Anten tái cấu hình theo giản đồ bức xạ và tần số sử dụng chuỗi padovan
Nội dung bài báo đề xuất một cấu trúc anten đa tái cấu hình: vừa có thể tái cấu hình theo giản đồ
bức xạ vừa có thể tái cấu hình theo tần số dựa trên các trạng thái bật – tắt khác nhau của bốn diode
PIN. Để làm được điều này, thiết kế anten được biến đổi theo hình vuông Padovan với 9 phần tử
trên mặt bức xạ và bốn phần tử trên mặt phẳng đất. Anten thu được có thể tái cấu hình theo giản
đồ bức xạ tại hai phương +520 và 270, tái cấu hình theo tần số từ 5Ghz đến 18.74GHz với kích
thước tổng thể khá nhỏ, đạt 44.44 x 35 x 1.52 mm3. Bên cạnh đó, các tham số quan trọng khác của
anten tái cấu hình như hiệu suất và băng thông thu được khá tốt ở phần lớn các tần số cộng hưởng
của anten.

Trang 1
Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Anten tái cấu hình theo giản đồ bức xạ và tần số sử dụng chuỗi padovan

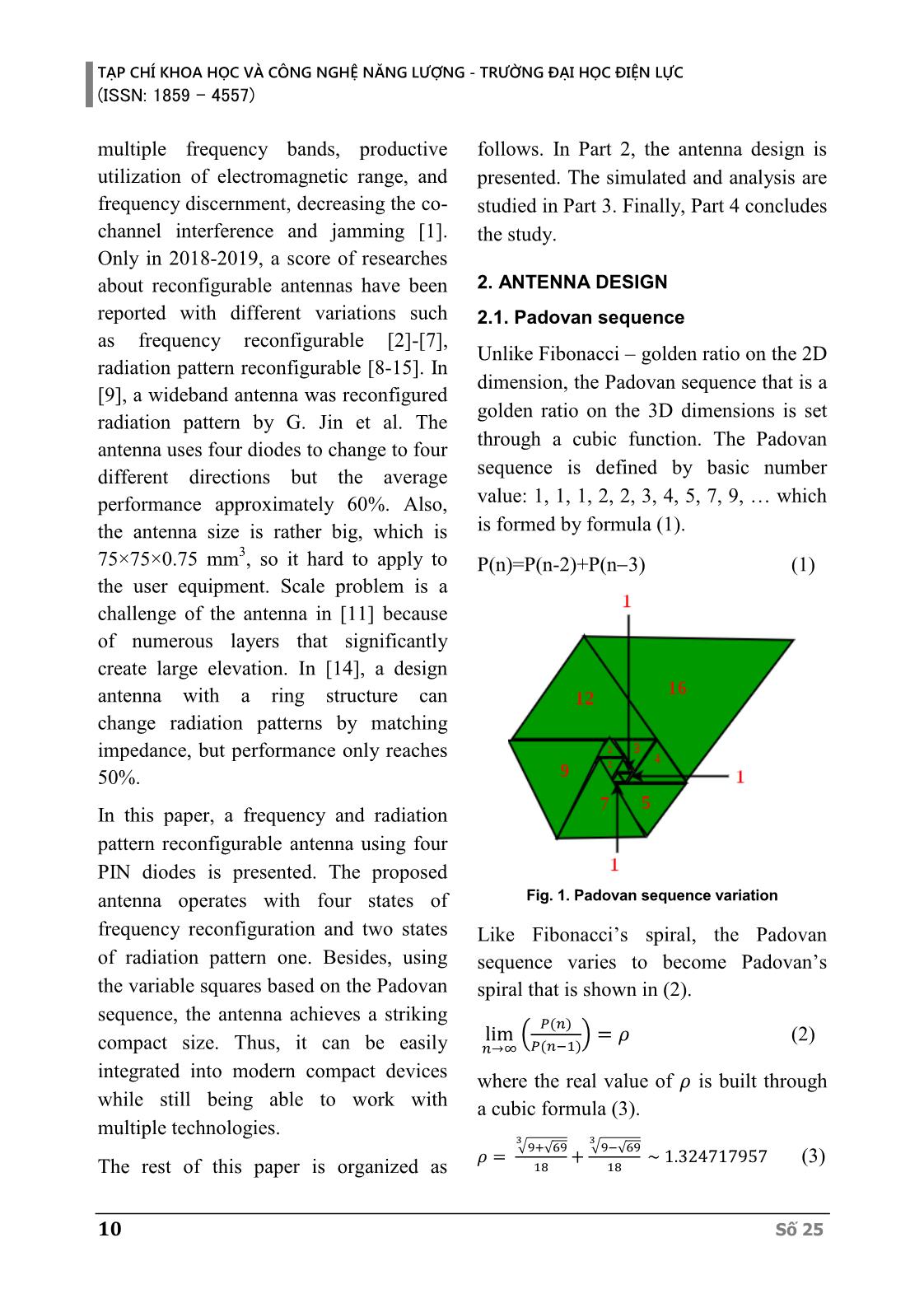
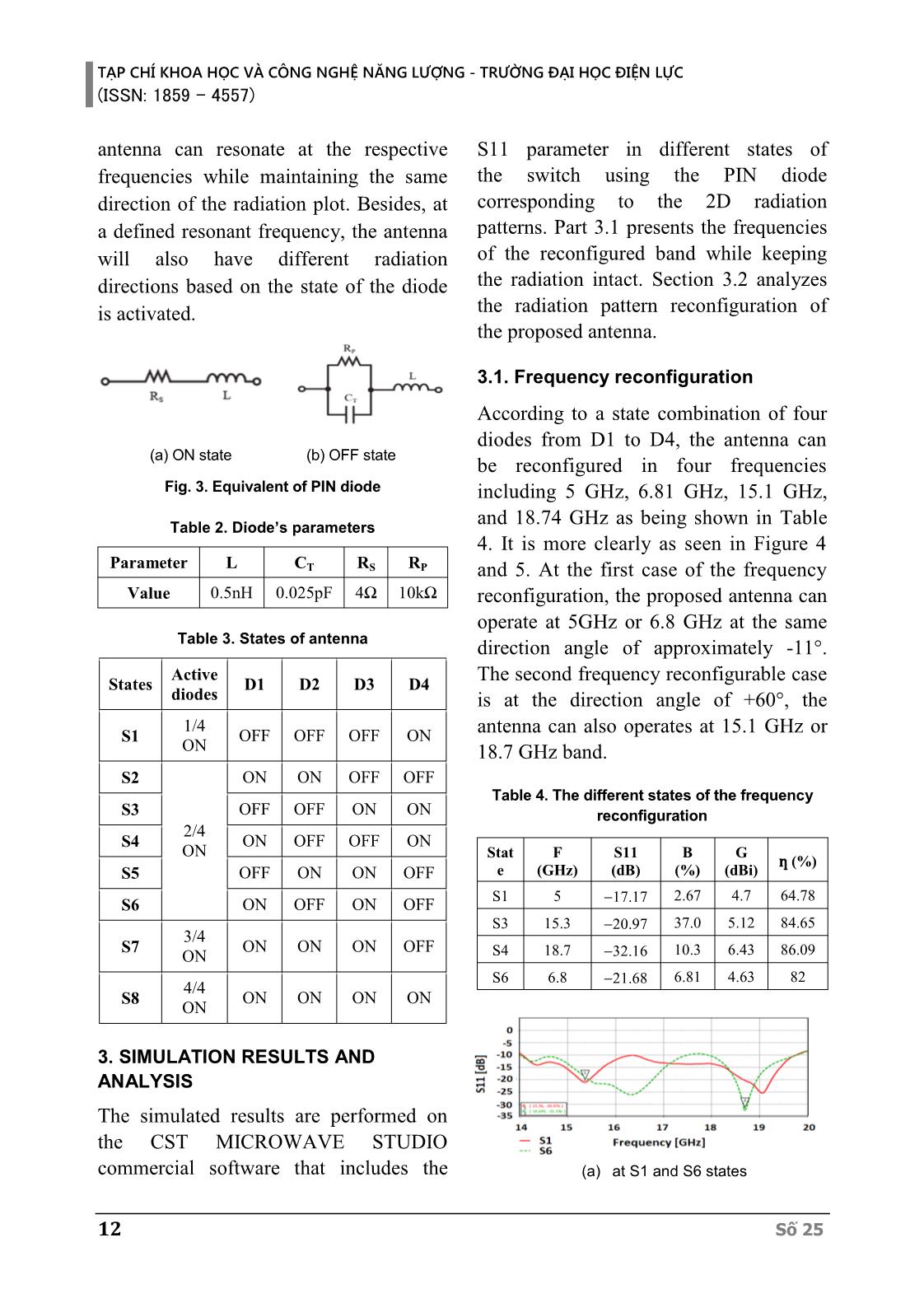
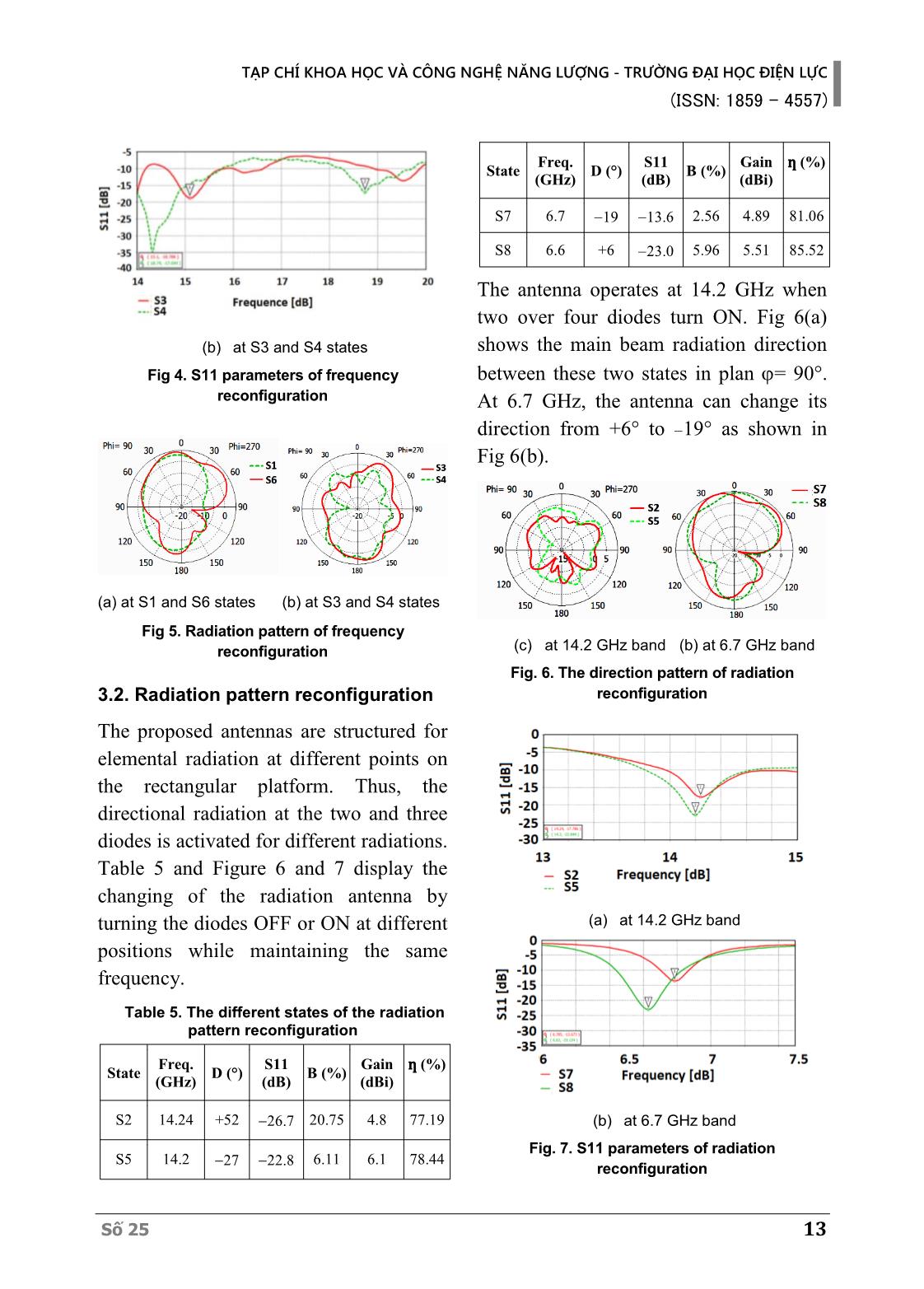
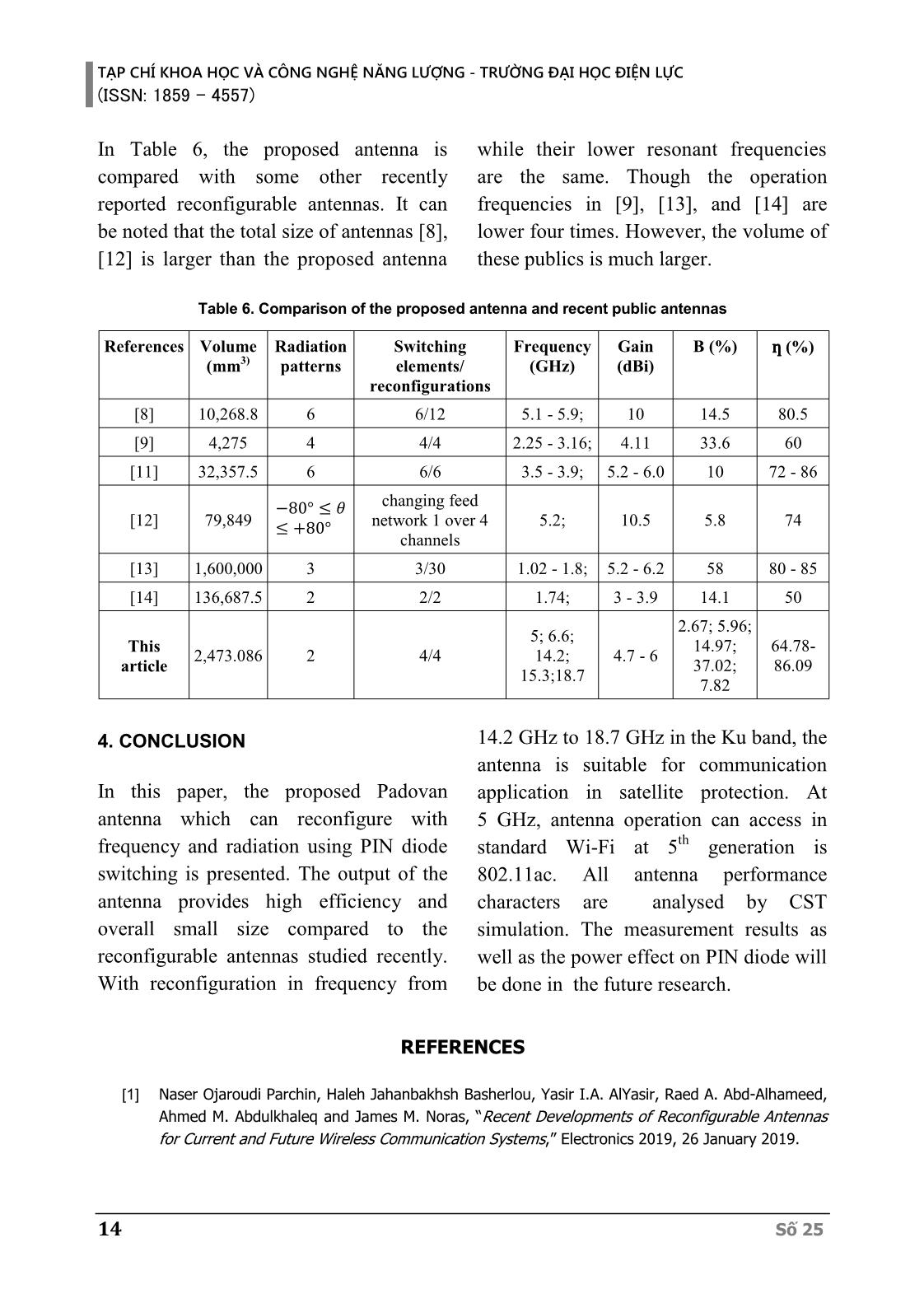
ble radiation patterns among all Số 25 9 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) multiple frequency bands, productive follows. In Part 2, the antenna design is utilization of electromagnetic range, and presented. The simulated and analysis are frequency discernment, decreasing the co- studied in Part 3. Finally, Part 4 concludes channel interference and jamming [1]. the study. Only in 2018-2019, a score of researches about reconfigurable antennas have been 2. ANTENNA DESIGN reported with different variations such 2.1. Padovan sequence as frequency reconfigurable [2]-[7], Unlike Fibonacci – golden ratio on the 2D radiation pattern reconfigurable [8-15]. In dimension, the Padovan sequence that is a [9], a wideband antenna was reconfigured golden ratio on the 3D dimensions is set radiation pattern by G. Jin et al. The through a cubic function. The Padovan antenna uses four diodes to change to four different directions but the average sequence is defined by basic number performance approximately 60%. Also, value: 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, which the antenna size is rather big, which is is formed by formula (1). 3 75×75×0.75 mm , so it hard to apply to P(n)=P(n-2)+P(n 3) (1) the user equipment. Scale problem is a challenge of the antenna in [11] because of numerous layers that significantly create large elevation. In [14], a design antenna with a ring structure can change radiation patterns by matching impedance, but performance only reaches 50%. In this paper, a frequency and radiation pattern reconfigurable antenna using four PIN diodes is presented. The proposed antenna operates with four states of Fig. 1. Padovan sequence variation frequency reconfiguration and two states Like Fibonacci’s spiral, the Padovan of radiation pattern one. Besides, using sequence varies to become Padovan’s the variable squares based on the Padovan spiral that is shown in (2). sequence, the antenna achieves a striking 푃(푛) lim ( ) = 휌 (2) compact size. Thus, it can be easily 푛→∞ 푃(푛−1) integrated into modern compact devices where the real value of 휌 is built through while still being able to work with a cubic formula (3). multiple technologies. 3 3 √9+ 69 √9− 69 휌 = √ + √ ~ 1.324717957 (3) The rest of this paper is organized as 18 18 10 Số 25 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) 2.2. Antenna structure Table 1. Parameters and their dimensions (mm) 2.2.1. Antenna using Padovan Parameter Value Parameter Value sequence W 35 P2 4 44.44 6 Figure 2 shows the proposed antenna's L P3 Ld 5.16 P4 8 geometrical structure that consists of three Wd 0.2 P5 10 parts: the radiation patch, the substrate, k 2 P7 14 and the ground plane. The substrate layer P1 2 is RO4350B with hs= 1.52 mm and ԑ=3.48, loss tangent 0.0037. The patch is constructed by the Padovan geometric sequence in the form of nine squares. These squares are arranged in ascending order in a counter-clockwise direction starting from 180° direction with incremental size 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7. The ratio k = 2 is built according to the following formula (4) and (5). (a) (b) Fig. 2. Antenna geometric. (a): Frontside; 푃(푛) = 푃(푛 − 2) + 푃(푛 − 3) (4) (b): Backside 푃( ) = 푃(푛) × (5) 2.2.2. PIN diode To switch the different antenna states, where P(n) is the value from the Padovan four PIN MA4AGBLP912 diodes are sequence, P(N) is the real value of the used due to low loss and high switching radiation patch. speed. The PIN diode can be turned on and off by using suitable polarity voltage. It is the same rule for the ground plane The ON state is made by a resistor in with the form of four DGS squares. The series with the inductor and the OFF state antenna is connected by coaxial cable is made by a resistor connected in parallel through the ground plane to be exposed to with the capacitor then in series with the the radiation patch. The position of inductor. The values R, L, C of the diode coordinates (x,y) is (-3.5;6.5). Four diodes PIN under both ON and OFF conditions are connected to the feeding network are shown in Table 2. by a microstrip line of 5.166 mm long The different states of the antenna are and 0.2 mm width. The other antenna shown in Table 3. Using four PIN diodes dimensions are detailed in Table 1. for the four radiating elements, the Số 25 11 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) antenna can resonate at the respective S11 parameter in different states of frequencies while maintaining the same the switch using the PIN diode direction of the radiation plot. Besides, at corresponding to the 2D radiation a defined resonant frequency, the antenna patterns. Part 3.1 presents the frequencies will also have different radiation of the reconfigured band while keeping directions based on the state of the diode the radiation intact. Section 3.2 analyzes is activated. the radiation pattern reconfiguration of the proposed antenna. 3.1. Frequency reconfiguration According to a state combination of four diodes from D1 to D4, the antenna can (a) ON state (b) OFF state be reconfigured in four frequencies Fig. 3. Equivalent of PIN diode including 5 GHz, 6.81 GHz, 15.1 GHz, and 18.74 GHz as being shown in Table Table 2. Diode’s parameters 4. It is more clearly as seen in Figure 4 Parameter L CT RS RP and 5. At the first case of the frequency Value 0.5nH 0.025pF 4Ω 10kΩ reconfiguration, the proposed antenna can operate at 5GHz or 6.8 GHz at the same Table 3. States of antenna direction angle of approximately -11°. Active The second frequency reconfigurable case States D1 D2 D3 D4 diodes is at the direction angle of +60°, the 1/4 S1 OFF OFF OFF ON antenna can also operates at 15.1 GHz or ON 18.7 GHz band. S2 ON ON OFF OFF Table 4. The different states of the frequency S3 OFF OFF ON ON reconfiguration 2/4 S4 ON OFF OFF ON ON Stat F S11 B G ƞ (%) S5 OFF ON ON OFF e (GHz) (dB) (%) (dBi) S1 5 2.67 4.7 64.78 S6 ON OFF ON OFF 17.17 S3 15.3 20.97 37.0 5.12 84.65 3/4 S7 ON ON ON OFF ON S4 18.7 32.16 10.3 6.43 86.09 S6 6.8 21.68 6.81 4.63 82 4/4 S8 ON ON ON ON ON 3. SIMULATION RESULTS AND ANALYSIS The simulated results are performed on the CST MICROWAVE STUDIO commercial software that includes the (a) at S1 and S6 states 12 Số 25 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) Freq. S11 Gain ƞ (%) State D (°) B (%) (GHz) (dB) (dBi) S7 6.7 19 13.6 2.56 4.89 81.06 S8 6.6 +6 23.0 5.96 5.51 85.52 The antenna operates at 14.2 GHz when two over four diodes turn ON. Fig 6(a) (b) at S3 and S4 states shows the main beam radiation direction Fig 4. S11 parameters of frequency between these two states in plan = 90°. reconfiguration At 6.7 GHz, the antenna can change its direction from +6° to 19° as shown in Fig 6(b). (a) at S1 and S6 states (b) at S3 and S4 states Fig 5. Radiation pattern of frequency reconfiguration (c) at 14.2 GHz band (b) at 6.7 GHz band Fig. 6. The direction pattern of radiation 3.2. Radiation pattern reconfiguration reconfiguration The proposed antennas are structured for elemental radiation at different points on the rectangular platform. Thus, the directional radiation at the two and three diodes is activated for different radiations. Table 5 and Figure 6 and 7 display the changing of the radiation antenna by turning the diodes OFF or ON at different (a) at 14.2 GHz band positions while maintaining the same frequency. Table 5. The different states of the radiation pattern reconfiguration Freq. S11 Gain ƞ (%) State D (°) B (%) (GHz) (dB) (dBi) S2 14.24 +52 26.7 20.75 4.8 77.19 (b) at 6.7 GHz band Fig. 7. S11 parameters of radiation S5 14.2 27 22.8 6.11 6.1 78.44 reconfiguration Số 25 13 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) In Table 6, the proposed antenna is while their lower resonant frequencies compared with some other recently are the same. Though the operation reported reconfigurable antennas. It can frequencies in [9], [13], and [14] are be noted that the total size of antennas [8], lower four times. However, the volume of [12] is larger than the proposed antenna these publics is much larger. Table 6. Comparison of the proposed antenna and recent public antennas References Volume Radiation Switching Frequency Gain B (%) ƞ (%) (mm3) patterns elements/ (GHz) (dBi) reconfigurations [8] 10,268.8 6 6/12 5.1 - 5.9; 10 14.5 80.5 [9] 4,275 4 4/4 2.25 - 3.16; 4.11 33.6 60 [11] 32,357.5 6 6/6 3.5 - 3.9; 5.2 - 6.0 10 72 - 86 −80° ≤ 휃 changing feed [12] 79,849 ≤ +80° network 1 over 4 5.2; 10.5 5.8 74 channels [13] 1,600,000 3 3/30 1.02 - 1.8; 5.2 - 6.2 58 80 - 85 [14] 136,687.5 2 2/2 1.74; 3 - 3.9 14.1 50 2.67; 5.96; 5; 6.6; This 14.97; 64.78- 2,473.086 2 4/4 14.2; 4.7 - 6 article 37.02; 86.09 15.3;18.7 7.82 4. CONCLUSION 14.2 GHz to 18.7 GHz in the Ku band, the antenna is suitable for communication In this paper, the proposed Padovan application in satellite protection. At antenna which can reconfigure with 5 GHz, antenna operation can access in frequency and radiation using PIN diode standard Wi-Fi at 5th generation is switching is presented. The output of the 802.11ac. All antenna performance antenna provides high efficiency and characters are analysed by CST overall small size compared to the simulation. The measurement results as reconfigurable antennas studied recently. well as the power effect on PIN diode will With reconfiguration in frequency from be done in the future research. REFERENCES [1] Naser Ojaroudi Parchin, Haleh Jahanbakhsh Basherlou, Yasir I.A. AlYasir, Raed A. Abd-Alhameed, Ahmed M. Abdulkhaleq and James M. Noras, “Recent Developments of Reconfigurable Antennas for Current and Future Wireless Communication Systems,” Electronics 2019, 26 January 2019. 14 Số 25 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) [2] Tayyaba Khan, MuhibUr Rahman, Adeel Akram, Yasar Amin and Hannu Tenhunen, “A Low-Cost CPW-Fed Multiband Frequency Reconfigurable Antenna for Wireless Applications,” Electronics 2019, 14 August 2019. [3] Jayendra Kumar, Banani Basu, Fazal Ahmed Talukdar, Arnab Nandi, “Stable-multiband frequency reconfigurable antenna with improved radiation efficiency and increased number of multiband operations,” IET Microwave, Antennas & Propagation, vol. 13, Iss.5, pp. 642-648, 28th February 2019. [4] Ajay Yadav, Minakshi Tewari, and Rajendra P. Yadav, “Pixed Shap Ground Inspired Frequency Reconfigurable Antenna,” Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 89, 75-85, 2019. [5] A. Vamseekrishna, B.T.P Madhav, T. Anilkumar, L.S.S. Reddy, “An IoT controlled octahedron frequency reconfigurable multiband antenna for microwave sensing applications,” IEEE Sensors Letters, vol. 2(3), 2019. [6] V. Arun and L.R. Karl Marx, “Internet of Things Controlled Reconfigurable Antenna for RF Harvesting,” Defense Science Journal, vol. 68, pp. 566-571, No. 6, November 2018. [7] M. Jenath Sathikbasha and V.Nagarajan, “DGS based Multiband Frequency Reconfigurable Antenna for Wireless Applications,” International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing, April 4-6, 2019, India. [8] Y. Yang and X. Zhu, "A Wideband Reconfigurable Antenna With 360° Beam Steering for 802.11ac WLAN Applications," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 600- 608, Feb. 2018. [9] G. Jin, M. Li, D. Liu and G. Zeng, "A Simple Planar Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based on Arc Dipoles," in IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, vol. 17, no. 9, pp. 1664-1668, Sept. 2018. [10] Z. Gan, Z. Tu and Z. Xie, "Pattern-Reconfigurable Unidirectional Dipole Antenna Array Fed by SIW Coupler for Millimeter Wave Application," in IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 22401-22407, 2018. [11] G. Yang, J. Li, D. Wei, S. Zhou and R. Xu, "Pattern Reconfigurable Microstrip Antenna With Multidirectional Beam for Wireless Communication," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 1910-1915, March 2019. [12] H. Zhou et al., "Reconfigurable Phased Array Antenna Consisting of High-Gain High-Tilt Circularly Polarized Four-Arm Curl Elements for Near Horizon Scanning Satellite Applications," in IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, vol. 17, no. 12, pp. 2324-2328, Dec. 2018. [13] S. Ahdi Rezaeieh and A.M. Abbosh, "Pattern-Reconfigurable Magneto electric Antenna Utilizing Asymmetrical Dipole Arms," in IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 688-692, April 2019. [14] Mingyu Sun, Zhe Zhang, Kang An, Xianghui Wang, Yuezhi Jiang, Aixin Chen, "Dual-Sense Circular Polarization Antenna Based on Reconfigurable Orthogonal Network", International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, vol. 2019, Article ID 1670786, 7 pages, 2019. [15] X. Yi, L. Huitema and H. Wong, "Polarization and Pattern Reconfigurable Cuboid Quadrifilar Helical Antenna," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 66, no. 6, pp. 2707- 2715, June 2018. Biography: Số 25 15 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) Duong Thi Thanh Tu, received B.E, M.E and PhD degrees in Electronics and Telecommunications from Hanoi University of Science in 1999 and 2005, and 2019, respectively. She is current senior lecturer at Faculty of Telecommunications 1, Posts and Telecommunications Institute of Technology. Research interests include antenna design for new generation wireless networks as well as the special structure of material such as metamaterial, electromagnetic band gap structure. Nguyen Tan Dung: His is current student at Faculty of Telecommunications 1, Posts and Telecommunications Institute of Technology. His current research interest is antenna design for new generation wireless networks. Hoang Thi Phuong Thao, Received B.E, M.E and PhD degrees in Electronics and Telecommunications from Hanoi University of Science in 2004 and 2007, and 2019, respectively. She is current senior Lecturer at Electronics and Telecommunications Faculty, Electric Power University. Her current research interests are designing antenna, metamaterial, and localization systems. 16 Số 25 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ NĂNG LƯỢNG - TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC ĐIỆN LỰC (ISSN: 1859 - 4557) Số 25 17
File đính kèm:
 anten_tai_cau_hinh_theo_gian_do_buc_xa_va_tan_so_su_dung_chu.pdf
anten_tai_cau_hinh_theo_gian_do_buc_xa_va_tan_so_su_dung_chu.pdf

