Bài giảng Quality & testing software requirement concepts & process - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Trúc
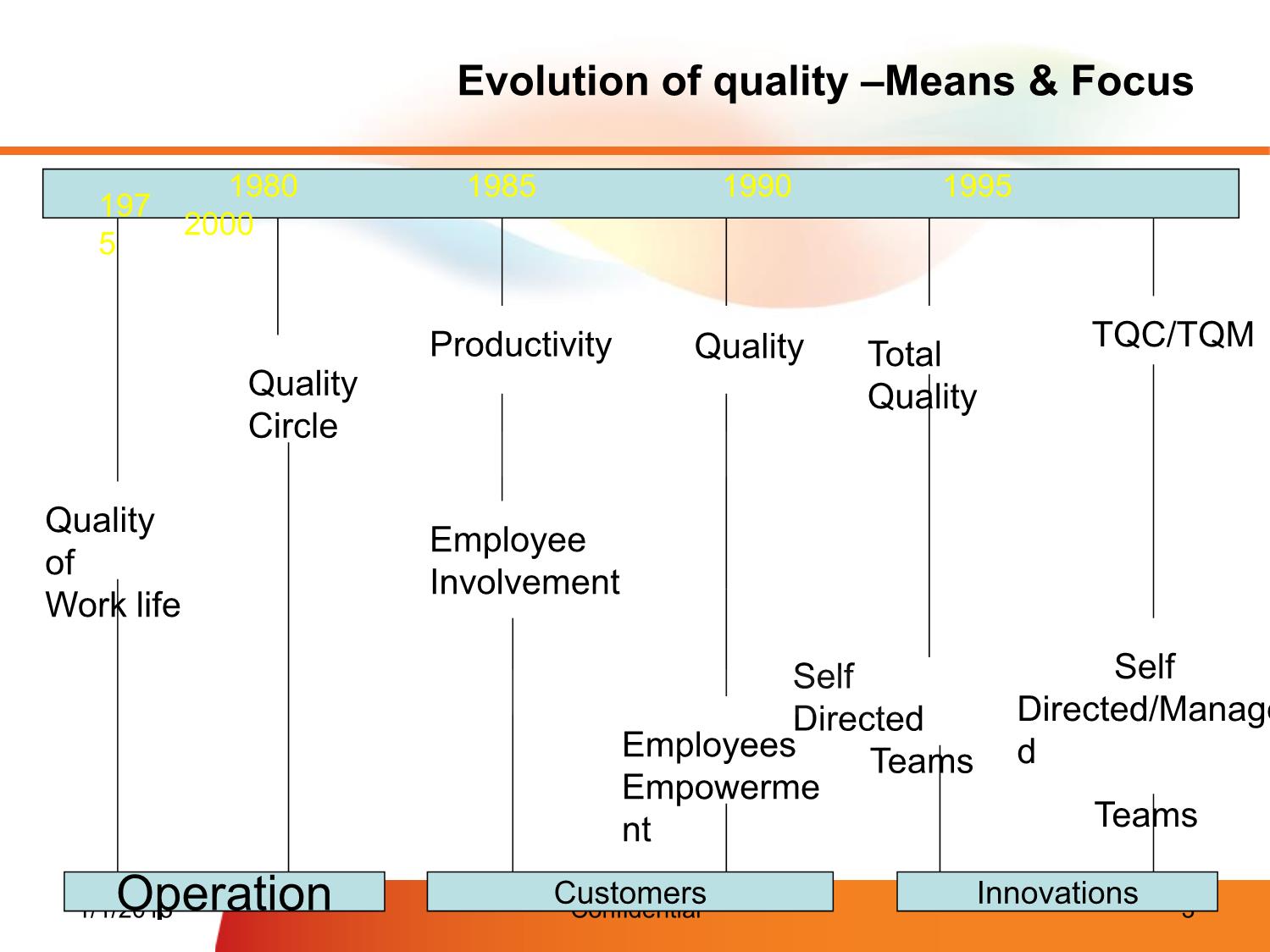
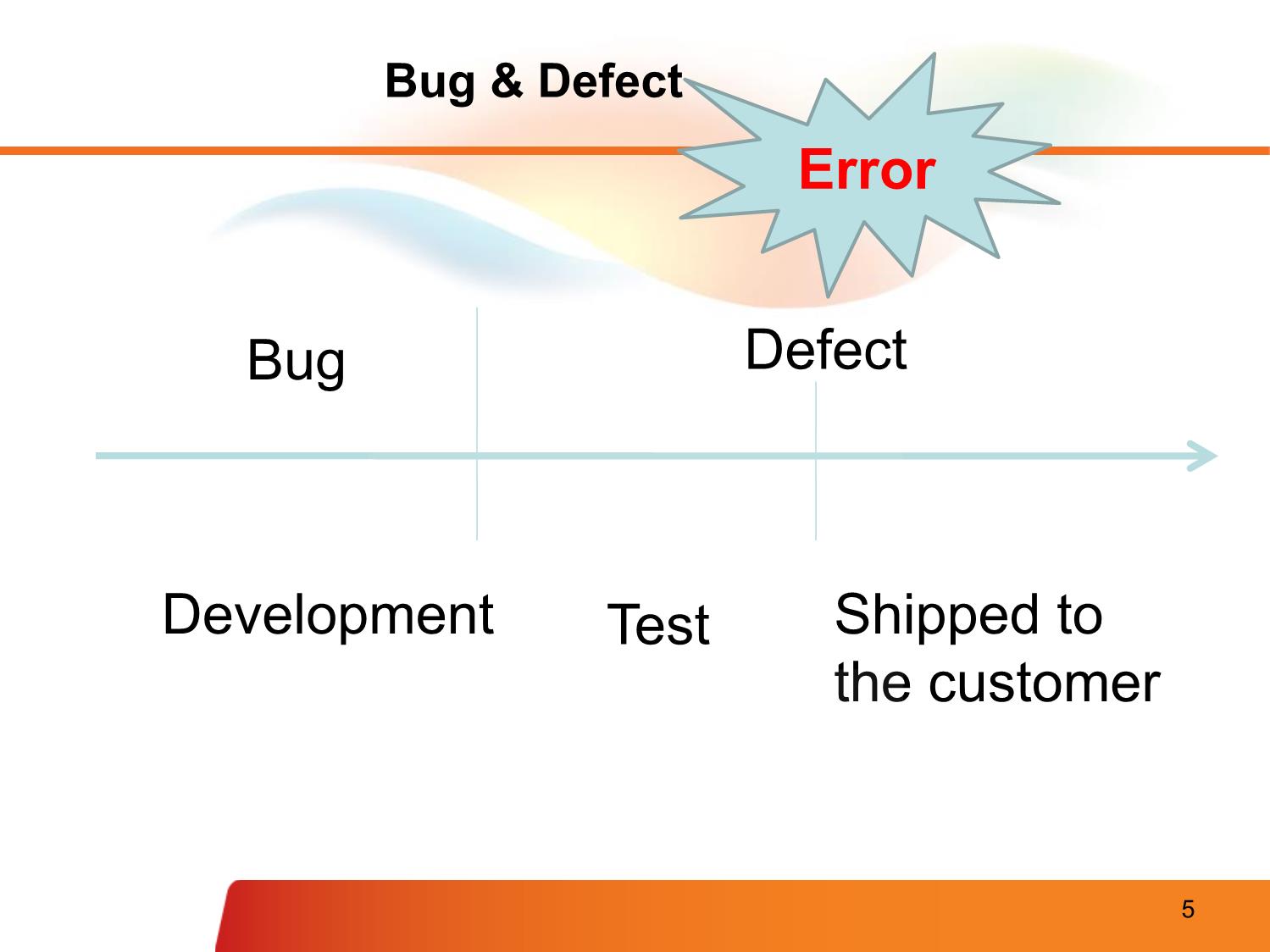
1. Quality & Testing
2. Requirement Concepts
3. Fsoft Requirement Process
4. Requirement Clarifying
5. Requirement Modeling
6. Modeling Tools
7. Common practices, problems

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Quality & testing software requirement concepts & process - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Trúc", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Quality & testing software requirement concepts & process - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Trúc

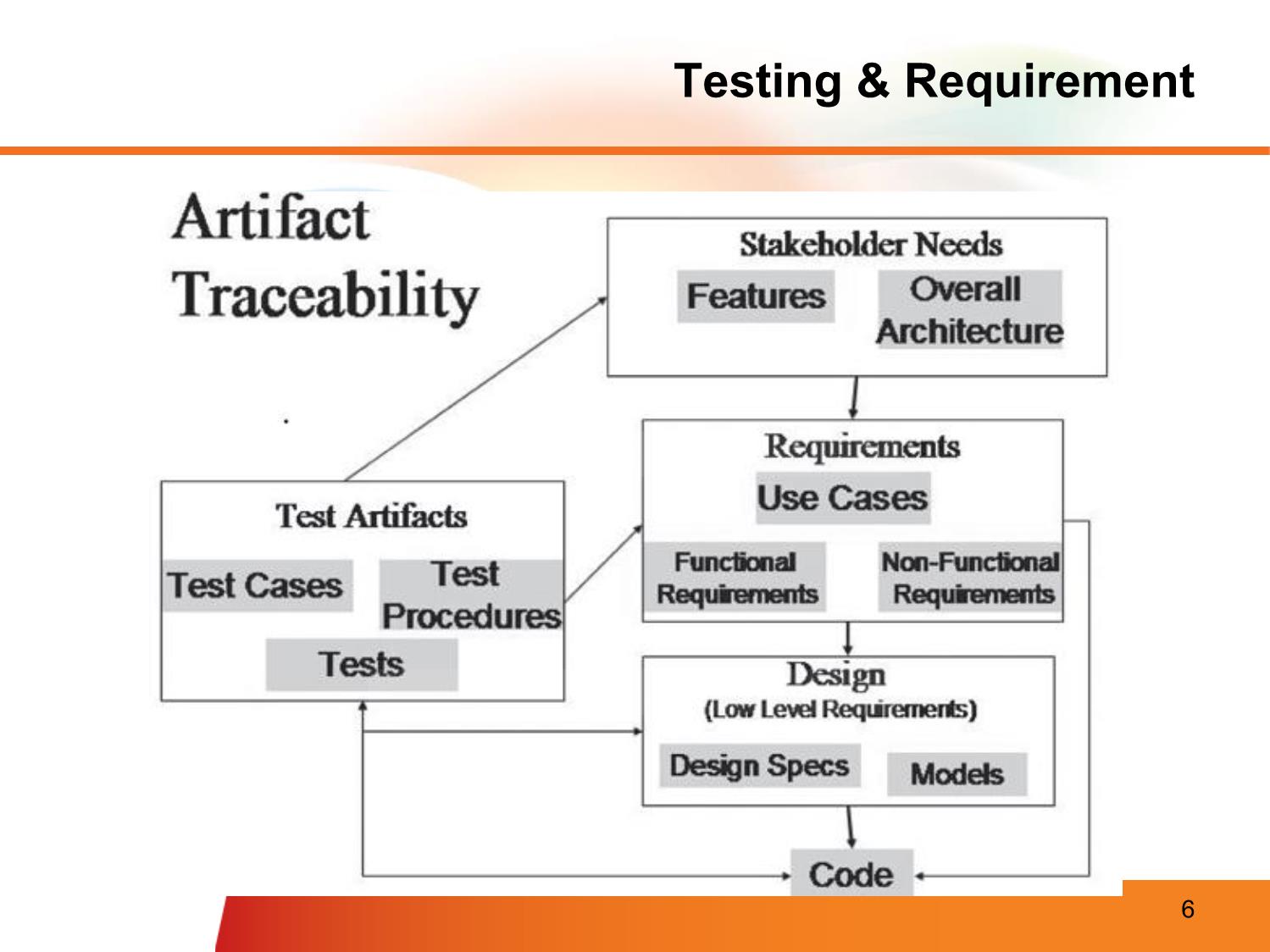
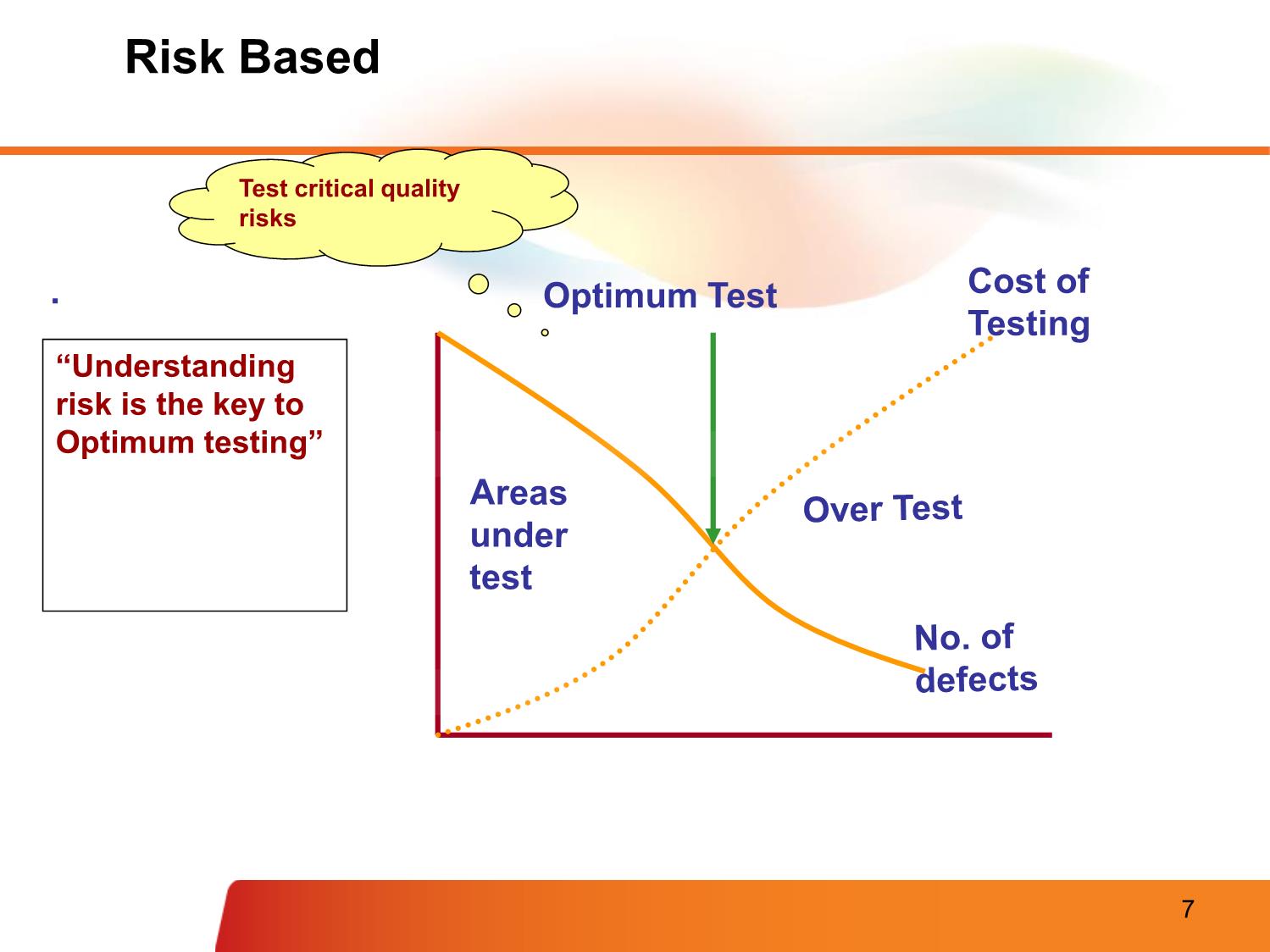
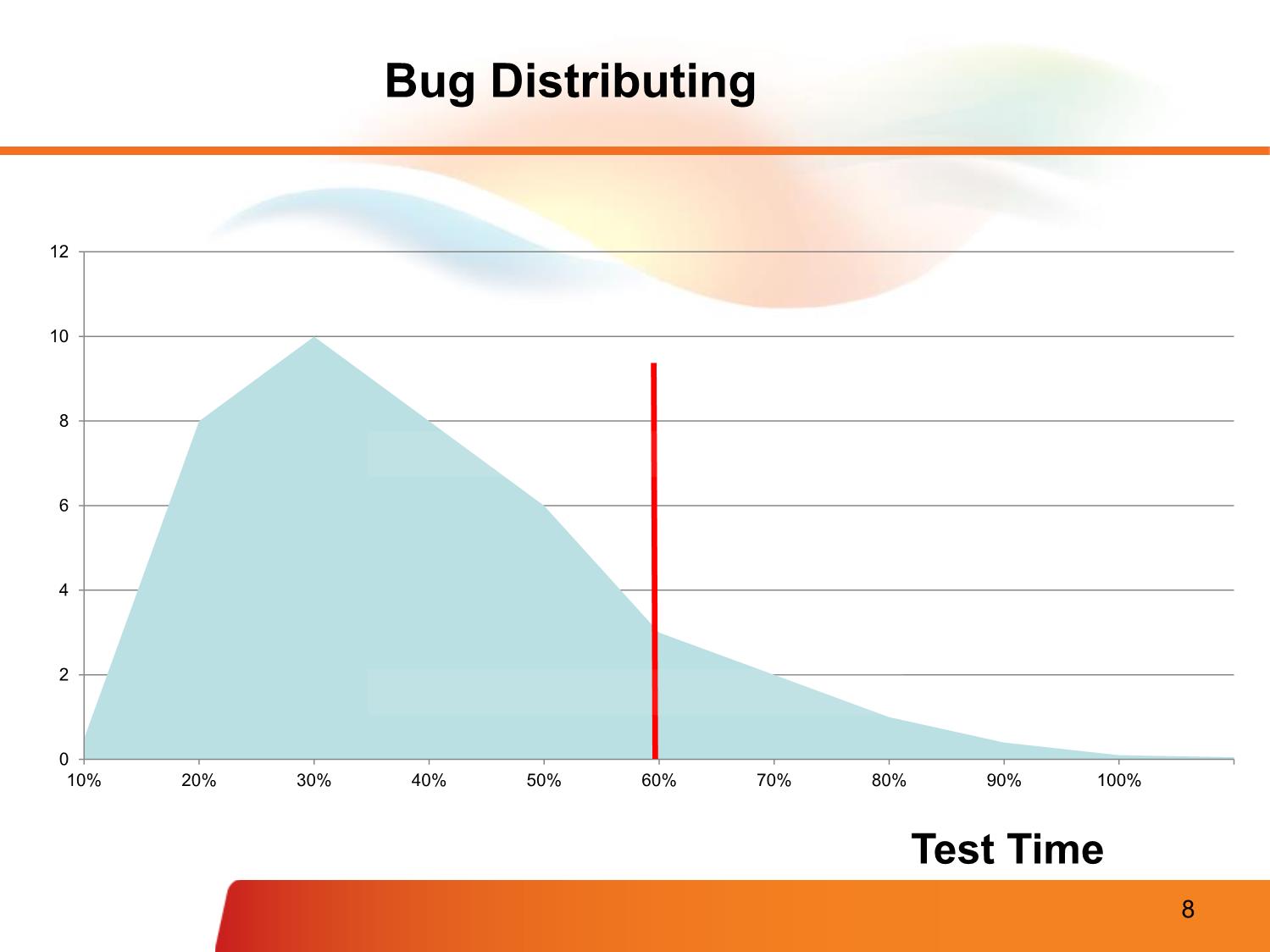
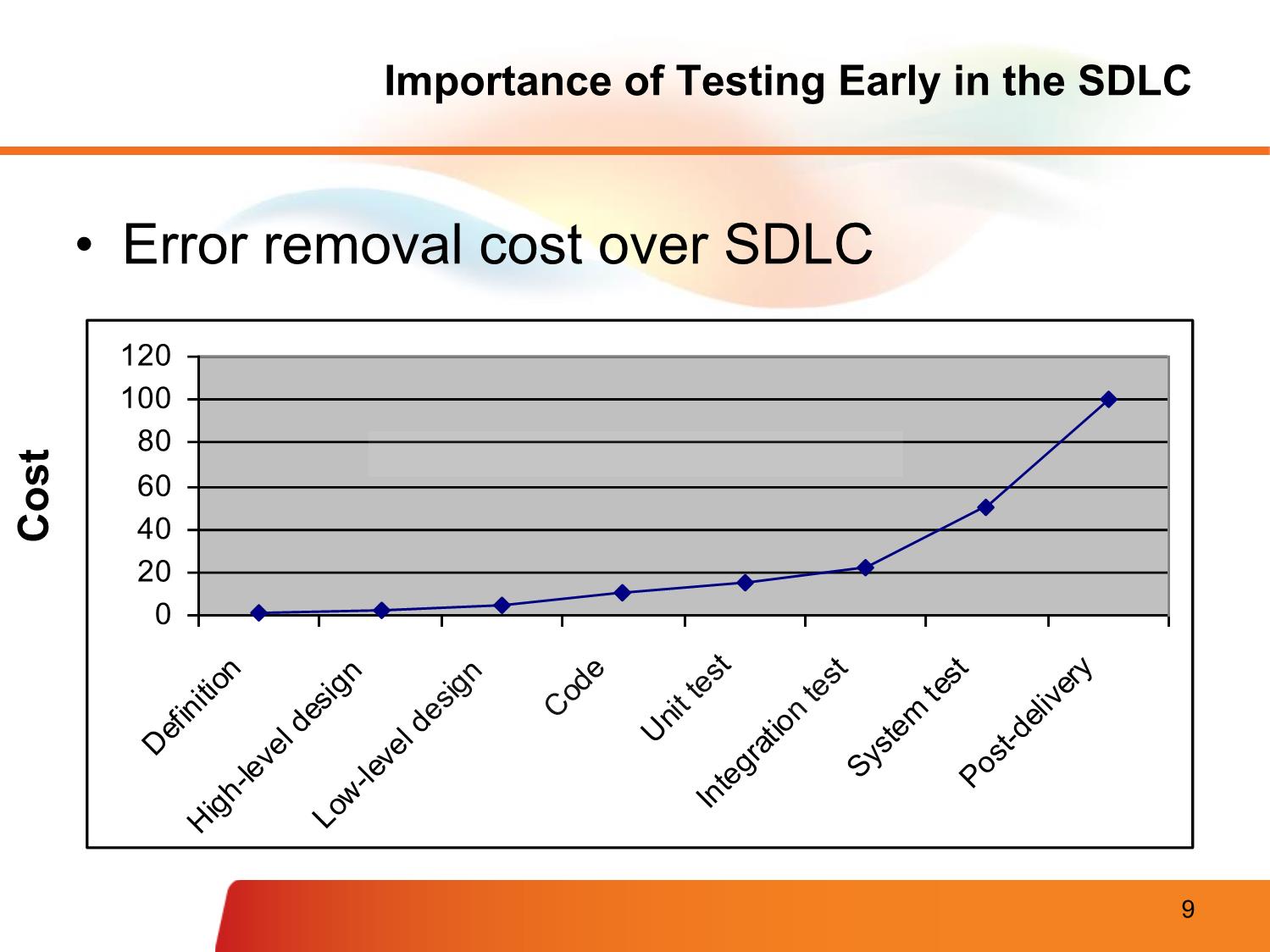
rrectness: no conflict, verifiable, in scope, message, etc. • Non-functional requirements, quality attributes, etc. – Template (See Checklist - Review Requirement.xlsx) Fsoft Requirement Process Validate Requirements – Purpose • Make sure that the requirements define the system that the customer really wants • Requirements error costs are high so validation is very important – Fixing a requirements error after delivery may cost up to 100 times the cost of fixing an implementation error Fsoft Requirement Process Validate Requirements – Process Verifiability check Realism check Completeness check Consistency check Validity check Fsoft Requirement Process Validate Requirements – Techniques • Requirements Review – Systematic manual analysis of the requirements – Involving development staff, customers and relevant stakeholders • Prototyping – Using an executable model of the system to check requirements • Model Validation – Validate the quality of the models developed during analysis • Test-case generation – Developing tests for requirements to check testability Fsoft Requirement Process Requirements management • Manage requirement in FSOFT – Requirement Management Sheet, Excel sheet, used to track the status, relationship and change of requirements during the whole project. – A mandatory document (dynamic version of SRS) • Classify requirement to functional/non-functional requirement • To maintain the common reference for all related parties (traceability of requirement and software product) • To track the project progress (status of requirement) • To track the change (including change request) • To collect requirement related metrics for reporting – The sheet is created the first time client requirement come Fsoft Requirement Process Requirement Traceability Why is traceability necessary? – The requirements can change at any stage during the product’s life. – If the requirements are traceable, then when changes happen, it is far easier to find the impacted parts of the product Software Work User Needs Requirements Products Use cases/ Software User Requirements Requirements Test cases Fsoft Requirement Process Requirement Changes Management • Requirements change (CR – Change request) – The priority of requirements from different viewpoints changes during the development process – Customers may specify requirements from a business perspective that conflict with end-user requirements – The business and technical environment of the system changes during its development • Requirements change process Requirement Clarifying • PM/TL/BA present the SRS to members in the team • Self study related materials: top-down approach • Using FSOFT’s SRS review checklist • Clarify unclear item(s) using Q&A • Discuss with other members – To clarify or confirm your understanding – Media: direct discussion or via team brainstorming • Inform the PM/TL/BA about – Any requirement conflicts – Changes, comparing to the last version Requirement Clarifying Clarifying requirement via Q&A • Why do we need Q&A? – Problems of understanding – Want for knowledge, must be ask Requirement Clarifying Clarifying requirement via Q&A (cont.) • How to make Q&A effectively? – Identify the issue: unclear, get for more information, etc. – Check in all documents that customer supplied to make sure your question has not solved; – With technical question, check your team /group/company or ask “Google” to solve it before asking out – Give the cross-reference clearly, completely – Attach sample screen, demo, give your suggestions if any – Convert questions to Y/N or multiple-choice types if possible – In Q&A, give deadline that you want to receive the answer. It there is no answer until the deadline, what is impact? – Take the receiver to re-read the question before sending Requirement Clarifying Clarifying requirement via Q&A (cont.) • Q&A focus: – Question for idea conveyed by words like: maybe, generally, etc. – What is the TBDs - Ask PL to remove all TBDs before handling to you for designing or coding – Conflict between requirements. Read the requirement matrix – Don’t make assumptions, just ask your PM, PL or BA • Follow up the Q&A – Track the discussion history for easier following up – If your question has not been replied or impacts to your task must be report to your PM, BA, or TL immediately – Keep in mind your manager/customer are very busy. So it is necessary to remind them about your pending issues daily, weekly. If not, your task will be impacted • Template on Q&A Management Sheet: 02_SWR_Software Requirement\Student\Assignments\Templates\StudentName - Topic - Q&AList.xls Requirement Modeling Modeling objectives • Why model requirement? To understand clearly the functionalities of system To present the system from different perspectives Requirement Modeling Model different perspectives • Model different perspectives Models help present different aspects of the system, using different abstraction Requirement Modeling System Modeling Tools • The system modeling presents an abstraction of the system in software aspects, which helps understanding of the functional requirements in block diagram form, and helps to identify all required software elements & tasks. • Common modeling tools: Data flow Use case diagram Behavioural Sequence Object Aggregation model diagram model State Activity machine diagram Inheritance diagram Modeling Tools - Use Case • Requirements capture – Requirements are reason-for-existence of any software development project – Defines and delineates user-requirements • Defines the functionality to be provided • Identifies the goals to be achieved – Must be precisely and completely understood – Requirements often changes, thus must be well-documented Modeling Tools - Use Case • Requirement capture with UML – Use Case diagram • Shows a set of use cases, actors and their relationships – Captures problem-domain in terms of: • functionality to be provided (Use Cases) • the “roles” (Actors) for whom these functions are performed Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Diagram Actor • overview the usage requirements • presentations project stakeholders • "the meat" of the actual requirements Actor:UseSystem case: boundary: AnAindicates use actor case isthe adescribes person,scope of organization, ayour sequence ofor actionssystem. that Anything provide within something the box of Use case external system that plays a role in onemeasurablerepresents or more functionality valueinteractions to an thatactor with is yourand in is systemdrawnscope andas a anythinghorizontal outside ellipse the box is not Online C2C shopping System boundary Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Diagram - Notations • Use case diagram: Notations use case A description of a set of sequences of actions that Do it system performs that provides an observable value to an actor actor The people or systems that provide or receive information from the system; they are among the stakeholders of a system include Specifies that the source use case explicitly incorporates the > behavior of another use case at a location specified by the source extend Specifies that the target use case extends the behavior of the > source. Modeling Tools - Use Case Example - Use Case 1/2 A company wants to develop a ticketing and • reservationUse case example system. This must support advance booking of tickets, cancellation of tickets and change A company wants to develop a ticketing and reservation of classsystem. of a Thisticket. must All support these advance are handled booking by of tickets,a Reservationcancellation Clerk. of tickets and change of class of a ticket. All these are handled by a Reservation Clerk. The system will also have a Web site where users can registerThe themselves system will also and have purchase a Web site tickets where usersonline. can They register themselves and purchase tickets online. They can can paypay either either byby usingusing their their online online banking banking account account or by credit or by creditcard. card. Reservations Reservations made over made the internet over canthe onlyinternet be can onlycancelled be cancelled across the across counter. the counter. The system will also have a querying facility that allows The systemusers to will check also train have time -atables, querying fares andfacility availability that of allows tickets.users to check train time-tables, fares and availability of tickets. Modeling Tools - Use Case Example - Use Case 2/2 Make Cancel Modify Class Reservation Reservation Check train Query Check Fare time-table Timetable Register as Member Modeling Tools - Use Case Example - Use Case Diagram • Use case diagram Modify Class Check Fare Query Reservation Timetable Passenger Clerk Make Reservation Cancel Check train Register Reservation time-table as Member Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 1/7 • Text description of use case functionality in the user language and terminology • No specific UML format • Describes WHAT and not HOW • Typically includes: – Objectives of the use case – How the use case is initiated – The flow of events (main flow, alternative flow) – How the use case finishes with a value to the actor and more... Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 2/7 • Use case description serves as a ‘bridge’ between stakeholders of a system and the development team. Systems analyst produce use case diagram & use case specification in consultation with end users Use Case Use Case Diagram Specification Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 3/7 • Flow of events – Use Case is an abstraction of behavior (set of sequences) – The behavior of the Use Case can be described by a “flow of events” - which spells out in detail what exactly the Use Case does • main flow: what happens and in what order when all is well • alternate flow(s): what happens and in what order when something goes wrong • exception flow: things don’t always go as planned. An exception is an error condition that is important enough to the application to capture Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 4/7 Key Explanation components Name Clear, unique name of the use case (verb, goal-driven) Actors Someone or something that interacts with the use case Description Brief overview of the use case, describing the main idea Goal What the actors achieve with this use case Pre-condition State(s) the system can be in before the use case starts Trigger Event that causes the use case to be initiated Post-condition State(s) the system can be in after the use case finishes Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 5/7 Key Explanation components Normal flow Typical (primary) processing path Alternative flow Alternative (secondary) processing path Exception flow When things go wrong at the system level Others Business rules, Assumption, Notes, etc. Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 6/7 • Example Make a seat reservation use case Name Make reservation Actors Passenger Description Allows a passenger to book a plane seat for a journey from the Website Goal Reserve a seat Pre-condition Main Webpage is displayed successfully Trigger User clicks on “Reserve seat” button on the main Webpage Post-condition • A seat is booked • Number of available seats is reduced Modeling Tools - Use Case Use Case Specification 7/7 • Example Make a seat reservation use case Normal flow [User log in and reserve a seat successfully] 1. User logs in 2. User specifies a flight and travel details 3. User specifies passenger details 4. User specifies payment details 5. User confirms transaction Alternative [When no seat is available on the selected date] flow • Show option to select another day • Repeat steps in normal flow Exception flow [When a payment is failed] • Notify error with the payment • Give an option to re-enter payment details or other payment method Modeling Tools - DFD DFD = Data Flow Diagram How data is processed How data by system flows through a sequence of processing steps Modeling Tools – DFD Sample DFD process Checked and Send to Completed Signed Signed signed order supplie order order form order form +order Order detail Recor r notification Complete Validate + blank d order form order order form order Signed Adjust order form availabl e budget Order Order amount data detail +account detail flow Orders Budget file file Data stores 65 Modeling Tools - Activities Diagram Activity diagrams describe the Start workflow behaviour of a system Fork including a sequence of activities performed from start to finish Activities could be performed: Branch - sequential order - parallel - conditional transition Merge Joint End Modeling Tools - State Machine A State Machine diagram shows the possible states of the object and the transitions that cause a change in state. What is different ? between activities and Statemachine diagram 67 Common Practices, Problems • Common issues – Requirement isn't clear. Don't understand customer mean. – Requirement analysis is not documented/centralized recorded -> misunderstanding – How to verify the understanding of team members about requirement • What should we do – Maintain SRS – Communicate with the customer = onsite – Don’t make assumption. Must confirm with customer about specs more and more about what are still not clear or too general. – Should involve all members to investigate requirements from the beginning of the project, not only PL. – Conduct meeting to verify the requirement understanding. – One meeting to introduce the requirement/design. – Another meeting to verified the understanding of team member. Every one have to present their understanding. Resources & References . Resources & References – Requirement development & management process – Q&A management sheet template – SRS review checklist – RMS template – SRS template Q & A
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_quality_testing_software_requirement_concepts_proc.pdf
bai_giang_quality_testing_software_requirement_concepts_proc.pdf

