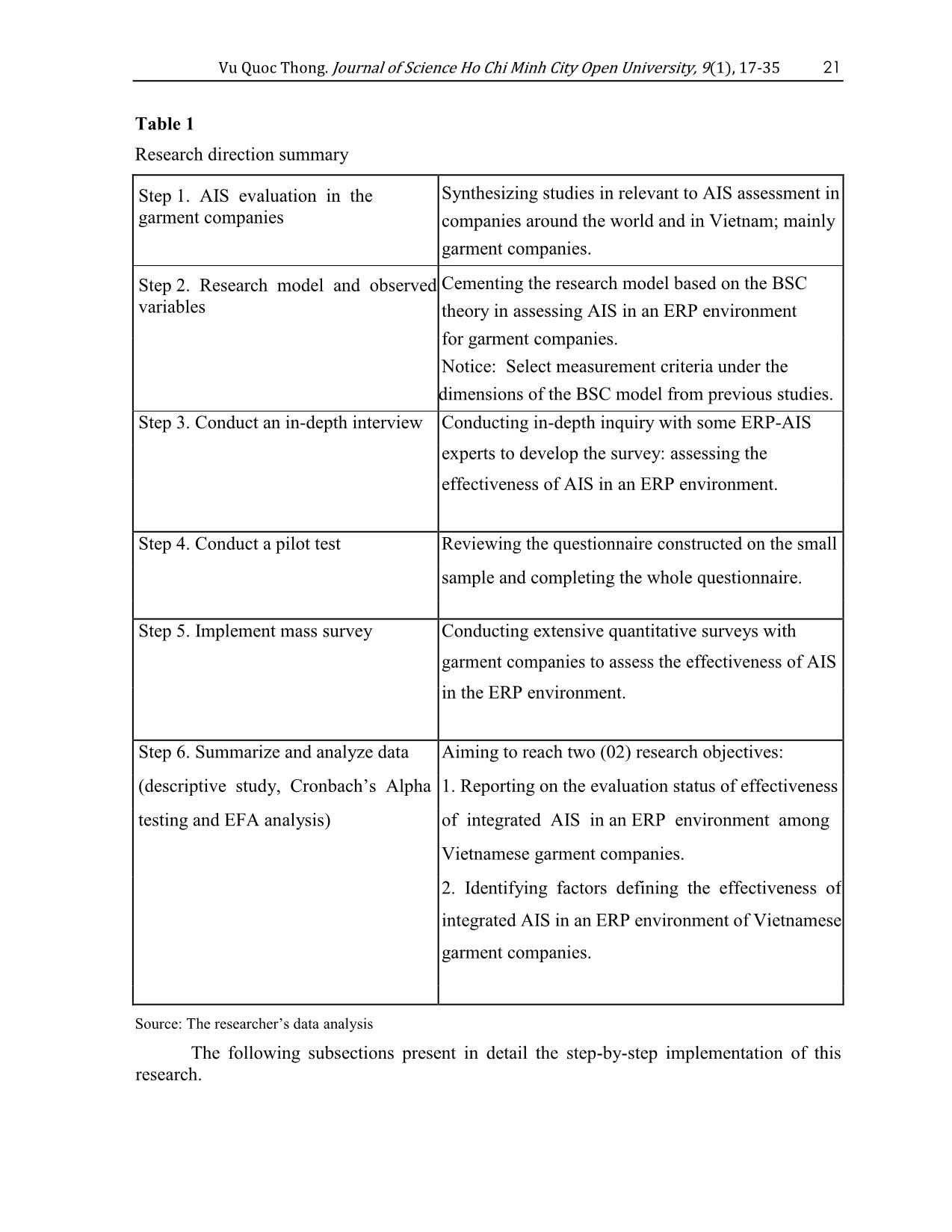
Evaluating the effectiveness of integrated accounting information Systems (AIS) in ERP environment of Vietnamese garment companies
Identifying factors defining the effectiveness of integrated
AIS in the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) environment is
really a challenging task. In our research, the effectiveness of
integrated AIS in ERP is presented in the form of a Balanced
Scorecard (BSC) model. This study analyzes data collected from
178 Vietnamese garment companies with AIS in an ERP
environment. Then, Cronbach’s Alpha test and Exploratory
Factor Analysis (EFA) are conducted to assess the reliability of
variables. The result identifies 28 variables from Vietnamese
garment companies’ managers view grouped into 4-dimensional
constructs of the BSC model that define the effectiveness of
integrated AIS in an ERP environment. The conclusion on
garment companies’ AIS evaluation factors paves the way for
future research on other Vietnamese industries’ AIS evaluation
in an ERP environment.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Evaluating the effectiveness of integrated accounting information Systems (AIS) in ERP environment of Vietnamese garment companies

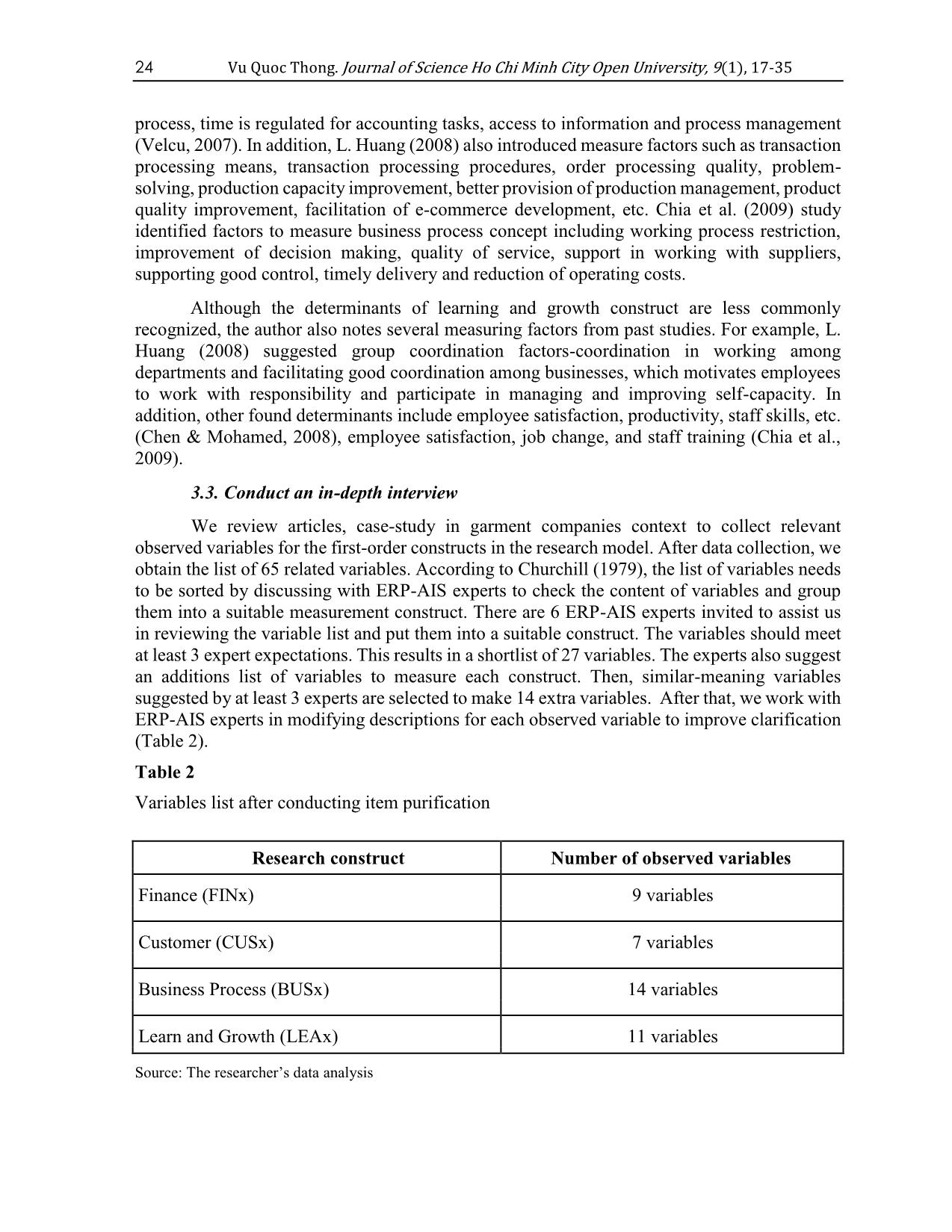
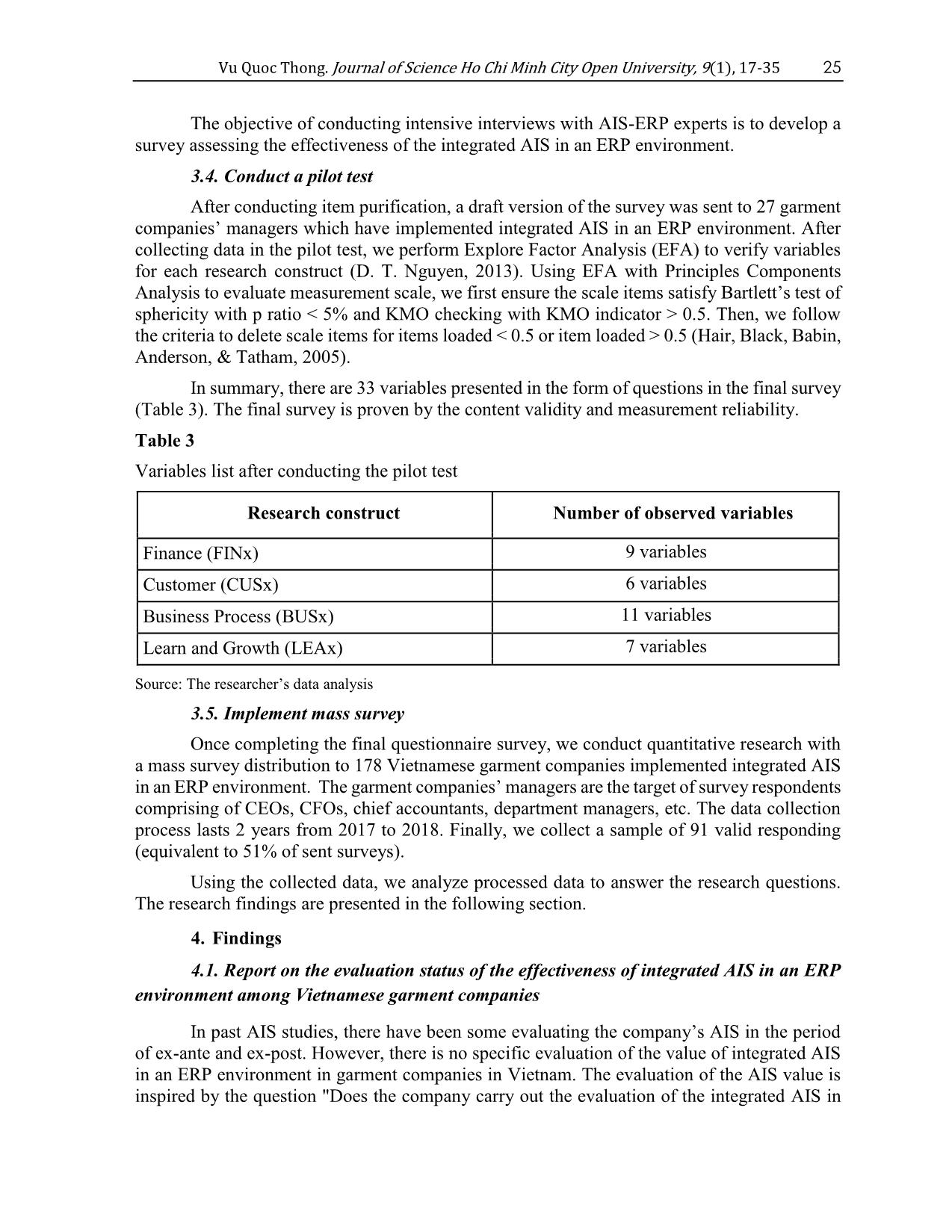
the business sector in the market 21.1262 7.353 0.608 LEA4 Encourage staff to actively solve problems 21.2393 7.485 0.594 LEA5 Allow employees to work independently 21.0436 7.658 0.592 LEA6 Support coordination among departments 21.0656 7.021 0.702 LEA7 Facilitate businesses to work with each other 20.8754 7.913 0.624 Source: Data analysis result of the research 4.2.2. Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) After Cronbach’s Alpha test, 30 observational variables were retained for further analysis of the EFA process. During the first EFA running, Minimize labor costs variable and Support for introducing new services variable presenting small load factors, respectively 0.389 and 0.378, were eliminated. The second EFA analysis outcome shows that the observational variables focused on 4 research constructs with the KMO = 0.827, which is satisfactory (Hair et al., 2005) (Table 8). Cronbach's Alpha No. of variables 0.837 7 30 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 9(1), 17-35 Table 8 Result of the EFA factor analysis No. Variables Research constructs Finance Customer Business Process Learning and Growth 01 FIN1 Increase business profits 0.833 02 FIN2 Increase Return on Equity (ROE) 0.812 03 FIN3 Increase sales revenue 0.775 04 FIN4 Minimize operating costs 0.754 05 FIN5 Increase Return on Investment (ROI) 0.747 06 FIN6 Increase Return on Assets (ROA) 0.722 07 CUS1 Support order delivery 0.801 Create better transaction value for 08 CUS2 customers 0.793 Support interactive services with 09 CUS3 customers 0.785 10 CUS4 Improve customer satisfaction 0.742 11 CUS5 Establish relationships with customers 0.708 12 CUS6 Improve the quality of customer service 0.694 13 BUS1 Improve productivity 0.812 14 BUS2 Restructure the working process 0.803 15 BUS3 Make changes in the working process 0.774 16 BUS4 Improve the quality of decision making 0.762 17 BUS5 Provide better production management 0.751 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 9(1), 17-35 31 No. Variables Research constructs Finance Customer Business Process Learning and Growth 18 BUS6 Support inventory management 0.738 19 BUS7 Improve management productivity 0.722 20 BUS8 Assist in working with suppliers 0.667 21 BUS9 Support for better control 0.657 22 LEA1 Improve employee motivation 0.802 Allow support services to be shared by all 23 LEA2 levels in businesses 0.797 Support the development of the business 24 LEA3 sector in the market 0.705 Encourage staff to actively solve 25 LEA4 problems 0.694 26 LEA5 Allow employees to work independently 0.656 27 LEA6 Support coordination among departments 0.649 Facilitate businesses to work with each 28 LEA7 other 0.573 Rotation: Promax with Kaiser Normalization; General variance deduction: 54.722 Bartlett test <0.05; KMO index = 0.827 Source: Data analysis result of the research By EFA analysis, the author retains 28 variables grouped by 4 research constructs of the BSC model (Figure 8). These are significant observation variables for evaluating the effectiveness of integrated AIS in ERP environments of Vietnamese garment companies from managers’ viewpoint. 5. Conclusions and future research Focusing on the evaluation of integrated AIS in an ERP environment from the managers’ viewpoint, this paper proposes a research model based on the BSC theory. The 32 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 9(1), 17-35 author (1) examine the status of assessing the effectiveness of integrated AIS in the ERP environment in Vietnamese garment companies and (2) identify the factors that determine the effectiveness of AIS in the ERP environment in such companies from managers’ view. The author studied to develop and test scales of four (04) BSC research constructs to determine the effectiveness of integrated AIS in ERP environments in Vietnamese garment companies. The results of the study presented the evaluation status of the effectiveness of integrated ERP-AIS in Vietnamese garment companies. Furthermore, based on the BSC theory model with four research constructs, the author has published 28 significant factors for assessing the effectiveness of integrated AIS in the ERP environment in Vietnamese garment companies from managers’ viewpoint (Figure 8). Hopefully, the initial results of this paper would become a reliable reference for future research in the field of integrated AIS in an ERP environment in Vietnam in the garment and other industries as well. In addition, more research must be done on the evaluation of integrated AIS’s effectiveness from the perspective of other stakeholders including AIS academic researchers, ERP-AIS solution providers and so on. References Ballantine, J. A., Galliers, R. D., & Stray, S. J. (1996). Information systems/technology evaluation practices: Evidence from UK organizations. Journal of Information Technology, 11(2), 129-141. doi:10.1177/026839629601100204 Bhagwat, R., & Sharma, M. K. (2007). Performance measurement of supply chain management: A balanced scorecard approach. Journal of Computers and Industrial Engineering, 53(1), 43-62. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2007.04.001 Blundell, B., Sayers, H., & Shanahan, Y. (2003). The adoption and use of the Balance Scorecard in New Zealand: A survey of the top 40 companies. Journal of Pacific Accounting Review, 15(1), 49-74. doi:10.1108/eb037971 Bryant, L., Jones, D. A., & Widener, S. K. (2004). Managing value creation within the firm: An examination of multiple performance measures. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 16(1), 107-131. doi:10.2308/jmar.2004.16.1.107 Carr, N. G. (2003). IT doesn’t matter. Harvard Business Review Journal, 81(5), 41-49. Chanopas, A., Krairit, D., & Khang, D. B. (2006). Managing information technology infrastructure: A new flexibility framework. Management Research News, 29(10), 632- 651. doi:10.1108/01409170610712335 Chen, L., & Mohamed, S. (2008). Contribution of knowledge management activities to organizational business performance. Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology, 6(3), 269-285. doi:10.1108/17260530810918289 Chia, A., Goh, M., & Hum, S.-H. (2009). Performance measurement in supply chain entities: Balanced scorecard perspective. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 16(5), 605- 620. doi:10.1108/14635770910987832 Chriyha, A., Beidouri, Z., & Bouksour, O. (2012). Proposal of a performance model based on the Balance Scorecard for the Moroccan textile industry. The International Journal of Computer Science Issues, 9(5), 410-417. Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 9(1), 17-35 33 Churchill, G. A., Jr. (1979). A paradigm for developing better measures of marketing constructs. Journal of Marketing Research, 16(1), 64-73. doi:10.2307/3150876 Coyne, J. G., Coyne, E. M., & Walker, K. B. (2017). Accountant and tech: A game changer? Strategic Finance Journal, 98(9), 40-47. Dao, V. T. (2002). Organizing public accounting system under computerized condition (Doctoral dissertation). Vietnamese Financial Institution, Vietnam. Dunn, S. C., Seaker, R. F., & Waller, M. A. (1994). Latent variables in business logistics research: Scale development and validation. Journal of Business Logistics, 15(2), 145- 172. Farbey, B., Land, F., & Targett, D. (1992). Evaluating investments in IT. Journal of Information Technology, 7(2), 109-122. doi:10.1057/jit.1992.16 Felice, F., D., & Petrillo, A. (2013). Key success for organizational innovation in the fashion industry. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 5(1), 27-36. doi:10.5772/56882 Gimžauskienė, E., & Klovienė, L. (2014). Development of accounting system according to an information technology. Review of Economic Studies and Research, 7(2), 59-74. Greenspan, A. (2000). Technology innovation and its economic impact. A speech before the National Technology Forum, St. Louis, Missouri via teleconference. Retrieved October 3, 2018, from Federal Reserve Board of Governors, Washington, D.C. website: https://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2000/20000407.htm Grembergen, W. V., & Haes, S. D. (2005). Measuring and improving IT governance through the balanced scorecard. Information Systems Control Journal, 2(1), 1-8. Grembergen, W. V., & Haes, S. D. (2017). Introduction to IT governance and its mechanisms minitrack. Paper presented at Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, USA. Hackman, D., Gundergan, S. P., Wang, P., & Daniel, K. (2006). A service perspective on modeling intentions of on-line purchasing. Journal of Services Marketing, 20(7), 459- 470. doi:10.1108/08876040610704892 Hair, J. F., Black, B., Babin, B., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2005). Multivariate data analysis (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. Hitt, M. A. (1988). The measuring of organizational effectiveness: Multiple domains and constituencies. Management International Review, 28(2), 28-40. doi:10.2307/40227880 Hoque, Z., & Wendy, J. (2000). Linking Balance Scorecard measures to size and market factors: Impact on organization performance. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 12(3), 1-17. doi:10.2308/jmar.2000.12.1.1 Huang, L. (2008). Strategic orientation and performance measurement model in Taiwan’s travel agencies. Service Industries Journal, 28(10), 1357-1383. doi:10.1080/02642060802250179 Huang, S. M., Lee, C.-L., & Kao, A.-C. (2006). Balancing performance measures for information security management: A balanced scorecard framework. Industrial 34 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 9(1), 17-35 Management and Data Systems Journal, 106(2), 242-255. doi:10.1108/02635570610649880 Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P. (1992). The balanced scorecard - Measures that drive performance. Harvard Business Review, 70(1), 71-79. Retrieved October 15, 2018, from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/13177691_The_Balance_Scorecard- Measures_That_Drive_Performance Lee, J., Kao, H.-A., & Yang, S. (2014). Service Innovation and Smart Analytics for Industry 4.0 and Big Data Environment. The 6th CIRP Conference on Industrial Product-Service Systems, Procardia CIRP, 16, 3-8. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2014.02.001 Lin, C., & Pervan, G. (2003). The practice of IS/IT benefits management in large Australian organizations. Information and Management Journal, 41(1), 13-24. doi:10.1016/S0378- 7206(03)00002-8 Luftman, J., & Brier, T. (1999). Achieving and sustaining business-IT alignment. California Management Review, 42(1), 109-122. doi:10.2307/41166021 MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, P. M., & Jarvis, C. B. (2005). The problem of measurement model misspecification in behavioral and organisational research and some recommended solutions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(4), 710-730. doi:10.1037/0021- 9010.90.4.710 Maqbool, M. H. (2015). A consolidated model of putting BSC into action textile industry in Pakistan. Science and Technology Journal, 6(2), 14-22. Nguyen, B. L. (2013). Identifying and controlling the accounting information quality in ERP- applied environment in Vietnamese enterprises (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Nguyen, D. H. (2011). Organizing accounting information systems under IT-applied conditions in Vietnamese import-export enterprises (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). National Economics University, Vietnam. Nguyen, D. T. (2013). Giáo trình phương pháp nghiên cứu khoa học trong kinh doanh – Tập 2 [Research methodology in business textbook (2nd ed.)]. University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City: NXB Tài chính. Nguyen, H. D. (2012). Improving accounting information systems for Vietnamese public universities (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). National Economics University, Vietnam. Palvia, P. C., Perkins, J. A., & Zeltmann, S. M. (1992). The PRISM system: A key to organizational effectiveness at Federal Express Corporation. MIS Quarterly, 16(3), 277- 292. doi:10.2307/249529 Park, J. H., Lee, J. K., & Yoo, J. S. (2005). A framework for designing the balanced supply chain scorecard. European Journal of Information Systems, 14(4), 335-346. doi:10.1057/palgrave.ejis.3000544 Petter, S., DeLone, W., & McLean, E. R. (2012). The past, present, and future of “IS Success”. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 13(5), 341-362. doi:10.17705/1jais.00296 Vu Quoc Thong. Journal of Science Ho Chi Minh City Open University, 9(1), 17-35 35 Santhanam, R., & Hartono, E. (2003). Issues in linking information technology capability to firm performance. MIS Quarterly, 27(1), 125-153. doi:10.2307/30036521 Seddon, P. B., Graeser, V., & Willcocks, L. P. (2002). Measuring organizational IS effectiveness: An overview and update of senior management perspectives. Database for Advances in Information Systems Journal, 33(2), 11-28. doi:10.1145/513264.513270 Silk, J. (1998). Caring at a distance. Journal of Philosophy and Geography, 1(2), 165-182. doi:10.1080/1366879X.1998.11644226 Sohal, A. S., & Ng, L. (1998). The role and impact of information technology in Australian business. Journal of Information Technology, 13(3), 201-217. doi:10.1080/026839698344846 Suanmali, S., Karabay, G., & Kurumer, G. (2011). A study of business performance through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Thai garment industry. Paper presented at the 5th International Congress on Logistics and SCM systems, Seoul, Korea, 2011. Sundin, L., Hochwälder, J., & Bildt, C. (2008). A scale for measuring specific job demands within the health care sector: Development and psychometric assessment. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 45(6), 914-923. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2007.03.006 Taipaleenmäki, J., & Ikaheimo, S. (2013). On the convergence of management accounting and financial accounting - The role of information technology in accounting change. International Journal of Accounting Systems,14(4), 321-348. Tran, P. (2007). Solutions for improving the quality of accounting software usage in Vietnamese enterprises (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Velcu, O. (2007). Exploring the effects of ERP systems on organizational performance: Evidence from finnish companies. Industrial Management and Data Systems Journal, 107(9), 1316-1334. doi:10.1108/02635570710833983 VIRAC Vietnam. (2018). Báo cáo tiêu chuẩn ngành dệt may Việt Nam [Report on Vietnam's garment industry standards]. Retrieved October 15, 2018, from ttp://viracresearch.com/industry/bao-cao-tieu-chuan-nganh-det-may-viet-nam-q22018.
File đính kèm:
 evaluating_the_effectiveness_of_integrated_accounting_inform.pdf
evaluating_the_effectiveness_of_integrated_accounting_inform.pdf

