Bài giảng Introduction to Computer Programming (C language) - Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming - Võ Thị Ngọc Châu
Content
Introduction
Computer Organization
Programming Languages
Programming Tasks
Data and Algorithms
Summary

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Introduction to Computer Programming (C language) - Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming - Võ Thị Ngọc Châu", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Introduction to Computer Programming (C language) - Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming - Võ Thị Ngọc Châu

Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology
Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering
Chapter 1: Introduction to
Computers and Programming
Introduction to Computer Programming
(C language)
TS. Võ Thị Ngọc Châu
(chauvtn@cse.hcmut.edu.vn,
chauvtn@hcmut.edu.vn)
2017 – 2018, Semester 2
Course Content
C.1. Introduction to Computers and
Programming
C.2. C Program Structure and its
Components
C.3. Variables and Basic Data Types
C.4. Selection Statements
C.5. Repetition Statements
C.6. Functions
C.7. Arrays
C.8. Pointers
C.9. File Processing 2
References
[1] “C: How to Program”, 7th Ed. – Paul
Deitel and Harvey Deitel, Prentice Hall, 2012.
[2] “The C Programming Language”, 2nd Ed.
– Brian W. Kernighan and Dennis M. Ritchie,
Prentice Hall, 1988
and others, especially those on the Internet
3
Content
Introduction
Computer Organization
Programming Languages
Programming Tasks
Data and Algorithms
Summary
4
Introduction
Computer Programming
Computer
a device that can perform computations and make
logical decisions billions of times faster than human
beings can
Programming
The act of writing the programs executable on the
computers to produce intended results
Program
A sequence of instructions written in a programming
language to perform a specified task by the computer
5
Introduction
Programs and
Computers Programming their Results 6
Computer Organization
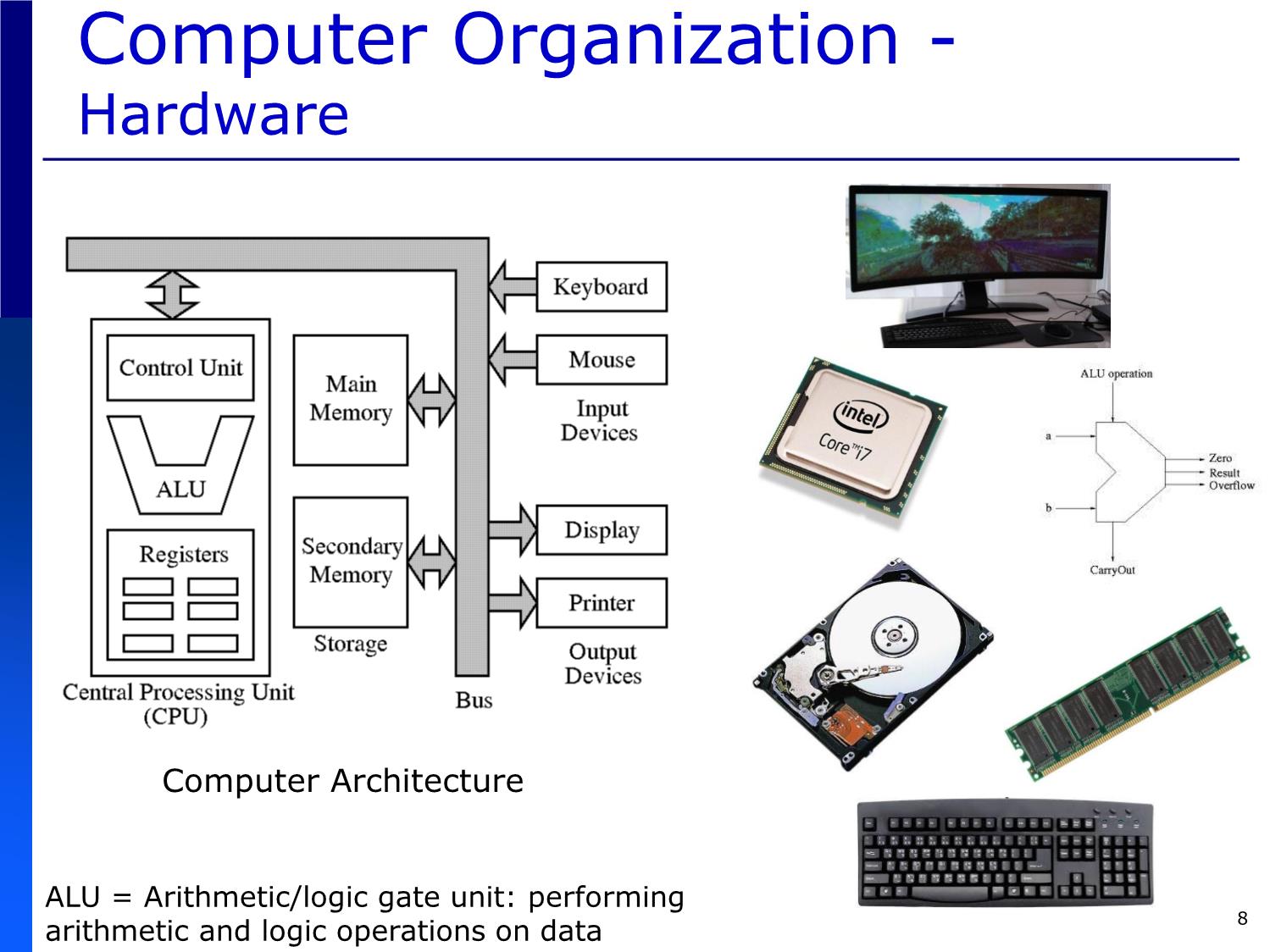
Hardware: physical components of
computer (including peripherals)
the keyboard, screen, mouse, hard disk,
memory, DVDs and processing units,
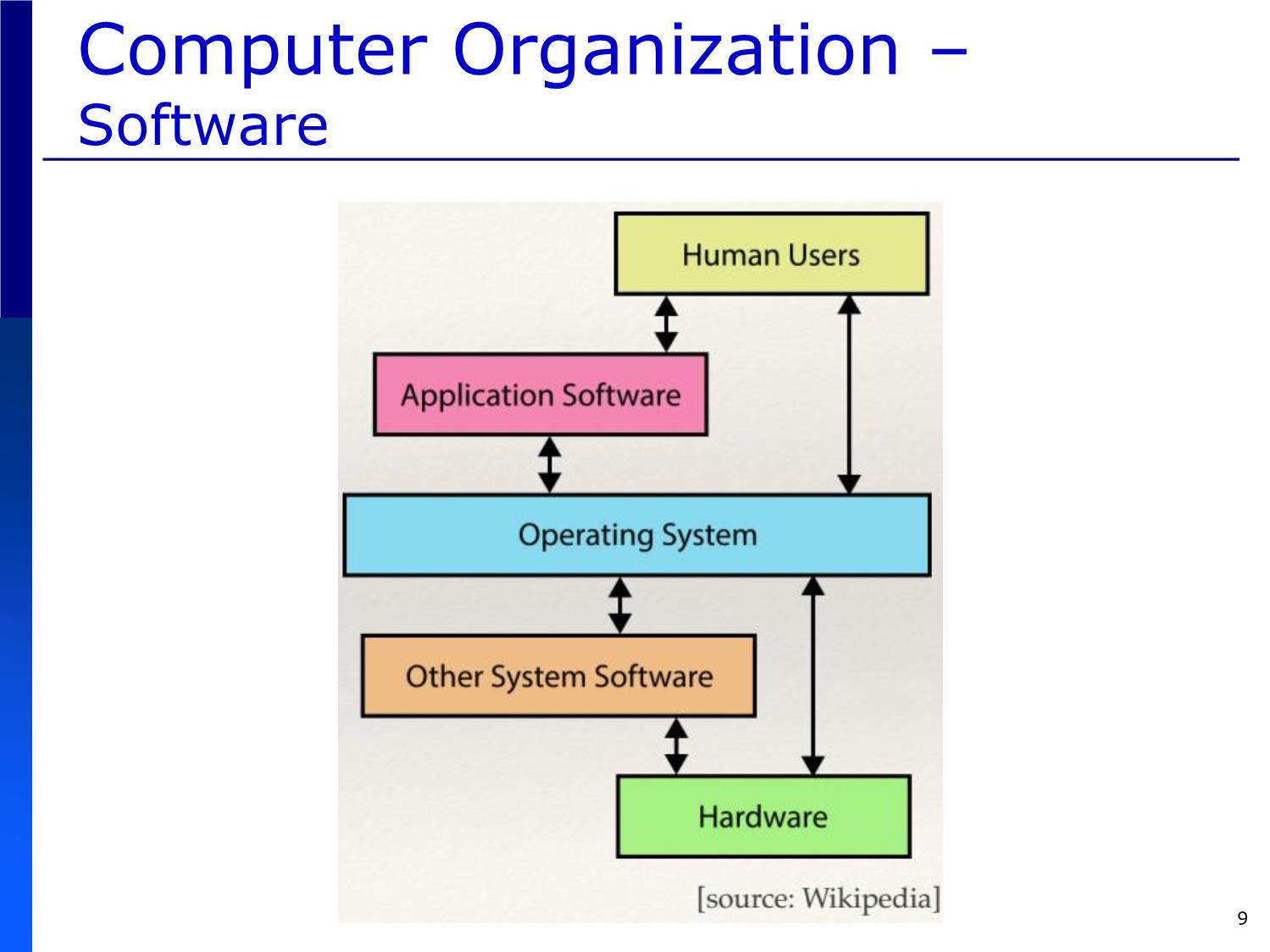
Software: a set of machine-readable
instructions that directs a computer's
processor to perform specific operations
[Wikipedia]
Application softwares
Operating system
System softwares
7
Computer Organization -
Hardware
Computer Architecture
ALU = Arithmetic/logic gate unit: performing
arithmetic and logic operations on data 8
Computer Organization –
Software
9
Programming Languages
Programming language: a formal language
for writing a computer program as a
sequence of instructions
C, C++, C#, Java, PHP, Python,
Three general types
Machine languages
Assembly languages
High-level languages
Providing a sequence of instructions that directly
understandable by computers or requiring some
intermediate translation steps
10
Programming Languages –
Machine Languages
First-generation language: strings of
numbers (ultimately reduced to 1s and 0s)
that instruct computers to perform their
most elementary operations one at a time
Directly understandable by computers
Machine-dependent
For example, instructions for
adding overtime pay to base
pay and then storing the
result in gross pay
11
Programming Languages –
Assembly Languages
Second-generation language: a low-level
language used to interface with computer
hardware using English-like abbreviations
to represent elementary operations
Less understandable by computers
Need for translation steps to convert an
assembly language program to machine codes
Translator = Assembler
For example, instructions for
adding overtime pay to base
pay and then storing the
result in gross pay 12
Programming Languages –
High-level Languages
Third-generation language: written
instructions that look almost like everyday
English and contain commonly used
mathematical notations
Less understandable by computers
Translator program is called compiler.
The C language is a high-level language that needs
a compiler.
Scripting languages such as PHP and Perl need an
interpreter.
For example, instructions for adding overtime pay to base pay and
then storing the result in gross pay: grosspay = basepay + overpay. 13
Programming Languages –
High-level Languages
Program File Compiler Binary File CPU Result
C, C++, Java,
Program File Interpreter CPU Result
PHP, Perl,
A history of computer programming languages – Wikipedia
Graph of programming language history – www.levenez
14
Programming Languages –
The C language
Evolved from B by Dennis Ritchie at Bell
Laboratories and originally implemented on
a DEC PDP-11 computer in 1972
Using many of the important concepts of
BCPL and B while adding data typing and
other powerful features
Used for many important application trends
Developing new major operating systems: UNIX,
Linux, Android,
Developing programs in the embedded systems
in cars, medical machines,
15
Programming Languages –
The C language
Ken Thompson (left) with Dennis Ritchie (right,
the inventor of the C programming language)
[Wikipedia]
The development of the C language
Dennis M. Ritchie
Full history of the C language
Wikipedia
16
Programming Tasks
Design of Library Library
program (Header: *.h) (Object code: *.lib; *.dll; *.so)
Editor Preprocessor Compiler Linker Executable
Program
Source code Enhanced source code Object code
*.h + *.c *.h + *.c (*.cpp) *.obj
(*.cpp)
gcc; g++
Integrated Development Environment (IDE):
Visual Studio; Eclipse; Qt Creator; Code block; Online tool; etc
17
Programming Tasks
Editor: supports text editing feature for
writing source code
Preprocessor: preprocesses the source code
with replacing macro, inserting library files
*.h,
Compiler: translates the source code into
target machine language
Linker: links the object code to other library
files
18
Data and Algorithms –
Concepts
Program
= A Sequence of Instructions Written in a
Programming Language to Perform a Specified
Task by the Computer
= Data and their Structures + Algorithms
Input/Output/ Process
Example 1: instructions for adding overtime pay to base pay and
then storing the result in gross pay: grosspay = basepay + overpay.
Example 2: given n positive numbers, find the smallest one.
19
Data and Algorithms –
Data
Atomic data: int, double, char, ...
Non-atomic data: array, struct, enum,
A strong relationship between the data
structures and the operations on the data in
the corresponding structures
Example 1: instructions for adding overtime pay to base pay and
then storing the result in gross pay: grosspay = basepay + overpay.
- Input Data: basepay and overpay are positive real numbers
(double).
- Output Data: grosspay is also a positive real number (double).
Example 2: given n positive numbers, find the smallest one.
- Input Data: n positive real numbers are treated individually OR as
a collection (double)
- Output Data: minNumber is a positive real number (double). 20
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms
Algorithm = a sequence of unambiguous
instructions for solving a problem, i.e. for
obtaining a required output for any
legitimate input in a finite amount of time
Anany Levitin, Introduction to the Design and
Analysis of Algorithms, 2nd Edition, Addison
Wesley, 2007
Algorithm representation
Pseudo code
Flowchart
Real code in a high-level programming language
21
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms
Example 2: given n positive numbers, find the
smallest one.
Task solution:
1. Suppose that the first number is the smallest one
(current one).
2. Check if the current smallest one is a real one as
compared to the next number.
If yes then compared to the next number of the next one
like step 2 till all numbers are checked.
Otherwise,
. update the smallest one with the smaller one
. And then move next to check with the next number of the
next number like step 2 till all numbers are checked. 22
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms – Pseudo Code
Header
Algorithm name Header
Input data and their data types
Task purpose
Body
Pre-conditions
Post-conditions
Output data and their data types
Body
(Numbered) (control) statements
Comments
23
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms – Pseudo Code
Algorithm findMinNumber
Example - Input: positiveNumber[n] which is an array of n positive double values
- Output: minNumber which is the smallest one whose type is double
2: given - Purpose: find the smallest number in a collection
- Precondition: n data inputs are positive.
n positive Begin Algorithm
Check positiveNumber[n] contains only positive values
numbers, minNumber = positiveNumber[1]
iteration = 2
find the While (iteration <= n)
smallest Begin While
If (minNumber <= positiveNumber[iteration]) Then
one. iteration = iteration + 1
Else
Begin
minNumber = positiveNumber[iteration]
iteration = iteration + 1
End
End While 24
End Algorithm
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms – Flowchart
Symbols used for drawing a flowchart
25
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
Terminal: starting point or end point
Input/Output: input data/output data of the
algorithm
Flow line: shows a control flow of the
algorithm. Execution follows this part.
Decision: allows a condition (expressed as
a boolean expression) to be checked
Process: data processing block
26
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
Predefined process: an existing data
processing block
On-page connector: a gathering point of
the flow lines in a flowchart
Off-page connector: a gathering point of
the flow lines from another page
Preparation: preparation steps, setting for
initial conditions
Annotation: comments
27
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
false
true
if Statement
28
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
false
true
if-else Statement 29
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
false false false
true true true
switch-case Statement
30
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
false
true
<Iteration Value
Modification>
for Statement
31
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms - Flowchart
false
true
true
false
while Statement do while Statement
32
Flowchart vs. Pseudo Code?
Example 2: minNumber = How to add the checking
positiveNumber[1]
given n of n positive numbers?
positive iteration = 2
numbers,
false
iteration <= n
find the
smallest true
minNumber<= true
one. iteration =
positiveNumber[iteration]
iteration + 1
false
minNumber =
positiveNumber[iteration]
33
Data and Algorithms –
Algorithms – Real code in C
void main() {
double positiveNumber[10] = {2, 1, 3, 10, 8, 3, 4, 5, 9, 12};
int n = 10;
How to add the checking
double minNumber = positiveNumber[0]; of n positive numbers?
int iteration = 1;
while (iteration < n) {
if (minNumber <= positiveNumber[iteration]) iteration = iteration + 1;
else {
minNumber = positiveNumber[iteration];
iteration = iteration + 1;
}
}
} Pseudo Code vs. Flowchart vs. Real Code in C? 34
Summary
Concepts related to computer programming
Short introduction to computers, programs,
programming, and programming languages
Short introduction to the C language
Preparation for computer programming
Programming tasks
Data and basic data types
Algorithms and their representations
35
Chapter 1: Introduction to
Computers and Programming
36 File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_introduction_to_computer_programming_c_language_ch.pdf
bai_giang_introduction_to_computer_programming_c_language_ch.pdf

