Determinants of accounting information systems quality: Empirical evidence from Vietnam
This research is conducted to investigate the factors affecting the accounting information systems quality. Data was collected by using questionnaire delivered to 347 participants who are board of director’s members and managers. The statistical methods approaches are employed to address the research issues including Explanatory Factor Analysis (EFA) and Ordinary Least Squares (OLS). The findings showed that various factors had significant impacts on the accounting information systems quality including (i) organization culture, (ii) manager participation, (iii) information technology, (iv) information technology knowledge of managers, (v) accounting knowledge of managers, (vi) accounting information applications, (vii) consultation of external experts and (viii) training activities for users in accounting information systems. Based on the research results, some key intuitive recommendations were proposed aiming to improve the accounting information systems quality of Vietnamese Enterprises

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Determinants of accounting information systems quality: Empirical evidence from Vietnam

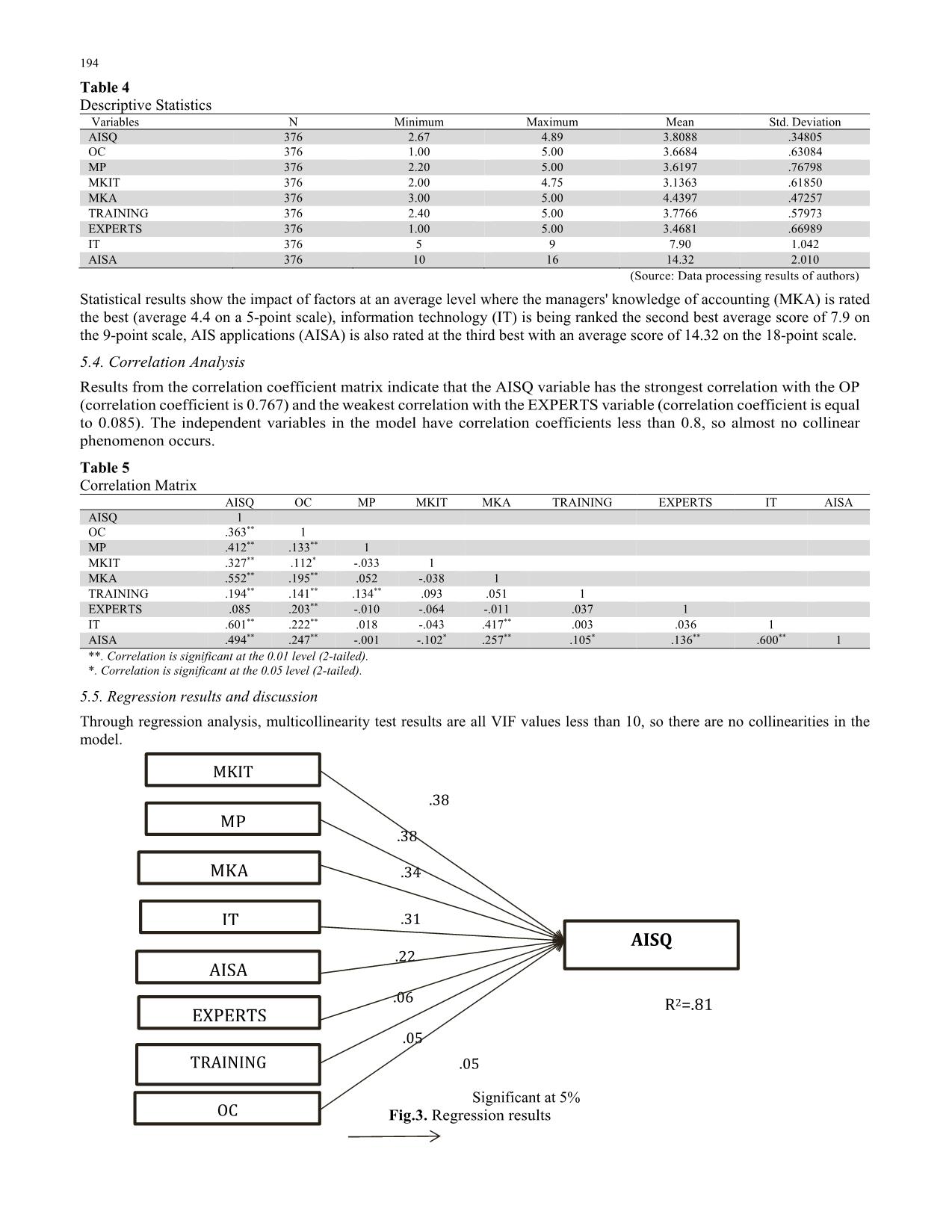
, experts (EXPERTS) and user training (TRAINING), managers’ accounting knowledge (MKA), managers' IT knowledge (MKIT), information technology (IT), and participation of managers (MP) were statistically significant at 5% level to the quality of accounting information 196 systems. These factors explain up to 81% of the fluctuations in the quality of accounting information systems (R2 value = 81%). Among those influential factors, manager IT knowledge (MKIT), information technology, management participation (MP), manager accounting knowledge (MKA) were the most powerful factors. Regression coefficient value of MKIT, MKA and MP are 0.38; 0.38 and 0.34 respectively. This study complements previous research by having supported this association within Vietnamese context. Further studies may replicate this study to enhance the external validity of the results. 6.2. Recommendations From the research results drawn above, the authors make the following suggestions to improve the quality of accounting information systems for companies listed on the stock exchange in Vietnam as follows: Firstly, fostering knowledge on accounting for managers. Being a manager, it is necessary to have clear understanding of the business activities. Accounting is the language of business and from this research result, accounting knowledge is the most important element of AIS quality. Therefore, managers need to have good knowledge of accounting in order to know the business situation, from which they can run a good business operation and bring high profits to the business. Managers need to acquire sufficient accounting knowledge. Company should also have policies that encourage managers to take short accounting courses with topics relevant to the business management like managerial accounting, tax accounting, internal control, etc. so that the manager will be proactive in managing the accounting information system. Secondly, enhancing information technology knowledge for managers. The knowledge is viewed as the primary determining factor of organizational success and is considered the foundation of competitive advantage. Manager should learn basic knowledge of computer science, software technology, computer engineering, information systems, computer and communications networks, and network information security. In addition, the specialized knowledge should be provided such as: research, development, processing or application of software systems; design, construction, installation, operation and maintenance of hardware and software components of computer systems and computer-based equipment systems; computer networks and communications. Thirdly, invest in innovation and application of modern information technology at companies. Firms with extensive resources may gain a competitive edge by deploying IT in support of or to strengthen their business (King et al., 1989). Information technology includes computers and computer software to convert, store, protect, process, transmit and collect information in order to develop the ability to repair, create and systems devices to provide information processing solutions based on personal and organizational technology required. Fourth, promote the participation of managers in all stages of work to develop the accounting information system. Managers should participate regularly and continuously in all jobs to build, operate and develop the system such as determining the need of developing accounting information systems and controlling information system. The involvement of managers in the planning, construction and operation of accounting information systems is both motivating, encouraging employees' work and supervising to system operate effectively. Fifth, open training classes for users of accounting information systems. The users of the accounting information system are quite diverse, including accountants, sales staff, production department, and material supply staff. The employees in the system need to understand their responsibilities in the system and the relationship between their work and the work of others in the system. The irresponsibility or carelessness of a person in the system seriously affects the operation of the system. Therefore, the training needs to be conducted periodically to ensure that all people in the system are proficient in using the system, updating the system's new points to make the system operate smoothly and bring high efficiency. Finally, recruitment of information technology qualified personnel As a graduate of Information technology who qualified can become a software developer that directly creates the software products, quality control of software that directly testing the quality of products created by the programmer, analyst system design, data management, network management, computer hardware engineering and specialist in management and coordination of information technology projects. References Alnajjar, M. (2016). Impact of Accounting Information System on Organizational Performance: A Study of Small and Mid- Sized Enterprises in UAE. International Journal of Accounting Research, 4(1),1-7. Azhar Susanto. (2008). Sistem Informasi Akuntansi. Struktur-Pengendalian Resiko-Pengembangan. Bandung: Lingga Jaya. H. Thanh Nguyen and A. Huu Nguyen /Accounting 6 (2020) 197 Berry, J.A., Sweeting, R. and Goto, J. (2006). The Effects of Business Advisers on the Performance of SMEs. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 13(1), 33-47. Bodnar, G.H., & dan Hopwood,W.S. (2010). Accounting Information Systems. Ninth Edition. USA: Pearson Education, Inc Breen, J., Sciulli, N., & Calvert, C. (2004). The role of the external accountant in small firms. Small Enterprise Research, 12(1), 5-14. Chang, C.-S., Chen, S.-Y., & Lan, Y.-T. (2012). Motivating medical information system performance by system quality, service quality, and job satisfaction for evidence based practice. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 12(135), 1–12. Choe, J.M. (1998). The Effects of User Participation on design of Accounting Information System. Information and Management, 34, 185-198 Chan, Y., Huff, S., Barclay, D., and Copeland, D. (1997). Business Strategic Orientation, Information Strategic Organization, and Strategic Alignment. Information Systems Research, 8(2), 125-150. Davis, M. (1997). Transforming your firm: Tools for successful technology consulting. The Practical Accountant, 30(8), S-3. Dessler, G. (2013). Fundamentals of human resource management. Pearson. Fitrios, R. (2016). Factors that influence accounting information system implementation and accounting information quality. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 5, 193-198. Foong, S.Y. (1999). Effect of end-user personal and systems attributes on computer-based information system success in Malaysian SMEs. Journal of Small Business Management, 37(3), 81-87. Grande, E. U., Estébanez, R. P., & Colomina, C. M. (2011). The impact of Accounting Information Systems (AIS) on performance measures: empirical evidence in Spanish SMEs. The international journal of digital accounting research, 11(1577-8517), 25-43. Gullkvist, B. (2002). Towards Paperless Accounting and Auditing. E-Business Research Center, Finland. Guinea, AO, Kelley, H & Hunter, MG. (2005). Information system effectiveness in small business: Extending a Singaporean model in Canada. Journal of Global Information Management, 13(3), 55-70. Hair, J., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Upper saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education International. Heidmann, M., Schäffer, U., & Strahringer, S. (2008). Exploring the role of management accounting systems in strategic sensemaking. Information Systems Management, 25(3), 244–257. Hla, D., & Teru, S.P. (2015), Efficiency of accounting information system and performance measures. International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research, 3, 976 984. Huber, G. P. (1990). A theory of the effects of advanced information technologies on organizational design, intelligence, and decision making. Academy of Management Review, 15(1), pp. 47-71. Hussin, H., King, M., & Cragg, P. (2002). IT alignment in small firms. European Journal of Information Systems, 11(2), 108- 127. Haddad & Atmeh. (2009). Accounting information system (1st Ed.). Amman: Al Mareekh. Hurt, R. L., & Zhen, F. (2008). Accounting information systems: Basic concepts and current issues. McGraw-Hill Irwin. Hartcher, J. (2003). Small Business Survey Program: Financial Management. Insolvency and Fraud, CPA Australia. Igbaria, M., Zinatelli, N., Cragg, P.B., & Cavaye, A.L.M. (1997). Personal computing acceptance factors in small firms: A structural equation model, MIS Quarterly, 21(3), 279-305. Ismail, N.A (2009). Factors influencing AIS effectiveness among manufacturing SMEs: Evidence from Malaysia. The Electronic Journal on Information Systems in Developing Countries, 38(10), 1-19. Ismail, N. A., & King, M. (2014). Factors influencing the alignment of accounting information systems in small and medium sized Malaysian manufacturing firms. Journal of Information Systems and Small Business, 1(1-2), 1-20. Jarvenpaa, S. L., & Ives, B. (1991). Executive involvement and participation in the management of information technology. MIS quarterly, 15(2), 205-227. Kouser, R., Awan, A., Rana, G., & Shahzad, F. (2011). Firm size, leverage and profitability: Overriding impact of accounting information system. Journal of Management and Business Review, 1(10), 58-64. Kaplan, R.S., & Atkinson, A.A. (1998). Advanced management accounting (3rd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall International. Kharuddin, S., Ashhari, Z., and Nassir, A., (2010). Information systems and firm’s performance: The case of Malaysian small medium enterprises, International Business Research, 3(4), 28-35. King, W. R., Grover, V., & Hufnagel, E. H. (1989). Using information and information technology for sustainable competitive advantage: some empirical evidence. Information & Management, 17(2), 87-93. Laudon, K.C., & Laudon, J.P. (2007). Management Information Systems Managing The Digital Firm. 10th Edition. Pearson Prentice Hall. McShane, S.L., & Glinow, M.A.V. (2010). Organizational behavior: Emerging knowledge and practice for the real world (5th ed.). New York: Mc Graw Hill. Napitupulu, I.H. (2018). Organizational culture in management accounting information system: Survey on state-owned enterprises (SOEs) Indonesia. Global Business Review, 19, 556-571. Nwinee, K., Akpos, Y., Vincent, N., & Ibinabo, T. (2016). Impact of accounting information system on organizational effectiveness: A study of selected small and medium scale enterprises in Woji, Portharcourt. International Journal of 198 Research, 3(1), 974-982. Nabizadeh, S.M., & Omrani, S.A. (2014). Effective factors on accounting information system alignment; A step towards organizational performance improvement. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 4(9), 1-5. Onaolapo, A.A., Odetayo, T.A. (2012). Effect of accounting information system on organisational effectiveness: A case study of selected construction companies in Ibadan, Nigeria. American Journal of Business and Management, 1(4), 183 189. O’Brien, J.A. (2004). Management Information Systems: Managing Information Technology in the Networked Enterprise 6th- Edition. NewYork: Mc Graw Hill Companies,Inc Ong, C.S., Day, M.Y., & Hsu, W.L. (2009). The measurement of user satisfaction with question answering systems. Information and Management, 46(7), 397–403. Piccoli, G. (2008). Information Systems for Managers: Text & Cases. USA: John Wiley & Sons,Inc Rapina. (2014). Factors influencing the quality of accounting information system and its implications on the quality of accounting information. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting, 5(2), 148-154. Raymond, L., & Pare, G. (1992). Measurement of information technology sophistication in small manufacturing businesses, Information Resources Management Journal, 5(2), 4-16. Rehab, U. (2018). The impact of accounting information systems on organizational performance: The context of Saudi’s SMEs. International Review of Management and Marketing, 8(2), 69-73. Romney, M. B., & Steinbart, P. J. (2015). Accounting Informations Systems. Thierteenth Edition. Pearson Education Limited. Robbins, S.P., & Judge, T.A. (2011). Organizational Behavior (14ed). Pearson education, Prentice Hall, UPPER Saddle, NJ. Schein, E.H. (2010). Organizational Culture and Leadership. 4th ed. San Fransisco: Jossey Bass-A Wiley Imprint. Soudani, S.N. (2012). The usefulness of an accounting information system for effective organizational performance. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 4(5), 136 140. Stair, R.M., & Reynolds, G.W. (2010). Principles of information systems (9th ed.). Boston, MA: Course Technology. Stair, R.M. & Reynolds, G.W. (2012). Information systems. Melbourne: Course Technology; Cengage Learning. Sajady, H., Dastgir, M., & Hashemnejad. (2008). Evaluation of the effectiveness of accounting information systems. International Journal of Information Science & Technology, 6(2), 49-59 Saeidi (2014). The impact of accounting information systems on financial performance – a case study of TCS – India. Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life, 4(4), 412-417 Tamoradi, F. (2014). Factors influencing the alignment of accounting information systems of accepted manufacturing firms in Tehran Stock Exchange. International Journal of Industrial Engineering Computations, 4(3). Thapayom, A., & Ussahawanitchakit, P. (2015). Accounting information system excellence and goal achievement: evidence from information and communication technology businesses in Thailand. The Business and Management Review, 6th International Trade and Academic Research Conference (ITARC), 9-10 November 2015, UK, 7(1), 309-321 Thong, J.Y.L., Yap, C.S., & Raman, K.S. (1996). Top management support, external expertise and information systems implementation in small businesses. Information Systems Research, 7(2), 248-267. Yap, C.S. and Thong, J.Y.L. (1997). Programme Evaluation of a Government Information Technology Programme for Small Businesses, Journal of Information Technology, 12, 107-120. Wilkinson, J. W. (2000). Accounting and information systems. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Wixom, B.H., & Todd, P.A. (2005). A theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology acceptance. Information Systems Research, 16(1), 85–102 © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science, Canada. This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (
File đính kèm:
 determinants_of_accounting_information_systems_quality_empir.pdf
determinants_of_accounting_information_systems_quality_empir.pdf

