths of the Higgs under different channels in Randall � Sundrum model are studied in detail. The results showed that the decay width depends strongly on the mass of radion. This suggests that the existence of radion in the Randall � Sundrum model is necessary. KeywordsKeywords: Higgs boson, Randall�Sundrum model, decay width. 1. INTRODUCTION In 1999, Randall and Sundrum proposed a 5�dimensional model for solving the gauge hierarchy problem [1,2]. The Randall – Sundrum (RS) model allows for a natural generation of Planck�weak and fermion mass hierarchies [3]. Goldberger and Wise have proposed and attractive mechanism to stabilize the distance between two branes introducting a bulk scalar field which has scalar potentials on both branes [2]. In RS 1 model, the extra dimension is assumed to be located on a S/ Z 2 orbifold, which has two fixed points, φ = 0 and φ= π . They correspond to the high energy brane and the brane we live on, respectively. Graviton is the only particle propagating through the bulk between these two branes [4]. The space�time metric ic given by: ds2= e− 2ky η dx� dx ν − dy 2 , (1) �ν where x� (� = 0, 1, 2, 3) , y and k denote the coordinate of 4D space�time, that of a fifth dimension, and the AdS 5 curvature, respectively. The Minkowski metric is −2ky η�ν =diag (1, −−− 1, 1, 1) and e is called a warp factor [1,2]. In four dimensional effective theory of RS model, there are two new particles beyond the Standard model. One (1) Nh�n bài ngày 8.8.2016; g�i ph�n bi�n và duy�t ñăng ngày 15.9.2016 Liên h� tác gi�: Đ�ng Văn Soa; Email: dvsoa@daihocthudo.edu.vn TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC −−− SỐ 8/2016 165 is a spin�2 graviton and a scalar�field radion φ which is metric fluctuation along the extra dimension. Having determined the vacuum structure of the model, we discuss the possibility of mixing between gravity and electroweak sector. The gravity�scalar mixing is described by the following action [5, 6, 7] S= −ξ dx4 − gRg( ) HHˆ+ ˆ , (2) ξ ∫ vis vis Where R( g vis ) is the Ricci scalar for the metric induced on the visible brane, �ν2 �ν �ν ˆ gvis= � b ()( xη + ε h ) . H is the Higgs filed in the 5D context before rescaling to canonical normalization on the brane. The parameter ξ denotes the size of the mixing term [1�10]. With ξ ≠ 0, neither a pure Higgs boson not pure radion mass eigenstate. We difine the mixing angle θ by: 2 mh θ= γξ Z 0 tan 2 12 2 22 22 . (3) mφ − mh ( Z − 36ξ γ ) 0 0 Where: Z2≡+16ξγ 2 (16) −≡− ξ β 36 ξγγ 22 , =Λ v / . (4) 0 φ In terms of these quantities, the new fields h and φ are the states that diagonalize the kinetic energy and have canonical normalization with: 6ξγ 6 ξγ h0 =−(cosθ sin θ ) h ++ (sin θ cos θφ ) ≡+ dhc φ , (5) Z Z φ h φ0 =−cos θ + sin θ ≡+ a φ bh . (6) Z Z The corresponding mass�squared eigenvalues are [11] 21 2 2 2 22222 mhφφ= m +±+β m h[ m φ β m h ] − 4 Zmm φ h . (7) , 2 ( 0 0 0 0 00 ) 2Z When ξ ≠ 0, there are four independent parameters that must be specified to fix the state mixing parameters a, b, c, d of Eqs. (5) and (6) defining the mass eigenstates Λ ,m , m , ξ . (8) φh φ m0 We consider the case of Λφ = 5TeV and = 0.1 , which makes the radion M P stabilization model most natural [12]. 166 TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC THỦ ĐÔ H� NỘI The search experiments of the Higgs boson at the LHC give stringent constraints on the parameters of the radion (a radion mass mφ and a scale parameter Λφ ). The recently discovered 125 GeV scalar at the LHC Run�I [13, 14], behaves like the SM Higgs boson and this fixes the last free parameter of the SM Lagrangian [15]. In this paper, we study the decay channels of Higgs. This paper is organised as follows. In Sec.II, we briefly review the interactions of Higgs to SM fields. In Sec.III, the widths of the Higgs decay channels and our numerical results are shown. Sec.IV is devoted to summary and discussion. 2. I NTERACTIONS n We turn to the important interactions of the h, φ and h�ν . We begin with the gg couplings of the h and φ . The h0 has standard gg or fermionic coupling and the φ0 has φ0 � ZZ or fermionic coupling from interaction − T� using the Yukawa interaction Λφ � contributions of T� . The results are obtained by: ab �ν ν � gggh= C g δ[( kk12 ) η − kk 12 ] , (9) g= Ckk[( )η �ν − kk ν � ] , (10) γγh γ 12 12 g me geeh = −( d + γ b ) , (11) 2 mW where g and cW denote the SU(2) gauge coupling and cosine of the Weinberg angle, respectively. There, αs Cg =−[( dbF +γ )∑ 1/2 ( τi ) − 2 ba 3 γ ], 4πv i αs 2 i Cγ =−[( dbeNF +γ )∑ i c1 ()( τ i −+ bbYa 2 )] γ 2πv i 3. D ECAY OF HIGGS We calculate the decay widths of the Higgs to the SM particles as follows: 1 (−α 2 ) Γ→=(hgg )s mbb3 (2) − γ 2 , (12) 32π (4 π v ) 2 h 3 0 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC −−− SỐ 8/2016 167 1 (α 2 ) Γ→=(hγγ ) mbbb3 ()() + 2 γ 2 , (13) 32π (2 π v ) 2 h2 Y 0 m2 g 2 Γ→=(hee+ − )e ()(4) dbmm +γ 2 2 − 2 , (14) 32 π m2 m h e W h m2 g 2 Γ→=(h�+ � − )� ()(4) dbmm + γ 2 2 − 2 , (15) 32 π m2 m h � W h m2 g 2 Γ→=(hbb )b ( dbmm +γ )(4)2 2 − 2 . (16) 32 π m2 m h b W h Using the parameters shown in Section I, we evaluate the widths of the Higgs decay channels dependence on the mass radion mφ in Fig.1. The mass range is chosen as 10GeV≤ mφ ≤ 100 GeV . The dominant decay mode is h→ bb . The widths of the decay in h→ gg and h → γγ channel increase when the mass radion increases. The widths of decay in h→ bb , h→ e+ e − , h → �+ � − channels change slowly when the mass radion increases. FigurFigureeee 11..1. The widths of the Higgs decay channels as the funtion of the mass radion mφ 4. CONCLUSION We have studied the decay channels of Higgs. The result shows that the h→ bb mode dominates over the other channels. The decay width depends strongly on the mass of radion, in which interactions are similar. 168 TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC THỦ ĐÔ H� NỘI REFERENCES 1. L. Randall and R. Sundrum (1999), Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3370, arxiv: hep�ph/9905221. 2. L. Randall and R. Sundrum (1999), Phys. Rev. Lett . 83, 4690, arxiv: hep�ph/9906064. 3. W. D. Goldberger and M. B. Wise (1999), Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4962, arxiv: hep�ph/9907447. 4. S. A. Li, C. S. Li, H. T. Li and J. Gao (2015), "Constraints on Randall�Sundrum model from the events of dijet production with QCD next�to�leading order accuracy at the LHC", [arXiv:1408.2762v2 [hep�ph]]. 5. J.J. Van der Bij (1994), Acta Phys. Podon, B 25, 827. 6. R. Raczka, M. Pawlowski (1994), Found. Phys. 24, 1305. 7. G. F. Giudice, R. Rattazzi and J. D. Wells (2001), "Graviscalars from higher dimensional metrics and curvature Higgs mixing", Nucl. Phys . B 595, 250 [hep�ph/0002178]. 8. D. V. Soa, D. T. L. Thuy, N. H. Thao and T. D. Tham (2012), Mod. Phys. Lett. A, Vol.27, N0.2, 1250126. 9. M. Chaichain, A. Datta, K Huitu and Z. Yu (2002), Phys. Lett . B 524, 161. 10. K. Cheung, C. S. Kim and J. �h. Song, (2003), "A Probe of the radion Higgs mixing in the Randall�Sundrum model at e+ e� colliders," Phys. Rev. D 67, 075017, [hep�ph/0301002]. 11. T. Han, G. D. Kribs and B. McElrath, (2001), Phys. Rev . D 63, 076003. 12. H. Davoudiasl, J. L Hewett and T. G. Rizzo (2001), Phys. Rev. D 63, 075004. 13. ATLAS Colllaboration, G. Aad et al (2012), Phys. Lett, B 716, 1�29, arxiv: hep�ph/1207.7214. 14. CMS Colllaboration, S. Chatrchyan et. Al (2012), Phys. Lett. B 716, 30�31, arxiv: hep� ph/1207.7235. 15. Goutam Das, Prakash Mathews (2015), Phys. Rev. D 92, 094034. QUÁ TRÌNH PHÂN Rà HIGGS TRONG MÔ HÌNH RANDALL � SUNDRUM Tóm tt�t�t�t�t: Trong bài báo này, chúng tôi nghiên c�u chi ti�t quá trình rã Higgs boson thành các c�p gg,,γγ e+− e , � + � − , bb . C� th�, chúng tôi ñã tính ñư�c bi�u th�c gi�i tích c�a ñ� r�ng phân rã và sau ñó kh�o sát s� ph� thu�c ñ� r�ng phân rã theo kh�i lư�ng c�a radion. K�t qu� thu ñư�c cho th�y, ñ�i v�i quá trình rã Higgs thành gg , γγ thì ñ� r�ng phân rã tăng khi kh�i lư�ng radion tăng. Còn ñ�i v�i quá trình rã Higgs thành e+− e,� + � − , bb thì ñ� rông thay ñ�i không ñáng k� khi kh�i lư�ng radion thay ñ�i. Đ� r�ng phân rã thu ñư�c là l�n nh�t ñ�i v�i quá trình rã h→ bb . TTT�T� khoákhoá: Higgs boson, mô hình Randall�Sundrum, ñ� r�ng phân rã.
File đính kèm:
 decays_of_higgs_in_randall_sundrum_model.pdf
decays_of_higgs_in_randall_sundrum_model.pdf

