Roadmap for the implementation of IFRS in Vietnam: Benefits and challenges
Since 2001, the International Accounting Standards Board has issued a set of accounting principles
with the name International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Along with the adoption of IFRS
in many countries around the world, Vietnam is preparing a roadmap for the implementation of IFRS
by 2022. This study was conducted by surveying 119 directors and corporate accountants for the
reasons: (1) to collect their opinions about the roadmap and the scope of IFRS implementation; (2) to
investigate the benefits to companies, investors, policy makers and government agencies; and (3) to
assess the challenges of IFRS implementation. The results show that IFRS implementation increases
the comparability and quality of financial information, reduces investment risks, increases market
efficiency and attracts foreign direct investment. However, organizations face many difficulties to
adopt IFRS as cost, human resources, legal and market issues. Analysis and comparison with the
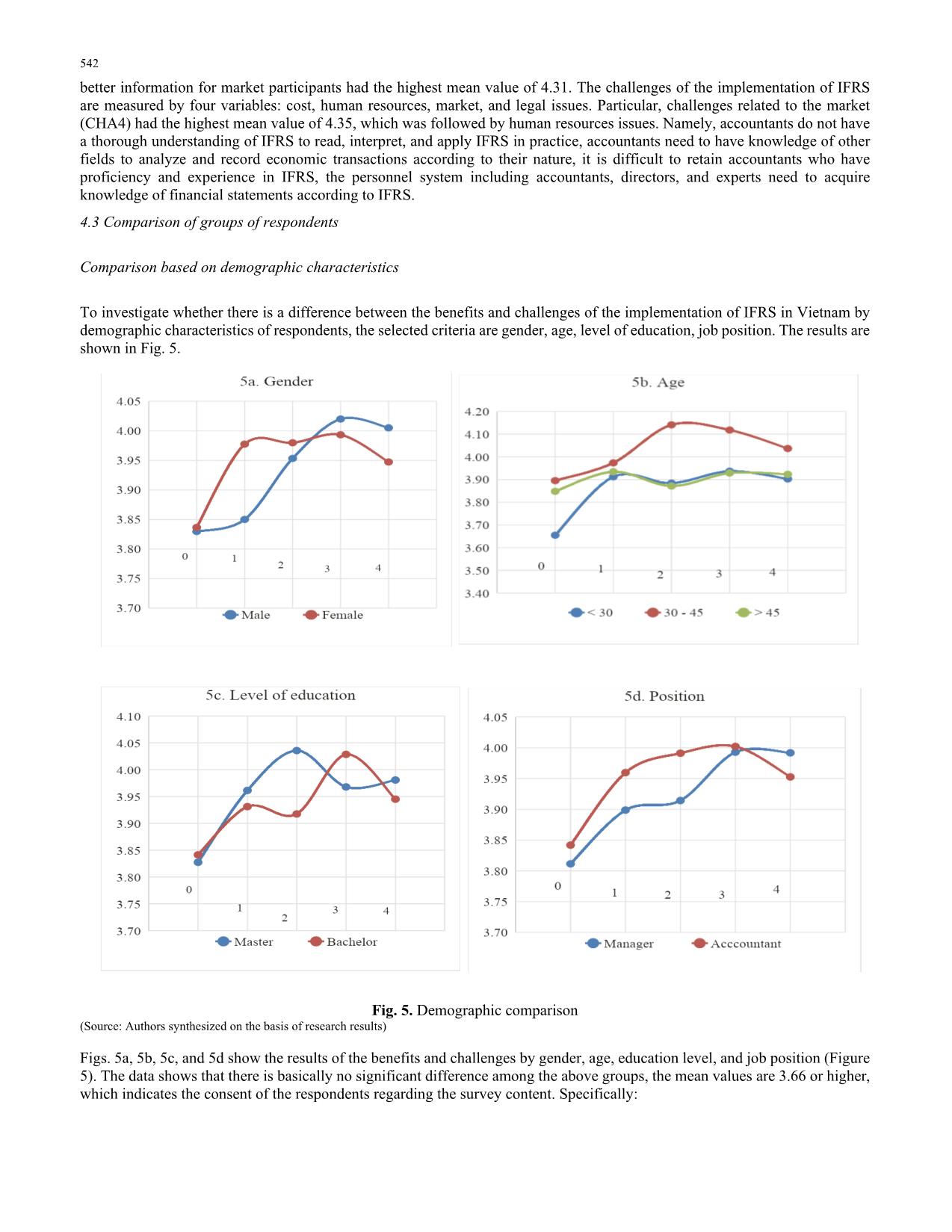
Sample Test show that there is no difference in assessing benefits and challenges by qualifications,
gender, position, region nor firm size. ANOVA analysis showed that there is a difference in the
benefits for policy makers by age, and for investors by type of business. This study also suggests
implications in policies for the implementation of IFRS in Vietnam.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
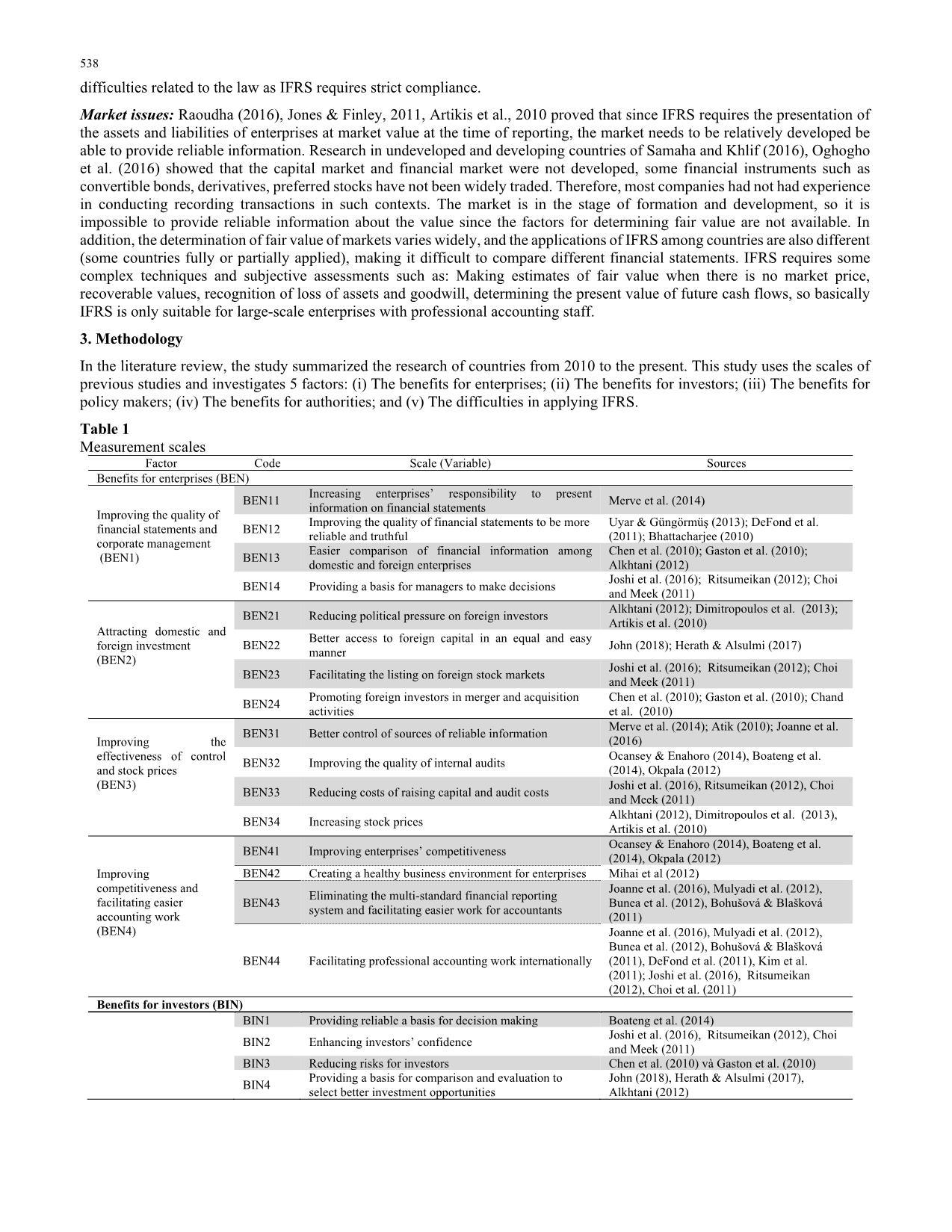
Trang 6
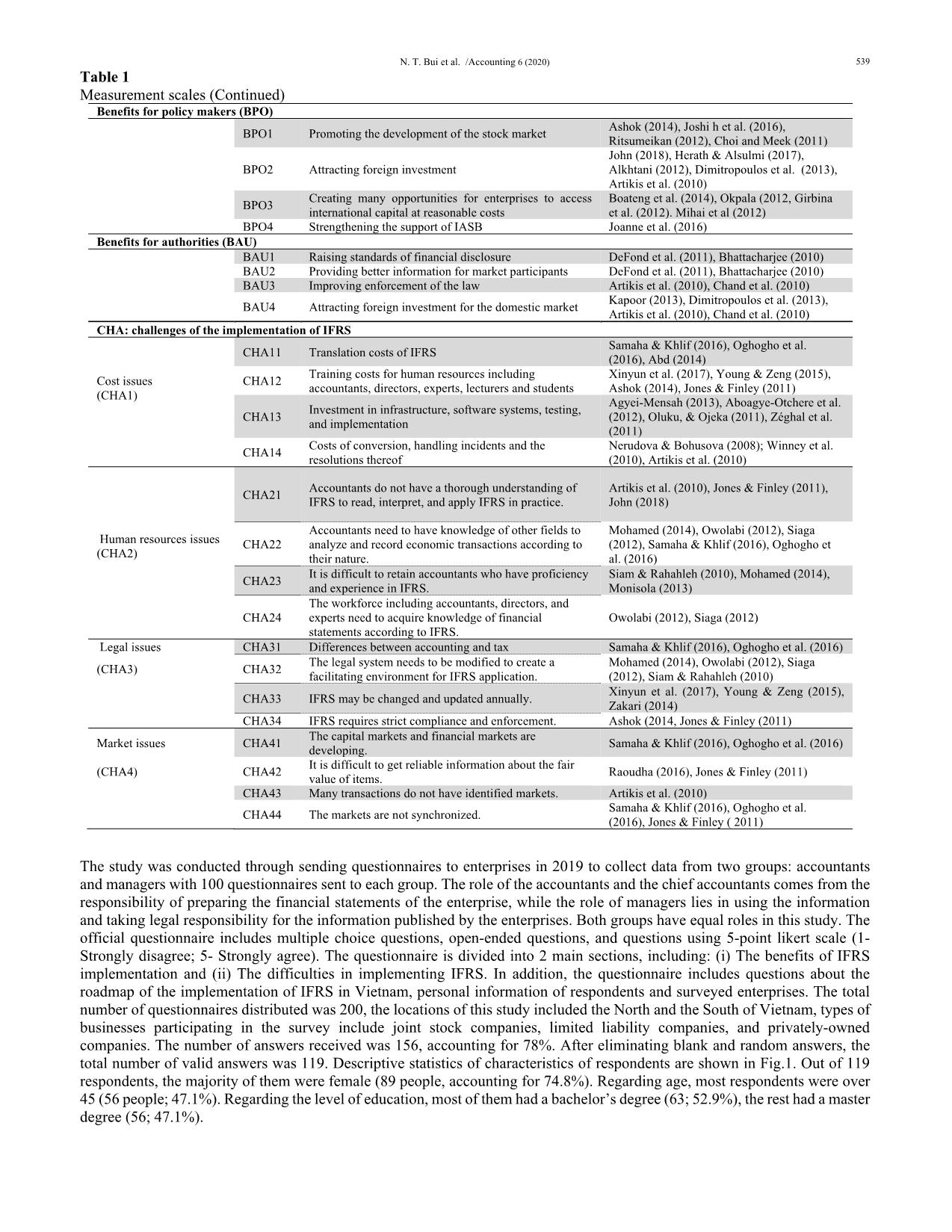
Trang 7
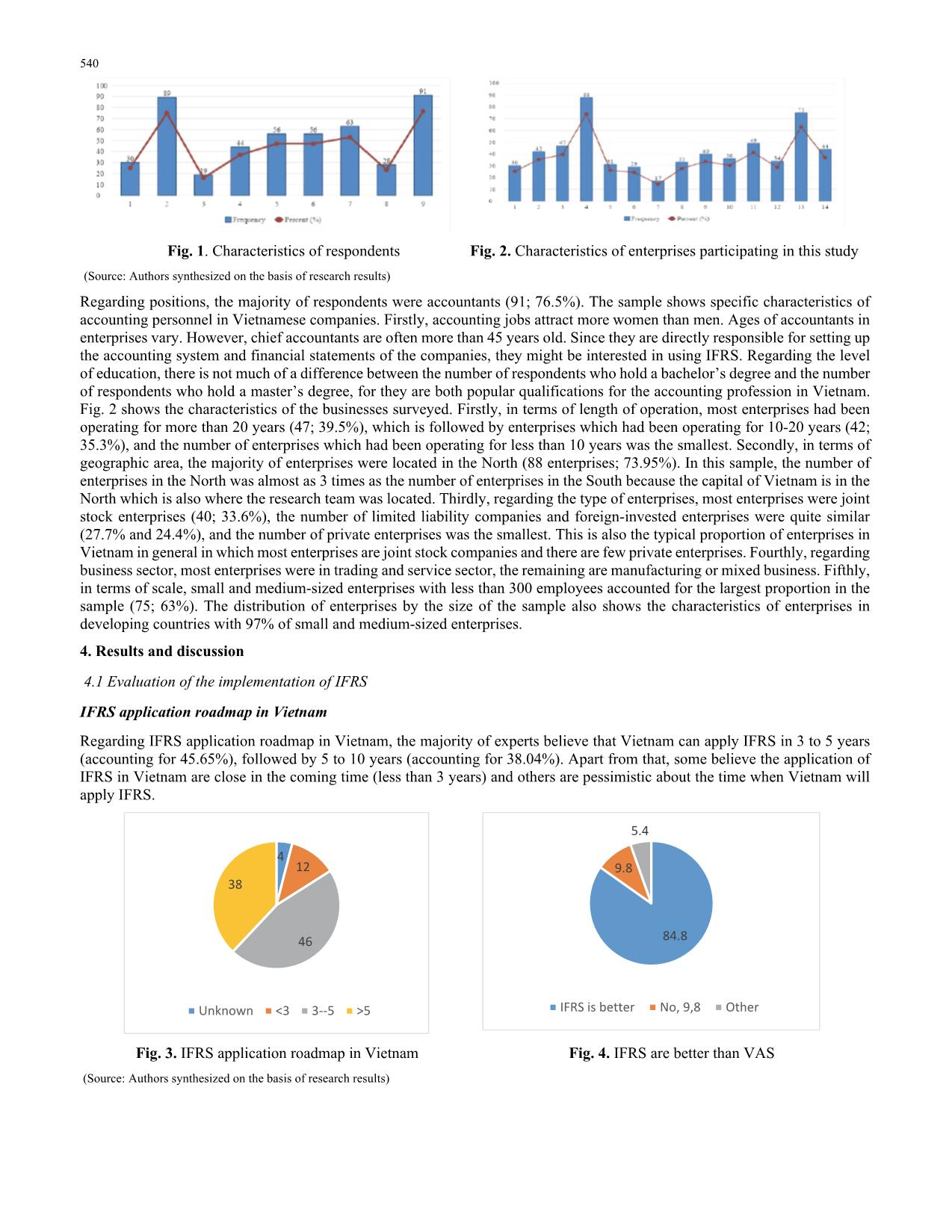
Trang 8
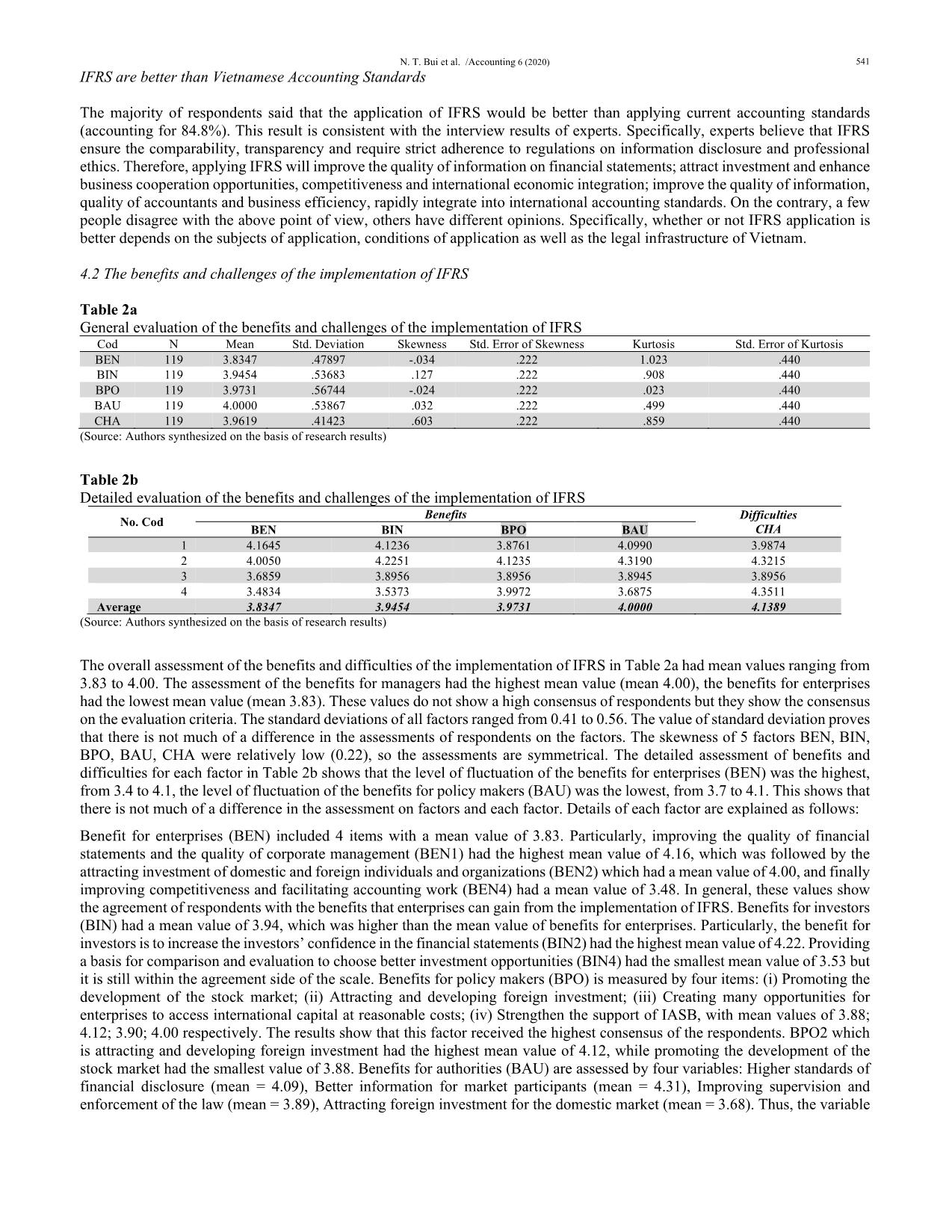
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Roadmap for the implementation of IFRS in Vietnam: Benefits and challenges

S requires fair value recognition, while capital and financial markets are developing, it is impossible to get reliable information about fair value and many transactions are difficult to identify because different markets are not synchronized. KPMG Vietnam (2018) also received a consensus from in-depth interviews with 27 enterprises who supposed that the first implementation of IFRS would be expensive. Tu Chuc Anh et al. (2019) showed that the application of IFRS is expensive in terms of training costs, hiring experts. Research by Tu Oanh et al. (2019) also pointed out one of the biggest difficulties when applying IFRS in Vietnam is the conversion cost. The results of group comparison with Sample Test showed that there was no difference in the benefits and challenges of IFRS implementation by educational level, gender, position, region and enterprise size. ANOVA analysis showed that there was a difference in the benefits for policy makers by age group, there was a difference in the benefits for investors by type of enterprise. The research results are an objective basis for the implementation of IFRS in Vietnam because of the expectation of benefits for enterprises and authorities. In order to widely implement IFRS in Vietnam, it is vital to have a macro strategy from the Government, the consensus of policy makers, managers, accountants and lecturers. Some recommendations to promote the IFRS application process and promote the benefits of IFRS application in Vietnam are proposed as follows: Firstly, it is important to strengthen the dissemination and training of IFRS for experts, lecturers, auditors and accountants. For universities, it is necessary to strengthen the training and retraining about IFRS to produce competent and knowledgeable financial and accounting staff to apply IFRS in Vietnam. This is very important because IFRS is very complicated even for developed countries. Secondly, it is necessary to reach a consensus about the role and significance of financial statements presented according to IFRS. It is necessary to propagandize and widely advertise in many ways so that managers, investors and accountants find it vital to present financial statements according to IFRS. Thirdly, it is critical to complete mechanisms and policies for IFRS application in Vietnam. Additionally, it is necessary to develop regulations and guidelines for the implementation of some special IFRS techniques, such as recognition of loss on assets, accounting derivative instruments for hedging purposes, fair value accounting, investment in properties or biological assets. The implementation of IFRS is really a challenge on the level of development of the market, the qualifications and proficiency of auditors, accountants and investors in the market. For the capital market, stock market, preparing and presenting Financial Statements according to IFRS will help improve the transparency and sustainability of the market. However, preparing and presenting financial statements according to IFRS requires significant efforts from the government agencies in charge of accounting, enterprises, professional organizations and accountants. References Abd El Razik, A. (2014). Challenges of international financial reporting standards (IFRS) in the Islamic accounting world, case Middle Eastern Countries. Scientific Bulletin –Economic Sciences, 8(14), 1-6. Aboagye-Otchere, F., & Agbeibor, J. (2012). The International Financial Reporting Standard for Small and Medium- sized Entities (IFRS for SMES): Suitabitity for Small businesses in Ghana. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 10(2), Adejoh, E & Hasnah, K. (2014). Adoption of international financial reporting standards in Nigeria: Concepts and issues. Journal of Advanced Management Science, 2(1), 72-75 Agyei-Mensah, B. K. (2013). Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) in Ghana and the quality of financial statement disclosures. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 3, 269-286. 550 Alkhtani, S. (2012). The relevance and usefulness of IFRSs to Saudi Arabia. Journal of Administrative and Economics Science, 5(2). Atik, A. (2010) “SME’s views on the adoption and application of “IFRS for SMEs” in Turkey”. European Research Studies, 13(4), 19–31. Artikis, G. P., Ballas, A. A., Skoutela, D., & Tzovas, C. A. (2010). The relevance of IFRS to an emerging market: evidence from Greece. Managerial Finance. Ashok, K. K. (2014). International financial reporting standard (IFRS): Prospects and challenges. J Account Mark, 3(111), 2. Bhattacharjee, S., & Hossain, M. S. (2010). Determinants of financial reporting outcomes following IFRS adoption-implications for Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Accountant, 69(40), 10-19, Retrieved 20 March 2017, from Boateng, A. A., Arhin, A. B., & Afful, V. (2014). International Financial Reporting Standard’s (IFRS) adoption in Ghana: Rationale, benefits and challenges. Journal of Advocacy, Research and Education, 1(1), 26-32. Bohušová, H., & Blašková, V. (2011). In What Ways are Countries Which Have Already Adopted IFRS for SMEs Different. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 4(2), 37-41. Bunea, S., Săcarin, M. & Minu, M. (2012). Romanian professional accountants' perception on the differential financial reporting for small and medium-sized enterprises. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 11(1), 27-43. Chand, P., Patel, C. & Patel, A. (2010) “Interpretation and application of “new” and “complex” international financial reporting standards in Fiji: Implications for convergence of accounting standards”. Advances in Accounting, 26(2), 280–289. Chen, H., Tang, Q., Jiang Y. & Lin, Z. (2010). The role of international financial reporting standards in accounting quality: Evidence from the European Union. Journal of International Financial Management and Accounting 21(3), 56- 61. Choi, F. D., & Meek, G. K. (2011). International accounting. Pearson Higher Ed. Daly, S. & Frikha, M. (2015). Islamic Finance in Favor to Development and Economic Growth: An Illustration of the Principle of “Zakat”. Arabian Journal of Business Management Review, 5, 145. Cirkveni, T. (2011). Motifs and impediments for the harmonization of accounting regulations for small and medium-sized companies in the EU. Chinese Business Review, 10(11), 1021-1027. Choi, J. S., & Nam, J. A. (2020). Does managerial discretion affect the value relevance of goodwill impairment information under IFRS? Korean evidence. Asia-Pacific Journal of Accounting & Economics, 27(1), 1-23. DeFond, M., Hu, X., Hung, M., & Li, S. (2011). The impact of mandatory IFRS adoption on foreign mutual fund ownership: The role of comparability. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 51(3), 240-258. Dimitropoulos, E.P., Asteriou, D., Kousenidis, D & Leventis, S. (2013). The impact of IFRS on accounting quality: Evidence from Greece. Advances in Accounting, 29(1), 108-123. Gastón, S. C., García, C. F., Jarne, J. I. J., & Gadea, J. A. L. (2010). IFRS adoption in Spain and the United Kingdom: Effects on accounting numbers and relevance. Advances in Accounting, 26(2), 304-313. Girbina, M., Mihaela, M.I.N.U., Bunea, S., & Sacarin, M. (2012). Perceptions of preparers from Romanian banks regarding IFRS application. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 11(2), 191-208. Hail, L., Leuz, C. & Wysocki, P. (2010). Global accounting convergence and the potential adoption of IFRS by the U.S. (Part I): Conceptual underpinnings and economics analysis. Accounting Horizons, 24, 355–394. Herath, S. K., & Alsulmi, F. H. (2017). International financial reporting standards (IFRS): The benefits, obstacles, and opportunities for implementation in Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Social Science and Business, 2(1), 1-18. Joanne, H., George, S., & Ioanna, S. (2016), Does mandatory IFRS adoption improve the information environment? https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1911-3846.2012.01159 John, O. O. (2018). Adoption of IFRS in Nigeria: Challenges and the way forward. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(8), 426 – 440. Joshi, M., Yapa, P. W. S., & Kraal, D. (2016). IFRS adoption in ASEAN countries: perceptions of professional accountants from Singapore, Malaysia and Indonesia. Malaysia and Indonesia (January 4, 2016), 211-240. Jones, S. & Finley, A. (2011). Have IFRS made a difference to intra-country financial reporting diversity? British Accounting Review, 43(1), 22-38; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2010.10.004 Judge, W., Li, S., & Pinsker, R. (2010) National adoption of international accounting standards: An institutional perspective. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 18(3), 161-174, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8683.2010.00798. Kapoor, B., & Ruhela, J. (2013). IFRS Implementation–Issues and Challenges for India. International Journal of Business and Management Research, 3(2), 103-106. Kim, J. B., Tsui, J. S., & Cheong, H. Y. (2011). The voluntary adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards and loan contracting around the world. Review of Accounting Studies, 16(4), 779-811. Kiliçaa, M., Atamanc, B., & Uyar, A. (2014). Preparedness for and perception of IFRS. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 13(3), 492. KPMG Company Ltd. (2018), Report on the results of the Survey on the application of International Financial Reporting Standards in Vietnam, Appendix 02 Mihai, S., Ionaşcu, M., & Ionaşcu, I. (2012). Economic benefits of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) adoption N. T. Bui et al. /Accounting 6 (2020) 551 in Romania: Has the cost of equity capital decreased? African Journal of Business Management, 6(1), 200-205. Mohamed, Z. (2014). Challenges of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) adoption in Libya. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 4 (2), 390-412. Monisola, O. (2013). Challenges of adoption of international accounting reporting standards in Nigeria: A counsel to Professional Accountants. Journal of Management Policy, 3(5), 10-31. Mulyadi, M.S., Soepriyanto, G., & Anwar, Y. (2012). IFRS adoption and taxation issue. International Journal of Artsand Commerce, 1(7), 159-165. Nerudova, D., & Bohusova, H. (2008). The empirical study of the SMEs position in the process of IFRS for SME application in the Czech Republic. Economics & Management, 13, 163-169 Ocansey, E. O.N.D., & Enahoro, J. A. (2014). Comparative study of the international financial reporting standard implementation in Ghana and Nigeria. European Scientific Journal (May 2014 ed.), 10(13), 529-546. Odia, J.O., & Ogiedu, K.O. (2013). IFRS Adoption: Issues, Challenges and Lessons for Nigeria and other Adopters. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 4(3), 389-399, https://doi.org/10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n3p389. Oghogho, G., Raphael, I. A., & Kingsley, O. O. (2016). Challenges of the implementation of IFRS in less developed and developing countries. Igbinedion University Journal of Accounting, 1. Okpala, K. (2012). Adoption of IFRS and Financial Statements Effects: The Perceived Implications on FDI and Nigeria Economy. Australian Journal of Business and Management Research, 2 (5), [76-83], 83-83. Oluku, M. D., & Ojeka, S. (2011). The challenge of culture to international financial reporting standards convergence. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 2(12), 914-925 Owolabi, A., & Iyoha, F. O. (2012). Adopting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) in Africa: benefits, prospects and challenges. African Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Finance, 1(1), 77-86. Raoudha, T. (2016). Are IFRS Harder to Implement for Emerging Economies, Compared to Developed Countries? A Literature Review, Journal of Modern Accounting and Auditing Ritsumeikan, L. (2012). Culture and the globalization of the international financial reporting standards (IFRS) in developing countries. Journal of International Business Research, 11(S2), 31. Samaha, K., & Khlif, H. (2016). Adoption of and compliance with IFRS in developing countries: A synthesis of theories and directions for future research. Journal of Accounting in Emerging Economies, 6(1), 33-49. Shima, K. M., & Yang, D. C. (2012). Factors affecting the adoption of IFRS. International Journal of Business, 17(3), 276-298 Siaga, S.F (2012). Challenges to the adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards in Africa. International Journal of Research in Commerce and Management 3(1), 50-69. Siam, W. Z., & Rahahleh, M. Y. (2010). Implications of applying the international financial reporting standards (IFRSs) for small and medium-sized enterprises on the accounting environment in Jordan. Journal of Accounting, Business and Management (JABM), 17(2). Sun, J., Cahan, S. F., & Emanuel, D. (2011). How would the mandatory adoption of IFRS affect the earnings quality of US firms? Evidence from cross-listed firms in the US. Accounting Horizons, 25(4), 837-860. Trabelsi, R. (2016). Are IFRS Harder to Implement for Emerging Economies Compared to Developed Countries? A Literature Review. Journal of Modern Accounting and Auditing, 12(1), 1-16. Tu Oanh Le Thi, Ngoc Bui Thi, Tu Chuc Anh (2019), Benefits and Difficulties of Adopting IFRSS. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 10(9), 205-225 Tu Chuc Anh, Ngoc Bui Thi, Oanh Le Thi Tu (2019), Relationship between experts and enterprises viewed via the IFRS application: An empirical study in Vietnam. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 9(8), 946-963, Uyar, A. & Güngörmüş, A.H. (2013). Perceptions and knowledge of accounting professionals on IFRS for SMEs: evidence from Turkey. Research in Accounting Regulation, 25, 77-87. Vietnam, Ministry of Finance (2017), IFRSs documents training Winney, K., Marshall, D., Bender, B., & Swiger, J. (2010). Accounting globalization: roadblocks to IFRS adoption in the United States. Global Review of Accounting and Finance, 1(1), 167-178. Young, S., & Zeng, Y. (2015). Accounting comparability and the accuracy of peer-based valuation models. The Accounting Review, 90(6), 2571–2601. Zakari, M. A. (2014). Challenges of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Adoption in Libya. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 4(2), 390-412. Zéghal, D., Chtourou, S. & Sellami, Y.M. (2011). An analysis of the effect of mandatory adoption of IAS/IFRS on earnings management. Journal of International Accounting, Auditing and Taxation, 20(2), 61-72. 552 © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science, Canada. This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (
File đính kèm:
 roadmap_for_the_implementation_of_ifrs_in_vietnam_benefits_a.pdf
roadmap_for_the_implementation_of_ifrs_in_vietnam_benefits_a.pdf

