A high-Performance routing protocol based on multi-metric for manet
With the development of mobile communication systems, Mobile Ad-Hoc Network (MANET) has been focus research and deployed in many domains server human life such as smart agriculture, smart retail, healthcare, and smart cities. Due to the natural mobility of network nodes in a MANET environment, the performance system is low and depend on routing protocols. Therefore, In order to more contribution to the next-generation network, these routing protocols should be more flexible, saving energy, and performance achievable. In this paper, we propose a multi-metric on-demand routing protocol based on three parameters: queue length, route quality, and hops number to improve the MANET performance. Base on the working conditions of the network system. One or more routing metrics will be integrated into the cost function. Besides, we also performance evaluation of the MM-AODV compared with traditional routing protocols such as AODV and DSR. Simulation results show that MM-AODV protocol improves in terms of the packet delivery ratio, time delay, and throughput better than DSR and AODV routing protocols

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: A high-Performance routing protocol based on multi-metric for manet

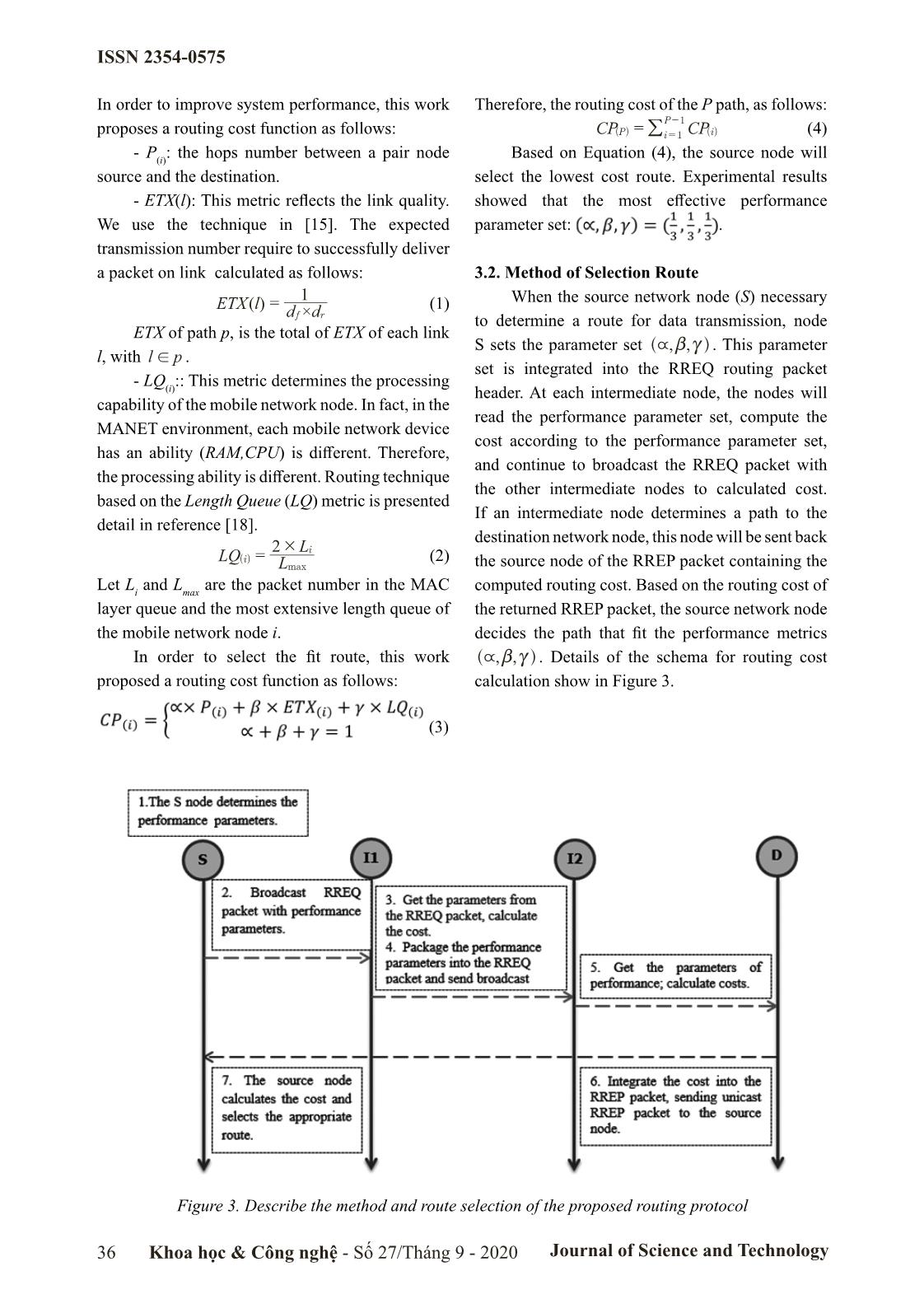
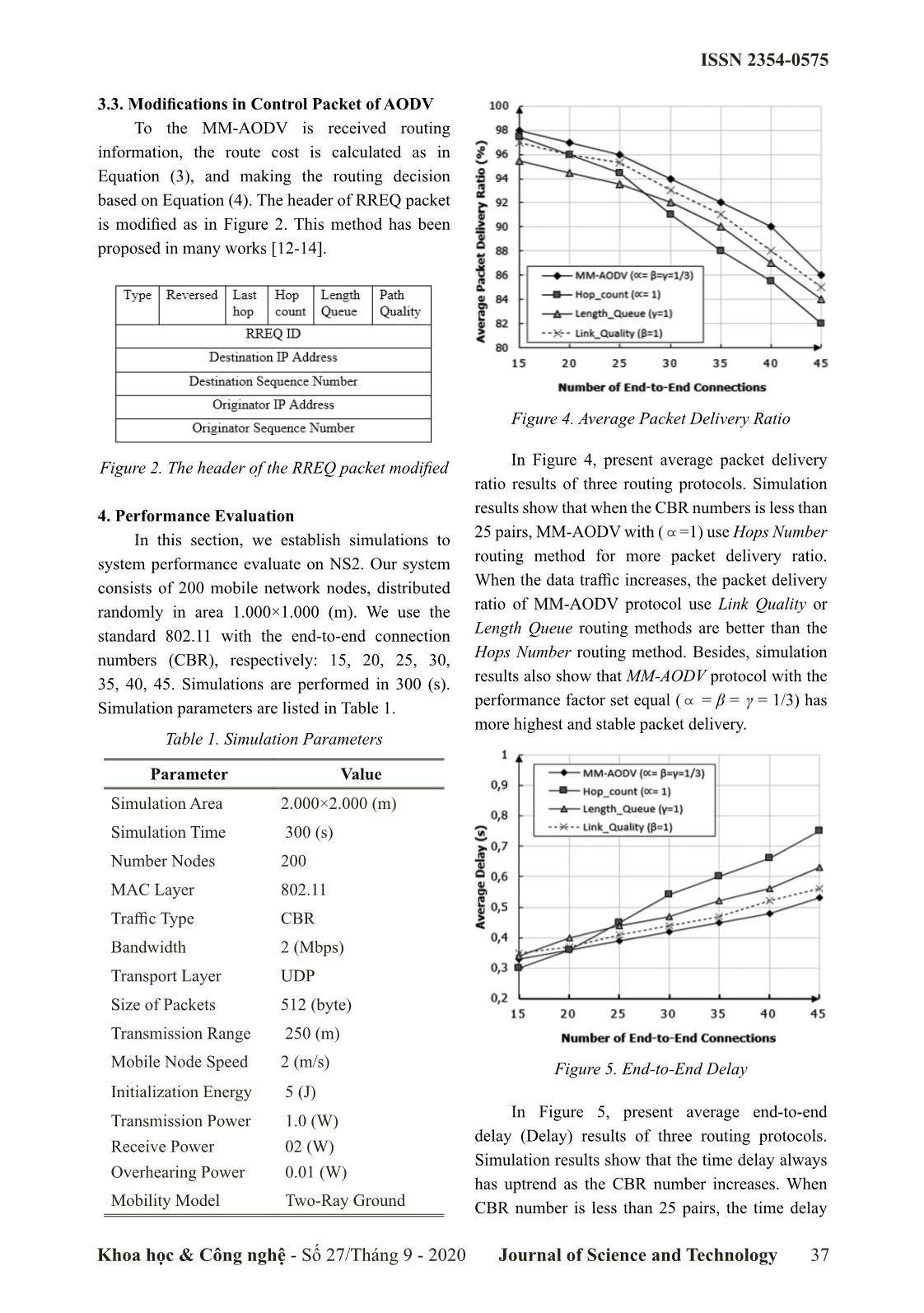
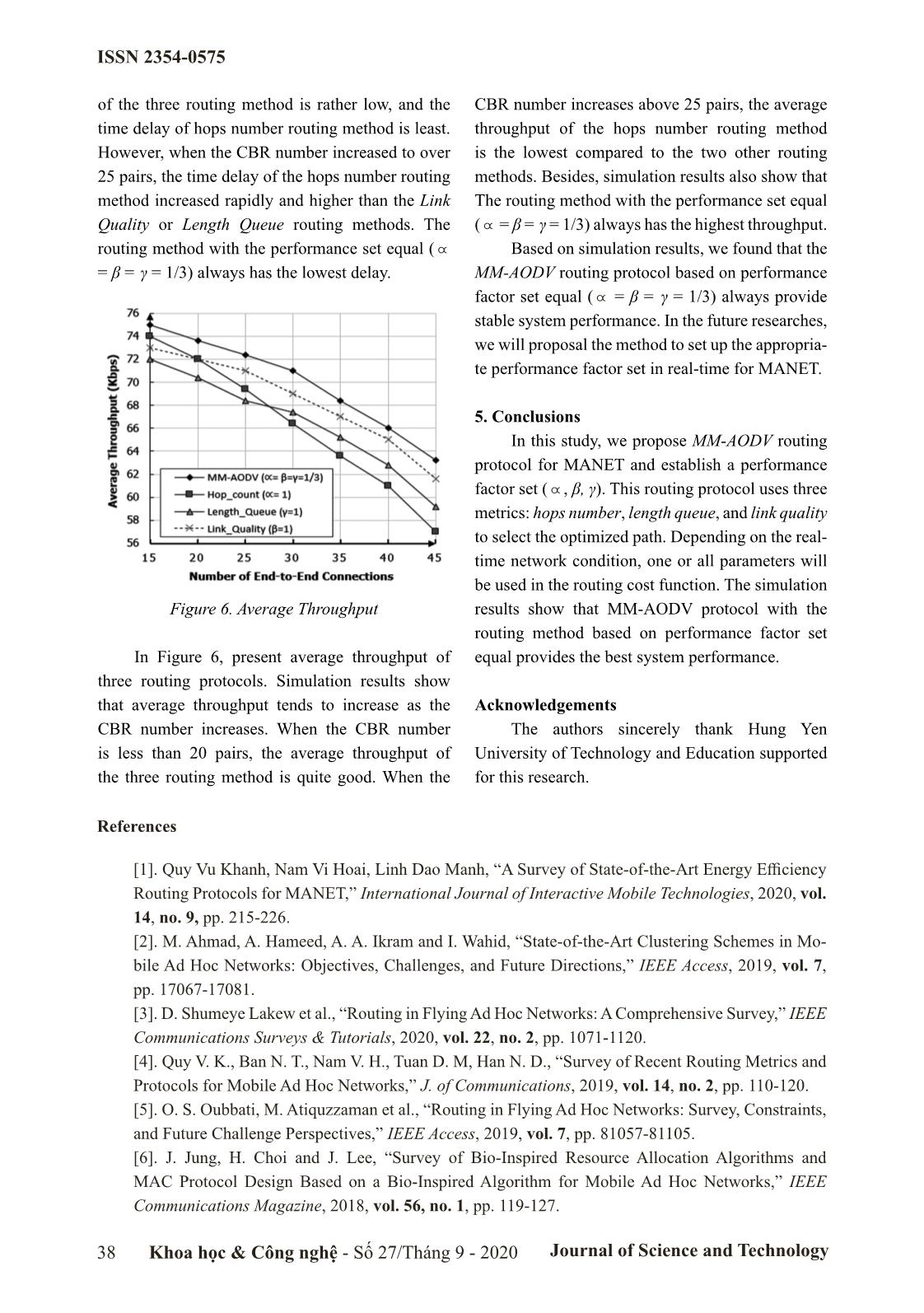
ocol for integrated metrics. According to this approach, MANET, our protocol using three routing metrics Geetha N. and et al. (2012) [16] proposed a new are queue length, link quality and hops number to routing protocol, called HCESDSR protocol to aim to select the high-performance route, namely improve the lifetime for MANET. This work MM-AODV (Multi-Metric – AODV). proposes a new routing metric, called the Expected This paper structure is organized as follows: Minimum Lifetime of the route. Based on this In the next section, we present the related work. metric, the routing cost function will select the Section 3 presents the proposed routing protocol. route. The simulation results show that HCESDSR Section 4 presents different simulation results to protocol improve the network lifetime and time verify the proposed protocol performance, and delay compare to other traditional protocols. Section 5 is Conclusions. Although these proposed protocols improved This paper is the extended result from our network performance in specific scenarios, with a research which we presented at the ACIIDS [20]. high mobile network environment as MANET, the system performance is affected by many factors 2. Related Work such as dynamic network structure, mobility of Survey recent works show that MANET network nodes, and network size. Therefore, the performance research direction is very active and issue of optimizing network performance is always achieved positive results [13-16], as follows: topical and attracts the attention of researchers. According to the multi-metric approach, A. M. Mezher and et al. (2017) [13] proposal the 3. MM-AODV Protocol 3MRP routing protocol to send video messages A visual way to select a set of parameters over Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks in smart cities. to improve routing performance is to identify This protocol uses five routing metrics to select problems that affect network performance. In [4, optimize the route. Simulation results on NS2 show 17], the main parameters that affect the MANET that the 3MRP routing protocol improves in term performance are hops number, link quality, and of time delay, and packet delivery ratio compares queue length at nodes. The detailed improvements with other traditional protocols. According to this are presented in the following subsections. research, D. Lin and et al. (2017) [14] proposal the 3.1 Routing Metrics MoZo routing protocol to communication between Traditional routing protocols such as AODV vehicles without relying on the fixed infrastructure. and DSR select the route based on the smallest The primary idea of the protocol is proposed that hops. In fact, the shortest route may not give the each vehicle will have a GPS module to obtain best bandwidth or time delay. Note again, system routing information, combined with clustering performance is determined by three metrics: techniques to improve system performance. throughput, time delay, and packet delivery ratio. Khoa học & Công nghệ - Số 27/Tháng 9 - 2020 Journal of Science and Technology 35 ISSN 2354-0575 In order to improve system performance, this work Therefore, the routing cost of the P path, as follows: P-1 proposes a routing cost function as follows: CP()Pi= /i = 1 CP() (4) - P(i): the hops number between a pair node Based on Equation (4), the source node will source and the destination. select the lowest cost route. Experimental results - ETX(l): This metric reflects the link quality. showed that the most effective performance We use the technique in [15]. The expected parameter set: . transmission number require to successfully deliver a packet on link calculated as follows: 3.2. Method of Selection Route 1 ETXl()= (1) When the source network node (S) necessary ddfr× to determine a route for data transmission, node ETX of path p, is the total of ETX of each link S sets the parameter set \,,bc . This parameter l, with lp! . ^h set is integrated into the RREQ routing packet - LQ :: This metric determines the processing (i) header. At each intermediate node, the nodes will capability of the mobile network node. In fact, in the read the performance parameter set, compute the MANET environment, each mobile network device cost according to the performance parameter set, has an ability (RAM,CPU) is different. Therefore, and continue to broadcast the RREQ packet with the processing ability is different. Routing technique the other intermediate nodes to calculated cost. based on the Length Queue (LQ) metric is presented If an intermediate node determines a path to the detail in reference [18]. destination network node, this node will be sent back 2 # Li LQ()i = (2) Lmax the source node of the RREP packet containing the Let Li and Lmax are the packet number in the MAC computed routing cost. Based on the routing cost of layer queue and the most extensive length queue of the returned RREP packet, the source network node the mobile network node i. decides the path that fit the performance metrics In order to select the fit route, this work \,,bc . Details of the schema for routing cost ^h proposed a routing cost function as follows: calculation show in Figure 3. (3) Figure 3. Describe the method and route selection of the proposed routing protocol 36 Khoa học & Công nghệ - Số 27/Tháng 9 - 2020 Journal of Science and Technology ISSN 2354-0575 3.3. Modifications in Control Packet of AODV To the MM-AODV is received routing information, the route cost is calculated as in Equation (3), and making the routing decision based on Equation (4). The header of RREQ packet is modified as in Figure 2. This method has been proposed in many works [12-14]. Figure 4. Average Packet Delivery Ratio Figure 2. The header of the RREQ packet modified In Figure 4, present average packet delivery ratio results of three routing protocols. Simulation 4. Performance Evaluation results show that when the CBR numbers is less than \ In this section, we establish simulations to 25 pairs, MM-AODV with ( =1) use Hops Number system performance evaluate on NS2. Our system routing method for more packet delivery ratio. consists of 200 mobile network nodes, distributed When the data traffic increases, the packet delivery randomly in area 1.000×1.000 (m). We use the ratio of MM-AODV protocol use Link Quality or standard 802.11 with the end-to-end connection Length Queue routing methods are better than the numbers (CBR), respectively: 15, 20, 25, 30, Hops Number routing method. Besides, simulation 35, 40, 45. Simulations are performed in 300 (s). results also show that MM-AODV protocol with the \ Simulation parameters are listed in Table 1. performance factor set equal ( = β = γ = 1/3) has more highest and stable packet delivery. Table 1. Simulation Parameters Parameter Value Simulation Area 2.000×2.000 (m) Simulation Time 300 (s) Number Nodes 200 MAC Layer 802.11 Traffic Type CBR Bandwidth 2 (Mbps) Transport Layer UDP Size of Packets 512 (byte) Transmission Range 250 (m) Mobile Node Speed 2 (m/s) Figure 5. End-to-End Delay Initialization Energy 5 (J) In Figure 5, present average end-to-end Transmission Power 1.0 (W) delay (Delay) results of three routing protocols. Receive Power 02 (W) Simulation results show that the time delay always Overhearing Power 0.01 (W) has uptrend as the CBR number increases. When Mobility Model Two-Ray Ground CBR number is less than 25 pairs, the time delay Khoa học & Công nghệ - Số 27/Tháng 9 - 2020 Journal of Science and Technology 37 ISSN 2354-0575 of the three routing method is rather low, and the CBR number increases above 25 pairs, the average time delay of hops number routing method is least. throughput of the hops number routing method However, when the CBR number increased to over is the lowest compared to the two other routing 25 pairs, the time delay of the hops number routing methods. Besides, simulation results also show that method increased rapidly and higher than the Link The routing method with the performance set equal Quality or Length Queue routing methods. The ( \ = β = γ = 1/3) always has the highest throughput. routing method with the performance set equal ( \ Based on simulation results, we found that the = β = γ = 1/3) always has the lowest delay. MM-AODV routing protocol based on performance factor set equal ( \ = β = γ = 1/3) always provide stable system performance. In the future researches, we will proposal the method to set up the appropria- te performance factor set in real-time for MANET. 5. Conclusions In this study, we propose MM-AODV routing protocol for MANET and establish a performance factor set ( \ , β, γ). This routing protocol uses three metrics: hops number, length queue, and link quality to select the optimized path. Depending on the real- time network condition, one or all parameters will be used in the routing cost function. The simulation Figure 6. Average Throughput results show that MM-AODV protocol with the routing method based on performance factor set In Figure 6, present average throughput of equal provides the best system performance. three routing protocols. Simulation results show that average throughput tends to increase as the Acknowledgements CBR number increases. When the CBR number The authors sincerely thank Hung Yen is less than 20 pairs, the average throughput of University of Technology and Education supported the three routing method is quite good. When the for this research. References [1]. Quy Vu Khanh, Nam Vi Hoai, Linh Dao Manh, “A Survey of State-of-the-Art Energy Efficiency Routing Protocols for MANET,” International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 2020, vol. 14, no. 9, pp. 215-226. [2]. M. Ahmad, A. Hameed, A. A. Ikram and I. Wahid, “State-of-the-Art Clustering Schemes in Mo- bile Ad Hoc Networks: Objectives, Challenges, and Future Directions,” IEEE Access, 2019, vol. 7, pp. 17067-17081. [3]. D. Shumeye Lakew et al., “Routing in Flying Ad Hoc Networks: A Comprehensive Survey,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 1071-1120. [4]. Quy V. K., Ban N. T., Nam V. H., Tuan D. M, Han N. D., “Survey of Recent Routing Metrics and Protocols for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks,” J. of Communications, 2019, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 110-120. [5]. O. S. Oubbati, M. Atiquzzaman et al., “Routing in Flying Ad Hoc Networks: Survey, Constraints, and Future Challenge Perspectives,” IEEE Access, 2019, vol. 7, pp. 81057-81105. [6]. J. Jung, H. Choi and J. Lee, “Survey of Bio-Inspired Resource Allocation Algorithms and MAC Protocol Design Based on a Bio-Inspired Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks,” IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 119-127. 38 Khoa học & Công nghệ - Số 27/Tháng 9 - 2020 Journal of Science and Technology ISSN 2354-0575 [7]. M. El-Semary and H. Diab, “BP-AODV: Blackhole Protected AODV Routing Protocol for MANETs Based on Chaotic Map,” in IEEE Access, 2019, vol. 7, pp. 95197-95211. [8]. Z. Chen, W. Zhou, S. Wu and L. Cheng, “An Adaptive on-Demand Multipath Routing Protocol With QoS Support for High-Speed MANET, IEEE Access, 2020, vol. 8, pp. 44760-44773. [9]. R. Shenbagapriya and N. Kumar, “A survey on proactive routing protocols in MANETs,” 2014 Inter. Conf. on Science Engineering and Management Research (ICSEMR), 2014, pp. 1-7. [10]. Daxesh N. Patel et al., “A Survey of Reactive Routing Protocols in MANET,” 2014 Inter. Con- ference (ICICES), IEEE, 2014, pp. 1-6. [11]. RFC3561, https://www.ietf.org, accessed, Oct. 05, 2020. [12]. RFC4728, https://www.ietf.org, accessed, Oct. 05, 2020. [13]. A. M. Mezher and M. A. Igartua, “Multimedia Multimetric Map-Aware Routing Protocol to Send Video-Reporting Messages Over VANETs in Smart Cities,” in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, vol. 66, no. 12, pp. 10611-10625; doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2715719. [14]. D. Lin, J. Kang, A. Squicciarini, Y. Wu, S. Gurung and O. Tonguz, “MoZo: A Moving Zone Based Routing Protocol Using Pure V2V Communication in VANETs,” in IEEE Transactions on Mo- bile Computing, 2017, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 1357-1370; DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2592915. [15]. C. T. Cuong, V. T. Tu and N. T. Hai, “MAR-AODV: Innovative Routing Algorithm in MANET Based on Mobile Agent,” 2013 27th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Barcelona, 2013, pp. 62-66; doi: 10.1109/WAINA.2013.175. [16]. Geetha N., Sankar A., “Hop Count Based Energy Saving Dynamic Source Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Network,” in Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, 2012, Vol. 108, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. [17]. Le Ngoc Hung and Vu Khanh Quy, “A Review: Performance Improvement Routing Protocols for MANETs,” Journal of Communications, 2020, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 439-446. [18]. Quy V.K., Ban N.T., Han N.D., “A Multi-metric Routing Protocol to Improve the Achievable Performance of Mobile Ad Hoc Networks,” in Sieminski A., Kozierkiewicz A., Nunez M., Ha Q. (eds) Modern Approaches for Intelligent Information and Database Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence, 2018, vol 769. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76081-0_38. MỘT GIAO THỨC ĐỊNH TUYẾN CẢI THIỆN HIỆU NĂNG DỰA TRÊN ĐA THAM SỐ CHO MẠNG MANET Tóm tắt: Trong thời gian gần đây, cùng với sự phát triển mạnh mẽ các hệ thống thông tin di động, Mạng MANET (Mobile Ad hoc Network) đã được triển khai và ứng dụng trong nhiều lĩnh vực phục vụ cuộc sống con người như nông nghiệp thông minh, giao thông thông minh, chăm sóc sức khỏe, quân sự, và các thành phố thông minh. Do đặc tính di động của các nút mạng trong môi trường mạng MANET, hiệu năng mạng rất thấp và phụ thuộc nhiều vào giao thức định tuyến được cài đặt trên đó. Để có thể đóng góp vai trò to lớn hơn vào các hệ thống mạng trong tương lai, các giao thức định tuyến cần linh hoạt, tiết kiệm năng lượng và thông minh hơn. Trong nghiên cứu này, chúng tôi đề xuất một giao thức định tuyến theo yêu cầu sử dụng đa chi phí là: số chặng, độ dài hàng đợi và chất lượng liên kết. Dựa trên điều kiện thực tế của hệ thống mạng, một trong số các hệ số này sẽ tham gia vào hàm tính chi phí tuyến đường. Bên cạnh đó chúng tôi còn thực hiện đánh giá hiệu năng của giao thức MM-AODV các các phương thức định tuyến khác nhau. Kết quả cho thấy, giao thức định tuyến MM-AODV với phương thức định tuyến dựa trên bộ hệ số hiệu năng cân bằng cung cấp hiệu năng hệ thống ổn định hơn các phương thức còn lại. Từ khóa: AODV, Routing Protocol, Multi-Metric, MANET. Khoa học & Công nghệ - Số 27/Tháng 9 - 2020 Journal of Science and Technology 39
File đính kèm:
 a_high_performance_routing_protocol_based_on_multi_metric_fo.pdf
a_high_performance_routing_protocol_based_on_multi_metric_fo.pdf

