Marketing competitiveness of home appliance supermarkets in Ha Noi
Supermarkets - a type of modern shops which either sell general goods or specializes in some kinds;
have a wide variety of products with high quality guarantee; meet criteria on business areas, technical equipment, management and business organization; have good and convenient serving modes to satisfy
customer shopping demand - have become a common trend in Vietnam's retail sector in recent time. Especially
with the trend of modern technology development, electronics supermarkets have become a fast-growing retail
business in big cities. The combination between specialized retailing and self-servicesof supermarkets has
brought electronics supermarkets many marketing competitive advantages. However in recent time, electronics supermarkets have revealed some limitations in their competitiveness in general and marketing competitiveness in particular such as they have not yet positioned the supply value of market offering, the efficiency
of integrating mix retailing and marketing tools remains low, core marketing competencies have not been
established and raised, the identities of supermarket-like distribution services are inadequate in terms of customers-based value and quality

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8

Trang 9
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Marketing competitiveness of home appliance supermarkets in Ha Noi

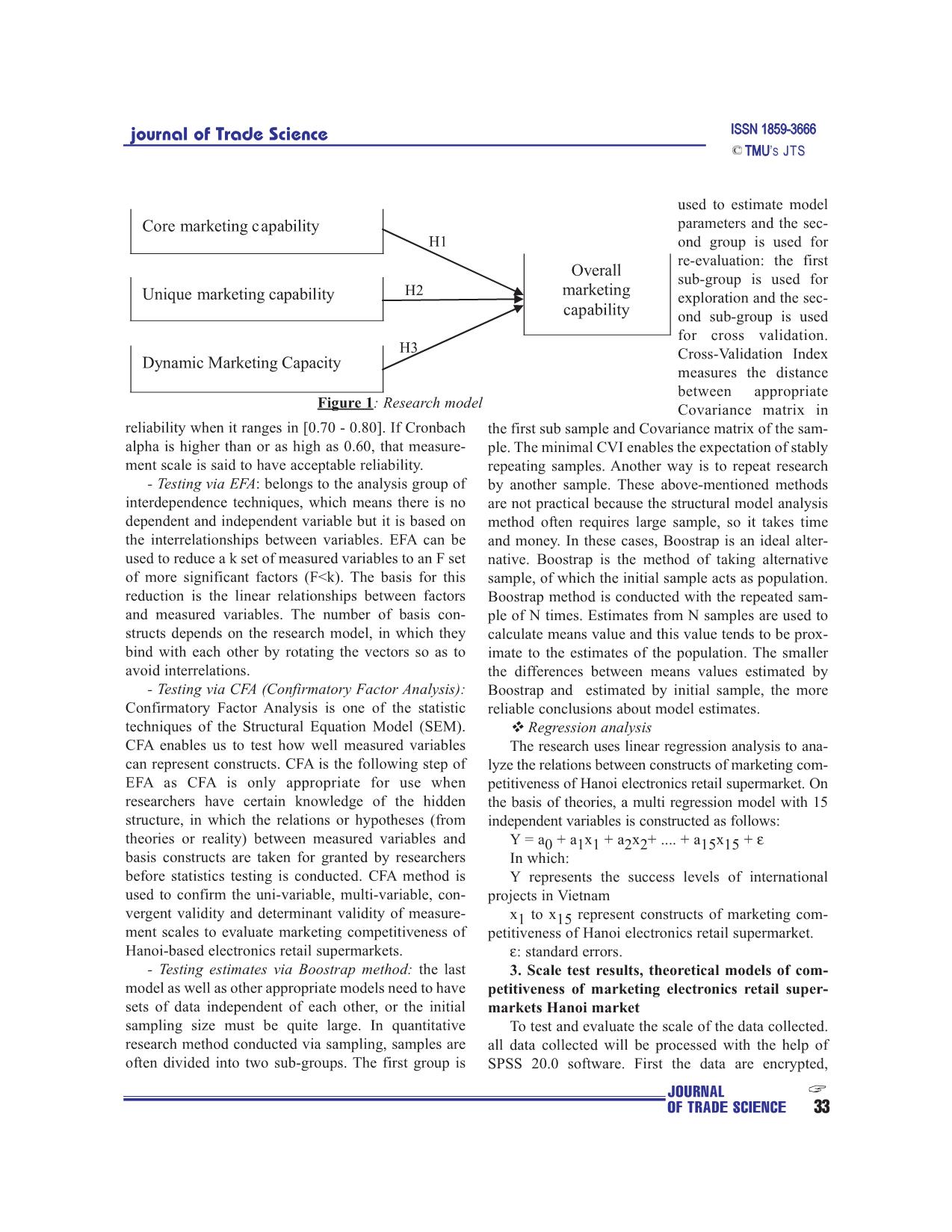
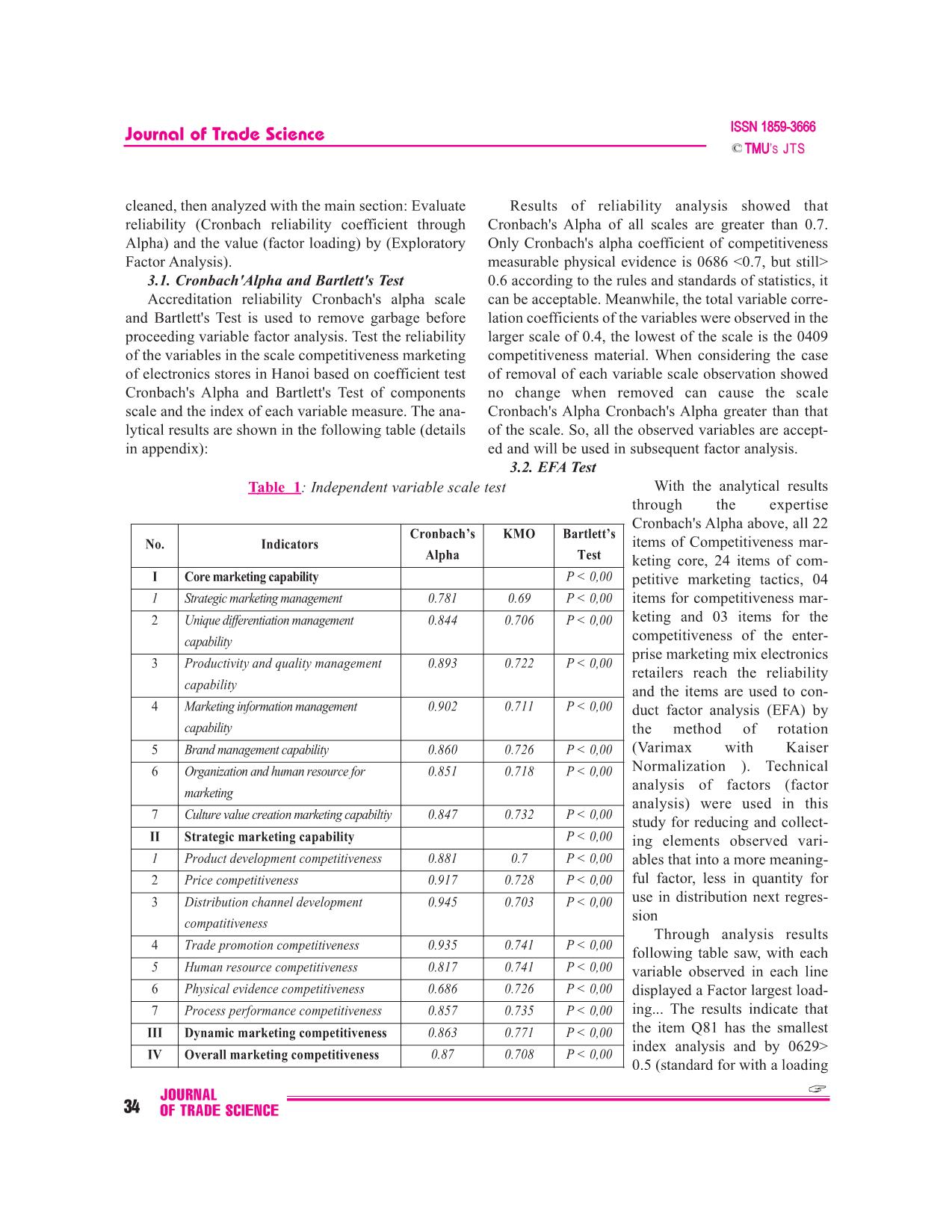
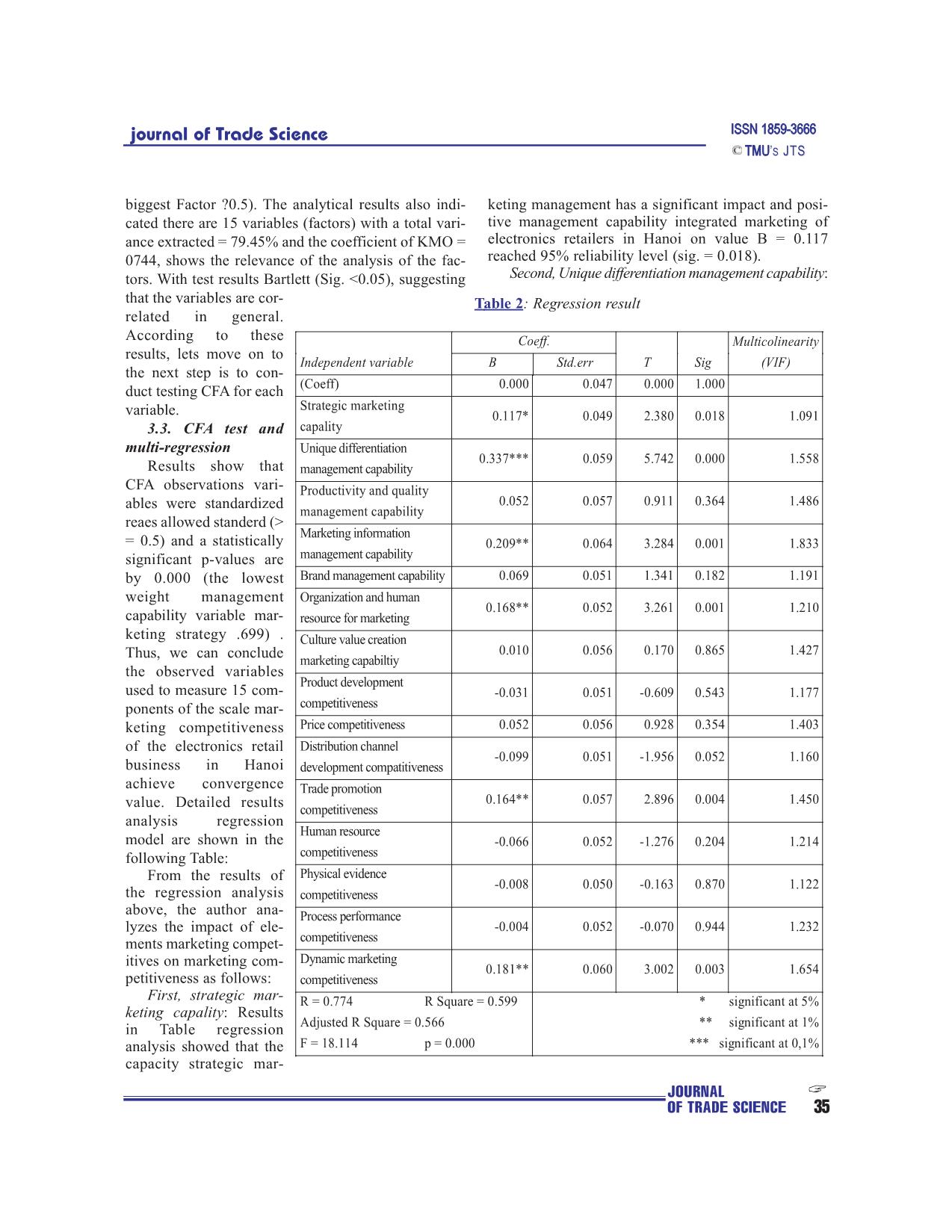
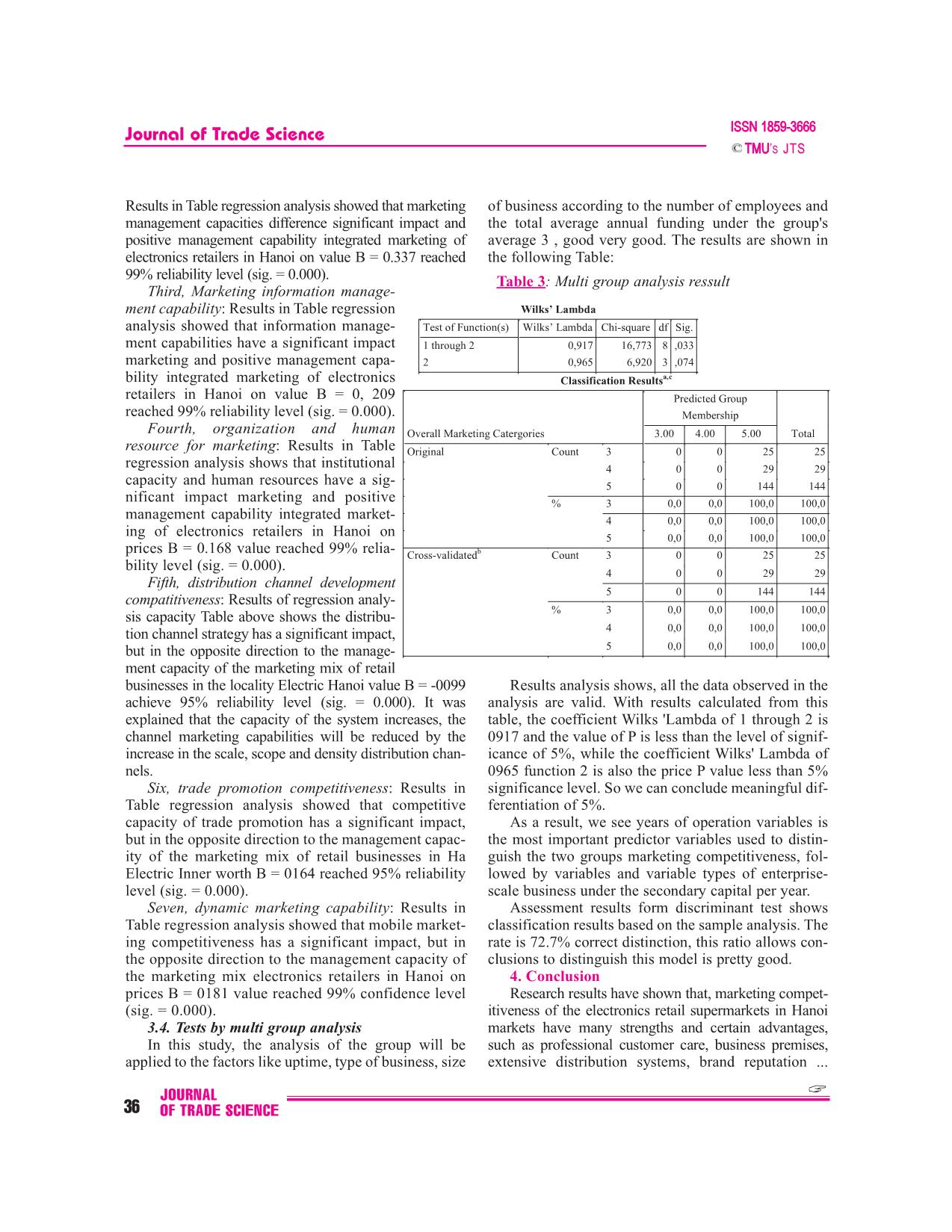
: standard errors. - Testing estimates via Boostrap method: the last 3. Scale test results, theoretical models of com- model as well as other appropriate models need to have petitiveness of marketing electronics retail super- sets of data independent of each other, or the initial markets Hanoi market sampling size must be quite large. In quantitative To test and evaluate the scale of the data collected. research method conducted via sampling, samples are all data collected will be processed with the help of often divided into two sub-groups. The first group is SPSS 20.0 software. First the data are encrypted, JOURNAL OF TRADE SCIENCE 33 Journal of Trade Science ’S JTS cleaned, then analyzed with the main section: Evaluate Results of reliability analysis showed that reliability (Cronbach reliability coefficient through Cronbach's Alpha of all scales are greater than 0.7. Alpha) and the value (factor loading) by (Exploratory Only Cronbach's alpha coefficient of competitiveness Factor Analysis). measurable physical evidence is 0686 3.1. Cronbach'Alpha and Bartlett's Test 0.6 according to the rules and standards of statistics, it Accreditation reliability Cronbach's alpha scale can be acceptable. Meanwhile, the total variable corre- and Bartlett's Test is used to remove garbage before lation coefficients of the variables were observed in the proceeding variable factor analysis. Test the reliability larger scale of 0.4, the lowest of the scale is the 0409 of the variables in the scale competitiveness marketing competitiveness material. When considering the case of electronics stores in Hanoi based on coefficient test of removal of each variable scale observation showed Cronbach's Alpha and Bartlett's Test of components no change when removed can cause the scale scale and the index of each variable measure. The ana- Cronbach's Alpha Cronbach's Alpha greater than that lytical results are shown in the following table (details of the scale. So, all the observed variables are accept- in appendix): ed and will be used in subsequent factor analysis. 3.2. EFA Test Table 1: Independent variable scale test With the analytical results through the expertise Cronbach's Alpha above, all 22 Cronbach’s KMO Bartlett’s No. Indicators items of Competitiveness mar- Alpha Test keting core, 24 items of com- I Core marketing capability P < 0,00 petitive marketing tactics, 04 1 Strategic marketing management 0.781 0.69 P < 0,00 items for competitiveness mar- 2 Unique differentiation management 0.844 0.706 P < 0,00 keting and 03 items for the capability competitiveness of the enter- prise marketing mix electronics 3 Productivity and quality management 0.893 0.722 P < 0,00 retailers reach the reliability capability and the items are used to con- 4 Marketing information management 0.902 0.711 P < 0,00 duct factor analysis (EFA) by capability the method of rotation 5 Brand management capability 0.860 0.726 P < 0,00 (Varimax with Kaiser 6 Organization and human resource for 0.851 0.718 P < 0,00 Normalization ). Technical analysis of factors (factor marketing analysis) were used in this 7 Culture value creation marketing capabiltiy 0.847 0.732 P < 0,00 study for reducing and collect- II Strategic marketing capability P < 0,00 ing elements observed vari- 1 Product development competitiveness 0.881 0.7 P < 0,00 ables that into a more meaning- 2 Price competitiveness 0.917 0.728 P < 0,00 ful factor, less in quantity for 3 Distribution channel development 0.945 0.703 P < 0,00 use in distribution next regres- compatitiveness sion Through analysis results 4 Trade promotion competitiveness 0.935 0.741 P < 0,00 following table saw, with each 5 Human resource competitiveness 0.817 0.741 P < 0,00 variable observed in each line 6 Physical evidence competitiveness 0.686 0.726 P < 0,00 displayed a Factor largest load- 7 Process performance competitiveness 0.857 0.735 P < 0,00 ing... The results indicate that III Dynamic marketing competitiveness 0.863 0.771 P < 0,00 the item Q81 has the smallest index analysis and by 0629> IV Overall marketing competitiveness 0.87 0.708 P < 0,00 0.5 (standard for with a loading JOURNAL 34 OF TRADE SCIENCE journal of Trade Science ’S JTS biggest Factor ?0.5). The analytical results also indi- keting management has a significant impact and posi- cated there are 15 variables (factors) with a total vari- tive management capability integrated marketing of ance extracted = 79.45% and the coefficient of KMO = electronics retailers in Hanoi on value B = 0.117 0744, shows the relevance of the analysis of the fac- reached 95% reliability level (sig. = 0.018). tors. With test results Bartlett (Sig. <0.05), suggesting Second, Unique differentiation management capability: that the variables are cor- Table 2: Regression result related in general. According to these Coeff. Multicolinearity results, lets move on to Independent variable B Std.err T Sig (VIF) the next step is to con- duct testing CFA for each (Coeff) 0.000 0.047 0.000 1.000 Strategic marketing variable. 0.117* 0.049 2.380 0.018 1.091 3.3. CFA test and capality multi-regression Unique differentiation 0.337*** 0.059 5.742 0.000 1.558 Results show that management capability CFA observations vari- Productivity and quality ables were standardized 0.052 0.057 0.911 0.364 1.486 management capability reaes allowed standerd (> Marketing information = 0.5) and a statistically 0.209** 0.064 3.284 0.001 1.833 significant p-values are management capability by 0.000 (the lowest Brand management capability 0.069 0.051 1.341 0.182 1.191 weight management Organization and human 0.168** 0.052 3.261 0.001 1.210 capability variable mar- resource for marketing keting strategy .699) . Culture value creation 0.010 0.056 0.170 0.865 1.427 Thus, we can conclude marketing capabiltiy the observed variables Product development used to measure 15 com- -0.031 0.051 -0.609 0.543 1.177 ponents of the scale mar- competitiveness keting competitiveness Price competitiveness 0.052 0.056 0.928 0.354 1.403 of the electronics retail Distribution channel -0.099 0.051 -1.956 0.052 1.160 business in Hanoi development compatitiveness achieve convergence Trade promotion 0.164** 0.057 2.896 0.004 1.450 value. Detailed results competitiveness analysis regression Human resource model are shown in the -0.066 0.052 -1.276 0.204 1.214 following Table: competitiveness From the results of Physical evidence -0.008 0.050 -0.163 0.870 1.122 the regression analysis competitiveness above, the author ana- Process performance lyzes the impact of ele- -0.004 0.052 -0.070 0.944 1.232 ments marketing compet- competitiveness itives on marketing com- Dynamic marketing 0.181** 0.060 3.002 0.003 1.654 petitiveness as follows: competitiveness First, strategic mar- R = 0.774 R Square = 0.599 * significant at 5% keting capality: Results in Table regression Adjusted R Square = 0.566 ** significant at 1% analysis showed that the F = 18.114 p = 0.000 *** significant at 0,1% capacity strategic mar- JOURNAL OF TRADE SCIENCE 35 Journal of Trade Science ’S JTS Results in Table regression analysis showed that marketing of business according to the number of employees and management capacities difference significant impact and the total average annual funding under the group's positive management capability integrated marketing of average 3 , good very good. The results are shown in electronics retailers in Hanoi on value B = 0.337 reached the following Table: 99% reliability level (sig. = 0.000). Table 3: Multi group analysis ressult Third, Marketing information manage- ment capability: Results in Table regression Wilks’ Lambda analysis showed that information manage- Test of Function(s) Wilks’ Lambda Chi-square df Sig. ment capabilities have a significant impact 1 through 2 0,917 16,773 8 ,033 marketing and positive management capa- 2 0,965 6,920 3 ,074 bility integrated marketing of electronics Classification Resultsa,c retailers in Hanoi on value B = 0, 209 Predicted Group reached 99% reliability level (sig. = 0.000). Membership Fourth, organization and human Overall Marketing Catergories 3.00 4.00 5.00 Total resource for marketing: Results in Table Original Count 3 0 0 25 25 regression analysis shows that institutional 4 0 0 29 29 capacity and human resources have a sig- 5 0 0 144 144 nificant impact marketing and positive % 3 0,0 0,0 100,0 100,0 management capability integrated market- 4 0,0 0,0 100,0 100,0 ing of electronics retailers in Hanoi on 5 0,0 0,0 100,0 100,0 prices B = 0.168 value reached 99% relia- Cross-validatedb Count 3 0 0 25 25 bility level (sig. = 0.000). 4 0 0 29 29 Fifth, distribution channel development 5 0 0 144 144 compatitiveness: Results of regression analy- sis capacity Table above shows the distribu- % 3 0,0 0,0 100,0 100,0 tion channel strategy has a significant impact, 4 0,0 0,0 100,0 100,0 but in the opposite direction to the manage- 5 0,0 0,0 100,0 100,0 ment capacity of the marketing mix of retail businesses in the locality Electric Hanoi value B = -0099 Results analysis shows, all the data observed in the achieve 95% reliability level (sig. = 0.000). It was analysis are valid. With results calculated from this explained that the capacity of the system increases, the table, the coefficient Wilks 'Lambda of 1 through 2 is channel marketing capabilities will be reduced by the 0917 and the value of P is less than the level of signif- increase in the scale, scope and density distribution chan- icance of 5%, while the coefficient Wilks' Lambda of nels. 0965 function 2 is also the price P value less than 5% Six, trade promotion competitiveness: Results in significance level. So we can conclude meaningful dif- Table regression analysis showed that competitive ferentiation of 5%. capacity of trade promotion has a significant impact, As a result, we see years of operation variables is but in the opposite direction to the management capac- the most important predictor variables used to distin- ity of the marketing mix of retail businesses in Ha guish the two groups marketing competitiveness, fol- Electric Inner worth B = 0164 reached 95% reliability lowed by variables and variable types of enterprise- level (sig. = 0.000). scale business under the secondary capital per year. Seven, dynamic marketing capability: Results in Assessment results form discriminant test shows Table regression analysis showed that mobile market- classification results based on the sample analysis. The ing competitiveness has a significant impact, but in rate is 72.7% correct distinction, this ratio allows con- the opposite direction to the management capacity of clusions to distinguish this model is pretty good. the marketing mix electronics retailers in Hanoi on 4. Conclusion prices B = 0181 value reached 99% confidence level Research results have shown that, marketing compet- (sig. = 0.000). itiveness of the electronics retail supermarkets in Hanoi 3.4. Tests by multi group analysis markets have many strengths and certain advantages, In this study, the analysis of the group will be such as professional customer care, business premises, applied to the factors like uptime, type of business, size extensive distribution systems, brand reputation ... JOURNAL 36 OF TRADE SCIENCE journal of Trade Science ’S JTS However, the supermarket business is still spontaneous, Summary customer service is still limited and the quality of human resources is not high here are some major limitations on Sieâu thò - loaïi hình cöûa haøng hieän ñaïi, kinh doanh the marketing competitiveness of the electronies home toång hôïp hoaëc chuyeân doanh, coù cô caáu chuûng loaïi appliance supermarket in Hanoi market. haøng hoùa phong phuù, ña daïng, ñaûm baûo chaát löôïng, ñaùp öùng caùc tieâu chuaån veà dieän tích kinh doanh, References: trang bò kyõ thuaät vaø trình ñoä quaûn lyù, toå chöùc kinh doanh. Coù caùc phöông thöùc phuïc vuï vaên minh, thuaän 1. Nguyeãn Baùch Khoa (2004), Phöông phaùp luaän tieän nhaèm thoûa maõn nhu caàu mua saém haøng hoùa cuûa xaùc ñònh naêng löïc caïnh tranh vaø hoäi nhaäp kinh teá khaùch haøng - moät trong nhöõng xu höôùng tieán boä trong quoác teá cuûa doanh nghieäp, Taïp chí KHTM soá 4+5 thöông maïi baùn leû nöôùc ta thôøi gian qua. Ñaëc bieät vôùi 2. Nguyeãn Baùch Khoa vaø Cao Tuaán Khanh xu höôùng phaùt trieån hieän ñaïi theo höôùng coâng ngheä (2011), Marketing thöông maïi, NXB Thoáng keâ thì caùc sieâu thò ñieän maùy trôû thaønh moät ngaønh kinh 3. Kotler Philip (2007), Marketing caên baûn doanh baùn leû raát phaùt trieån thôøi gian qua ôû caùc ñoâ thò (Marketing Essentials - Philip Kotler; Dòch giaû: Phan lôùn. Ñaây vöøa laø söï keát hôïp giöõa hình thöùc baùn leû Thaêng - Vuõ Thò Phöôïng - Giang Vaên Chieán), NXB chuyeân doanh vôùi coâng ngheä baùn leû töï phuïc vuï kieåu Lao ñoäng - Xaõ hoäi. sieâu thò ñaõ mang laïi nhieàu lôïi theá caïnh tranh market- 4. Kotler Philip, Keller Kevin Lane (2015), ing cho loaïi hình naøy. Tuy nhieân, thôøi gian qua cuõng Marketing Management, Pearson; 15 edition. ñaõ boäc loä nhöõng maët haïn cheá naêng löïc caïnh tranh noùi 5. Levy Michael, Weitz Barton A (2008), chung vaø caïnh tranh marketing noùi rieâng nhö ñònh vò Retailing Management, McGraw-Hill Higher giaù trò cung öùng cuûa chaøo haøng thò tröôøng, hieäu naêng Education; 7 edition. phoái thöùc baùn leû hoãn hôïp cuõng nhö caùc coâng cuï mar- 6. Porter M.E. (1985), Competitive Advantage, keting ñöôïc vaän duïng, caùc naêng löïc marketing coát loõi Free Press, New York. coøn chöa ñöôïc xaùc laäp vaø taäp trung naâng cao, baûn saéc 7. Cuïc Thoáng keâ Thaønh phoá Haø Noäi (2015), Thoáng dòch vuï phaân phoái kieåu sieâu thò coøn nhieàu maët baát keâ Nieân giaùm thoáng keâ Haø Noäi, NXB Thoáng keâ. caäp caû veà giaù trò vaø chaát löôïng döïa treân khaùch haøng. CAO TUAN KHANH 1. Personal Profile: - Name: Cao Tuan Khanh - Date of birth: September 13, 1968 - Title: PhD in economy - Workplace: Vietnam University of Commerce - Position: Head of Marketing Management Department 2. Major research directions: - The intensive areas, such as: Commercial Marketing, Banking Marketing, Customer rela- tionship Management, Business to Business Marketing, Communication Marketing, PR Management, International Marketing - The fields of international trade 3. Publications the author has published his works: - Vietnam Trade Review - Vietnam Industry and Trade Review - Trade Science Review - Asian Social Science Review - International Business Research Review - International Journal of Marketing Studies JOURNAL OF TRADE SCIENCE 37
File đính kèm:
 marketing_competitiveness_of_home_appliance_supermarkets_in.pdf
marketing_competitiveness_of_home_appliance_supermarkets_in.pdf

