Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành Kế toán
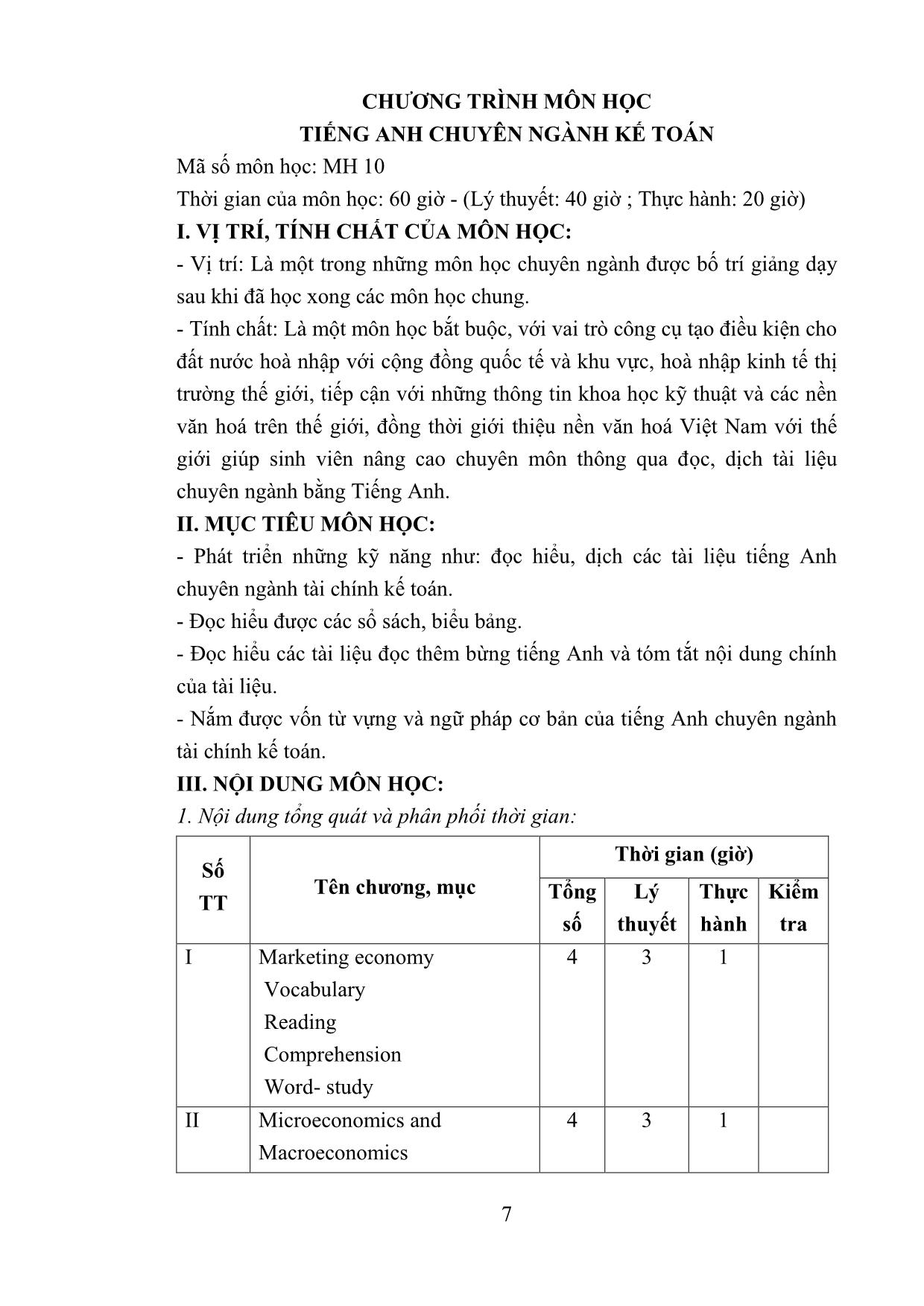
UNIT 1: THE MARKET ECONOMY
READING COMPREHENSION
Planned economy: A system whereby the structure of the market is
deliberately planned by the state, in which production and consumption
quotas are fixed beforehand and where there is no real competition between
industrial or commercial organizations. In the Soviet model, for instance,
all the means of production and the channels are state controlled. Private
ownership does not exist in this field.
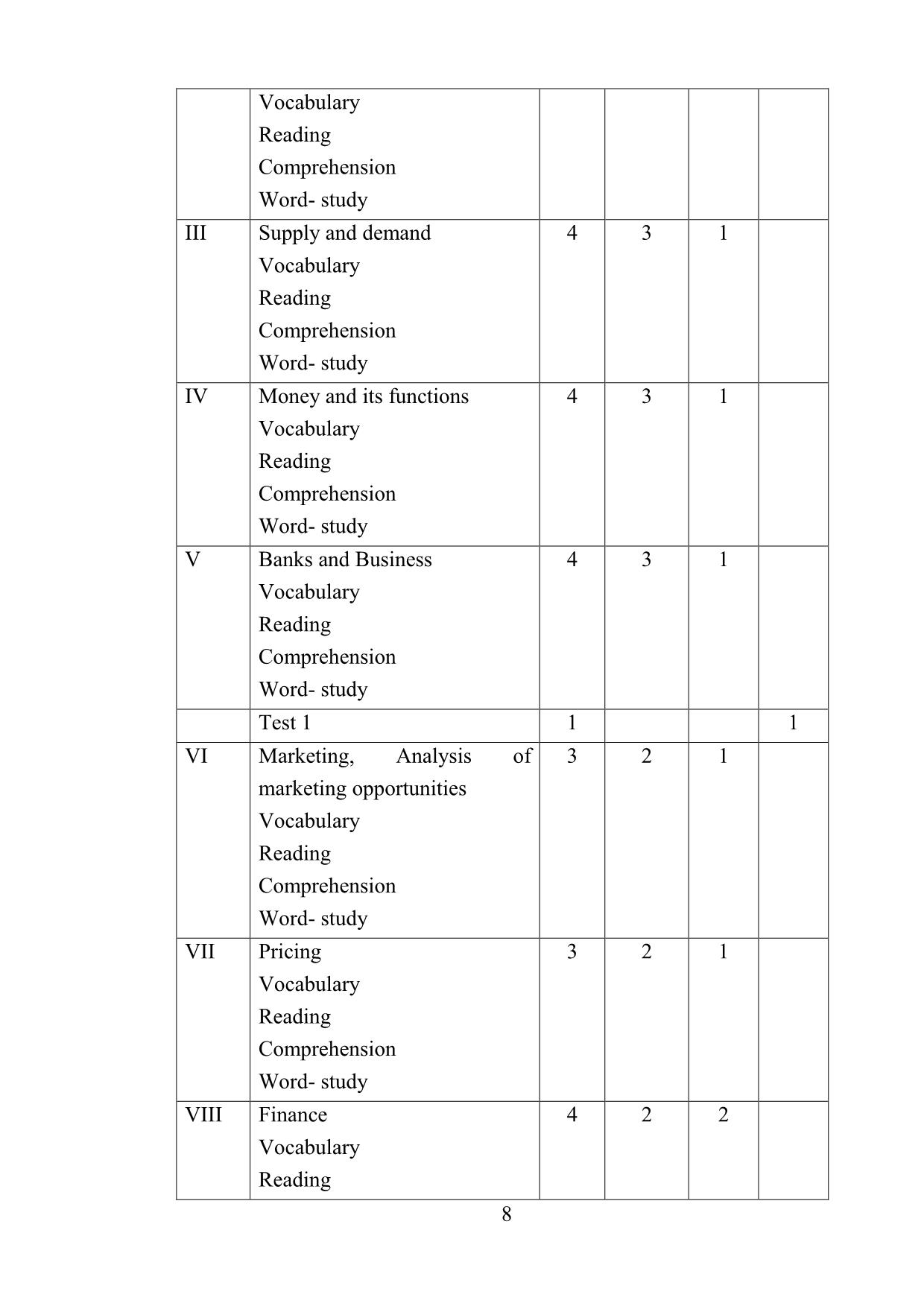
In practice, there is wide gap between the theoretical model and
economy realities: the so- called market economies rely more and more on
Government planning and intervention, whereas in planned economies,
such capitalistic notions as profit tend to be reintroduced.
Free market economy: An economic system in which the market –
that is the relation between producers and consumers, buyers and sellers,
investors and workers, management and labour – is supposed to be
regulated by the law of supply and demand. Business firms are supposed to
complete freely, and any attempt at hindering free competition (‘restrictive
practices’) is punishable by law.
Direct government intervention is theoretically ruled out although
the government will influence the economic situation through its fiscal and
budgetary policies.
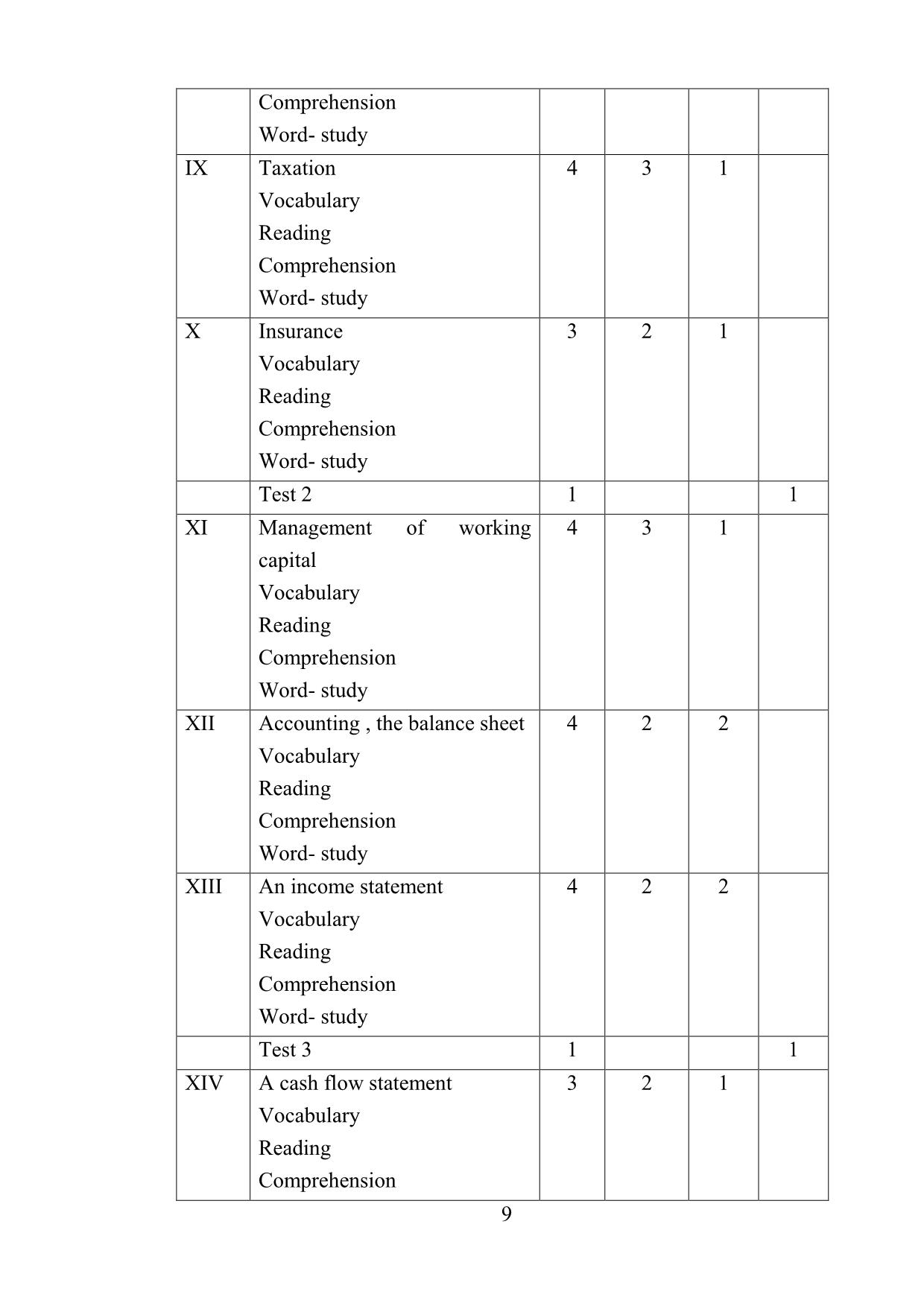
Mixed economy: An economic system in which some goods and
services are produced by the government and some by private enterprise. It13
lies between a command economy and a complete laissez- faire economy.
In practice, most economies are mixed: the significant feature is whether an
economy is moving towards or away from a more laissez – faire situation.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành Kế toán

ball 127 bell 7. I own 1,000 ____________________ of their stock. shares pieces papers 8. The scandal ______________________ ( = caused/contributed to) the sell-off. fooled failed fueled 9. The earnings were higher than __________________________, which sent the stock through the roof ( = increased its value dramatically). accepted expected escaped 10. The stock market was down 400 points, but finished up 50 points. What are some of the reasons for this _________________________? turnaround turnstile roundabout 128 Appendix 14 Trường Cao Đẳng nghề Công Nghiệp Hà Nội I. Một số thuật ngữ Kế Toán bằng Tiếng Anh (cơ bản) - st Accounting entry: ---- bút toán Accrued expenses ---- Chi phí phải trả - Accumulated: ---- lũy kế Advance clearing transaction: ---- quyết toán tạm ứng (???) Advanced payments to suppliers ---- Trả trước ngưòi bán – Advances to employees ---- Tạm ứng – Assets ---- Tài sản Assets liquidation: ---- thanh lý tài sản Balance sheet ---- Bảng cân đối kế toán – Bookkeeper: ---- người lập báo cáo Capital construction: ---- xây dựng cơ bản Cash ---- Tiền mặt Cash at bank ---- Tiền gửi ngân hàng Cash in hand ---- Tiền mặt tại quỹ Cash in transit ---- Tiền đang chuyển Check and take over: ---- nghiệm thu Construction in progress ---- Chi phí xây dựng cơ bản dở dang Cost of goods sold ---- Giá vốn bán hàng Current assets ---- Tài sản lưu động và đầu tư ngắn hạn Current portion of long-term liabilities ---- Nợ dài hạn đến hạn trả Deferred expenses ---- Chi phí chờ kết chuyển Deferred revenue ---- Người mua trả tiền trước Depreciation of fixed assets ---- Hao mòn tài sản cố định hữu hình Depreciation of intangible fixed assets ---- Hoa mòn tài sản cố định vô hình Depreciation of leased fixed assets ---- Hao mòn tài sản cố định thuê tài chính Equity and funds ---- Vốn và quỹ Exchange rate differences ---- Chênh lệch tỷ giá Expense mandate: ---- ủy nghiệm chi Expenses for financial activities ---- Chi phí hoạt động tài chính Extraordinary expenses ---- Chi phí bất thường 129 Extraordinary income ---- Thu nhập bất thường Extraordinary profit ---- Lợi nhuận bất thường Figures in: millions VND ---- Đơn vị tính: triệu đồng Financial ratios ---- Chỉ số tài chính Financials ---- Tài chính Finished goods ---- Thành phẩm tồn kho Fixed asset costs ---- Nguyên giá tài sản cố định hữu hình Fixed assets ---- Tài sản cố định General and administrative expenses ---- Chi phí quản lý doanh nghiệp Goods in transit for sale ---- Hàng gửi đi bán Gross profit ---- Lợi nhuận tổng Gross revenue ---- Doanh thu tổng Income from financial activities ---- Thu nhập hoạt động tài chính Income taxes ---- Thuế thu nhập doanh nghiệp Instruments and tools ---- Công cụ, dụng cụ trong kho Intangible fixed asset costs ---- Nguyên giá tài sản cố định vô hình Intangible fixed assets ---- Tài sản cố định vô hình Intra-company payables ---- Phải trả các đơn vị nội bộ Inventory ---- Hàng tồn kho Investment and development fund ---- Quỹ đầu tư phát triển Itemize: ---- mở tiểu khoản Leased fixed asset costs ---- Nguyên giá tài sản cố định thuê tài chính Leased fixed assets ---- Tài sản cố định thuê tài chính Liabilities ---- Nợ phải trả Long-term borrowings ---- Vay dài hạn Long-term financial assets ---- Các khoản đầu tư tài chính dài hạn Long-term liabilities ---- Nợ dài hạn Long-term mortgages, collateral, deposits ---- Các khoản thế chấp, ký cược, ký quỹ dài hạn Long-term security investments ---- Đầu tư chứng khoán dài hạn Merchandise inventory ---- Hàng hoá tồn kho Net profit ---- Lợi nhuận thuần Net revenue ---- Doanh thu thuần Non-business expenditure source ---- Nguồn kinh phí sự nghiệp 130 Non-business expenditure source, current year ---- Nguồn kinh phí sự nghiệp năm nay Non-business expenditure source, last year ---- Nguồn kinh phí sự nghiệp năm trước Non-business expenditures ---- Chi sự nghiệp Non-current assets ---- Tài sản cố định và đầu tư dài hạn Operating profit ---- Lợi nhuận từ hoạt động SXKD Other current assets ---- Tài sản lưu động khác Other funds ---- Nguồn kinh phí, quỹ khác Other long-term liabilities ---- Nợ dài hạn khác Other payables ---- Nợ khác Other receivables ---- Các khoản phải thu khác Other short-term investments ---- Đầu tư ngắn hạn khác Owners' equity ---- Nguồn vốn chủ sở hữu Payables to employees ---- Phải trả công nhân viên Prepaid expenses ---- Chi phí trả trước Profit before taxes ---- Lợi nhuận trước thuế Profit from financial activities ---- Lợi nhuận từ hoạt động tài chính Provision for devaluation of stocks ---- Dự phòng giảm giá hàng tồn kho Purchased goods in transit ---- Hàng mua đang đi trên đường Raw materials ---- Nguyên liệu, vật liệu tồn kho Receivables ---- Các khoản phải thu Receivables from customers ---- Phải thu của khách hàng Reconciliation: ---- đối chiếu Reserve fund ---- Quỹ dự trữ Retained earnings ---- Lợi nhuận chưa phân phối Revenue deductions ---- Các khoản giảm trừ Sales expenses ---- Chi phí bán hàng Sales rebates ---- Giảm giá bán hàng Sales returns ---- Hàng bán bị trả lại Short-term borrowings ---- Vay ngắn hạn Short-term investments ---- Các khoản đầu tư tài chính ngắn hạn Short-term liabilities ---- Nợ ngắn hạn 131 Short-term mortgages, collateral, deposits ---- Các khoản thế chấp, ký cược, ký quỹ ngắn hạn Short-term security investments ---- Đầu tư chứng khoán ngắn hạn Stockholders' equity ---- Nguồn vốn kinh doanh Surplus of assets awaiting resolution ---- Tài sản thừa chờ xử lý Tangible fixed assets ---- Tài sản cố định hữu hình Taxes and other payables to the State budget ---- Thuế và các khoản phải nộp nhà nước Total assets ---- Tổng cộng tài sản Total liabilities and owners' equity ---- Tổng cộng nguồn vốn Trade creditors ---- Phải trả cho người bán Treasury stock ---- Cổ phiếu quỹ Welfare and reward fund ---- Quỹ khen thưởng và phúc lợi - Work in progress ---- Chi phí sản xuất kinh doanh dở dang – II. Một số thuật ngữ khác (st): Types of Accounts:-------- Các loại tài khoản kế toán Account Type 1: Short-term assets-----Loại tài khoản 1: Tài sản ngắn hạn Account Type 2: Long-term assets------Loại tài khoản 2: Tài sản dài hạn Account Type 3: Liabilities------Loại tài khoản 3: Nợ phải trả Account Type 4: Equity-------Loại tài khoản 4: Vốn chủ sở hữu Account Type 5: Revenue------Loại tài khoản 5: Doanh thu Account Type 6: Production costs, business-----Loại tài khoản 6: Chi phí sản xuất, kinh doanh Account Type 7: Other income-------Loại tài khoản 7: Thu nhập khác Account Type 8: Other expenses-----Loại tài khoản 8: Chi phí khác Account Type 9: Determining business results-----Loại tài khoản 9: Xác định kết quả kinh doanh Account Type 0: Balance sheet accounts------Loại tài khoản 0: Tài khoản ngoài bảng 129 - Provision for short-term investments------Dự phòng giảm giá đầu tư ngắn hạn 133 - Deductible VAT----Thuế GTGT được khấu trừ 136 - Inter-----Phải thu nội bộ 139 - Provision for bad debts-------Dự phòng phải thu khó đòi 132 217 - Real estate investment--------Bất động sản đầu tư 221 - Investment in subsidiaries-------Đầu tư vào công ty con 243 - Property tax deferred--------Tài sản thuế thu nhập hoãn lại 244 - collateral long-term deposits--------Ký cược ký quỹ dài hạn 343 - Bonds issued--------Trái phiếu phát hành 344 - Get escrow, long-term deposits------Nhận ký cược, ký quỹ dài hạn 347 - Deferred tax payable--------Thuế thu nhập hoãn lại phải trả 412 - Margin of property revaluation-----Chênh lệch đánh giá lại tài sản 413 - exchange rate differences----Chênh lệch tỷ giá hối đoái 414 - Fund Development------Quỹ đầu tư phát triển 415 - Fund financial reserve------Quỹ dự phòng tài chính 466 - Funds that form of fixed assets-----Nguồn kinh phí đã hình thành tài sản cố định 001 - Leasehold assets-----Tài sản thuê ngoài 002 - Materials, goods kept for processing-----Vật tư, hàng hóa nhận giữ hộ, nhận gia công 003 - Goods deposited deposit, or escrow------Hàng hóa nhận bán hộ, nhận ký gửi, ký cược 004 - Bad debts treated-------Nợ khó đòi đã xử lý 007 - Foreign currencies------Ngoại tệ các loại 008 - Project for public services and- projects-------Dự án chi sự nghiệp, dự án 133 Appendix 15 ACCOUNTING EQUATION I. ACCOUNTING ELEMENTS 1. Dialogue between Betty and Tom B: - Good morning, Tom. Would you mind explaining accounting elements to me? T: - Oh, not at all. They are referred to as assets, equities, liabilities, revenues, expenses, profit, etc. B: - What do assets mean? T: - Assets are the properties owned by an organization or a person. They may include things such as cash, land, supplies, business equipment, buildings and intangible assets. B: - I can understand that. Then what about liabilities? T: - Liabilities are debts owned by a company or creditor’s equity B: - I see. Then owner’s equity is the net assets of a company or a person. T: - Yes, it is equal to assets minus liabilities. B: - Sounds interesting. Thanks a lot. T: - You are welcome. 2. Oral drill. Pair work: Practice the following dialogue with your partner: A: - What does the term ‘ Revenue” mean? B: - Revenue is the inflow of assets ( such as cash ) resulting from the sale of products or the rendering of services to customers. A: - Well. It is cash received in the process of goods and services rendered. B: - Quite right. 3.Make “true” or “false” choices .(1) Cash is an asset. .(2) Liabilities indicate what the customer owes to the creditor. .(3) Equities belong to those who supply the assets. .(4) If I buy a book for $ 5 from a bookshop. I am the creditor. II. ACCOUNTING EQUATION Read and answer the questions I think accounting equations includes: Assets , liabilities, owner’s equity. The basic accounting equation is the following: 134 Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. Total assets always equal the total liabilities and owner’s equity and why? Let me make an example: Assume that the Longman Company was organized at the end of March. It invested $ 200,000 and borrowed $ 50,000 from a bank. Now it has $ 250,000 of assets. In other words, the bank’s equity is $ 50,000. It can be described as ‘ the company’s liabilities’ because the company owns the bank $ 50,000. This is expressed as follows: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. Well, the dollar amounts of two sides of equation are equal. The basic accounting equation must be in balance. Questions: What is the basic accounting equation? Why are the total assets equal the total liabilities and owner’s equity? Write the basic accounting equation. 2. Put the missing words and numbers: Assets = Liabilities +. (1) $ 38,500 $ 6,400 $ .. (2) $ 24,000 $ $ 13,000 (3) $ . $ 5,400 $ 18,500 III. VOCABULARY equation [i'kwei∫n] danh từ phương trình element ['elimənt] danh từ yếu tố asset ['æset] danh từ (số nhiều) của cải, tài sản, vật thuộc quyền sở hữu equity ['ekwiti] danh từ vốn cung cấp cho một doanh nghiệp thông qua việc bán cổ phiếu giá trị tài sản bị cấm cố (sau khi trừ thuế má) 135 liability [,laiə'biliti] danh từ (số nhiều) tiền nợ, khoản phải trả, tiêu sản revenue ['revənju:] danh từ (số nhiều) tổng thu nhập expense [iks'pens]danh từ (số nhiều) phụ phí, công tác phí profit ['prɔfit] danh từ lợi nhuận, lời lãi; tiền lãi, tiền lời loss [lɔs] danh từ sự thiệt hại, tổn hại, tổn thất, thua lỗ equipment [i'kwipmənt] danh từ sự trang bị intangible [in'tændʒəbl] tính từ không thể sờ thấy được không thể hiểu thấu được, không thể nắm được, mơ hồ debt [det] danh từ số tiền vay chưa trả; nợ owe [ou] động từ ( to owe somebody for something; to owe something to somebody) nợ creditor ['kreditə] danh từ người chủ nợ, người cho vay owner ['ounə] danh từ người sở hữu cái gì; chủ nhân net [net] danh từ mạng lưới total ['toutl] tính từ hoàn toàn; toàn bộ; tuyệt đối assume [ə'sju:m] ngoại động từ cho rằng; thừa nhận express [iks'pres] ngoại động từ biểu lộ, bày tỏ (tình cảm...); phát biểu ý kiên balance ['bæləns] danh từ (thương nghiệp) bản đối chiếu thu chi, bản quyết toán Phrases and special terms accounting equation: Phương trình kế toán accounting element: Yếu tố kế toán intangible assets: Tài sản vô hình owner’s equity: Vốn của chủ sở hữu net assets: Tài sản ròng as follows: Như sau in balance: cân bằng 136 Appendix 16 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 1. Conversation A: - How many categories does a financial statement include? B: - It includes three basic categories: the balance sheet, the income statement and the statement of cash flow. A: - Shall we make any analysis of detailed in preparing these statements? B: - No, they are ready – made data. The data have been measured, collected, summarized and classified, such as the following chart – a financial statement. ABC CORPORATION Statement of cash flows For the year ended December 31st, 2004 Net cash flows from operating activities $ 50,000 Net cash flows used in investing activities $ 115,000 Net cash flows provided by financial activities $ 100,000 Increase in cash balance $ 35,000 Beginning cash balance ( December 31st,2003) $ 20,000 Ending cash balance ( December 31st,2004) $ 55,000 2. Oral drill. Pair works: Practice the following dialogue with a partner. A: - Can you make clear the term ‘ liabilities’? B: - Yes, liabilities are debts owned by a company or creditor’s equity. A: - Oh, do liabilities include notes payable and accounts payable? B: - Yes, by the way, do you understand the term ‘equity”? A: - Broadly speaking, equities are all claims to or interests in assets, including liabilities and owner’s equity. B: - Exactly. 3. Make ‘true’ or ‘false’ choices (1) Every business prepares a balance sheet at the beginning of the year or the month. .. (2) The balance sheet shows that a firm’s assets are always equal to its liabilities and owner’s equity (3) Owner’s equity = Assets + Liabilities 137 (4) The income statement contains assets, liabilities and owner’s equity (5) The balance sheet usually includes the heading and the body.. 138 REFERENCES 1. Cao Xuân Thiều, Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành tài chính, NXB Tài chính, Hà Nội, 2006. 2. Keith F Bird, How to pass Book-keeping, LCCI. 3. Ian MacKenzie, English for Business Studies 2nd editon, Cambridge University Press, UK, 2002. 4. P.H.Collin, David York, Adrian Joliffe, Dictionary of Accounting 2nd edition, Peter Collin Publishing, London, 2001. 5. Thomas P.Fitch, Dictionary of Banking term 5th edition, Barron’s Educational Series, USA, 2006.
File đính kèm:
 giao_trinh_tieng_anh_chuyen_nganh_ke_toan.pdf
giao_trinh_tieng_anh_chuyen_nganh_ke_toan.pdf

