Phân tích xác suất dừng hệ thống chuyển tiếp hai chiều sử dụng công nghệ thu thập năng lượng từ nguồn phát
Trong những năm gần đây, công nghệ thu thập
năng lượng là một hướng nghiên cứu sôi động và
được các nhóm nghiên cứu trên thế giới quan tâm
[1-3] như là một phần của công nghệ truyền thông
xanh [4-7]. Bên cạnh thu thập năng lượng từ nguồn
tự nhiên ví dụ như gió, thủy triều, ánh sáng mặt
trời, thu thập năng lượng từ sóng vô tuyến có
nhiều ưu điểm như tính ổn định, chủ động, và dễ
dàng áp dụng cho các mạng thông tin vô tuyến [8-
10]. Công nghệ thu thập năng lượng vô tuyến cho
phép các nút mạng thu năng lượng bên cạnh thông
tin từ tín hiệu vô tuyến để chuyển đổi thành năng
lượng phục vụ cho các hoạt động truyền phát của
mạng [11, 12]. Công nghệ này này cho phép kéo
dài thời gian hoạt động của các nút mạng vô tuyến
ngay cả khi nút mạng không được cấp nguồn tại
chỗ, đặc biệt hữu dụng cho các mạng cảm biến
không dây. Hiện này, có hai kiến trúc trúc cơ bản
trong thu thập năng lượng vô tuyến, đó là (i) thu
thập năng lượng phân chia theo thời gian và (ii)
thu thập năng lượng phân chia theo công suất [12].
Cho đến nay, có rất nhiều nghiên cứu nhằm cải
thiện hiệu năng và vùng phủ sóng của mạng thu
thập năng lượng, ví dụ như: [13] đề xuất phương
pháp phân tích hiệu năng của mạng chuyển tiếp
thu thập năng lượng, [14] đề xuất phương pháp
phân tích hiệu năng dựa trên chuỗi Taylor cho
mạng chuyển tiếp có lựa chọn nút chuyển tiếp,
[15] đề xuất phương pháp phân tích hiệu năng mới
cho mạng Multi-Input Multi-Output chuyển tiếp
thu thập năng lượng thu thập năng lượng, [16]
khảo sát ảnh hưởng của kênh truyền không hoàn
hảo trong lựa chọn nút chuyển tiếp của mạng
chuyển tiếp thu thập năng lượng, [17, 18] áp dụng
kỹ thuật distributed switch-and-stay cho mang
chuyển tiếp thu thu thập năng lượng, [19] tận dụng
kênh truyền trực tiếp cho hệ thống chuyển tiếp đa
người dùng sử dụng kỹ thuật SWIPT
(Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power
Transfer), [20] khảo sát hiệu năng của mạng
chuyển tiếp đa chặng theo cụm với kỹ thuật thu
thập năng lượng, [21] khảo sát thông lượng của
mạng thu thập năng lượng có nguồn phát.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
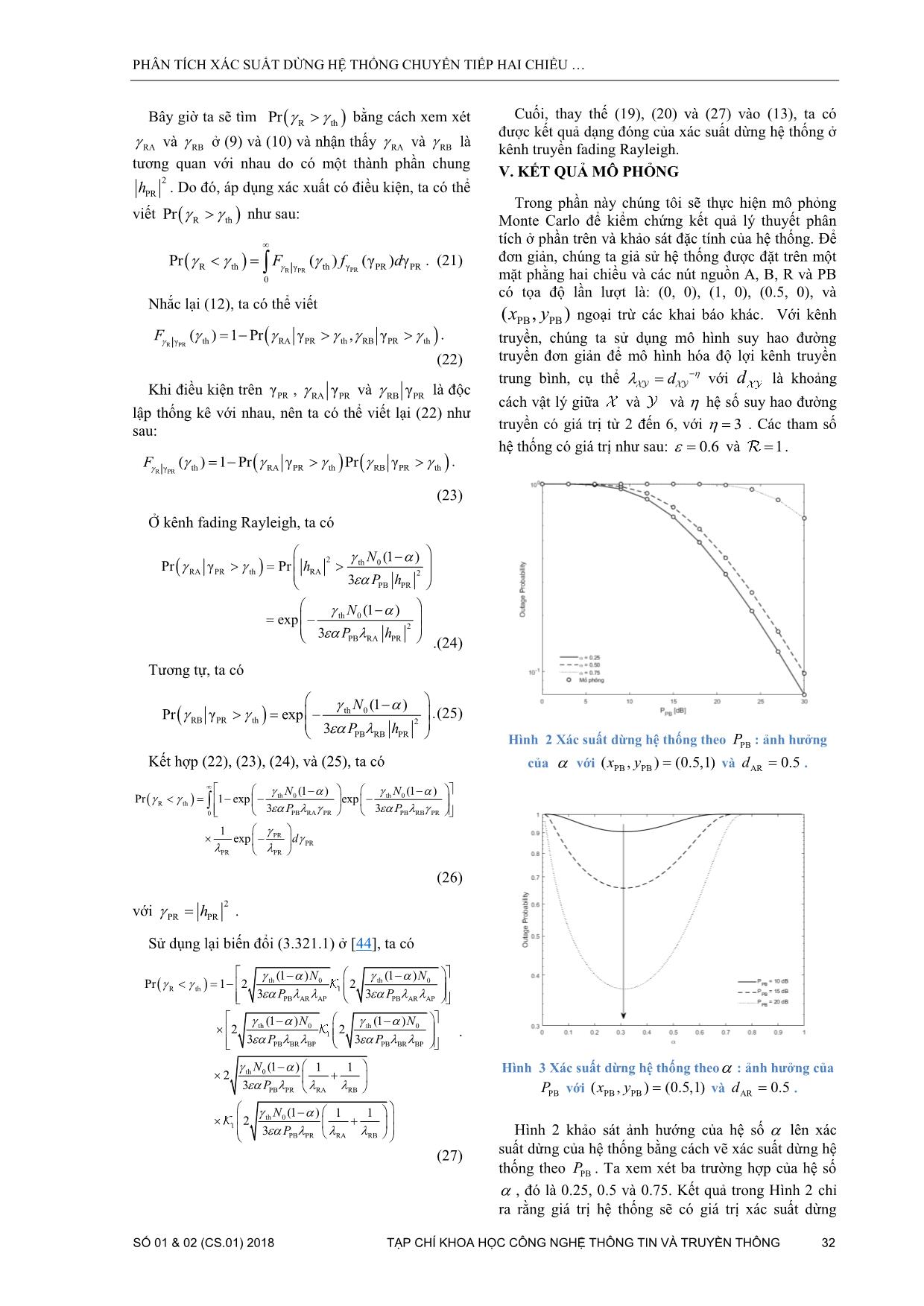
Trang 4
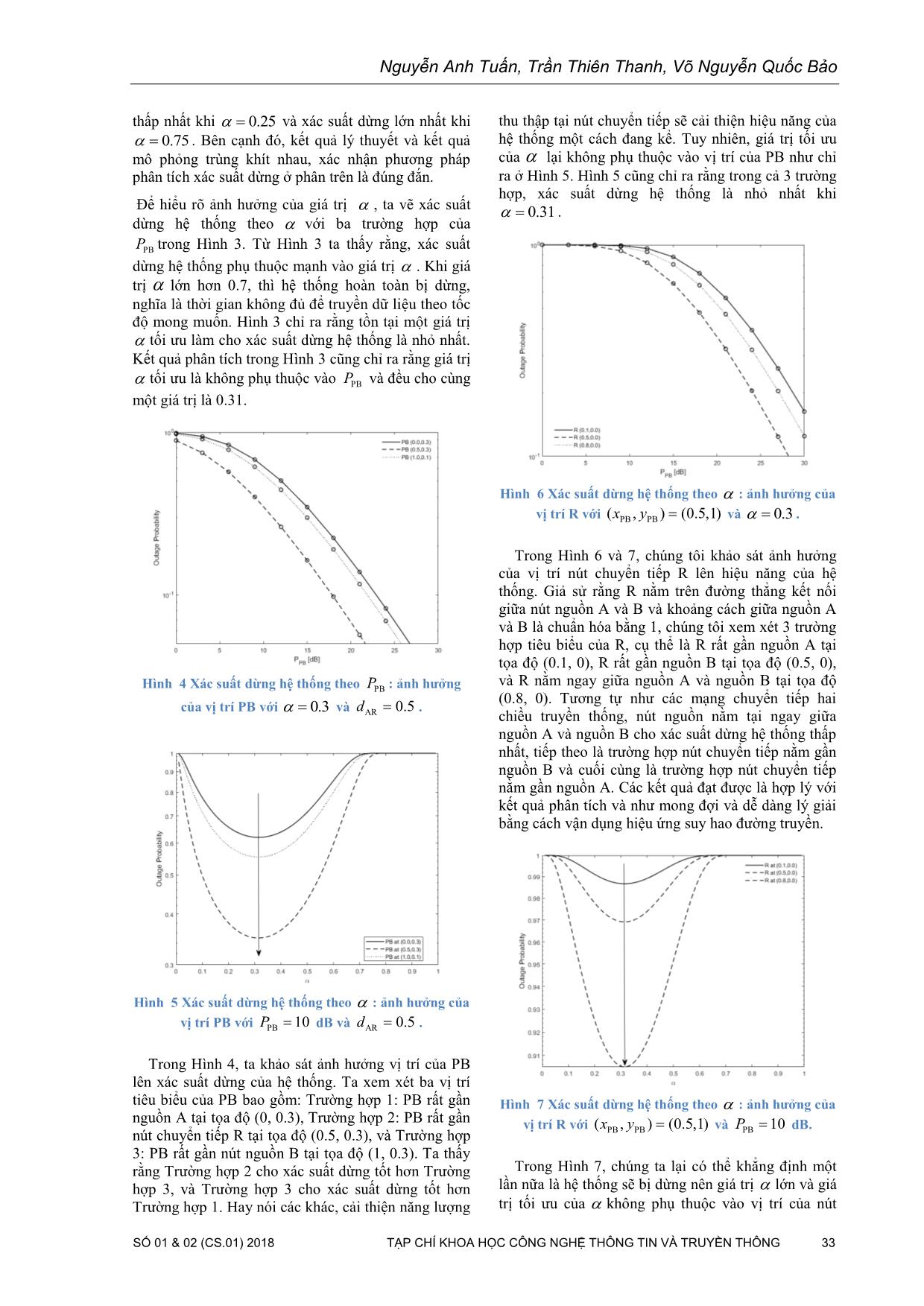
Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Phân tích xác suất dừng hệ thống chuyển tiếp hai chiều sử dụng công nghệ thu thập năng lượng từ nguồn phát

tiếp
nằm gần nguồn A. Các kết quả đạt được là hợp lý với
kết quả phân tích và như mong đợi và dễ dàng lý giải
bằng cách vận dụng hiệu ứng suy hao đường truyền.
Hình 7 Xác suất dừng hệ thống theo : ảnh hưởng của
vị trí R với PB PB( , ) (0.5,1)x y và PB 10P dB.
Trong Hình 7, chúng ta lại có thể khẳng định một
lần nữa là hệ thống sẽ bị dừng nên giá trị lớn và giá
trị tối ưu của không phụ thuộc vào vị trí của nút
SỐ 01 & 02 (CS.01) 2018 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC CÔNG NGHỆ THÔNG TIN VÀ TRUYỀN THÔNG 33
PHÂN TÍCH XÁC SUẤT DỪNG HỆ THỐNG CHUYỂN TIẾP HAI CHIỀU
chuyển tiếp trong cả ba trường hợp mà chúng ta khảo
sát. Trong phạm vi bài báo này, chúng tôi chưa tìm
dạng đóng của giá trị tối ưu, tuy nhiên các kết quả
đạt được trong bài báo này sẽ là một trong những sở
cứ quan trọng để chúng tôi tìm tòi và phân tích giá trị
tối ưu
V. KẾT LUẬN
Trong bài báo này, chúng tôi đề xuất mô hình
chuyển tiếp hai chiều giải mã và chuyển tiếp với một
nút cung cấp năng lượng. Chúng tôi đã phân tích xác
suất dừng hệ thống ở kênh truyền fading Rayleigh và
sử dụng mô phỏng Monte Carlo để kiểm chứng tính
chính xác của phương pháp phân tích đề xuất. Các kết
quả mô phỏng đã chỉ ra rằng giá trị tối ưu không
phụ thuộc vào vị trí của PB và R và hiệu năng của hệ
thống sẽ cải thiện tốt nhất nếu PB được đặt gần nút
chuyển tiếp.
LỜI CẢM ƠN
Nghiên cứu này được tài trợ bởi Quỹ Phát triển khoa
học và công nghệ Quốc gia (NAFOSTED) trong đề
tài mã số 102.04-2014.32
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
[1] A. A. Nasir, Z. Xiangyun, S. Durrani, and R.
A. Kennedy, "Relaying Protocols for
Wireless Energy Harvesting and Information
Processing," Wireless Communications,
IEEE Transactions on, vol. 12, no. 7, pp.
3622-3636, 2013.
[2] N. Zlatanov, R. Schober, and Z. Hadzi-
Velkov, "Asymptotically Optimal Power
Allocation for Energy Harvesting
Communication Networks," IEEE
Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol.
PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1, 2017.
[3] V. D. Nguyen, T. Q. Duong, H. D. Tuan, O.
S. Shin, and H. V. Poor, "Spectral and
Energy Efficiencies in Full-Duplex Wireless
Information and Power Transfer," IEEE
Transactions on Communications, vol. PP,
no. 99, pp. 1-1, 2017.
[4] X. Huang, T. Han, and N. Ansari, "On Green
Energy Powered Cognitive Radio
Networks," Communications Surveys &
Tutorials, IEEE, vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1,
2015.
[5] M. Yuyi, L. Yaming, Z. Jun, and K. B.
Letaief, "Energy harvesting small cell
networks: feasibility, deployment, and
operation," Communications Magazine,
IEEE, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 94-101, 2015.
[6] S. A. Raza Zaidi, A. Afzal, M. Hafeez, M.
Ghogho, D. C. McLernon, and A. Swami,
"Solar energy empowered 5G cognitive
metro-cellular networks," Communications
Magazine, IEEE, vol. 53, no. 7, pp. 70-77,
2015.
[7] Y. Zou, J. Zhu, and R. Zhang, "Exploiting
Network Cooperation in Green Wireless
Communication," Communications, IEEE
Transactions on, vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-12,
2013.
[8] Z. Ding et al., "Application of smart antenna
technologies in simultaneous wireless
information and power transfer,"
Communications Magazine, IEEE, vol. 53,
no. 4, pp. 86-93, 2015.
[9] I. Krikidis, S. Timotheou, S. Nikolaou, Z.
Gan, D. W. K. Ng, and R. Schober,
"Simultaneous wireless information and
power transfer in modern communication
systems," Communications Magazine, IEEE,
vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 104-110, 2014.
[10] L. Xiao, P. Wang, D. Niyato, D. Kim, and Z.
Han, "Wireless Networks with RF Energy
Harvesting: A Contemporary Survey," IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol.
PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1, 2015.
[11] L. Liu, R. Zhang, and K. C. Chua, "Wireless
Information and Power Transfer: A Dynamic
Power Splitting Approach," IEEE
Transactions on Communications, vol. 61,
no. 9, pp. 3990-4001, 2013.
[12] X. Zhou, R. Zhang, and C. K. Ho, "Wireless
Information and Power Transfer:
Architecture Design and Rate-Energy
Tradeoff," Communications, IEEE
Transactions on, vol. 61, no. 11, pp. 4754-
4767, 2013.
[13] A. A. Nasir, Z. Xiangyun, S. Durrani, and R.
A. Kennedy, "Relaying Protocols for
Wireless Energy Harvesting and Information
Processing," IEEE Transactions on Wireless
Communications, vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 3622-
3636, 2013.
[14] N. Do, V. Bao, and B. An, "Outage
Performance Analysis of Relay Selection
Schemes in Wireless Energy Harvesting
Cooperative Networks over Non-Identical
Rayleigh Fading Channels," Sensors, vol. 16,
no. 3, p. 295, 2016.
[15] N. A. Tuan, V. N. Q. Bao, and L. Q. Cường,
"A New Derivation Approach for
Simultaneous Wireless Information and
Power Transfer for MIMO Dual-Hop Relay
Networks," Journal of Science and
Technology on Information and
Communications, no. 1, pp. 50-56%V 1,
2017-09-19 2017.
[16] V. N. Q. Bao and N. A. Tuấn, "Effect of
imperfect CSI on wirelessly powered
transfer incremental relaying networks,"
Journal of Science and Technology on
Information and Communications, no. 3-4,
pp. 48-57%V 1, 2017-04-11 2017.
[17] Q. N. Le, N. T. Do, V. N. Q. Bao, and B. An,
"Full-duplex distributed switch-and-stay
networks with wireless energy harvesting:
design and outage analysis," EURASIP
SỐ 01 & 02 (CS.01) 2018 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC CÔNG NGHỆ THÔNG TIN VÀ TRUYỀN THÔNG 34
Nguyễn Anh Tuấn, Trần Thiên Thanh, Võ Nguyễn Quốc Bảo
Journal on Wireless Communications and
Networking, journal article vol. 2016, no. 1,
p. 285, December 15 2016.
[18] Q. N. Le, V. N. Q. Bao, and B. An, "Full-
duplex distributed switch-and-stay energy
harvesting selection relaying networks with
imperfect CSI: Design and outage analysis,"
Journal of Communications and Networks,
vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 29-46, 2018.
[19] N. T. Do, D. B. da Costa, T. Q. Duong, V. N.
Q. Bao, and B. An, "Exploiting Direct Links
in Multiuser Multirelay SWIPT Cooperative
Networks With Opportunistic Scheduling,"
IEEE Transactions on Wireless
Communications, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 5410-
5427, 2017.
[20] N. T. Van, T. N. Do, V. N. Q. Bao, and B.
An, "Performance Analysis of Wireless
Energy Harvesting Multihop Cluster-Based
Networks Over Nakagami- ${m}$ Fading
Channels," IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 3068-
3084, 2018.
[21] N. P. Le, "Throughput Analysis of Power-
Beacon-Assisted Energy Harvesting
Wireless Systems Over Non-Identical
Nakagami- <tex-math
notation="LaTeX">${m}$ </tex-
math> Fading Channels,"
IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 22, no.
4, pp. 840-843, 2018.
[22] C. R. Valenta and G. D. Durgin, "Harvesting
Wireless Power: Survey of Energy-Harvester
Conversion Efficiency in Far-Field, Wireless
Power Transfer Systems," Microwave
Magazine, IEEE, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 108-120,
2014.
[23] A. Costanzo and D. Masotti, "Smart
Solutions in Smart Spaces: Getting the Most
from Far-Field Wireless Power Transfer,"
IEEE Microwave Magazine, vol. 17, no. 5,
pp. 30-45, 2016.
[24] Y. Liu, Z. Ding, M. Elkashlan, and H. V.
Poor, "Cooperative non-orthogonal multiple
access with simultaneous wireless
information and power transfer," IEEE
Journal on Selected Areas in
Communications, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 938-953,
2016.
[25] B. Rankov and A. Wittneben, "Achievable
rate regions for the two-way relay channel,"
in Information Theory, 2006 IEEE
International Symposium on, 2006, pp. 1668-
1672: IEEE.
[26] P. Popovski and H. Yomo, "Physical
Network Coding in Two-Way Wireless
Relay Channels," in Communications, 2007.
ICC '07. IEEE International Conference on,
2007, pp. 707-712.
[27] H. V. Toan and V. N. Q. Bao, "Opportunistic
relaying for cognitive two-way network with
multiple primary receivers over Nakagami-m
fading," in 2016 International Conference on
Advanced Technologies for Communications
(ATC), 2016, pp. 141-146.
[28] H. V. Toan, V. N. Q. Bao, and K. N. Le,
"Performance analysis of cognitive underlay
two-way relay networks with interference
and imperfect channel state information,"
EURASIP Journal on Wireless
Communications and Networking, journal
article vol. 2018, no. 1, p. 53, March 06
2018.
[29] T. H. Van, B. Vo-Nguyen, and N.-L. Hung,
"Cognitive Two-Way Relay Systems with
Multiple Primary Receivers: Exact and
Asymptotic Outage Formulation," (in En),
IET Communications, 2017.
[30] F. Jameel, S. Wyne, and Z. Ding, "Secure
Communications in Three-step Two-way
Energy Harvesting DF Relaying," IEEE
Communications Letters, vol. PP, no. 99, pp.
1-1, 2017.
[31] Z. Zhang, Z. Ma, Z. Ding, M. Xiao, and G.
Karagiannidis, "Full-Duplex Two-Way and
One-Way Relaying: Average Rate, Outage
Probability and Tradeoffs," IEEE
Transactions on Wireless Communications,
vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1, 2016.
[32] Y. Gu, H. Chen, Y. Li, L. Song, and B.
Vucetic, "Short-Packet Two-Way Amplify-
and-Forward Relaying," IEEE Signal
Processing Letters, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 263-
267, 2018.
[33] J. Zhang, Q. Li, K. J. Kim, Y. Wang, X. Ge,
and J. Zhang, "On the Performance of Full-
Duplex Two-Way Relay Channels With
Spatial Modulation," IEEE Transactions on
Communications, vol. 64, no. 12, pp. 4966-
4982, 2016.
[34] D. K. Nguyen, M. Matthaiou, T. Q. Duong,
and H. Ochi, "RF energy harvesting two-way
cognitive DF relaying with transceiver
impairments," in IEEE International
Conference on Communication Workshop
(ICCW), 2015, no. Jun. , pp. 1970-1975.
[35] K. Tutuncuoglu, B. Varan, and A. Yener,
"Throughput Maximization for Two-Way
Relay Channels With Energy Harvesting
Nodes: The Impact of Relaying Strategies,"
Communications, IEEE Transactions on,
vol. 63, no. 6, pp. 2081-2093, 2015.
[36] W. Li, M. L. Ku, Y. Chen, K. J. R. Liu, and
S. Zhu, "Performance Analysis for Two-Way
Network-Coded Dual-Relay Networks with
Stochastic Energy Harvesting," IEEE
Transactions on Wireless Communications,
vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1, 2017.
[37] N. T. P. Van, S. F. Hasan, X. Gui, S.
Mukhopadhyay, and H. Tran, "Three-Step
Two-Way Decode and Forward Relay With
Energy Harvesting," IEEE Communications
Letters, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 857-860, 2017.
[38] R. Boris and W. Armin, "Spectral efficient
protocols for half-duplex fading relay
SỐ 01 & 02 (CS.01) 2018 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC CÔNG NGHỆ THÔNG TIN VÀ TRUYỀN THÔNG 35
PHÂN TÍCH XÁC SUẤT DỪNG HỆ THỐNG CHUYỂN TIẾP HAI CHIỀU
channels," Selected Areas in
Communications, IEEE Journal on, vol. 25,
no. 2, pp. 379-389, 2007.
[39] S. Atapattu, J. Yindi, J. Hai, and C.
Tellambura, "Relay Selection Schemes and
Performance Analysis Approximations for
Two-Way Networks," Communications,
IEEE Transactions on, vol. 61, no. 3, pp.
987-998, 2013.
[40] K. Hwang, M. Ju, and M. Alouini, "Outage
Performance of Opportunistic Two-Way
Amplify-and-Forward Relaying with
Outdated Channel State Information,"
Communications, IEEE Transactions on,
vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-10, 2013.
[41] I. Krikidis, Z. Gan, and B. Ottersten,
"Harvest-use cooperative networks with
half/full-duplex relaying," in Wireless
Communications and Networking
Conference (WCNC), 2013 IEEE, 2013, pp.
4256-4260.
[42] T. T. Thanh and V. N. Quoc Bao,
"Wirelessly Energy Harvesting DF Dual-hop
Relaying Networks: Optimal Time Splitting
Ratio and Performance Analysis," Journal of
Science and Technology: Issue on
Information and Communications
Technology, no. 2, pp. 16-20%V 3, 2017-12-
31 2017.
[43] B. Vo Nguyen Quoc and K. Hyung Yun,
"Error probability performance for multi-hop
decode-and-forward relaying over Rayleigh
fading channels," in Advanced
Communication Technology, 2009. ICACT
2009. 11th International Conference on,
2009, vol. 03, pp. 1512-1516.
[44] I. S. Gradshteyn, I. M. Ryzhik, A. Jeffrey,
and D. Zwillinger, Table of integrals, series
and products, 7th ed. Amsterdam ; Boston:
Elsevier, 2007, pp. xlv, 1171 p.
[45] M. Abramowitz, I. A. Stegun, and Knovel
(Firm). (1972). Handbook of mathematical
functions with formulas, graphs, and
mathematical tables (10th printing, with
corrections. ed.). Available:
ence/AMS55.ASP?Res=200&Page=-1
EXACT CLOSED-FORM EXPRESSION
OUTAGE PROBABILITY OF DECODE-AND-
FORWARD TWO-WAY RELAYING SYSTEM
WITH POWER-BEACON-ASSISTED ENERGY
HARVESTING
Abstract: This paper investigates two-way decode-
and-forward relay networks with power beacon
assisted energy harvesting. All nodes are assumed to
have limited power supply and harevest energy from
RF signals to support operation. We propose a new
derivation approach to obtain the exact close form of
system outage probability over Rayleigh fading
channels. Monte Carlo simulations are used to verify
the corerectness of the analysis results and pointing
out that the positions of power beacon and relay have
significant effecton on the system performance.
Keywords- relaying, two-way relaying, fading
Rayleigh, energy harvesting, power beacon.
Nguyễn Anh Tuấn nhận
bằng kỹ sư và bằng thạc sĩ tại
Trường Đại Học Bách Khoa
Hà Nội năm 2002 và năm
2006. ThS. Tuấn hiện đang
công tác tại Cục Tần Số Vô
Tuyến Điện – Bộ Thông tin
và Truyền thông và là nghiên
cứu sinh của Học Viện Công
Nghệ Bưu Chính Viễn
Thông. Hướng nghiên cứu
hiện tại đang quan tâm bao
gồm: thông tin vô tuyến, quy hoạch tần số, kỹ thuật
thu thập năng lượng vô tuyến, phân tích hiệu năng
mạng vô tuyến.
Trần Thiên Thanh hiện đang là
giảng viên thuộc Khoa Công
nghệ Thông tin, trường Đại học
Giao thông Vận tải HCM, nhận
bằng Tiến sĩ vào năm 2016 tại
Trường Đại học Bách Khoa
HCM. Hướng nghiên cứu tập
trung vào các kỹ thuật tiên tiến
cho mạng 5G bao gồm NOMA, thu thập năng lượng
vô tuyến, bảo mật lớp vật lý.
Võ Nguyễn Quốc Bảo tốt
nghiệp Tiến sĩ chuyên
ngành vô tuyến tại Đại học
Ulsan, Hàn Quốc vào năm
2010. Hiện nay, TS. Bảo là
phó giáo sư của Bộ Môn Vô
Tuyến, Khoa Viễn Thông 2,
Học Viện Công Nghệ Bưu
Chính Viễn Thông Cơ Sở
Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh và
đồng thời là giám đốc của phòng thí nghiệm nghiên
cứu vô tuyến(WCOMM). TS. Bảo hiện là thành viên
chủ chốt (senior member) của IEEE và là tổng biên
tập kỹ thuật của tạp chí REV Journal on Electronics
and Communication. TS. Bảo đồng thời là biên tập
viên (editor) của nhiều tạp chí khoa học chuyên ngành
uy tín trong và ngoài nước, ví dụ: Transactions on
Emerging Telecommunications Technologies (Wiley
ETT), VNU Journal of Computer Science and
Communication Engineering. TS. Bảo đã tham gia tổ
chức nhiều hội nghị quốc gia và quốc tế, ví dụ: ATC
(2013, 2014), NAFOSTED-NICS (2014, 2015, 2016),
REV-ECIT 2015, ComManTel (2014, 2015), và
SigComTel 2017. Hướng nghiên cứu hiện tại đang
quan tâm bao gồm: vô tuyến nhận thức, truyền thông
hợp tác, truyền song công, bảo mật lớp vật lý và thu
thập năng lượng vô tuyến.
SỐ 01 & 02 (CS.01) 2018 TẠP CHÍ KHOA HỌC CÔNG NGHỆ THÔNG TIN VÀ TRUYỀN THÔNG 36
File đính kèm:
 phan_tich_xac_suat_dung_he_thong_chuyen_tiep_hai_chieu_su_du.pdf
phan_tich_xac_suat_dung_he_thong_chuyen_tiep_hai_chieu_su_du.pdf

