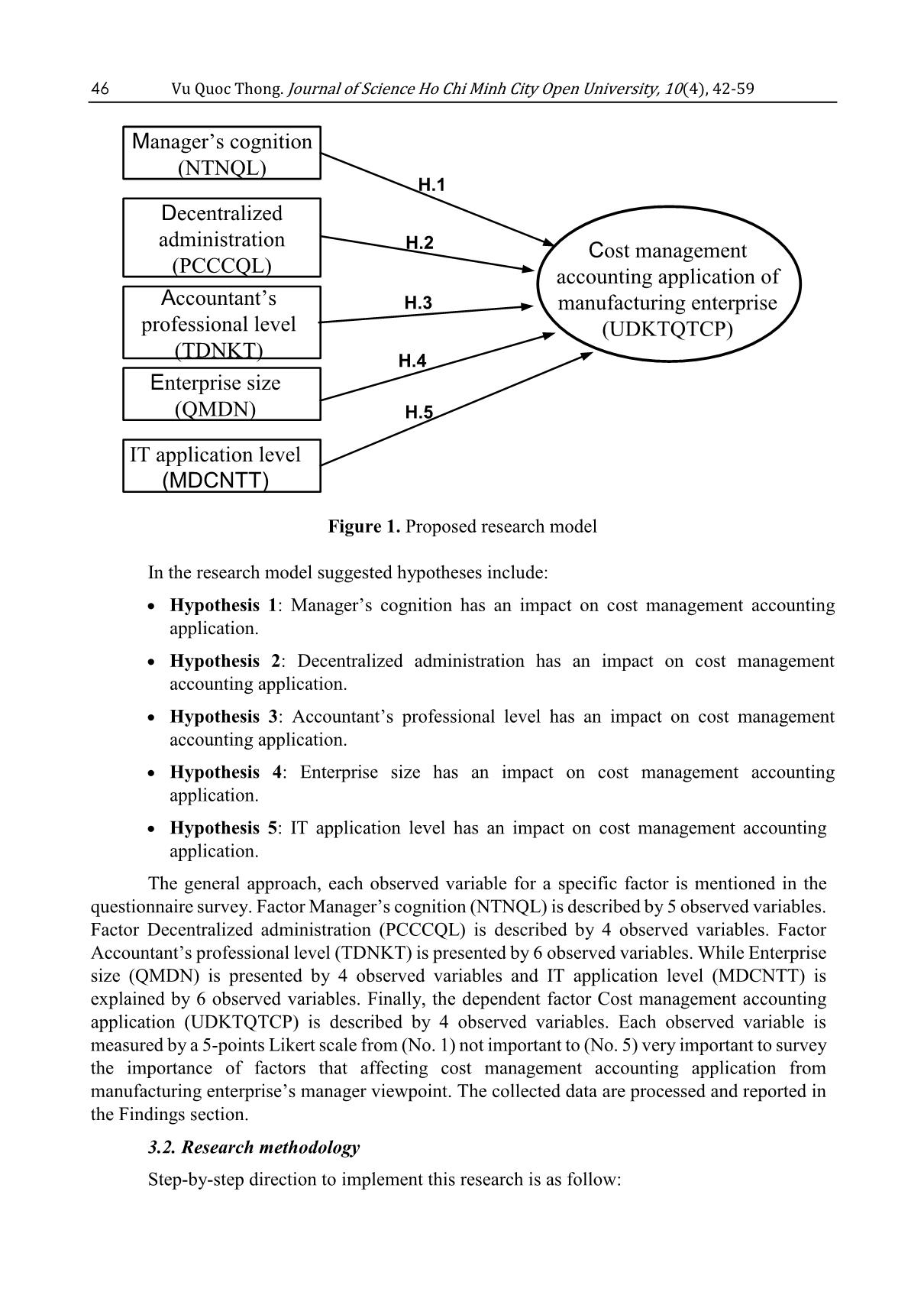
Factors affect cost management accounting application of manufacturing enterprises in Southern Vietnam
To identify factors affecting cost management accounting
application of manufacturing enterprises is a challenge. By
quantitative approach, we propose our research model and five
hypotheses. During the implementation, we surveyed 179
manufacturing enterprises in southern Vietnam. Then, the research
model is Cronbach Alpha tested, conducted exploratory factor
analysis, and run regression analysis to explain our proposed
hypothesis. The result indicates there are 26 variables from
Vietnamese manufacturing enterprise’s managers view grouped
into 5 factors affecting the cost management accounting
application. These factors are manager’s cognition, accountant’s
professional level, enterprise size, IT application level, and
decentralized administration. The paper conclusion progressively
paves the way for further researches on cost management
accounting application.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Factors affect cost management accounting application of manufacturing enterprises in Southern Vietnam

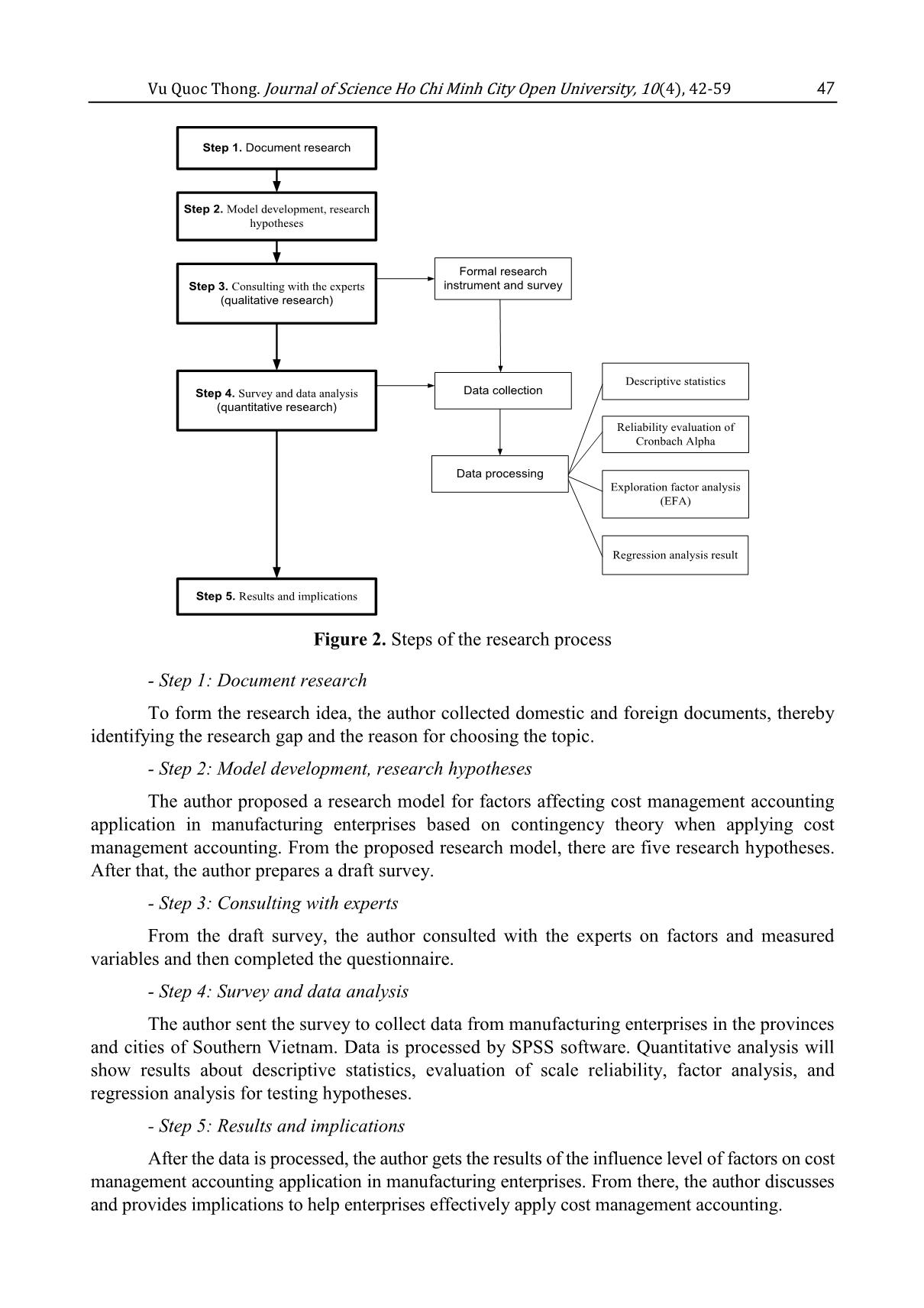
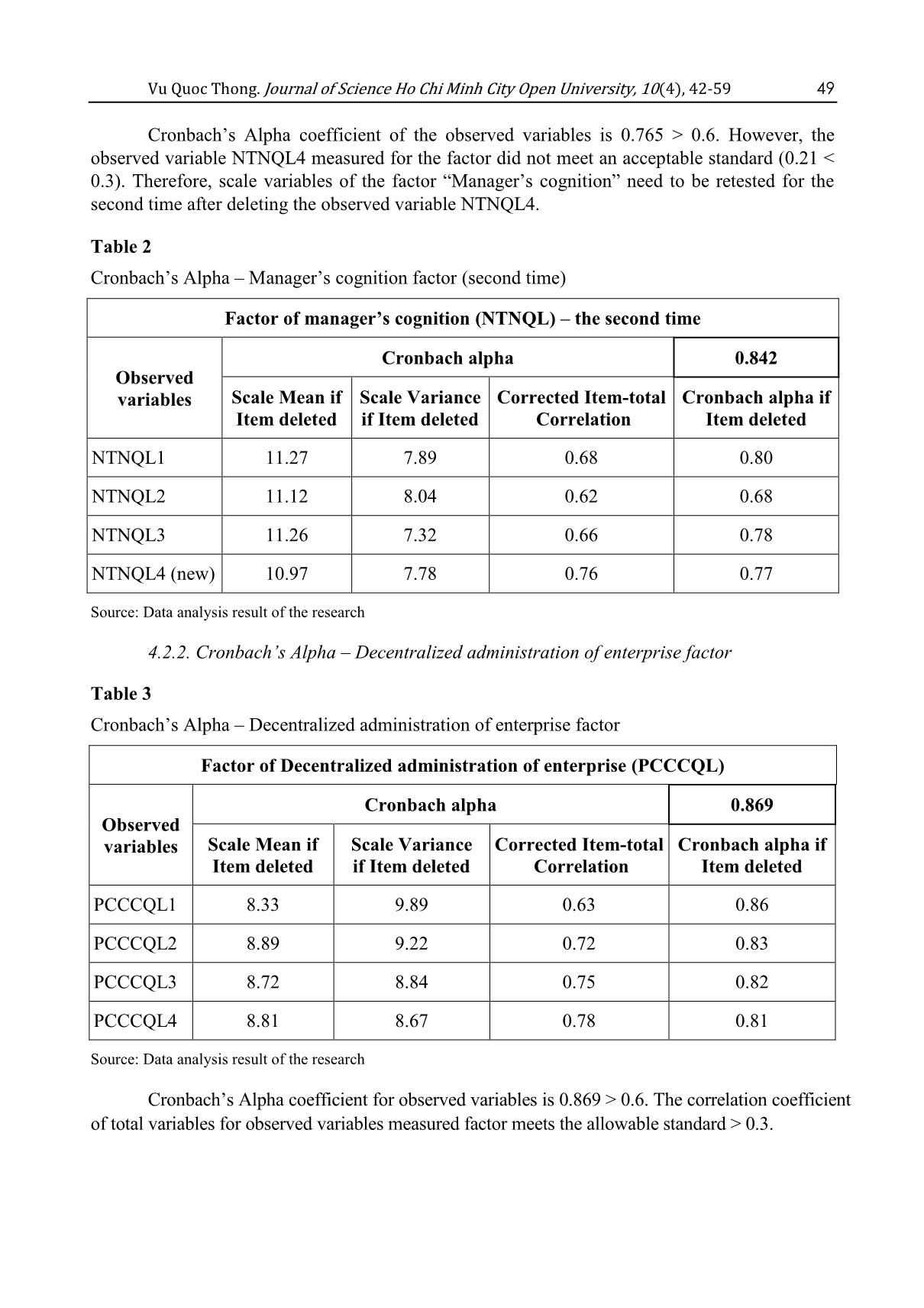
Table 13 Research model interpretation level Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimation Durbin- Watson 1 0.833 0.692 0.691 0.27203 1.72 Source: Data analysis result of the research Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 10(4), 42-59 55 R Square (R2) equals to 0.692. This means that 69.2% of cost management accounting application variation is interpreted by independent (affecting) factors. Based on the standardized regression coefficient (Table 12), the author confirms all research hypotheses: - The coefficient of factor NTNQL is 0.582 (+), therefore, it has a positive relationship with UDKTQTCP (H1). - The coefficient of factor TDNKT is 0.476 (+), therefore, it has a positive relationship with UDKTQTCP (H3). - The coefficient of factor QMDN is 0.453 (+), therefore, it has a positive relationship with UDKTQTCP (H4). - The coefficient of factor MDCNTT is 0.438 (+), therefore, it has a positive relationship with independent factor UDKTQTCP (H5). - The coefficient of factor PCCCQL is 0.336 (+), therefore, it has a positive relationship with independent factor UDKTQTCP (H2). 5. Conclusion and future research In a brief discussion, the research outcome includes descriptive statistics, reliability evaluation of Cronbach Alpha, exploration factor analysis (EFA), and regression analysis. After checking factor reliability for observed variables by Cronbach Alpha, the author excludes 2 variables (NTNQL4 and QMDN3) and retained 27 variables. Next, by conducting EFA method, the author obtains the consequence of 5 convergent independent factor groups and 1 dependent factor group shown in Table 11. There is an invalid variable (MDCNTT2). The rest of the 26 variables are continued to implement regression analysis to define the impacting level of each identified factor to cost management accounting application in manufacturing enterprises. The regression result indicates five (5) impacting factors with the decremental order as the bellow conclusion. 5.1. Conclusion and implication Research result shows 5 factors affecting cost management accounting application according to decreasing impact level as follow factor of manager’s cognition (0.582, rate of 25.47%), accountant’s professional level (0.476, rate of 20.83%), enterprise size (0.453, rate of 19.82%), IT application level (0.438, rate of 19.17%) and decentralized administration (0.336, rate of 14.70%). The selected independent factors interpret 69.2% of the variation for cost management accounting application. Based on the research result, the author proposes recommendations in an aim to assist manufacturing enterprise managers to apply cost management accounting effectively: - In term of manager’s cognition The author supposes that it is necessary to raise the manager’s cognition in the enterprise about the importance of cost management accounting application for decision making. Most managers in manufacturing enterprises in Vietnam remain thinking that financial accounting plays the main role in the accounting system. Therefore, manufacturing enterprises should facilitate managers to participate in courses and training programs related to cost management accounting application from reputable universities or invite experts from enterprises which successfully applying cost management accounting model to share experiences, thus enhancing cognition in practical aspect. - In term of the accountant’s professional level In a competitive economic environment and subject to the influence of Technology 56 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 10(4), 42-59 Industry 4.0, employees of cost management accounting must regularly update new knowledge and cost management accounting technique. Accountants are those who directly operate on the cost management accounting system, are considered as key personnel in the development and operation of cost management accounting. The author suggests that: - Periodically and regularly develop training plans to update knowledge and skills for accountants. Organizing training courses with clear goals to enhance and improve qualification following the practical needs of tasks based on current work and future application. - Depending on the specific cost management accounting tasks, the enterprise conducts designing an accountant evaluation form according to each assigned job completion criteria. - In term of enterprise size The small and medium-sized enterprises often have a “flat structure” so there are few obstacles in cost management accounting application. However, there is a weakness as the financial issue to organize a cost management accounting system consistent with the characteristics of a specific small-size manufacturing enterprise. The organizations with large- scale production and business will have high potential for financial resources, the number of accountants, and the capacity of modern IT applications. A difficulty for cost management accounting application in large-size enterprises is that they should pay attention to information exchange and accounting reporting needs at many administration levels with specific requirements on data from the cost management accounting system and set up more control procedures than small-size enterprises. Gordon and Miller (1976) noted that there is no single management accounting model is consistent with all manufacturing enterprises. As a result, cost management accounting application must be considered depending on size and each development stage of a specific enterprise. - In term of IT application level We acknowledge that data volume that the cost management accounting system in a manufacturing enterprise has to collect, process, and export reports is very large. Cost management accounting processing often requires a combination of many complex methods and techniques (Raphael & Artus, 2018). The author thinks that information technology infrastructure including networked computers, accounting software, or enterprise resource planning (ERP) is necessary for cost management accounting application, so: - Top management instructions in the enterprise are needed to raise the IT application level in accordance with each management level. - IT application level in an enterprise requires investment and infrastructure integration including computer configuration, network system - transmission line, and software. - Note that there are required pieces of training and supports of specialized software for accountants to be able to utilize the functions for the service of cost management accounting in the enterprise. - In term of decentralized administration Cost management accounting system can only work effectively if there is a clear assignment between organizational departments and the division of cost management accounting (Zimmerman, 2010). The author noted that depending on the characteristics of each enterprise, the appointment of powers will be different and if the enterprise decentralizes management structure too much, it can lead to reduce operational efficiency. In contrast, superficial decentralized Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 10(4), 42-59 57 management will result in difficulty to control and deciding responsibility for accounting data in coordination among departments throughout the organization. The author’s conclusions are similar to Colmenares (2009) that appropriate decentralized management leads to a positive impact on cost management accounting application in manufacturing enterprises. 5.2. Future research Firstly, this topic collects data to identify the factors affecting cost management accounting application in manufacturing enterprises in Southern Vietnam. However, the independent factors shown in the research model only interpret 69.2% of the variation in cost management accounting application. Therefore, there will be possibly other factors affecting cost management accounting application. This suspicion may lead to a future research direction to identify more unexplored impacting factors. Secondly, this study identifies the influence level of five (05) independent factors affecting cost management accounting application. However, the survey data form is only collected in a range of manufacturing enterprises over Ho Chi Minh City and several neighboring provinces. For the research model to be more general, upcoming researches are needed to conduct a survey at a nationwide level or expand the survey scope to Southeast Asia or Asia Pacific regions Lastly, when collecting data for the study, the author surveys according to the opinion of manufacturing enterprise managers about the importance of factors that affecting cost management accounting application. To consider the concept cost management accounting application in a variety of aspects, the author proposes more findings to explore cost management accounting application according to different stakeholder views, for example from the perception of accounting staff or consulting companies who conduct cost management accounting application services for clients References Bui, N. T. (2015). Factors affecting cost management accounting application in IT enterprises in the HCM City (Unpublished master’s thesis in Accounting). University of Economics and Finance, Vietnam. Chenhall, R. H. (2003). Management control systems design within its organizational context: Findings from contingency-based research and directions for the future. Accounting, Organizations and Society Journal, 28(1), 127-168. doi:10.1016/S0361-3682(01)00027-7 Colmenares, L. (2009). Benefits of ERP systems for accounting and financial management. Proceedings of the Academy of Information and Management Sciences, New Orleans, 13(1), 3-7. Doan, A. N. P. (2016). Factors affecting the use and consequences of management accounting practices in a transitional economy: The case of Vietnam. Journal of Economics and Development, 18(1), 54-73. doi:10.33301/2016.18.01.04 Etemadi, H., & Kazeminia, S. (2014). Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning systems (ERP) on management accountants. Management and Administrative Sciences Review, 3(4), 507-515. Godil, D. I., & Shabib-ul-Hasan, S. (2018). An investigation of a contingency framework of management accounting practices in manufacturing companies of Pakistan. Global Management Journal, 8(1), 53-64. Gordon, L. A., & Miller, D. (1976). A contingency framework for the design of accounting systems. Accounting, Organizations and Society Journal, 1(1), 59-69. 58 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 10(4), 42-59 Hair, J. F., Black, B., Babin, B., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2005). Multivariate data analysis (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. Hansen, D. R., & Mowen, M. M. (2006). Managerial accounting (8th ed.). Mason, OH: Thomson South-Western Publication. Hoang Trong & Chu, N. N. M. (2008). Research data analysis with SPSS (Vol. 2). Hanoi, Vietnam: Hong Duc Publishing House. Huynh, P. N. (2016). Completion of cost management accounting task at Scancom Vietnam manufacturing company (Unpublished master’s thesis in Accounting). University of Economics and Finance, Vietnam. James, A. H. (2019). Accounting information systems (10th ed.). Boston, MA: Cengage publication. Kanellou, A., & Spathis, C. (2011). Accounting benefits and satisfaction in an ERP environment. Paper presented 8th International Conference on Enterprise Systems, Accounting and Logistics: 8th ICESAL 2011, Thassos Island, Greece. La, D. X., Tran, N. T. V., & Tran, P. T. K. (2020). Factors affecting management accounting application in food processing enterprises at Ben Tre province. Industry and Trade Magazine, 1(3), 8-14. Le, B. T. N. (2017). Completion of cost management accounting task in seafood processing enterprises in Hau Giang province (Unpublished master’s thesis in Accounting). Lac Hong University, Vietnam. Mullins, L. (2013). Management and organizational behaviour (10th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: FT Publishing International. Nguyen, G. V. T. (2017). Factors affecting management accounting application in HCM City enterprises (Unpublished master’s thesis in Accounting). University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Nguyen, L. T. N. (2012). Organization of cost management accounting for freight in Vietnam road transport enterprises. Journal of Finance, 2(4), 17-25. Otley, D. T. (1980). The contingency theory of management accounting: Achievement and prognosis. Accounting, Organizations and Society Journal, 5(4), 413-428. doi:10.1016/0361-3682(80)90040-9 Pervan, I., & Dropulic, I. (2019). The impact of integrated information systems on management accounting: Case of Croatia. Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 24(1), 21-38. doi:10.30924/mjcmi.24.1.2 Pomberg, M., Pourjalali, H., Daniel, S., & Kimbro, M. B. (2012). Management accounting information systems: A case of a developing country in Vietnam. Asia-Pacific Journal of Accounting and Economics, 19(1), 100-114. doi:10.1080/16081625.2012.668060 Raphael, G., & Artus, K. G. (2018). Business intelligence and analytics cost accounting: A survey on the perceptions of stakeholders. Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 750-759. doi:10.24251/HICSS.2018.095 Talha, M., Raja, J. B., & Seetharaman, A. (2010). A new look at management accounting. Journal of Applied Business Research, 26(4), 83-96. doi:10.19030/jabr.v26i4.309 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 10(4), 42-59 59 Topor, D. I. (2013). New dimensions of cost type information for decision making in wine industry. Hyperion Economic Journal, Faculty of Economic Sciences, Hyperion University of Bucharest, Romania, 1(4), 109-127. Tran, H. T. T. (2014). Development of cost management accounting model in Vietnamese cement production enterprises. Journal of Accounting – Auditing, 3(2), 15-32. VCCI, Vietnam. (2018). Chỉ số hoạt động ngành sản xuất Việt Nam nhảy vọt dẫn đầu ASEAN [The index of Vietnam’s manufacturing activities jumped by the top of ASEAN]. Retrieved June 1, 2020, from https://www.vcci.com.vn/chi-so-hoat-dong-nganh-san-xuat-viet-nam- nhay-vot-dan-dau-asean Waterhouse, J. H., & Tiessen, P. (1978). A contingency framework for management accounting systems research. Accounting, Organizations and Society Journal, 2(4), 65-76. doi:10.1016/0361-3682(78)90007-7 Zimmerman, J. L. (2010). Accounting for decision making and control. Accounting organizations and Society Journal, 2(3), 28-40. doi:10.2308/iace.2011.26.1.258
File đính kèm:
 factors_affect_cost_management_accounting_application_of_man.pdf
factors_affect_cost_management_accounting_application_of_man.pdf

