Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành - Kỹ thuật lắp ráp, sửa chữa máy tính
1 A computer has high speed of calculation, diligence, accuracy, reliability, or
versatility which made it an integrated part in all business organizations. Computer
is used in business organizations for:
Payroll calculations
Budgeting
Sales analysis
Financial forecasting
Managing employees database
2 The computer has provided a lot of facilities in the education system.
The computer provides a tool in the education system known as CBE
(Computer Based Education).
CBE involves control, delivery, and evaluation of learning.
6The computer education is rapidly increasing the graph of number of
computer students.
There are number of methods in which educational institutions can use
computer to educate the students.
It is used to prepare a database about performance of a student and analysis
is carried out on this basis.
3 Computers are widely used in Engineering purpose.
One of major areas is CAD (Computer aided design). That provides creation and
modification of images. Some fields are:
Structural Engineering - Requires stress and strain analysis for design of
Ships, Buildings, Budgets, Airplanes etc.
Industrial Engineering - Computers deal with design, implementation and
improvement of integrated systems of people, materials and equipments.
Architectural Engineering - Computers help in planning towns, designing
buildings, determining a range of buildings on a site using both 2D and 3D
drawings.

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9
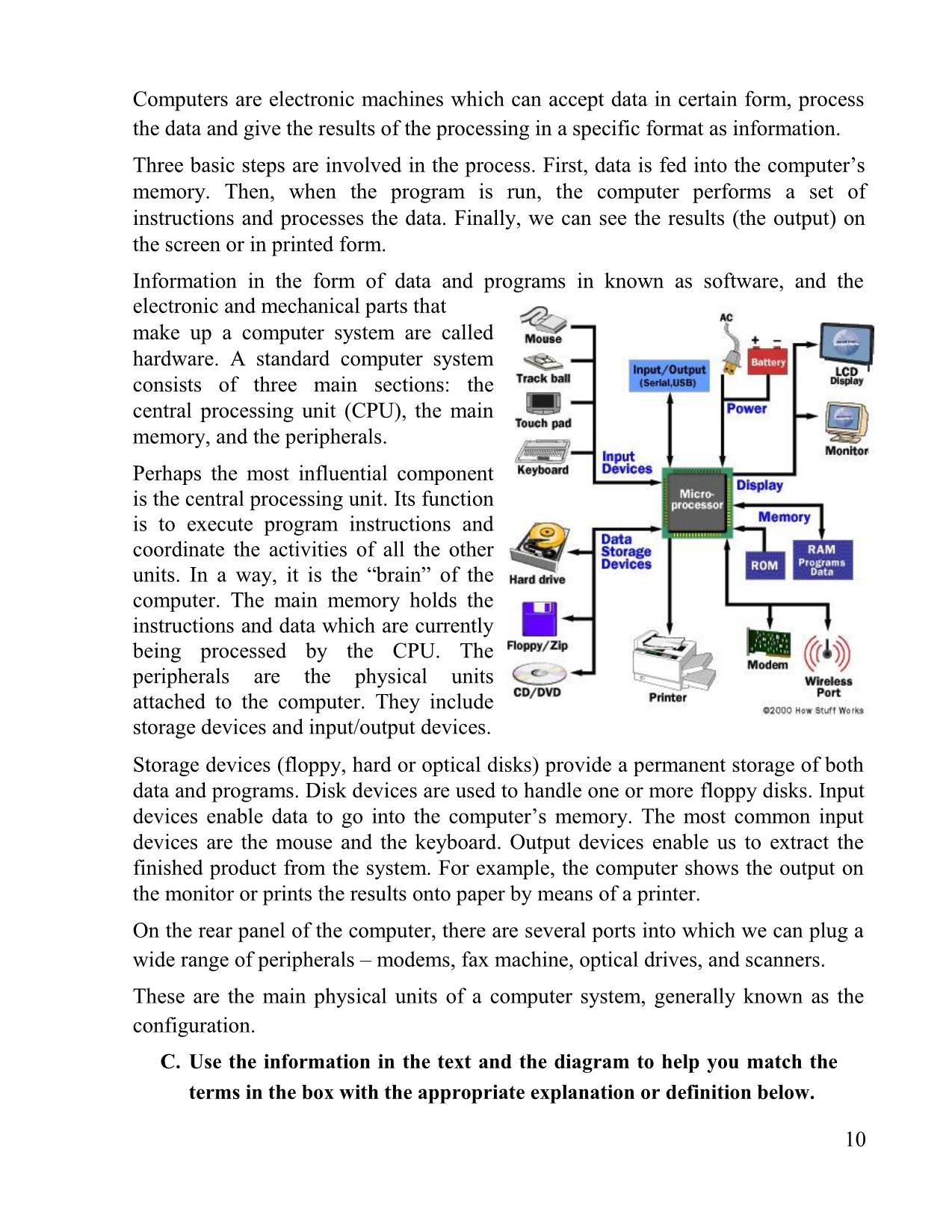
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành - Kỹ thuật lắp ráp, sửa chữa máy tính

charge. See RAM, ROM. VR: Abbreviation for Virtual Reality. Top W W3C: Abbreviation for World Wide Web Consortium. An international non-profit organisation which acts as a resource centre for the World Wide Web, and is active in setting technical standards. The current Director of W3C is Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the Web. The W3C website can be found at the URL See World Wide Web. WAN: Abbreviation for Wide Area Network. A network of computers located at geographically separate sites. See LAN, MAN. WAP: Abbreviation for Wireless Application Protocol. A system that enables you to browse online services, e.g. relating to information about the weather, traffic conditions, shopping, etc via a special type of mobile phone. WAP is the mobile phone equivalent of the World Wide Web. Newer mobile phones include WAP browser software to allow users access to WAP sites. See also Smartphone. Warchalking: Warchalkers make chalk markings on walls or pavements to indicate that there is an insecure wireless access point nearby. The symbols not only mark the location of the wireless access point but also indicate the network type, name, and bandwidth. The markings are similar to the symbols used by tramps to communicate information to fellow itinerants about the friendliness of a place or its inhabitants. The term derives from the 1983 film War Games in which a teenager uses software to dial randomly selected telephone numbers, eventually managing to hack into a military computer and start World War III. People initiated in the ways 100 of warchalking recognise the symbols and then all they need to do is take up a comfortable position with their laptop computer, suitably equipped with a wireless network card, and get online using someone else's bandwidth. See Wifi. WAV: Short for Waveform Audio Format. A format for storing high-quality audio files. Somewhat hungry in terms of storage space compared to the MP3 and WMA audio file formats. See Media Player. See Section 2.2.3.3, Module 2.2, headed Sound recording and editing software. Web: See World Wide Web. Web 2.0: Contrary to what many people think, Web 2.0 is not a new version of the World Wide Web. The term arose as the name of a series of conferences, the first of which was held in 2004: Essentially, Web 2.0 is an attempt to redefine what the Web is all about and how it is used, for example new Web-Based communities using Blogs, Podcasts, Wikis and Social Networking websites that promote collaboration and sharing between users - in other words, a more democratic approach to the use of the Web. In order to achieve this, Web-based applications have to work more like applications on your computer's hard disc, allowing you to use the Web in much the same way as you would use applications such as Word or PowerPoint. To what extent the concept of Web 2.0 is truly innovative is a matter of debate, as it is broadly in line with the concept of the Web as defined by its inventor, Tim Berners-Lee, way back in 1998. SeeSection 2.1, Module 1.5, headed What is Web 2.0? Web Address: See URL. Webcam: A camera connected to a computer that enables it to transmit images and videos to the Internet . For example, webcams can be set to transmit a live picture every few minutes from a location to a website, displaying a live view of a landscape, cityscape or interior of a building. Webcams are essential for Videoconferencing. See Section 1.2.6, Module 1.2 for an illustration of a webcam, and see Section 14.1.3, Module 1.5, headed Videoconferencing: a synchronous communications medium. Many laptop computers have an integrated webcam - which appears as a small "eye" in the top of the frame of the Display Screen. WebCT: A Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). Blackboard and WebCT announced an agreement to merge in October 2005. Effectively, Blackboard has now taken over WebCT. Weblog: The full form of the term Blog. Webmail: A facility for creating, sending and and receiving messages via the Internet.Webmail offers an alternative to using email software such as such as Outlook or Eudora: see Email. In order to use webmail you have to register with anInternet Service Provider (ISP) and you can then access their email service via your Web Browser. See Section 14, Module 1.5, headed Computer Mediated Communication (CMC). Webquest: A webquest is a task-oriented activity in which the learner draws on material from different websites in order to achieve a specific goal. The skills that are required in a webquest 101 mainly involve reading and listening, but there may also be communicative speaking exercises. See Section 7.3.1, Module 1.5, headed Webquests and scavenger hunts. Web Server or Webserver: A computer or a software package running on a computer that delivers, i.e. serves, Web pages to its clients: see Client and Host. Every Web server has an IP Address and possibly a Domain Name. For example, if you enter the URL in your Browser, this sends a request to the Server whose domain name is ict4lt.org. The server then fetches the page named index.htm and sends a copy of it to your browser. Any computer can be turned into a Web server by installing Web server software and connecting the machine to the Internet. By far the most popular Web server software in use worldwide is the Open Source Apache software: Website: An area on the World Wide Web where an organisation or individual stores a collection of pages of material - Web pages . The pages are usually interlinked with one another and with other websites. Every website has a unique Web Address or URL. The full URL of the ICT4LT website is Webwhacking: This involves saving entire websites for use offline. It may breach copyright because it involves copying the website to a local drive, either a network server or a stand-alone computer's hard drive. See Section 4, General guidelines on copyright. WELL: Acronym for Web Enhanced Language Learning. The WELL Projectwas co-ordinated by William Haworth, Liverpool John Moores University. It was set up in 1997 with assistance from the higher education Fund for the Development of Teaching and Learning (FDTL) in order to promote wider awareness and more effective use of the World Wide Web in Modern Foreign Languages teaching across higher education in the UK. The funding period came to an end in August 2001 and the website has been closed down. Whiteboard: See Interactive Whiteboard. Wide Area Network (WAN): See WAN. Wifi: Wireless Fidelity, also known as wireless networking, a way of transmitting information without cables that is reasonably fast and is often used for laptop computers within a business or a university or school campus instead of a Local Area Network (LAN) that uses cable connections. Wifi systems use high frequency radio signals to transmit and receive data over distances of several hundred feet. Many hotels and airports now offer wifi access to people travelling with laptop computers. Wiki: A website or similar online resource which allows anyone to set up a resource in which content can be created collectively. It's important feature is that it allows anyone who views the wiki to add to or edit the existing content as if they were adding to or editing, for example, someone else's Word document. Wiki also refers to the software used to create such a website. The word "wiki" derives from the Hawaiian "wiki-wiki", meaning "quick". Wikipedia is the best known example of a wiki. It's a collaboratively written encyclopaedia: There is an article on Computer Assisted Language Learning in Wikipedia, which you can add to or edit yourself: It is also possible to set up a personal wiki that cannot be added to or edited by other people, e.g. here is 102 Graham Davies's personal wiki: Wikis may also be used forConferencing: see Section 12, Module 1.5, headed Discussion lists, blogs, wikis, social networking. Wild Card or Wildcard: In a question-answer dialogue which aims not to be over-sensitive about spelling, the teacher may decide to allow for aberrations by declaring certain characters "wild". For example, the answer "relitivaty" would match with 'r?l?t?v?t?', the question marks representing wild card characters: i.e. whatever the learner types in place of them is accepted. Conventionally, a question mark is used for a single character and an asterisk for a string of characters. A technique also used in programs that help you cheat at crossword puzzles! Wildcards can also be used in search engines such as Google when you are not sure of the spelling of the item you are searching for. See Section 4, Module 1.5, headedSearch engines: How to find materials on the Web. Window: An area of a computer screen set aside for a special purpose. Modern computers, such as the Macintosh and most personal computers, divide the screen into discrete sections, known as windows , within which different pieces of software can be run at the same time - although not necessarily strictly at the same time, as normally only one window is active: see Multitasking. The user can control the size, shape and positioning of each window. Data, e.g. a piece of text, a picture or numerical data, can be moved or copied and pasted from one window to another. See Windows. Windows: The name of a range of several different Graphical User Interface (GUI) operating systems produced by the Microsoft Corporation. Windows 3.0 and Windows 3.1 were the first operating systems of this type, produced by Microsoft, to appear in the early 1990s. The Apple Macintosh computer, however, had been using a GUI (which was not known as Windows) from the mid-1980s. Microsoft Windows is currently the most widely used GUI for personal computers. It exists in various versions, e.g.Windows 95, 98, ME, NT, 2000 and XP. See MS DOS, Operating System. Windows Explorer: Microsoft's tool, provided as part of Windows, that enables you to inspect and manage folders and files stored on your computer. My Computer is an alternative tool, also provided as part of Windows. See File, Folder. Wireless Fidelity: See Wifi. Wireless Mouse: A Mouse that does not require a cable connection to a computer, but which operates via infrared or radio signals. Wizard: Software that guides the user step-by-step through a complex task, such as setting up software on a network or configuring a printer to output data in a special format, e.g. for printing labels from a database program. WMA: Abbreviation for Windows Media Audio. Microsoft's audio encoding format which offers high-quality output with lower file sizes. See MP3, WAV, which are alternative audio file formats. See Media Player. See Section 2.2.3.3, Module 2.2, headed Sound recording and editing software. 103 Word: A popular word-processing package, produced by Microsoft. See Word-processor. Word-processor: Probably the most widely used computer Application. Modern word- processors allow the user to create fine-looking documents including images, tables, photographs, and even sound and video recordings if they are to be viewed on screen rather than from the printed page. In many respects they are similar to Desktop Publishing applications. Word- processors normally include a spellchecker, a grammar checker, a style checker and a thesaurus, as well as tools for writing in HTML, the coding language used for producing Web pages.Word- processors have been widely used in teaching and learning foreign languages ever since they first appeared. See Module 1.3, Using word-processing and presentation software in the Modern Foreign Languages classroom. Wordsnake: An exercise in which all the spaces in a sentence have been removed, the learner's task being to put the spaces back into the correct positions in the sentence. See Section 3.1, Module 1.3, headed Using the space bar: Wordsnake exercises. Workstation: A term that is rather loosely used these days. Most people use it in the context of any computer that forms part of a Network. Formerly, this term was applied to a particular type of powerful computer used for scientific and engineering calculations, e.g. the Sun Workstation. WorldCALL: The worldwide umbrella association for CALL. which has the aim of helping countries that are currently underserved in the applications of ICT. The First World Conference on CALL was held at the University of Melbourne, Australia, in 1998. The Second World Conference on CALL took place in Banff, Canada, in 2003. The 2008 WorldCALL conference will take place in Japan. World Wide Web: Usually referred to simply as the Web. This is the most powerful and fastest growing Internet service. The World Wide Web was the brainchild of Tim Berners-Lee, who in 1989 invented the HTML coding language that is the basis of the Web. The Web became a public service in 1993. It is a huge collection of resources of information, including learning materials, which is accessed by means of a computer program known as a Browser. The World Wide Web is only part of the Internet, but many people treat both terms as synonyms. See Module 1.5, Introduction to the Internet, Module 2.3, Exploiting World Wide Web resources online and offline, Module 3.3, Creating a World Wide Web site. See alsoWeb 2.0. Worldwide Web Consortium (W3C): An international non-profit organisation which acts as a resource centre for the World Wide Web, and is active in setting technical standards. The current Director of W3C is Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the Web. The W3C website can be found at the URL See World Wide Web. Worm: A computer worm is a self-replicating hostile computer program, similar to a computer Virus. A virus attaches itself to and becomes part of another program, but a worm is self- contained and does not need to be part of another program to propagate itself. Worms can cause considerable damage to computers. See Trojan. WORM: Acronym for Write Once Read Many. Now a rather dated term, originally applied to a type of Optical Disc on which information could be written just once and could not be amended or erased. 104 Write Protect: To protect a Storage Device, File or Folder so that its contents cannot normally by altered or erased. This may be done physically, e.g. by moving a notch on a floppy disc's casing, or - more commonyl these days - through software that designates the device, file or folder as read-only. WWW: Abbreviation for World Wide Web. WYSIWYG: Acronym for What You See Is What You Get, dating back to the pre-Windows and pre-Mac period, when what you saw on the screen, e.g. in a Word document, was not necessarily what appeared on your Printer - something we now take for granted. 105
File đính kèm:
 giao_trinh_tieng_anh_chuyen_nganh_ky_thuat_lap_rap_sua_chua.pdf
giao_trinh_tieng_anh_chuyen_nganh_ky_thuat_lap_rap_sua_chua.pdf

