The factors affecting the supply chain integration in the fishery industry – Research in Ben Tre province
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between the antecedents and
business performance of organizations participating in the supply chain of the fisheries sector
in Ben Tre. Although the concept of supply chain has become more popular not only in
developed countries but also in Vietnam in recent years. However, not a lot of research
focused on how Vietnamese business organizations are integrated, what factors influence this
integration, and whether business performance is affected by the degree of integration.
Therefore, the research on this issue is necessary to not only help the managers but also
enrich the scientific knowledge in this field.
Supply chain integration is defined under many different ways. However, the integration used
in this area is the process of integrating partners in the chain including upstream and
downstream partners to better meet customer needs, which will increases the sustainable
competitiveness and revenue of organizations participating in the supply chain. The premise
factors that affect the supply chain integration of fisheries in Ben Tre are identified include:
risks in the supply chain and business strategy. Some of the basic theories used in this study
include the theory of resource – based view, the theory of the relationship between strategy,
structure and business performance and the theory of randomness or situation.
The structural equation modeling is used to examine the relationship between the
antecedents, the supply chain integration of fisher industry in Ben Tre province and the
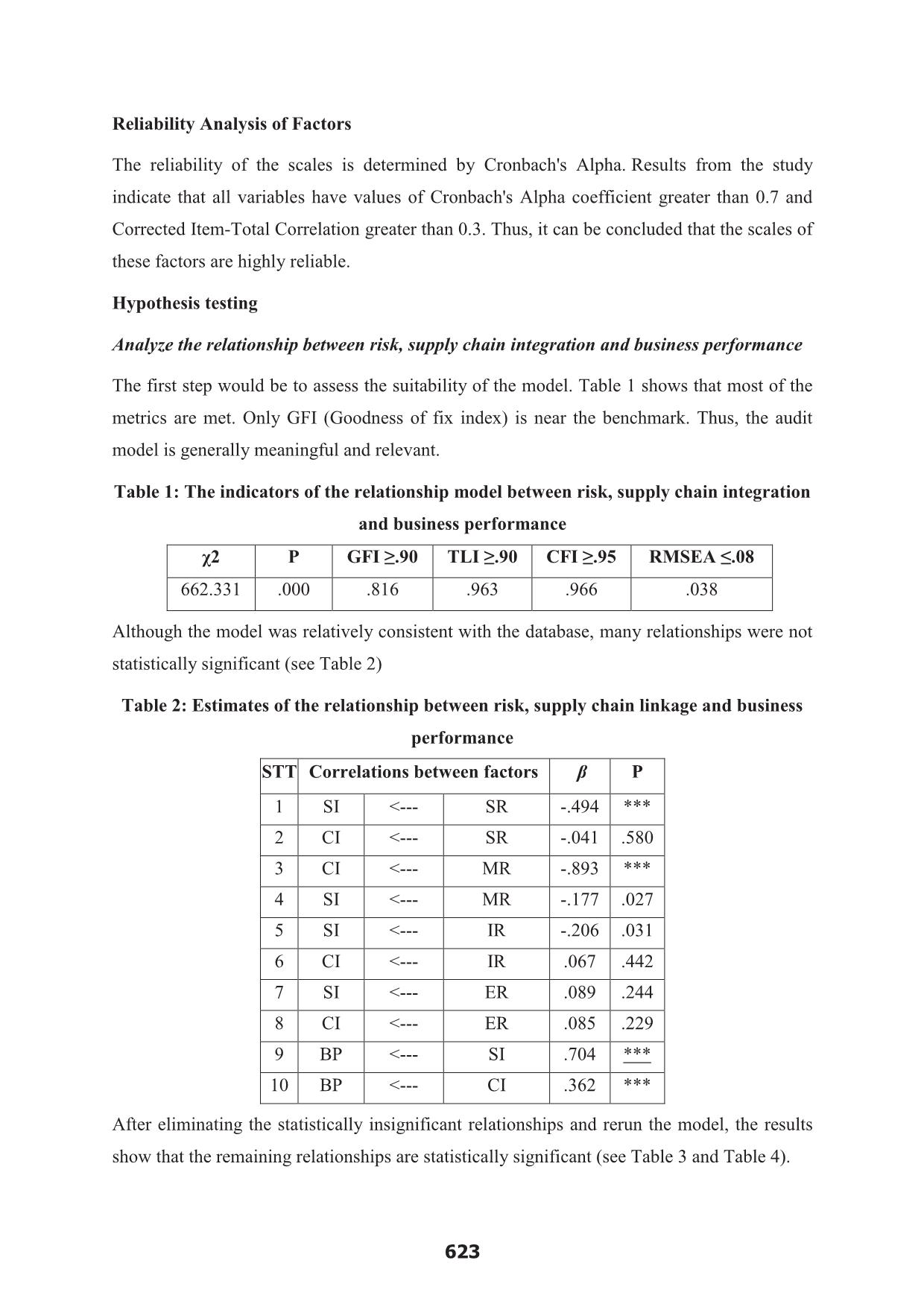
business performance. Most risk factors affect the link with the supplier, while only the
market risk affects the integration with the customer. Both cost-oriented, customer-oriented
and combined strategies have effect on the supply chain integration which in turn has an
impact on business performance.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: The factors affecting the supply chain integration in the fishery industry – Research in Ben Tre province

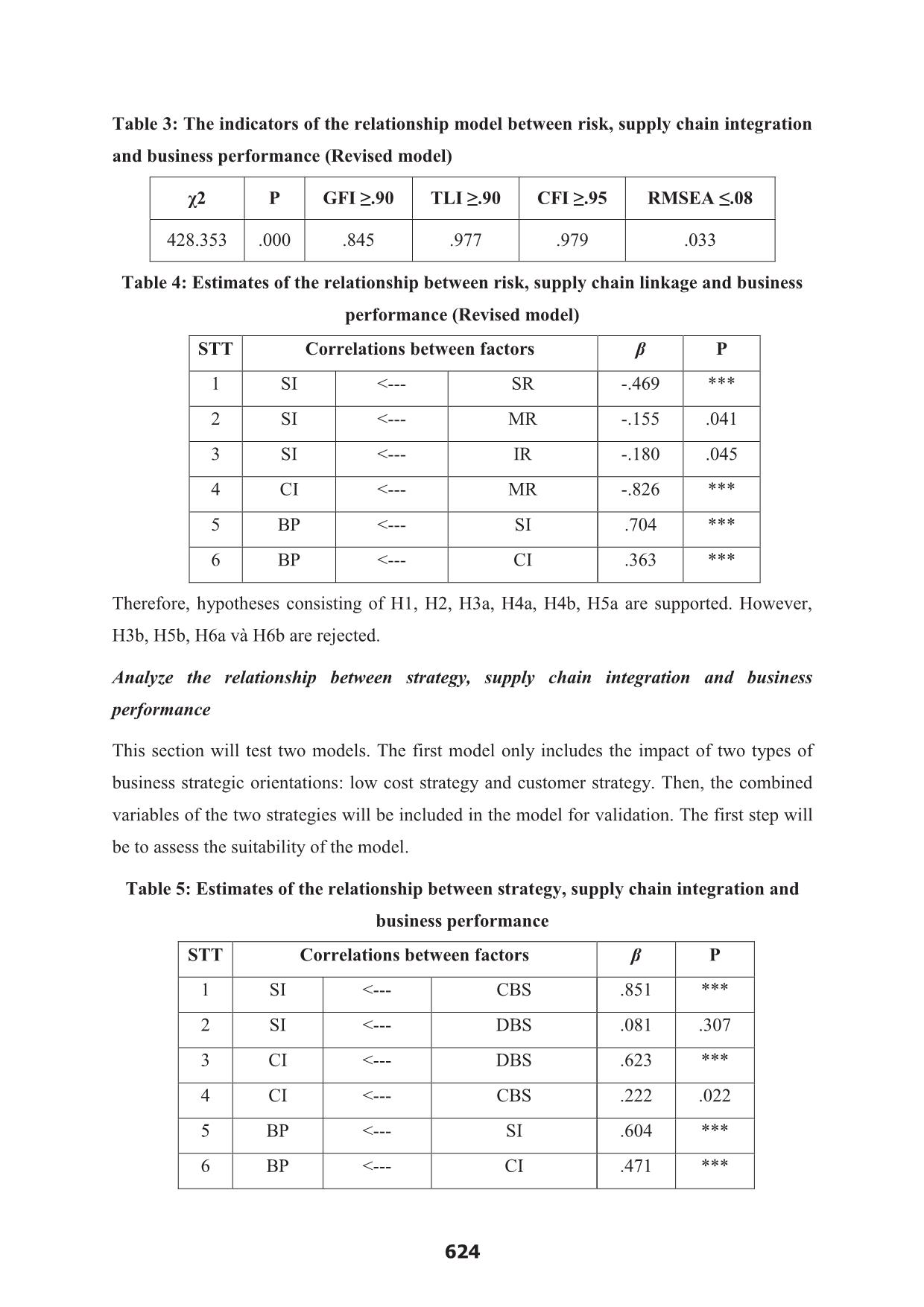
etween risk, supply chain linkage and business performance STT Correlations between factors β P 1 SI <--- SR -.494 *** 2 CI <--- SR -.041 .580 3 CI <--- MR -.893 *** 4 SI <--- MR -.177 .027 5 SI <--- IR -.206 .031 6 CI <--- IR .067 .442 7 SI <--- ER .089 .244 8 CI <--- ER .085 .229 9 BP <--- SI .704 *** 10 BP <--- CI .362 *** After eliminating the statistically insignificant relationships and rerun the model, the results show that the remaining relationships are statistically significant (see Table 3 and Table 4). 623 Table 3: The indicators of the relationship model between risk, supply chain integration and business performance (Revised model) χ2 P GFI ≥.90 TLI ≥.90 CFI ≥.95 RMSEA ≤.08 428.353 .000 .845 .977 .979 .033 Table 4: Estimates of the relationship between risk, supply chain linkage and business performance (Revised model) STT Correlations between factors β P 1 SI <--- SR -.469 *** 2 SI <--- MR -.155 .041 3 SI <--- IR -.180 .045 4 CI <--- MR -.826 *** 5 BP <--- SI .704 *** 6 BP <--- CI .363 *** Therefore, hypotheses consisting of H1, H2, H3a, H4a, H4b, H5a are supported. However, H3b, H5b, H6a và H6b are rejected. Analyze the relationship between strategy, supply chain integration and business performance This section will test two models. The first model only includes the impact of two types of business strategic orientations: low cost strategy and customer strategy. Then, the combined variables of the two strategies will be included in the model for validation. The first step will be to assess the suitability of the model. Table 5: Estimates of the relationship between strategy, supply chain integration and business performance STT Correlations between factors β P 1 SI <--- CBS .851 *** 2 SI <--- DBS .081 .307 3 CI <--- DBS .623 *** 4 CI <--- CBS .222 .022 5 BP <--- SI .604 *** 6 BP <--- CI .471 *** 624 Most relationships are statistically significant, with the exception of the relationship between the customer strategy and the association with the supplier (see Table 5). Thus, the Hypotheses H7a, H7b and H8b are accepted. Hypotheses H1 and H2 continue to be supported. However, the H8a hypothesis is not accepted. The next step is to incorporate the variable into the model for testing. Most relationships are not statistically significant when introducing a customer and low cost strategic orientations (see Table 6). Table 6: Estimates of the relationship between business strategy, mix strategy, supply chain integration, and business performance STT Correlations between factors β P 1 SI <--- CBS -.034 .873 2 SI <--- DBS -1.135 *** 3 CI <--- DBS .229 .207 4 SI <--- CBS.DBS .205 *** 5 CI <--- CBS.DBS .056 .071 6 CI <--- CBS -.044 .775 7 BP <--- SI .624 *** 8 BP <--- CI .460 *** CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMENDATIONS This section will focus on evaluating and analyzing the results of this study compared with the past studies. The next section will focus on solutions and recommendations to promote the integration among members in the fishery supply chain in Ben Tre. The relationship between risks, supply chain integration and business performance The study results showed that the variables of risk in the supply chain that affect the supply chain integration, including supply risks and market risks, risks from information sources. Particularly, the risks from supply related inversely to link with suppliers. This was proved by past studies in this field (Frohlich, 2002; Zsidisin, 2003; Zhao et al., 2013); however, it is contrary 625 to the theory of the relationship between the environment and the organization. While this theory suggests that the more unstable the environment, the more demanding the business is in order to limit that instability. The results of this study also indicate that the risk from the supply does not have an impact on customer integration. This is in contrast to previous studies (Frohlich, 2002; Zsidisin, 2003; Zhao et al., 2013). Market risk impacts the forms of association with both the customer and the supplier. This is in line with the research done by Jaffee et al. (2010). Risk from information sources only affects the degree of linkage between firms and suppliers (Christopher and Lee, 2004). However, this risk does not affect the association with customers, as opposed to the results of studies by Lee et al. (1997). In addition, the risk from the environment is quite surprising when there is no impact on supply chain integration. This is absolutely contrast to previous studies (Khan and Burnes, 2007). Finally, supply chain integration in turn has a positive impact on business performance. The results in this case study are consistent with previous studies, which suggest that the relationships with suppliers and customers affect business outcomes ( Rosenzweig et al., 2003; Paulraj and Chen, 2007; Li et al., 2006). The above results show that managers need to pay more attention to risk management in the supply chain, especially the risks from supply, market risk and risk from the information. Effective risk management improves the relationships between actors in the supply chain and hence improves sustainable competition and business efficiency. The relationship between strategy, supply chain integration and business performance The relationship between strategic orientations and form of integration will influence the business performance supported in this study. This result reinforces the relevance of the theory of the relationship between strategy, organizational structure and business performance (SSP). The low cost strategy affects the degree of integration among business organizations, suppliers and customers. This has also been confirmed in previous studies (Grant, 1991). However, customer-oriented strategies only affect customer integration, in line with Lambert's (2004) and Lee (2004) studies. This is also understandable because customer- oriented strategies also mean doing more to satisfy customers. One of the important activities is to understand and stick with the customer, so that the strategy and action is appropriate through the production and delivery of the right products and services that customers need. The results are not only true for organizations that follow by a single business strategy but also for enterprises which use the combined strategy have impact on supply chain integration which in turn affect business performance. 626 Contribution and limitations of the study Theoretical contribution This study validated and clarified the impact of supply chain integration on business outcome. Although there is quite a lot of research on this relationship, validating a relationship that has not yet yielded consistent results is still necessary to clarify the nature and the theoretical system (Fabbe-Costes and Jahre, 2008). Further evidence from a particular industry in a developing country would provide a meaningful comparison to previous studies primarily conducted in developed countries. Testing the relationship between risk, supply chain integration and business performance confirms the theory of the relationship between the environment and organizational structure in supply chain management (Aldrich and Pfefer, 1976). This also confirms that the environment has an impact on organizations and organizations need to change in organizational structure in order to adapt new environment. At the root of the supply chain, organizations need to change in the direction of supply chain integration to match changing trends in the current environment. In particular, due to competitive pressure and high global specialization, businesses have to change their structure in the direction of linking and developing their relationship in order to increase efficiency and sustainable competitiveness. Clarifying the relationship between strategy, supply chain integration and business performance also contributes to determine the correctness of the theory of strategic relationships, organizational structure and business outcomes (Chandler, 1962). William, 1975) in the supply chain. Thus, organizational change is not only due to environmental change, external volatility and risk but also to internal demand. Business strategy is one of the most important thing. This research has contributed to explaining the impact of combined strategies on the level of integration as well as the improvement of business performance of organizations. Practical contribution This research provides managers insight view about the impact of supply chain integration on business outcomes. To improve business performance, organizations need to strengthen the integration not only with suppliers but also with customers; as both types of integration have a positive impact on business performance. This research also helps managers understand the important role of identifying and mitigating the impact of risk on supply chain integration. Measures must be taken to identify 627 the types of risks that occur from the supplier, market, information and environment. The next step is measuring the magnitude of the impact on supply chain integration. Finally, possible solutions will be introduced to limit the impact of these risks. Lastly, the thesis also shows the influence of business strategy on supply chain integration. Managers need to identify the organization's business strategy in line with the current supply chain context in order to determine the form and degree of integration that can deliver optimum business performance. Some limitations of the study The first limitation of the study is to conduct data surveys in short-term. While the impact of supply chain integration on business performance generally takes place over a period of time. Therefore, future studies should test this relationship over a period of time large enough to produce more accurate results. The second limitation of the study is to measure the performance of the enterprise by qualitative indicators. In addition, the scales depend heavily on the perception of the respondents to fill in the questionnaire. Therefore, future research should use quantitative and objective data that will give better results. Finally, this study was conducted in Ben Tre province and the results of the research can only be applied to some provinces in the Mekong Delta, where the context is similar to Ben Tre province. This study is difficult to apply to provinces in other parts of Vietnam. Therefore, further studies should be conducted in other regions to provide a more comprehensive overview of the study of the fishery sector in Vietnam. 628 REFERENCES 1. Afuah, A. (2001), “Dynamic boundaries of the firm: are firms better off being vertically integrated in the face of a technological change?”, Academy of Management Journal, số 6, tập 44, trang 1211-1228. 2. Aldrich, H. E. and Pfeffer, J. (1976), “Environments of organizations”, Annual Review of Sociology 3. Anderson, J.C., Narus, J.A. (1990), “A model of distributor firm and manufacturer firm working partnerships”, Journal of Marketing, số 54, trang 42 -58. 4. Benchtel, C., Jayaram, J., (1997), “Supply chain management: A strategic perspective”, The international Journal of Logistics Management, số 1, tập 8, trang 15 - 34. 5. Calantone, R., Garcia, R. and Dro¨ge, C. (2003), “The effects of environmental turbulence on new product development strategy planning”, Journal of Product Innovation Management, sô 20, tập 2, trang 90-103. 6. Chandler, A.D. (1962). Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of American Enterprise. MIT Press, Boston. 7. Chen, I.J., Paulraj, A. (2004). Towards a theory of supply chain management: the constructs and meansurement. Journal of Operations Managements, số 22, trang 119- 150. 8. Christopher, M., và Lee, H. L. (2004), “Mitigating Supply Chain Risk through Improved Confidence”, International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics Management, số 34, tập 5, trang 388 - 396. 9. Habib, M. M., & Victor, B. (1991). Strategy, structure, and performance of U.S. manufacturing and service MNCs: A comparative analysis. Strategic Management Journal 10. Higgins, J.M., and Vincze, J.W. (1989). Strategic Management Text and Cases, New York, NY: The Dryan Press. 11. Khan, O. and Burnes, B. (2007). Risk and supply chain management: creating a research agenda. The International Journal of Logistics Management, số 18, tập 2, trang 197-216. 12. Lambert, D.M., Stock, J.R. (1993). Strategic Logistics Management (Homewood: Dow- Jones Irwin). 13. Lee, H. L., Padmanabhan, V., và Seungjin, W. (1997), Information Distortion in a Supply Chain: The Bullwhip Effect, Management Science, số 43, tập 4, trang 546-558. 629 14. Lee, H.L., Whang, S. (2000). Information sharing in a supply chain. International Journal of Technogogy Management, số 20 (3-4), trang 373-387. 15. Li, S., Ragu-Nathan, B., Ragu-Nathan, T.S., Rao, S.S. (2006). The impact of supply chain management practieson competitive advantage and organizational performance. The International Journal of Management Science, số 34, trang 107-124. 16. Liu, Y. (2010). Social Media Tools as a Learning Resource. Journal of Educational Technology Development and Exchange, số 1, tập 3, trang 101-114. 17. Mentzer, J.T., DeWitt, W., Keebler, J.S., Min, S., Nix, N.W., Zacharia, Z.G. (2001). “Defining supply chain management”, Journal of Business Logistics, số 22, tập 2, trang 1 - 25. 18. Miles, R.E. & Snow, C.C. (1978). Organizational strategy, structure, and process. New York, West, số 3, tập 3, trang 546 – 562. 19. Neuman, W.L. (2000). Social research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches (4thed.) Boston; Allyn and Bacon. 20. Paulraj, A. (2007). Environmental Uncertainty and Strategic Supply Management: A Resource Dependence Perspective and Performance Implications. The Journal of Supply Chain Management số 43, tập 3, trang 29-42. 21. Trkman, P. and McCormack, K. (2009). Supply chain risk in turbulent environments – a conceptual model for managing supply chain network risk. International Journal of Production Economics, số 119 (2), trang 247 - 258. 22. William, J.R. (1992). How sustainable is your comperitive advantage? California Management Review, số 34, tập 2, trang 29-51. 23. Woodward, J. (1965): Industrial organization: Theory and practice. New York: Oxford University Press. 24. Zhao, L., Sun, L., Zhao, Xiande. (2013). The impact of supply chain risk on supply chain integration and company performance: a global investigation. Supply chain management: An International Journal, số 182, trang 115 - 131. 630
File đính kèm:
 the_factors_affecting_the_supply_chain_integration_in_the_fi.pdf
the_factors_affecting_the_supply_chain_integration_in_the_fi.pdf

