Bài giảng English for marketing - Unit 1: Marketing introduction
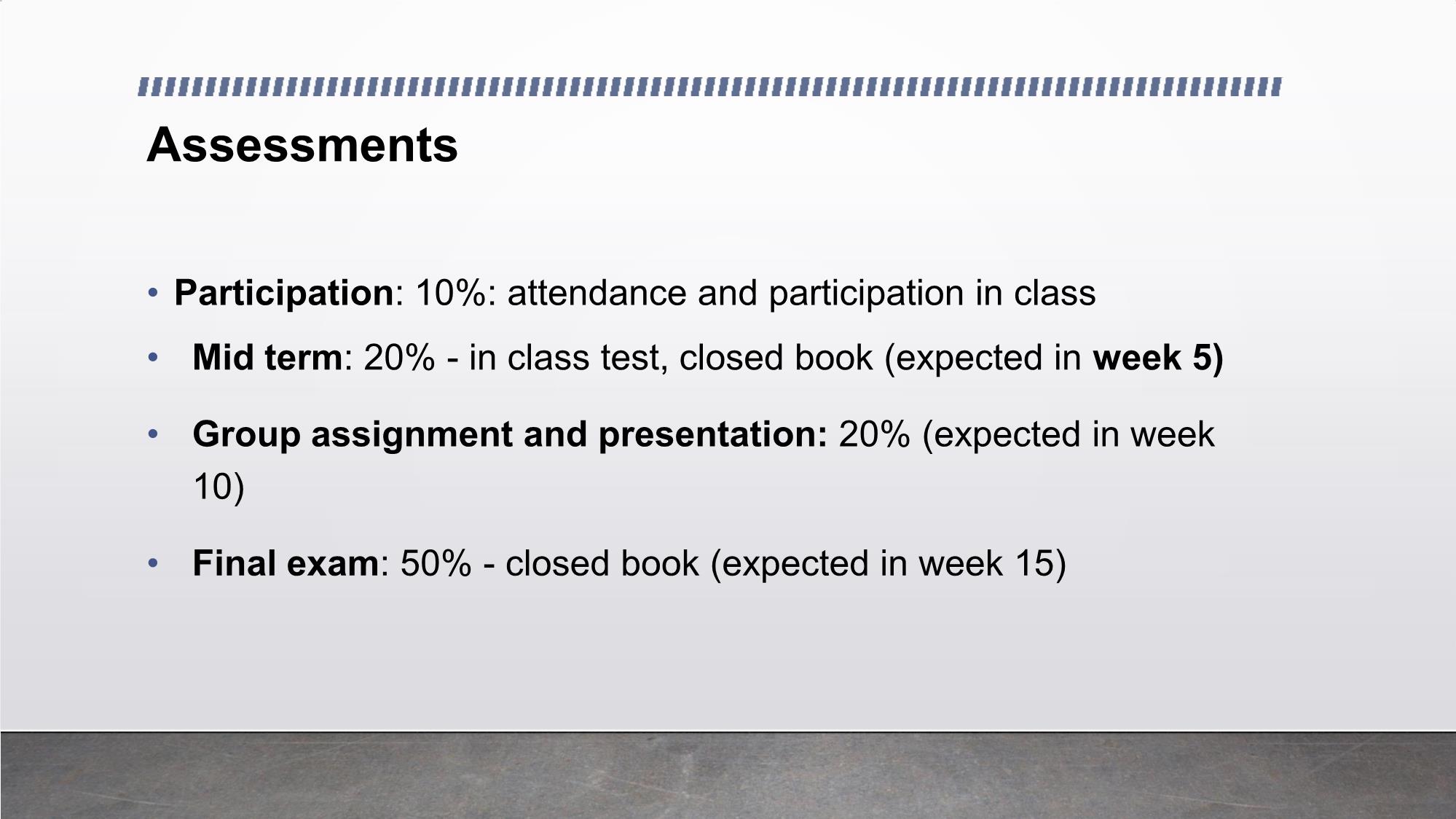
Objectives
• Understand and being able to use marketing basic terms correctly
• Understand the marketing process extended model
• Understand the marketing management orientation
• Being aware of the modern marketing landscapeMarketing Introduction
Core concepts:
• What is marketing?
• Market basic definitions
• Marketing strategy and the marketing plan
• The marketing mix
• The Changing Marketing Landscape

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng English for marketing - Unit 1: Marketing introduction", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng English for marketing - Unit 1: Marketing introduction

tself affect the consumer behaviour Culture is the set of basic values, perceptions, wants, and behavior learned by a member of society from family and other important institutions Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Membership Groups • Groups with direct influence and to which a person belongs Aspirational Groups • Groups an individual wishes to belong to Reference Groups • Groups that form a comparison or reference in forming attitudes or behavior Groups and Social Networks Groups Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Personal factors Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Lifestyle is a person’s pattern of living as expressed in his or her activities, interests, and opinions Personal factors Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Personality is the unique psychological characteristics that distinguish a person or group Personal factors Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior A motive (or drive) is a need that is sufficiently pressing to direct the person to seek satisfaction. Psychological factors Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Perception is the process by which people select, organize, and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world. Psychological factors TYPES OF BUYING DECISION BEHAVIOUR Consumer buying behavior in situations characterized by high consumer involvement in a purchase and significant perceived differences among brands. Consumer buying behavior in situations characterized by high involvement but few perceived differences among brands. Consumer buying behavior in situations characterized by low consumer involvement but significant perceived brand differences. Consumer buying behavior in situations characterized by low consumer involvement and few significant perceived brand differences. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products Adoption process is the mental process an individual goes through from first learning about an innovation to final regular use. Awarene ss Interes t Evaluatio n Trial Adoption Review • The Buyer Decision Process • Model of Consumer Behavior • Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior: • Social • Groups and social networks • Personal • Cultural • Buying decision behavior • The Buyer Decision Process for New Products UNIT 5 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Creating Value for Target Customers • Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy • Market Segmentation • Market Targeting • Differentiation and Positioning Topic Outline Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Creating Value for Target Customers MARKETING STRATEGY Market segmentation is dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes. Market Segmentation Market Segmentation Bases GeographicNations, States, Regions, Counties, Cities DemographicAge, Gender, Income, Marriage status PsychographicPersonality, Lifestyle BehavioralKnowledge, attitudes, uses . Market Segmentation To be useful, market segments must be: Measurable Accessible Substantial Differentiable Actionable Requirements for Effective Segmentation Evaluating Market Segments 1. Segment size and growth 2. Segment structural attractiveness 3. Company objectives and resources HOW TO CHOOSE A SEGMENT? Selecting Target Market Segments Selecting Target Market Segments Target several market segments & designs separate offers for each Goes after a large share of one or few segments or niches Tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and wants of specific individuals and local customer segments Selecting Target Market Ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer Undifferentiated marketing Differentiated marketing Concentrated marketing Micromarketing Positioning The way product is defined by consumers on important attributes – the place the product occupies in consumers’ minds relative to competing products Positioning Map: Large Luxury SUVs What is your positioning strategy? Positioning for Competitive Advantage Differentiation and Positioning Competitive advantage is an advantage over competitors gained by offering greater customer value either by having lower prices or providing more benefits that justify higher prices. Identifying Possible Value Differences and Competitive Advantages Differentiation and Positioning • Value proposition is the full mix of benefits upon which a brand is positioned • The answer to the customers’ question: why should I buy this brand? Selecting an Overall Positioning Strategy • Market Segmentation: basis, criteria • Market Targeting: undifferentiated, differentiated, concentrated (niche), micro • Differentiation and Positioning: • Positioning maps • Differentiation • Competitive advantages • Value proposition REVIEW UNIT 6: Company – Wide Strategic Planning The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities Strategic Planning Strategic Planning Business portfolio: The collection of businesses and products - SBUs- that: • Make up the company • Best fits the company’s strengths and weaknesses to opportunities in the environment • SBUs: Strategic business units • An SBU can be a company division, a product line within a division, or sometimes a single product or brand Growth-share matrix A portfolio-planning method that evaluates a company’s SBUs in term of its market growth rate and relative market share Developing strategies for growth and downsizing Planning Marketing 1. Choose the real product 2. Define your target customer and target customer behavior 3. Marketing Environment Analysis 4. Positioning Proposal 5. Product strategy 6. Price strategy 7. Place Strategy 8. Promotion Strategy 9. Marketing Action Plan Marketing Plan Products, Services, and Brands Building Customer Value Product, Services, and Branding Strategy • What Is a Product? • Product and Services Decisions • Services Marketing • New Product Development • Product Life Strategy Topic Outline Market offerings Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want ServicesProducts Places Ideas People Experience Products, Services and Experiences Marketing-mix planning begins with building an offering that brings value to target customers 3 levels of Products and Services Levels of Product and Services Core customer value What is the buyer really buying? The core, problem-solving benefits or services that the consumers seek Levels of Product and Services Actual product Turn the core benefit into an actual product Levels of Product and Services Augmented product Offering additional consumer services and benefits Products and Services Classifications • Consumer products • Convenience products • Shopping products • Specialty products • Unsought products • Industrial products • Organizations, Persons, Places, Ideas What Is a Product? Industrial products are products purchased for further processing or for use in conducting a business • Classified by the purpose for which the product is purchased • Materials and parts • Capital • Raw materials Product and Service Classifications What Is a Product? Organization marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward an organization Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas What Is a Product? Person marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward particular people Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas What Is a Product? Place marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward particular places Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas What Is a Product? Social marketing is the use of commercial marketing concepts and tools in programs designed to influence individuals’ behavior to improve their well-being and that of society Organizations, Persons, Places, and Ideas Product and Service Decisions Product and Services Decisions Product mix (or product portfolio) consists of all the products and items that a particular seller offers for sale • Width: Product mix width refers to the number of different product lines the company carries. • Length: Product mix length refers to the total number of items a company carries within its product lines. • Depth: Product line depth refers to the number of versions offered of each product in the line • Consistency: the consistency of the product mix refers to how closely related the various product lines are in end use, production requirements, distribution channels, or some other way. Product Mix Decisions Services Marketing New-Product Development Strategy New Product Development Process Product Life-Cycle Strategies The course of a product’s sales and profits over its lifetime Product Life-Cycle Strategies Review • What Is a Product? • Consumer products: convenience, shopping, specialty, unsoughted • Industrial products: capital, materials and parts, raw materials • Organization, people, place, social • Product and Services Decisions: features, brand, package, labels, product support services • Services Marketing • New Product Development • Product Life Strategy CHAPTER 10: PRICING Pricing Concepts Understanding and Capturing Customer Value Understanding the meaning and the use of: • What Is a Price? • Pricing approaches • Pricing strategies Topic Outline Price is the amount of money charged for a product or service. It is the sum of all the values that customers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service Price is the only element in the marketing mix that produces revenue; all other elements represent costs What Is a Price? Major pricing approaches Customer value – based pricing Cost – based pricing Competition – based pricing Customer Value – Based Pricing Setting price based on buyer’s perceptions of value rather than on the seller’s cost Assess customer needs and value perceptions Set target price to match customer perceived value Determine costs that can be incurred Design product to deliver desired value at target price Cost – Based Pricing Setting prices based on the costs for producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for effort and risk28 Set price based on cost Convince buyers of product’s value Design a good product Determine product costs Competition – Based Pricing Setting prices based on competitor’s strategies, prices, costs, and market offerings Considerations affecting pricing decisions Internal Considerations Overall marketing strategy, objectives and mix Organizational considerations The market and demand Pricing in different types of markets Analyzing the price-demand relationship External Considerations The Economy Other External Factors Pricing Strategies New – Product Pricing Strategies Product Mix Pricing Strategies Price Adjustment Strategies New Product Pricing Strategies Market – Skimming Pricing Setting a high price for a new product to skim maximum revenues layer by layer from the segments willing to pay the high price, the company markets fewer but more profitable sales Market – Penetration Pricing Setting a low price for a new product to attract a large number of buyer and a large market share To penetrate the market quickly and deeply Product Mix Pricing Strategies Product line pricing Optional product pricing Captive product pricing By – product pricing Product Bundle Pricing Price Adjustment Strategies Discount Allowance Segmented pricing Psychological pricing Reference prices Promotion pricing Geographical pricing Dynamic pricing International pricing Review • What Is a Price? • Pricing approaches • Cost based • Customer value-perceived • Competitors based • Pricing strategies • New Product Pricing • Product Mix Pricing • Price Adjustment Pricing UNIT 9: PLACE Marketing Channels (Distribution Channel) Delivering Customer Value Objectives Understanding: The nature and importance of marketing channel Channel Behavior and Organization Channel design decisions Marketing channel decisions Marketing channel A set of interdependent organizations that help make a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user The Nature and Importance of marketing channel Number of Channel Levels Channel level: A layer of intermediaries that performs some work in bringing the product and its ownership closer to the final buyer Direct marketing channel Has no intermediary levels Indirect marketing channel Channel containing one or more intermediary levels Channel Behavior and Organization Channel conflict Disagreement among marketing channel members on goals, roles and rewards Horizontal conflict Horizontal conflict occurs among firms at the same level of the channel Vertical conflict Conflict between different levels of the same channel Channel Behavior and Organization Vertical Marketing System Conventional and Vertical marketing system Channel Design Decisions Analyzing Consumer Needs Setting Channel Objectives Identifying Major Alternatives Evaluating the Major Alternatives Designing effective marketing channels by analyzing customer needs, setting channel objectives, identifying major channel alternatives, and evaluating those alternatives hann l Desig Decisions Selecting Channel Members Managing and Motivating Channel Members Evaluating Channel Members Selecting, managing, and motivating individual channel members and evaluating their performance over time Marketing channel management Review The nature and importance of marketing channel Channel Behavior and Organization Channel conflicts Vertical and conventional marketing system Channel design decisions Analyzing consumer needs Setting channel objectives Identifying major alternatives Evaluating the alternatives Marketing channel decisions Integrated Marketing Communication Review The Promotion Mix Advertising PR (Public Relations) Direct Marketing Sales Promotion Personal selling Integrated Marketing Communication Push and Pull Marketing
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_english_for_marketing_unit_1_marketing_introductio.pdf
bai_giang_english_for_marketing_unit_1_marketing_introductio.pdf

