Bài giảng Đồ họa hiện thực ảo - Bài 12: Hiện thực ảo - Lê Tấn Hưng
I. Virtual Reality
Khái niệm “virtual” ?
“Virtual” là 1 trong những từ được lạm dụng trong ngành công nghệ cao
ngày nay và được dùng phổ biến.
“virtual bank”, “virtual heritage”,. ngụ ý đến 1 điều kỳ quái -
monstrosities.
virtual X
với X có thể là bất cứ thứ gì , điều gì. virtual X không phải là X nhưng
có giao diện (hình dáng, hoạt động .) giống hệt như X
Ví dụ: virtual memory không phải là bộ nhớ nhưng nó làm việc với vi
xử lý đúng như là bộ nhớ.
Tương tự virtual disks, virtual terminals, virtual networks, etc.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
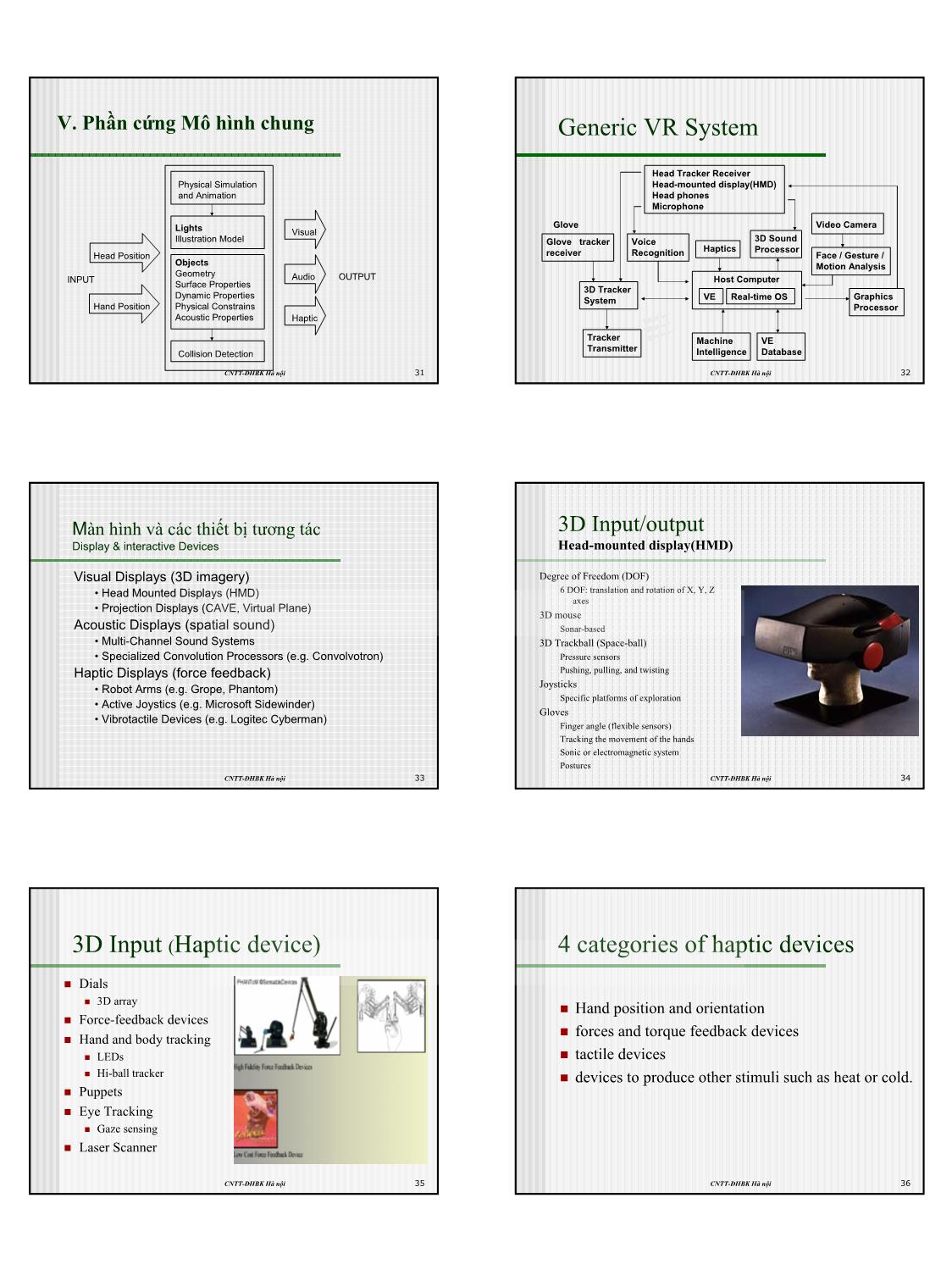
Trang 6
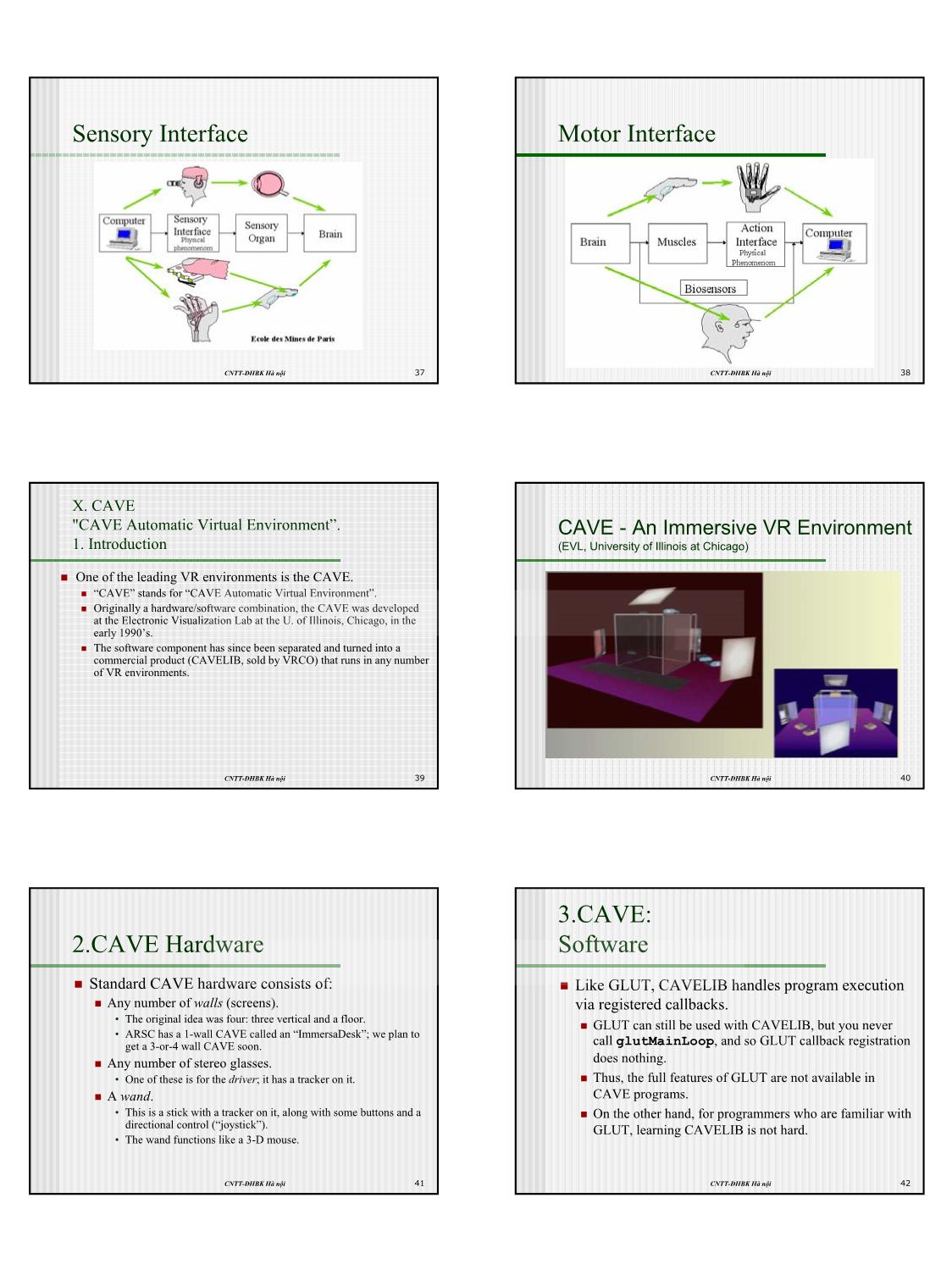
Trang 7

Trang 8
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài giảng Đồ họa hiện thực ảo - Bài 12: Hiện thực ảo - Lê Tấn Hưng", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Đồ họa hiện thực ảo - Bài 12: Hiện thực ảo - Lê Tấn Hưng

is by focus: the lens in the eye focuses light differently for near vs. - multiplexing with polarizer filters far objects. The user needs to be able to affect the scene somehow. - providing two views simultaneously Tracking capability (to determine head/eye placement), the user a hand-held Color Encoded Stereo Image Pair object with a tracker on it. User’s motions directly, either through placement of tracking devices on the user’s clothes, or by giving the computer several video feeds of the user. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 13 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 14 An Immersive Car Simulator Science Ứng dụng – Computational Neuroscience Using HMD(© British Aerospace) – Molecular modeling Engineering – Phobias ~ Virtual Therapy Aero Engine design – Telepresence Submarine design – Ultrasound Echolography Architecture Training Human factors modeling – High-risk work Industrial concept design – Flight simulation Telecoms engineering – Medicine Entertainment – Military training Computer animator – Nuclear industry Television – Accident simulation (Airline, Game system car collision testing) CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 15 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 16 A BOOM Display Application in Phân loạiVR-Desktop VR Aerodynamics (© NASA Ames Research Center) Desktop VR Non-immersive: chuột 3d, window system 3D world hiểnthị tren màn hình, chuột và bàn phím là đầuvàotương tác. Giá thấp, dùng cả vớiPC thôngdụng. VRML, Games Window on a World (WoW) Một số hệ thống sử dụng một màn hình truyền thống để hiển thị thế giới trực quan (visual world). Người ta phải xem màn hình hiển thị như là một cửa sổ mà qua cửa sổ đó người ta có thể thấy một thế giới ảo. Thách thức đối với lĩnh vực đồ hoạ máy tính là làm cho hình ảnh trong cửa sổ đó trông giống như thật, âm thanh nghe giống thật và các đối tượng hành động giống thật. “One must look at a display screen as a window through which one beholds a virtual world. The challenge to computer graphics is to make the picture in the window look real, sound real and the objects act real” [quoted from Computer Graphics V26#3]. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 17 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 18 Khoa CNTT - ĐHBK Hà nội hunglt@it-hut.edu.vn 0913030731 3 Bài 12 Thực tại ảo Thế giới thực bổ xung- Ánh xạ Video (Video Mapping) Augmented Reality Đây là một biến thể của cách tiếp cận theo kiểu WoW. Tiếp cận theo kiểu này Sự kết hợp giữa đồ hoạ và thế giới thực tạo thành 1 hệ thống sẽ kết hợp một đoạn video hình ảnh người sử dụng với đồ hoạ 2D. Người sử dụng sẽ thấy một màn hình hiển thị tương tác của hình anh ta với máy tính. chung phục vụ cho việc nhìn nhận và đánh giá thế giới thực. Kết hợp Telepresence và các hệ thống thực tại ảo cho ta một DVR hệ thống đơn giản sử dụng các thiết bị tương tác thông thường như : chuột 3d, window system. Thế giới 3D được hiển thị trên màn hình, chuột và thực tại hỗn hợp(Mixed Reality) hay các hệ thống mô phỏng bàn phím là đầu vào tương tác. liền mạch (Seamless Simulation systems). Ưu điểm của hệ thống và các ứng dụng loại nay là chi phí và giá cả thấp, có Ở đây, các dữ liệu vào sinh sinh ra bởi máy tính sẽ được hợp thể dùng được cả với PC thông dụng và các thiết bị thông dụng khác. nhất (kết hợp) với các dữ liệu vào telepresence và/hoặc quan Phù hợp với việc phát triển những ứng dụng đại tràvàcác sản phẩm cấp thấp điểm (cách nhìn) về thế giới thực của người sử dụng. không cần đến đội chính xác tuyệt đối. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 19 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 20 Xuất hiện - Presence Telepresence Telepresence : Là thuật ngữ mô tả việc sử dụng các công nghệ khác nhau gây hiệu ứng đặt ngưòi dùng tại một vị trí khác. Xuất hiện ảo-Virtual presence Telepresence là một cách mường tượng, hình dung các thế giới được sinh ra hoàn toàn trong máy tính. Đây là một kỹ thuật kết nối các cảm biến từ xa ... Is experienced by a person when sensory information generated only by and within a trong thế giới thực với cảm giác của người điều khiển. Các cảm biến từ xa computer compels a feeling of being present in an environment other than the one the person is actually in” (Sheridan, 1992, pg.6) này có thể được định vị trên một robot, giống như là các công cụ. Lính cứu hoả sử dụng các phương tiện điều khiển từ xa để xử lý những trường Presence: là cảm nhận tâm lý xuất hiện ở một môi trường dựa vào công nghệ hình hợp nguy hiểm. Các bác sĩ giải phẫu sử dụng các thiết bị vô cùng nhỏ trên thành theo kiểu hoà nhập - immersive. những dây cáp để thực hiện ca phẫu thuật mà không cần rạch ra một lỗ lớn Trên thực tế hệ thống hoạt động theo kiêu này không cần thiết áp dụng cho tất cả mọi trên cơ thể bệnh nhân. Các thiết bị này có một video camera nhỏở đầu làm người mà chỉ cho một vài người có vai trò nhất định trong cộng đồng. việc (business end). Việc tích hợp giữa immersive và presence luôn là bài toán khó cho công nghệ . Một Các robot được trang bị các hệ thống telepresence này đã thay đổi cách thức ứng dụng của Presence là: Telepresence và teleoperate thực hiện các cuộc thí nghiệm về biển sâu hoặc núi lửa. Kỹ thuật này ngoài ra còn được áp dụng trong các cuộc nghiên cứu vũ trụ... CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 21 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 22 II. Immersion( hoà nhập) Kỹ thuật sinh immersive Tạoracảm giác hoà nhậpgiữangườidùngvàmôitrường, hình ảnh quan Head-Mounted Display: Put the screen right in front of the sát là hình ảnh ngườisử dụng nhìn đượcbaogồmcả không gian và user’s eyes. Include a lens, for comfortable focusing. phương hướng. Advantage: It is easy to give the eyes different views. Phầnhìnhảnh người dùng quan sát đượcchỉ là 1 phầnrấtnhỏ so với Disadvantage: Need separate screen for each user. không gian hiểnthị BIG Disadvantage: When the user’s head moves, there is noticeable lag Thông thường công nghệ cho hiển thị đóng vai trò quan trọng và các cảm before the image updates. (Faster computers should fix this problem.) nhận khác cũng được kiểm tra. Large-Screen Display: Use a very large screen or group of Hệ thống thực tại ảo - VR systems sẽ tạo cho người dùng là một phần của screens that fill the user’s vision. thế giới ảo đang được mô phỏng chứ không đơn thuần môi trường ảo đang Advantage: Image-update lag is not as much of a problem. (Why not?) mô phỏng là 1 góc của thế giới thực mà người dùng hiện hữu. Advantage: Multiple users can view a single screen (but only one gets a precisely correct view). Hệ thống immersive VR đầu tiên là hệ thống mô phỏng lái máy bay mà ở BIG Disadvantage: The setup is incredibly expensive. đósự hoà nhập là sự kết hợp tinh xảo giữa các thiết bị thật và các hình ảnh Challenge: How to give the eyes different views? ảo. Buồng lái thật với các thiết bị thực tế cho phép phi công sử dụng như 1 chuyến bay bình thường. Hình ảnh hiển thị là những cảnh ảo được chuẩn bị sẵn. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 23 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 24 Khoa CNTT - ĐHBK Hà nội hunglt@it-hut.edu.vn 0913030731 4 Bài 12 Thực tại ảo Hoà nhập mức độ thấp Phân loại First Level of Immersion / Immersive - Virtual Environments Interactivity Low level, Physical level 1. Immersive Virtual Environments- môi trường ảo hoà nhập Because the computer is physically connected to the human • các đối tượng tương tác quan sát được và độc lập hoàn toàn với thế giới thật body by its senses and its motor responses. •Cảnh ảo phản ứng lại các hành động tương tác của đối tượng. The physical devices, Which interface to use ? • các đối tượng không thể tác động lên môi trường thật You have to know that not only Sight interface exist (HMD...), 2. Semi-Immersive Virtual Environments-môi trường ảo bán hoà nhập but lots of other,l you should have an idea of all the others • các đối tượng có thể tác động lên cả môi trường thật và ảo •vai trò của các đối tượng trong môi trường ảo lớn hơn nhiều so với môi trường What Hardware (interface, computer) ? thật What Software (Driver, Toolkit, Programming Language...) ? •tác động nên môi trường thực là rất hạn chế 3. Non-Immersive Virtual Environments – VR thông thường • các cảnh 3D như là 1 phần của thế giới thật (môi trường vật lý) • các đối tượng đáp lại hoàn toàn trong thế giới thật •Tồn tại rất ít quan hệ với môi trường ảo - VE CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 25 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 26 Các bướcthiếtkế Second Level : Mental Immersion / Interactivity of the user Triadic diagram for the behavioral interfacing VR Environments Desired Behavior... where are the Content shemas... • story writing Effective motor function : what the • scenario setup user will do : Schema, Schema by • semantics substitution or Metaphore Objects Effective perception : as natural as • geometry and static attributes (color etc) possible, with as many senses as • textures possible, and as weel synchorised •sound (cohering) as possible Dynamics programmed motor function : • object relationships Behavorial Software Assistance •events • dynamic object properties (behavior) Programmed perception : what is available from the virtual world System Implementation CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 27 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 28 Low Level Tools High Level Tools • Keep Track of Primitive Lists • Loading Objects (Geometry, Sounds) • Scene Graph Construction • Transformation of Vertices • Advanced Camera Models • Drawing of Primitives • Automatic Sensor Handling • Reading Devices on Driver Level • Automatic Collision Detection • Polygon Intersection Testing Examples • C++ Compiler Examples • Simulation Libraries (WorldToolKit, VRT, DIVE, dVise) • C++ Compiler • WorldUp, Superscape • OpenGL, Direct3D CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 29 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 30 Khoa CNTT - ĐHBK Hà nội hunglt@it-hut.edu.vn 0913030731 5 Bài 12 Thực tại ảo V. Phầncứng Mô hình chung Generic VR System Head Tracker Receiver Physical Simulation Head-mounted display(HMD) and Animation Head phones Microphone Glove Video Camera Lights Visual Illustration Model Glove tracker Voice 3D Sound Haptics Processor Head Position receiver Recognition Face / Gesture / Objects Motion Analysis Geometry INPUT Audio OUTPUT Host Computer Surface Properties 3D Tracker Dynamic Properties System VE Real-time OS Graphics Hand Position Physical Constrains Processor Acoustic Properties Haptic Tracker Machine VE Transmitter Collision Detection Intelligence Database CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 31 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 32 Màn hình và các thiếtbị tương tác 3D Input/output Display & interactive Devices Head-mounted display(HMD) Visual Displays (3D imagery) Degree of Freedom (DOF) • Head Mounted Displays (HMD) 6 DOF: translation and rotation of X, Y, Z axes • Projection Displays (CAVE, Virtual Plane) 3D mouse Acoustic Displays (spatial sound) Sonar-based • Multi-Channel Sound Systems 3D Trackball (Space-ball) • Specialized Convolution Processors (e.g. Convolvotron) Pressure sensors Haptic Displays (force feedback) Pushing, pulling, and twisting • Robot Arms (e.g. Grope, Phantom) Joysticks Specific platforms of exploration • Active Joystics (e.g. Microsoft Sidewinder) Gloves • Vibrotactile Devices (e.g. Logitec Cyberman) Finger angle (flexible sensors) Tracking the movement of the hands Sonic or electromagnetic system Postures CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 33 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 34 3D Input (Haptic device) 4 categories of haptic devices Dials 3D array Hand position and orientation Force-feedback devices forces and torque feedback devices Hand and body tracking LEDs tactile devices Hi-ball tracker devices to produce other stimuli such as heat or cold. Puppets Eye Tracking Gaze sensing Laser Scanner CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 35 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 36 Khoa CNTT - ĐHBK Hà nội hunglt@it-hut.edu.vn 0913030731 6 Bài 12 Thực tại ảo Sensory Interface Motor Interface CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 37 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 38 X. CAVE "CAVE Automatic Virtual Environment”. CAVE - An Immersive VR Environment 1. Introduction (EVL, University of Illinois at Chicago) One of the leading VR environments is the CAVE. “CAVE” stands for “CAVE Automatic Virtual Environment”. Originally a hardware/software combination, the CAVE was developed at the Electronic Visualization Lab at the U. of Illinois, Chicago, in the early 1990’s. The software component has since been separated and turned into a commercial product (CAVELIB, sold by VRCO) that runs in any number of VR environments. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 39 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 40 3.CAVE: 2.CAVE Hardware Software Standard CAVE hardware consists of: Like GLUT, CAVELIB handles program execution Any number of walls (screens). via registered callbacks. • The original idea was four: three vertical and a floor. GLUT can still be used with CAVELIB, but you never • ARSC has a 1-wall CAVE called an “ImmersaDesk”; we plan to get a 3-or-4 wall CAVE soon. call glutMainLoop, and so GLUT callback registration Any number of stereo glasses. does nothing. • One of these is for the driver; it has a tracker on it. Thus, the full features of GLUT are not available in A wand. CAVE programs. • This is a stick with a tracker on it, along with some buttons and a On the other hand, for programmers who are familiar with directional control (“joystick”). GLUT, learning CAVELIB is not hard. • The wand functions like a 3-D mouse. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 41 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 42 Khoa CNTT - ĐHBK Hà nội hunglt@it-hut.edu.vn 0913030731 7 Bài 12 Thực tại ảo CAVE: CAVE: Software [2/3] Software [3/3] CAVE programs run as a collection of processes. CAVELIB includes facilities for: The processes are created and managed by CAVELIB. The Determining head position and orientation. programmer does no forking. Computing projection matrices for each wall, for each eye. • This is done automatically. There is a main process, one process for each wall (and various other • For example, a standard 4-wall CAVE needs 8 projection matrices for each frame processes that the programmer does not need to worry about). of animation (assuming the user has 2 eyes). These processes may need to access common data. Determining wand position and orientation, as well as the state of the wand • There are facilities for allocating shared memory. buttons and joystick. • Read/write locks are available. Managing all the various processes. Most of this is handled by CAVELIB, but the programmer needs to Allocating shared memory areas. explicitly allocated shared memory and set/clear locks. Setting and clearing read/write locks on objects. Determining the time. Starting up and ending the whole mess. CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 43 CNTT-ĐHBK Hà nội 44 Khoa CNTT - ĐHBK Hà nội hunglt@it-hut.edu.vn 0913030731 8
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_do_hoa_hien_thuc_ao_bai_12_hien_thuc_ao_le_tan_hun.pdf
bai_giang_do_hoa_hien_thuc_ao_bai_12_hien_thuc_ao_le_tan_hun.pdf

