Results of Operation and Utilization of the Dalat Nuclear Research Reactor
The Dalat Nuclear Research Reactor (DNRR) with the nominal power of 500 kW was
reconstructed and upgraded from the USA 250-kW TRIGA Mark-II reactor built in early 1960s. The
renovated reactor was put into operation on 20th March 1984. It was designed for the purposes of
radioisotope production (RI), neutron activation analysis (NAA), basic and applied researches, and
nuclear education and training. During the last 30 years of operation, the DNRR was efficiently
utilized for producing many kinds of radioisotopes and radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine
centers and other users in industry, agriculture, hydrology and scientific research; developing a
combination of nuclear analysis techniques (INAA, RNAA, PGNAA) and physic-chemical methods
for quantitative analysis of about 70 elements and constituents in various samples; carrying out
experiments on the reactor horizontal beam tubes for nuclear data measurement, neutron radiography
and nuclear structure study; and establishing nuclear training and education programs for human
resource development. This paper presents the results of operation and utilization of the DNRR. In
addition, some main reactor renovation projects carried out during the last 10 years are also mentioned
in the paper.

Trang 1

Trang 2
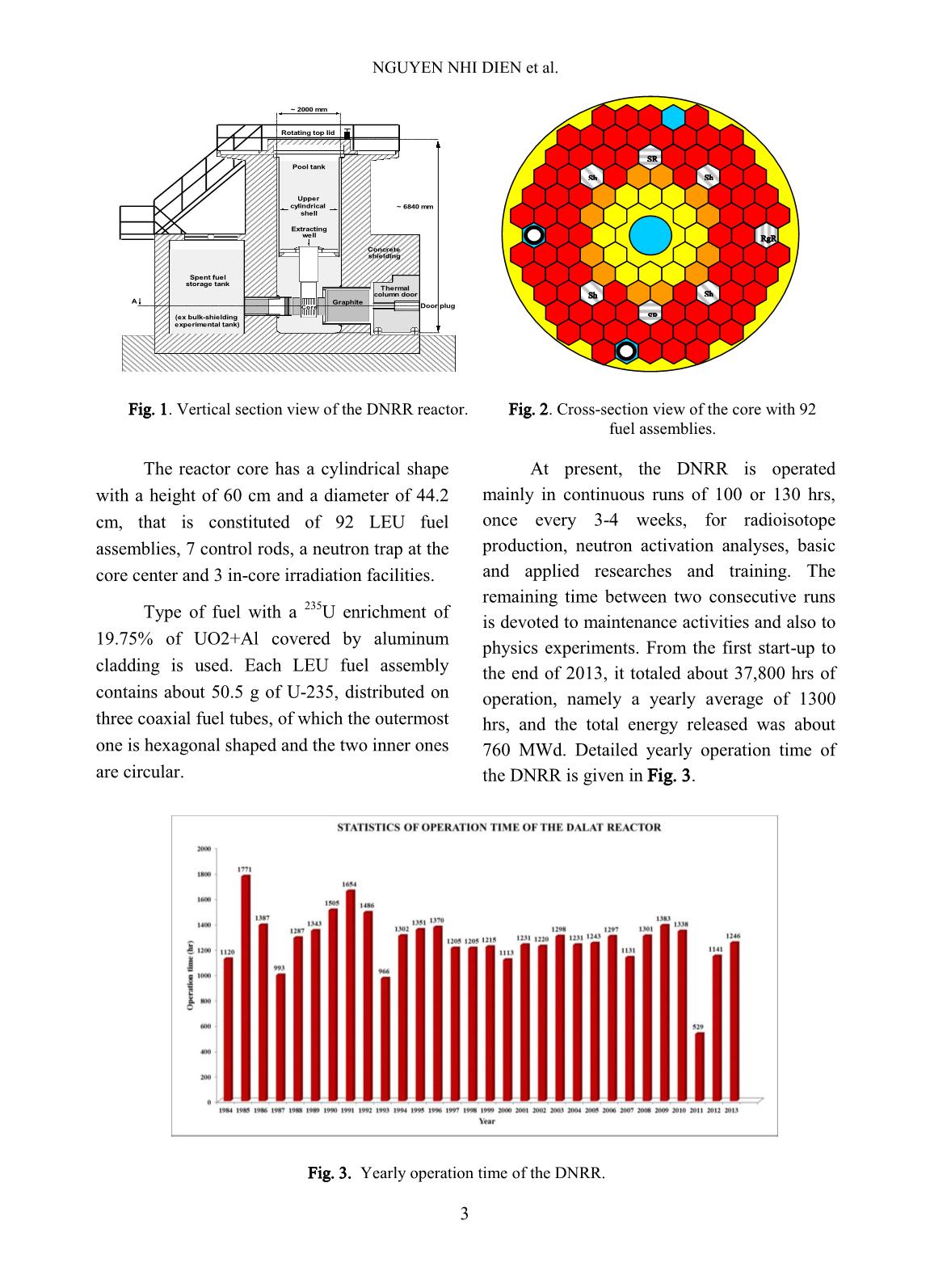
Trang 3
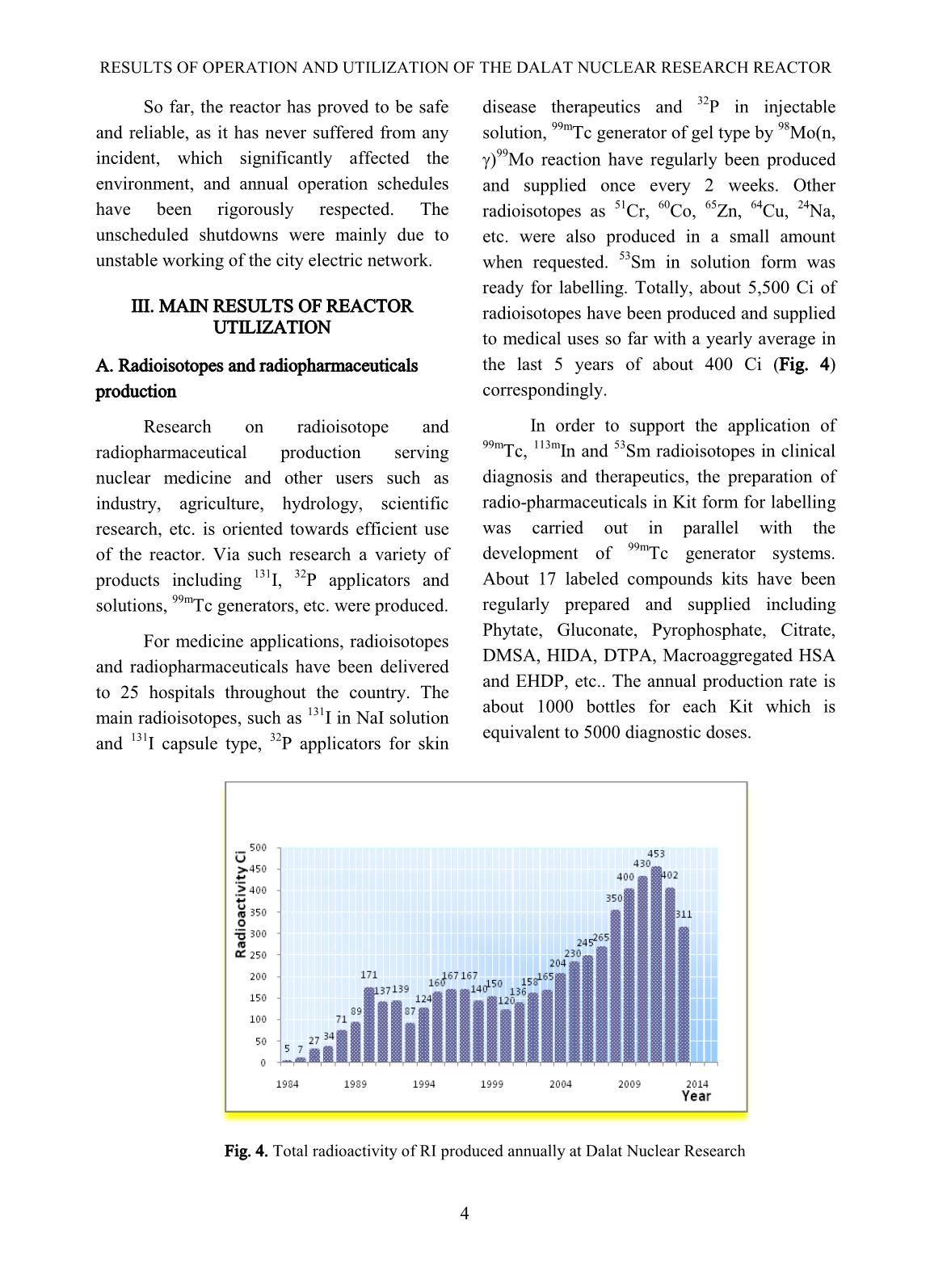
Trang 4

Trang 5
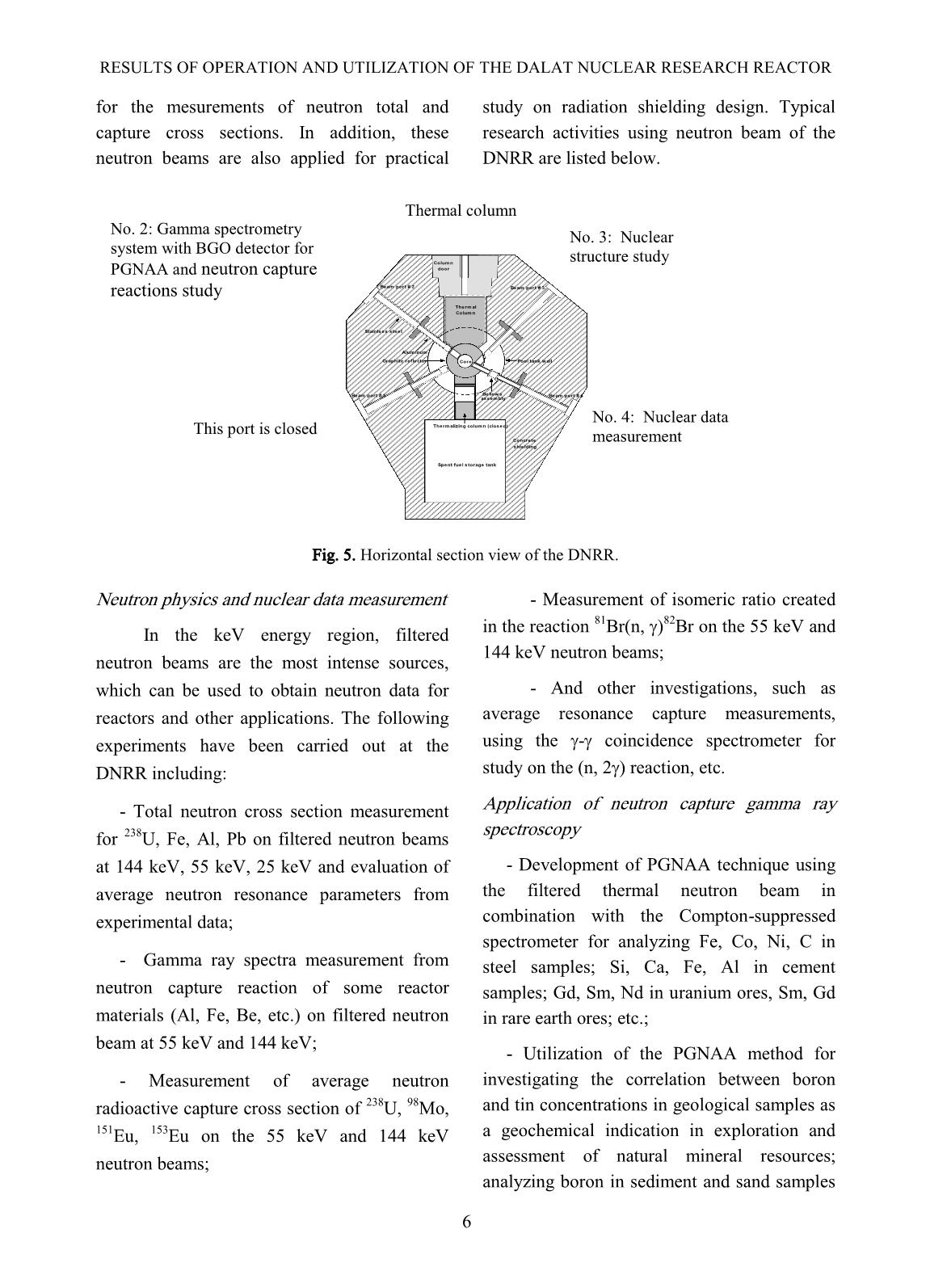
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Results of Operation and Utilization of the Dalat Nuclear Research Reactor

actor with a yearly average of 2000 samples. It can be estimated that those make up 60% of geological samples, 10% of biological samples, 20% of environmental samples, 5% of soil and agriculture materials, 3% of industrial materials. In order to determine the elements having short-lived radionuclides, the method of cyclic INAA with the alternation of irradiation and measurement was implemented by using the thermal column and vertical irradiation channel. An auto-pneumatic transfer system installed in 2012 at the DNRR can transfer a sample from irradiation position to measuring detector about 3 seconds. The k-zero method for INAA has been also developed to analyse airborne particulate samples for investigation of air pollution; crude oil samples and base rock samples for oil field study. Based on developed k-zero-INAA method, a multi-elements analysis procedures have been applied to simultaneously determine concentration for about 31 elements including Al, As, Ba, Br, Ca, Cl, Cr, Cu, Dy, Eu, Fe, Ga, Hf, Ho, K, La, Lu, Mg, Mn, Na, Sb, Sc, Sm, Sr, Th, Ti, V, Yb, Zn. C. Neutron beam utilization The reactor has four horizontal beam ports, which provide beams of neutron and gamma radiation for a variety of experiments. They also provide irradiation facilities for large specimens in a region close to the reactor core. Besides, the reactor also has a large thermal column with outside dimensions of 1.2m by 1.2m in cross section and 1.6m in length (Fig. 5). Up to now, only three beam ports (No.2, No.3 and No.4) and the thermal column have been used for reseaches and applications. At the beam port No.2, a BGO-HPGe gamma-rays Compton suppression spectrometer has been recently installed for PGNAA and experimental researches on neutron capture reactions. The filtered thermal neutron beams extracted from the tangential beam port No.3 are used for nuclear structure studies, especially for experimental determination of nuclear energy levels and level density in regions below neutron binding energy. The filtered neutron beams at the piercing beam port No.4 with quasi-monoenergies of 24keV, 54keV, 59keV, 133keV and 148keV are used RESULTS OF OPERATION AND UTILIZATION OF THE DALAT NUCLEAR RESEARCH REACTOR 6 for the mesurements of neutron total and capture cross sections. In addition, these neutron beams are also applied for practical study on radiation shielding design. Typical research activities using neutron beam of the DNRR are listed below. Beam port # 1 Beam port # 2 Beam port # 3 Beam port # 4 Core Therm alizing column (closed) Therm al Column Pool tank w all Spent fuel s torage tank Concrete shielding Graphite reflector door Column Bellow s assem bly Stainless steel Aluminum Fig. 5. Horizontal section view of the DNRR. Neutron physics and nuclear data measurement In the keV energy region, filtered neutron beams are the most intense sources, which can be used to obtain neutron data for reactors and other applications. The following experiments have been carried out at the DNRR including: - Total neutron cross section measurement for 238 U, Fe, Al, Pb on filtered neutron beams at 144 keV, 55 keV, 25 keV and evaluation of average neutron resonance parameters from experimental data; - Gamma ray spectra measurement from neutron capture reaction of some reactor materials (Al, Fe, Be, etc.) on filtered neutron beam at 55 keV and 144 keV; - Measurement of average neutron radioactive capture cross section of 238 U, 98 Mo, 151 Eu, 153 Eu on the 55 keV and 144 keV neutron beams; - Measurement of isomeric ratio created in the reaction 81 Br(n, )82Br on the 55 keV and 144 keV neutron beams; - And other investigations, such as average resonance capture measurements, using the - coincidence spectrometer for study on the (n, 2) reaction, etc. Application of neutron capture gamma ray spectroscopy - Development of PGNAA technique using the filtered thermal neutron beam in combination with the Compton-suppressed spectrometer for analyzing Fe, Co, Ni, C in steel samples; Si, Ca, Fe, Al in cement samples; Gd, Sm, Nd in uranium ores, Sm, Gd in rare earth ores; etc.; - Utilization of the PGNAA method for investigating the correlation between boron and tin concentrations in geological samples as a geochemical indication in exploration and assessment of natural mineral resources; analyzing boron in sediment and sand samples No. 2: Gamma spectrometry system with BGO detector for PGNAA and neutron capture reactions study This port is closed No. 3: Nuclear structure study No. 4: Nuclear data measurement Thermal column NGUYEN NHI DIEN et al. 7 to complement reference data for such samples from rivers; - Development of the spectrometer of summation of amplitudes of coinciding pulses for (n, 2) reaction research and for measuring activity of activated elements with high possibility of cascade transitions. D. Eduacation and training activities Training Center at Dalat Nuclear Research Institute which was established in 1999 is responsible for organizing training courses and training in reactor engineering, nuclear and radiation safety, application of nuclear techniques and radioisotopes in industry, agriculture, biology and environment, etc. Training courses on non-destructive evaluation (NDE) including radiographic testing, ultrasonic testing as well as on security of nuclear facilities and radiation sources have also been done. The center also is the training facility for expertise students from local universities and foreign postgraduate students. Thereby, the human resource development is conducted annually so that it can deal with scientific works of higher and higher quality and meet a huge demand in the field of nuclear science and technology in Vietnam in the future. Thanks to the bilateral co-operation with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, US Department of Energy, Bhabha Atomic Research Center of India, and Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, we have conducted a variety of training courses in the four following key areas: - Reactor engineering for nuclear power programme; - Research and development activities; - State management in the field; - And University lecturer training program. Besides, the DNRR has been used as a main tool for practical training, a set of equipment was supported under IAEA TC project, bilateral projects with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Bhabha Atomic Research Center of India. The measuring systems for practices at the Training Center can meet the fast increasing demand and is expected to move forward to the regional standard in the field of nuclear training. E. Other applications Research on sediment using radiotracer techniques was carried out to investigate bed load layers displacement at estuaries navigation channel region and to explain the sediment deposition phenomenon causing frequent dredging activities. Research on radio-biology consists of using gamma radiation associated with other factors for improving agricultural seeds and applying radioactive tracers for studying biological metabolism, especially nutrition problems. These studies are to investigate phosphorus absorption and other nutritional problems during the growing processes of rice and other plants. Irradiation effects on some plants to gain higher yield or environment adapted varieties were also studied. Gemstone colorizing experiments of topaz and sapphire in the reactor core, in the rotary rack as well as in horizontal channels has been done. As research purpose, silicon mono- crystals have been irradiated at the central neutron trap of the reactor. Irradiated products of good quality, appropriate for fabrication of power diodes and thyristors have been created thanks to proper neutron distribution in this irradiation facility and suitable cadmium ratio. RESULTS OF OPERATION AND UTILIZATION OF THE DALAT NUCLEAR RESEARCH REACTOR 8 IV. SOME MAIN REACTOR RENOVATION PROJECTS PERFORMED A. Reactor conversion from HEU to LEU fuels In the framework of the program on Russian Research Reactor Fuel Return (RRRFR) and the program on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactor (RERTR), the DNRR core was partly converted from HEU to LEU in September 2007. After this success, the full core conversion study from HEU to LEU of the DNRR was also carried out during years 2008 - 2010. The results of neutronics, thermal hydraulics and safety analysis showed that a LEU core loaded with 92 fuel assemblies and 12 beryllium rods around the neutron trap satisfies the safety requirements while maintaining the utilization possibility similar to that of the previous HEU and recent mixed fuel cores. Physics and energy start-up of the DNRR for full core conversion to low enriched uranium (LEU) fuel were performed from November 24 th , 2011 until January 13 th , 2012 according to a planned program that was approved by Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VINATOM). At 15:35 on November, 30 th , 2011 the reactor reached criticality with core configuration including 72 LEU FAs and neutron trap in center. Then the fuel loading for working core and power ascension test were also carried out from December, 6 th , 2011 to January, 13 th , 2012. Experimental results of physical and thermal hydraulics parameters of the reactor during start up stages and long operation cycles at nominal power showed very good agreement with calculated results and met the safety requirements. B. Reactor control and instrumentation system modification The Control and Instrumentation System (C&I) of the DNRR was designed and manufactured by the former Soviet Union and put into operation in November 1983. Due to the spare part procurement problem was suspected and using technology of the 1970’s with discrete and low-level integrated electronic components, the system technology was somewhat obsolete and un-adapted to tropical climate. The first renovation work was implemented during 1992-1993 period and the renovated C&I system was commissioned at the end of 1993. The most important renovation task was to redesign and construct a number of electronic systems/blocks, which play the key role in enhancing the reliability of the system. This renovation work was focused mainly on the process and instrumentation system, but not on the neutron measurement and data processing parts. Because of that, it was necessary to fulfill the second renovation and modernization during the years of 2005- 2007 to replace neutron measurement and signal processing parts of the existing C&I system by the digital system named ASUZ- 14R. The main items replaced under the second modification are neutron detector channels; neutron flux control system (NFCS), reactor protection system, control console and control panels, reactor protocol and diagnostic system, etc. The commissioning of the new I&C system was finished in August 2007 and operating license was approved in October 2007. NGUYEN NHI DIEN et al. 9 V. CONCLUSIONS The DNRR has been safely operated and effectively utilized for 30 years. To achieve that, maintaining and upgrading the reactor technological facilities have been done with a high quality. The reactor physics and thermal hydraulics studies have also provided the important bases for safety evaluation and in- core fuel management to ensure its safe operation and effective exploitation. The safety and security for the reactor are one of the main issues that national and local authorities are particularly interested in and strongly support up. During 30 years of operation, the DNRR has been playing an important role in the use of atomic energy for peaceful purpose in Vietnam. The reactor has been used for radioisotope production for medicine and industry purposes, NAA of geological, crude oil and environment samples, performance of fundamental and applied researches on nuclear and reactor physics, as well as creation of a large amount of human resource with high skills and experiences on application of nuclear techniques in the country. A strategic plan and long-term working plan for the DNRR has been set up in order to continue its safe operation and effective utilization at least to 2025. It should be mentioned that a project for establishment of a new nuclear science and technology center with a high power research reactor expected to put into operation between 2020-2022 is now under preparation and consideration. Therefore, the DNRR will be necessary and keep playing an important role in scientific research, applications and human resource development for Vietnam in the coming time. REFERENCES [1] Nguyen Nhi Dien, Dalat Nuclear Research Reactor - Twenty five years of safe operation and efficient exploitation, Dalat, (March 2009). [2] Duong Van Dong, Status of Radioisotope Production and Application in Vietnam, Dalat Sym. RR-PI-09, Dalat, (2009). [3] V. V. Le, T. N. Huynh, B. V. Luong, V. L. Pham, J. R. Liaw, J. Matos, Comparative Analyses for Loading LEU Instead of HEU Fuel Assemblies in the DNRR, RERTR Int’l Meeting, Boston, (2005). [4] P.V. Lam, N.N. Dien, T.D. Hai, L.B. Vien, L.V. Vinh, H.T. Nghiem, N.M. Tuan and N.K. Cuong, Results of the reactor control system replacement and reactor core conversion at the Dalat nuclear research reactor, The 12th Annual Topical Meeting on Research Reactor Fuel Management, Hamburg, Germany, (2008). [5] P.V. Lam, N.N. Dien, L.V. Vinh, H.T. Nghiem, L.B. Vien and N.K. Cuong, Neutronics and thermal hydraulics calculation for full core conversion from HEU to LEU fuel of the Dalat nuclear research reactor, RERTR Int’l Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, (2010). [6] L.B. Vien, L.V. Vinh, H.T. Nghiem and N.K. Cuong, Transient/ accident analyses for full core conversion from HEU to LEU fuel of the Dalat nuclear research reactor, RERTR Int’l Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, (2010). [7] C.D. Vu, Study on application of k0-IAEA at Dalat research reactor, Project report (code CS/09/01-01), (2010). [8] N.N. Dien, L.B. Vien, P.V. Lam, L.V. Vinh, H.T. Nghiem, N.K. Cuong, N.M. Tuan, N.M. Hung, P.Q. Huy, T. Q. Duong, V.D.H. Dang, T.C. Su, T.T. Vien, Some main results of commissioning of the Dalat Nuclear Research Reactor with low enriched fuel, Nuclear Research Institute, (2012). [9] Safety Analysis Report (SAR) for the Dalat Research Reactor, Dalat, (2012).
File đính kèm:
 results_of_operation_and_utilization_of_the_dalat_nuclear_re.pdf
results_of_operation_and_utilization_of_the_dalat_nuclear_re.pdf

