Nuclear Science and Technology - Volume 9, Number 3, September 2019
Abstract: An investigation on the nuclear transmutation of elemental long-lived fission product
(LLFP) in a fast reactor is being conducted focusing on the I-129 LLFP (half-life 15.7 million
years) to reduce the environmental burden. The LLFP assembly is loaded into the radial blanket
region of a Japanese MONJU class sodium-cooled fast reactor (710 MWth, 148 days/cycle). The
iodine element containing I-129 LLFP (without isotope separation) is mixed with YD2 and/or YH2
moderator material to enhance the nuclear transmutation rate. We studied the optimal moderator
volume fraction to maximize the transmutation rate (TR, %/year) and the support factor (SF is
defined as the ratio of transmuted to produced LLFP). We also investigated the effect of LLFP
assembly loading position in the radial blanket and the severe power peak appeared at the fuel
assembly adjacent to the LLFP assembly.
Keywords: Nuclear transmutation, long-lived fission product, I-129, radial blanket, sodium-cooled
fast reactor.
I. INTRODUCTION
Transmutation of long-lived fission
products (LLFPs: Se-79, Zr-93, Tc-99, Pd-
107, I-129, and Cs-135) into short-lived or
stable nuclides by fast neutron spectrum
reactors is being revisited in Japan [1]. The
geological disposal of high-level radioactive
wastes (HLRW) as the nuclear fuel cycle byproducts raises public concern in Japan and
many other countries since even after
thousands of years, minor actinides (MAs)
and some LLFPs remain and become the main
contributors of the radioactive hazard. Under
the partitioning and transmutation (P&T)
strategy, research and development efforts are
being conducted to reduce the radioactive
waste to be stored and the above-mentioned
long-term hazard for future generations [2].
The P&T strategy in general is implemented
first by elemental separation of MAs and
LLFPs from HLRW using chemical processes
(partitioning) and then followed by nuclear
reactions of the MAs and LLFPs into shortlived or stable nuclides (transmutation). The
transmutation can be done in a nuclear reactor
or in an accelerator-driven transmutation
system (ADS).
In this present study, we focus on the
transmutation of one LLFP, i.e. I-129 (half-life
15.7 million years) using a sodium-cooled fast
reactor, in particular in the radial blanket
region.

Trang 1
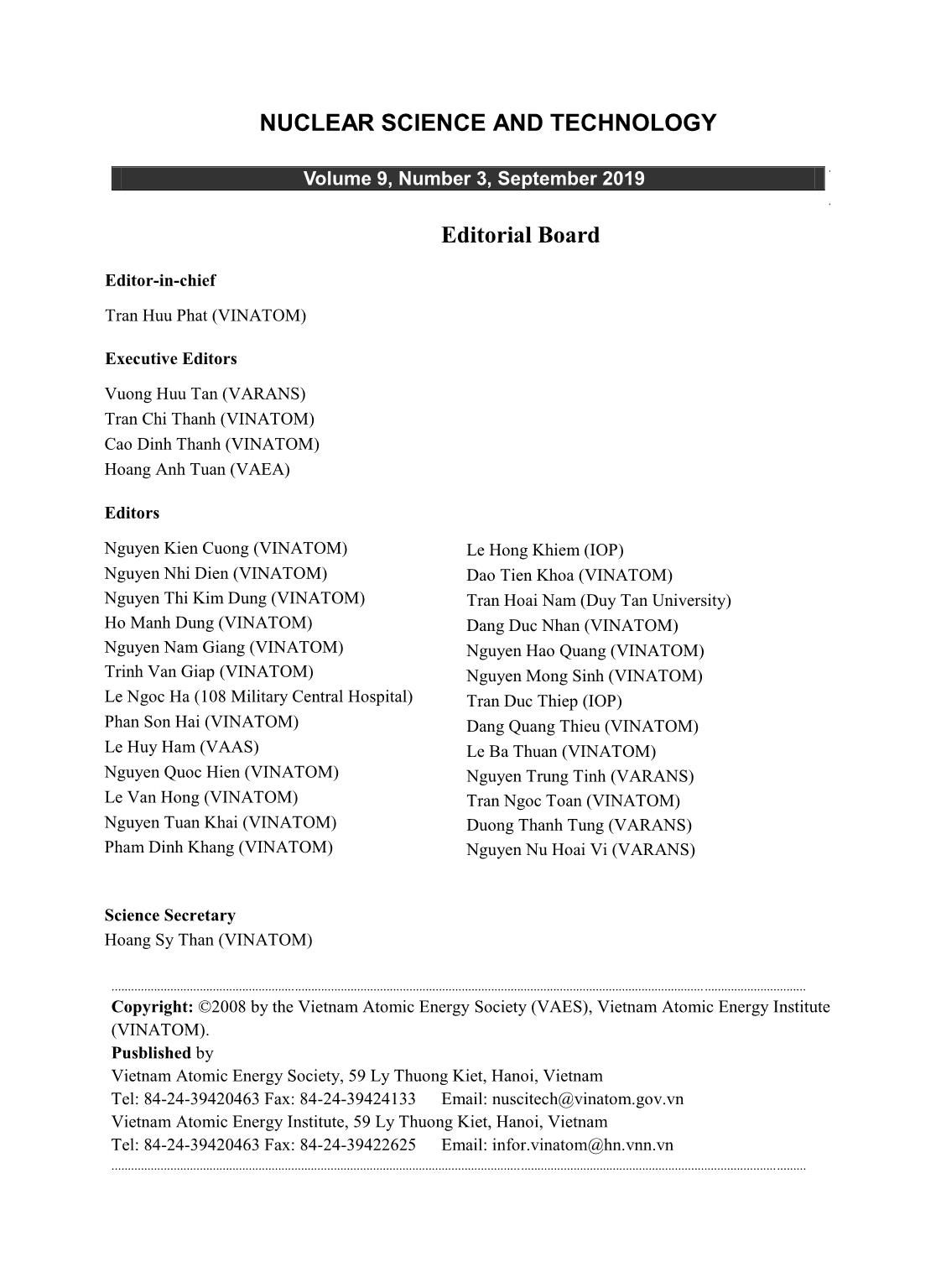
Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
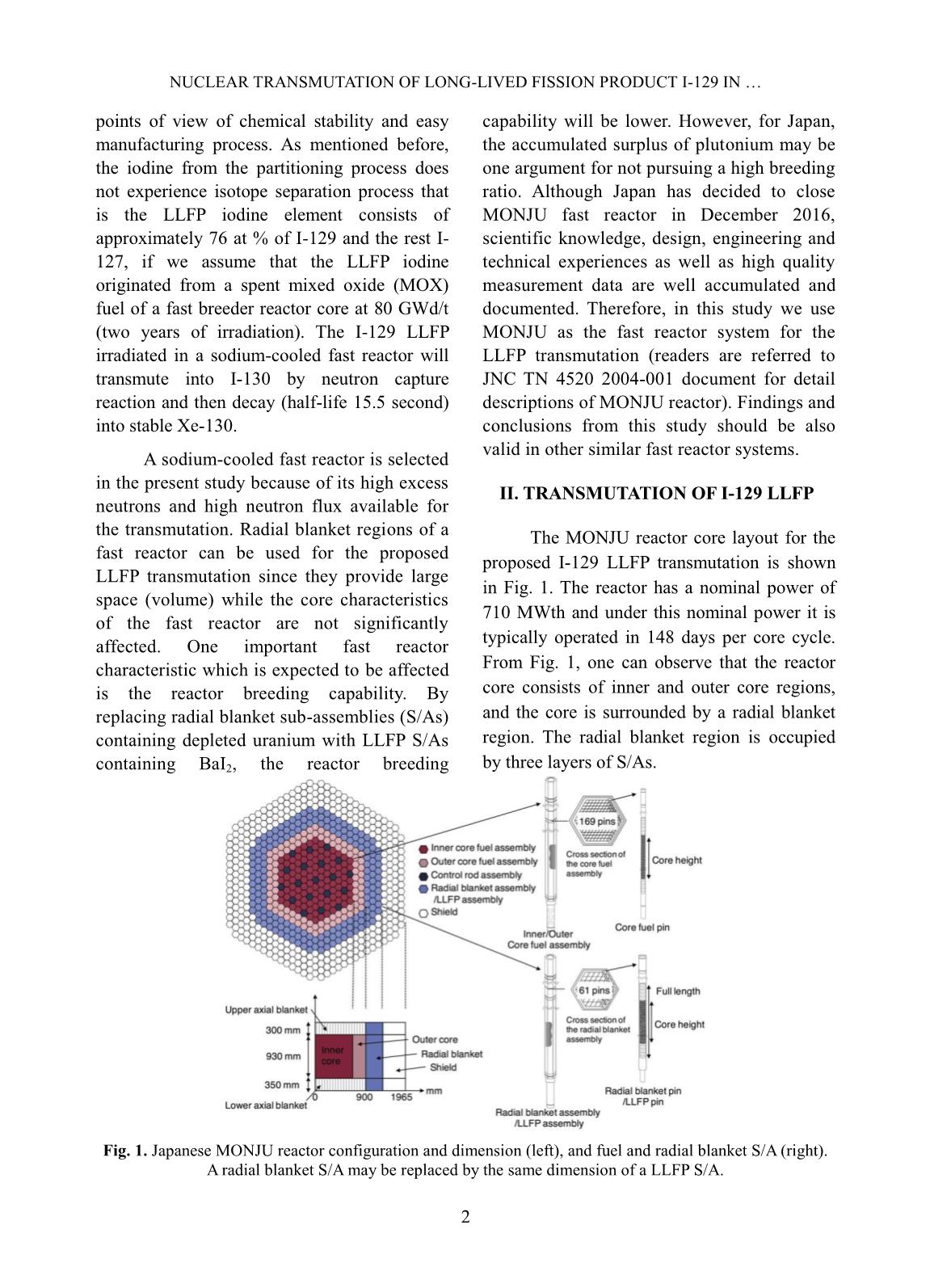
Trang 5
Trang 6
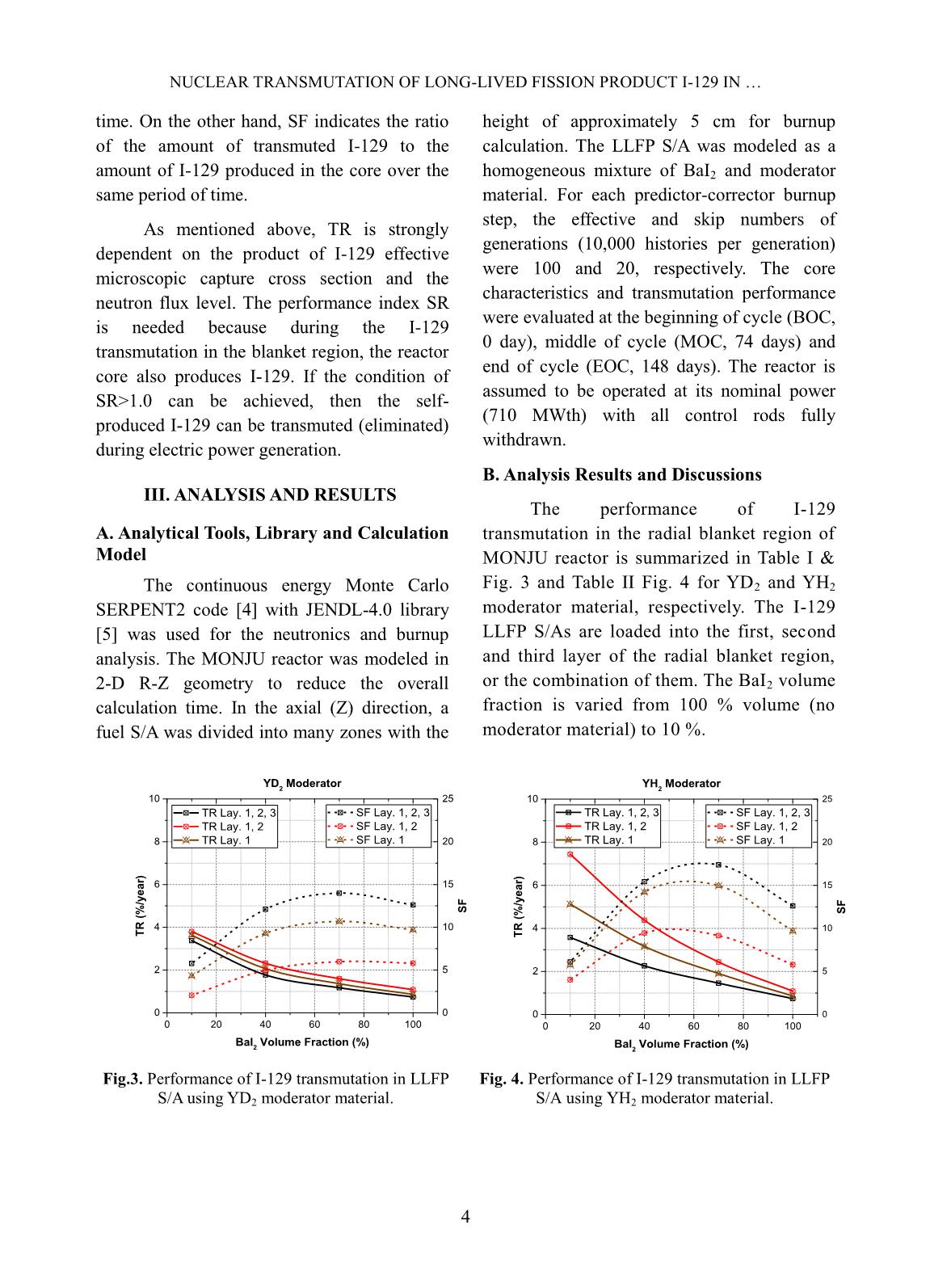
Trang 7
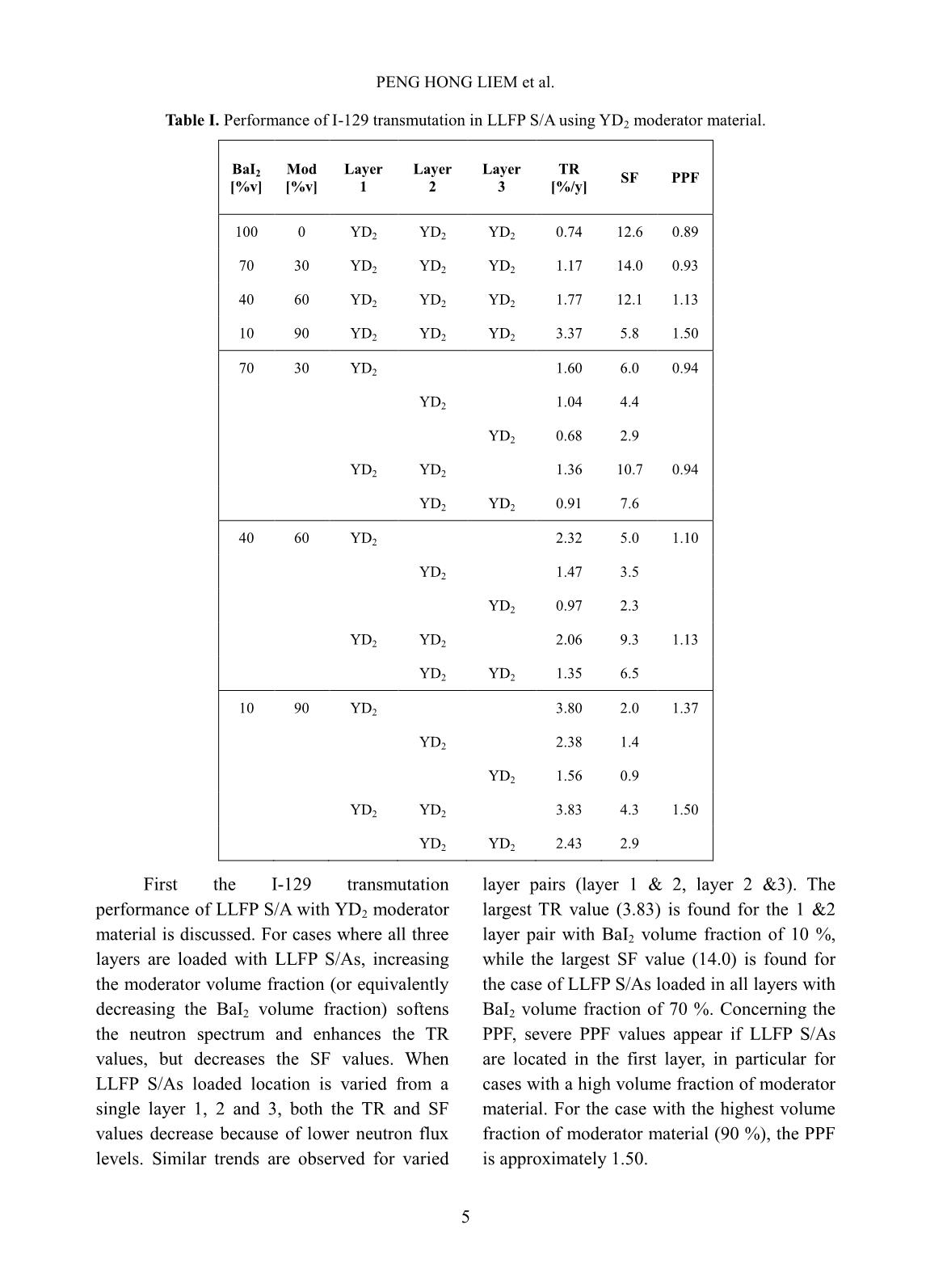
Trang 8
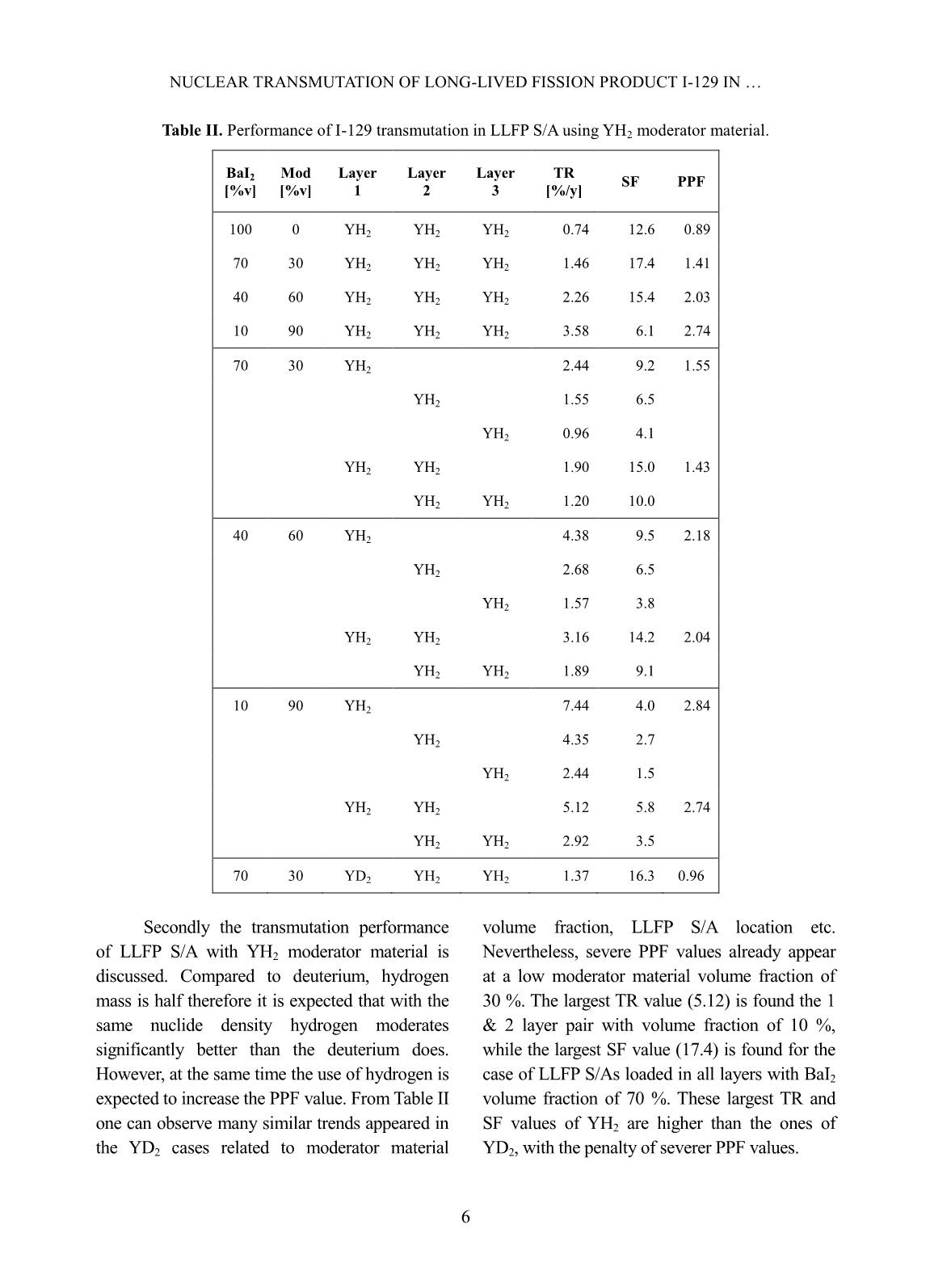
Trang 9
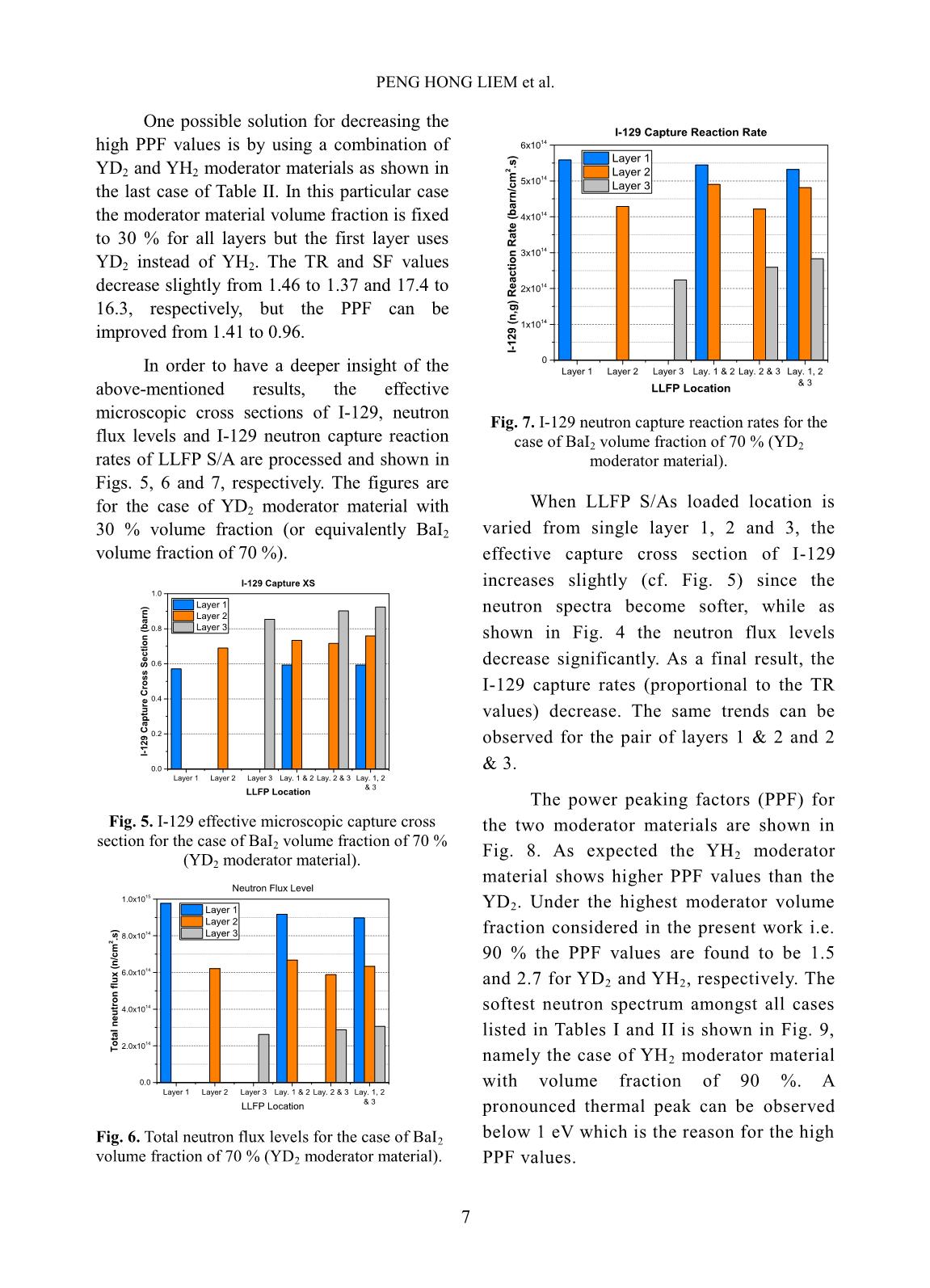
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Nuclear Science and Technology - Volume 9, Number 3, September 2019

still controversial. The first study LE XUAN CHUNG et al. 49 observed the 367 keV transition [9]. This level was thought to be isomeric state 9/2 + decaying to the ground state 5/2 - via a M2 transition, see Figure 1.a. Afterwards, M. Sawicka et al. reported that beside 367 keV they also observed 387 keV transition from 67 Fe isomer [10]. The 387 keV level was concluded isomeric and the 367 keV was in the cascade of this isomer when it decays to the ground state. The branching ratio (I ) of these two transitions was I(387)/I(367)=0.11(2) [10]. The summary of the study in Ref. [10] is presented in Figure 1.b. Recently, an important conclusion was reported by J.M. Daugas et al. in Ref. [11]. Where, the 367 and 387 keV prompt transitions of 67 Fe were observed in the -decay of 67Mn. It meant that the 387 keV level is not isomeric. Moreover, the ratio of these transitions were determined to be I(387)/I(367)=0.77(26), different from the above value of 0.11(2) obtained in Ref. [10]. This led to the conclusion that the initial isomers of the 367 and 387 keV transitions may be different. No information concerning the direct feeding of the isomeric states was extracted by the 67 Mn -decay experiment in Ref. [11]. Together with the studies in Refs. [9- 10], the isomeric levels were proposed to be above 387 keV, which decays via highly converted transition or transition of too low energy to be observed. Therefore, the isomeric levels were proposed to be less than 420 keV. The explanation for the measurement in Ref. [11] is shown in Figure 1.c. According to the calculation [11], the 2 possibly isomeric states are 5/2 + and 7/2 + . The ground state is 1/2 - obtained from Ref. [13]. In addition to the gamma spectrum, the half-life of the isomeric state which decays to the 367 keV level was determined with large discrepancy, 43(30) µs in Ref. [9] and 75(21) µs in Ref. [10]. In this paper, a study of the above mentioned isomers of 67 Fe is reported. First, we discuss the delayed-gamma-ray energy spectrum. Afterwards, we discuss the half-life of the isomeric state based on the time- dependence of the observed events. The experiment was performed within the framework of the “Shell Evolution And Search for Two-plus energies At RIBF” (RIBF- Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory) project [14], in short SEASTAR. II. EXPERIMENTAL METHOD A 238 U primary beam with the mean intensity of 12 pnA was accelerated up to 345 MeV/u energy by the Superconducting Ring Cyclotron (SRC). Afterwards, it bombarded a 9 Be primary target at the F0 focal plane of the BigRIPS [15] separator to produce the secondarily cocktail beam. The secondary beam was transported to the user location at the F8 focal plane and interacted with MINOS [16] LH2 active target. Prompt gamma de-excitation from residues was detected by the DALI2 [17] NaI crystals surrounding the MINOS target. Measuring prompt gamma-ray energies was the main purpose of the SEASTAR experiments. The experimental setup for this purpose is shown in Figure 2, and described in details in Refs. [18-19]. For the delayed-gamma study, an additional detector setup, EURICA (Euroball- RIKEN Cluster Array) [20], was located at the end of the experimental setup described in Figure 2, at the F11 focal point. This gamma- ray detector array consists of 84 high-purity germanium crystals (HPGe) subdivided into 12 7-crystal clusters distributed in three different rings at 51 o (five clusters), 90 o (two clusters), and 129 o (five clusters) relative to the beam axis at a nominal distance of 22 cm from the center. The energy resolution of the HPGe crystal detector was better than 3 keV at Eγ=1.3 MeV with a photo-peak efficiency of about STUDY ON THE ISOMERIC DECAY OF NEUTRON-RICH ISOTOPE 67 FE 50 15% for Eγ= 662 keV [20]. The beam was stopped in a thick-aluminium plate centered in the arrays. A picture of the stopper surrounded by the EURICA clusters is shown in Figure 3. Fig. 2. Experimental setup for prompt-gamma detection in SEASTAR experiments. The label Fn indicates the position of foci. BigRIPS is from F1-F8. ZeroDegree is from F9-F11. PPACs and MUSICs were used for tracking and identifying purpose. The inset is a sketch of the main detectors MINOS and DALI2 with an illustration for 68 Fe(p, pn) 67 Fe. Zv is the vertex point. EURICA was located at F11 for the decay study. Fig. 3. Illustration of EURICA detector with a thick-aluminium-plate stopper at the center. III. DATA ANALYSIS AND RESULTS For the present isomeric study, the identification for the implanted 67 Fe ions in the aluminium stopper was considered. This required the particle identification (PID) from the ZeroDegree spectrometer [15], in other words the PID for outgoing particles from the MINOS target. EURICA detected the gammas emitted from implanted ions. The independent ZeroDegree and EURICA LE XUAN CHUNG et al. 51 data was merged according to their time stamp with an additional in-beam trigger from DALI2 for separation of the data into different reaction channels, or analyzed independently for high-statistics total isomer-yield. Due to the inclusion of BigRIPS data via the DALI2 data stream, it was possible to identify the relative ratio of 67 Fe isomeric- decay intensity from the different channels [21]. The channel PID has been discussed in details in Ref. [18-19]. As an example, the 68 Fe(p, pn) 67 Fe identification is shown in Figure 4. Fig. 4. Particle identification via atomic charge (Z) versus mass-to-charge ratio (A/Q). The marked crowns are identified for 68,67 Fe at BigRIPS and ZeroDegree, respectively, for 68 Fe(p,pn) 67 Fe channel. Fig. 5. Delayed gamma energy spectra of 67 Fe from (p,2p) and (p,pn) channels detected by EURICA. STUDY ON THE ISOMERIC DECAY OF NEUTRON-RICH ISOTOPE 67 FE 52 The delayed gamma energy spectra of 67 Fe from (p,2p) and (p,pn) channels are presented in Figure 5. In both cases, the gamma of 367 keV are clearly observed. For higher statistics, the trigger without DALI2 gamma detection was used. In this case, only the ZeroDegree trigger was consider to identify implanted 67 Fe ions into aluminium thick-plate stopper, see Figure 3. The total isomeric spectrum is presented in Figure 6. Two lines are observed at 367 and 387 keV. The relative ratio I(387)/I(367) is determined to be equal to 0.126(3) in agreement with the value 0.11(2) reported in Ref. [10]. This might be from the fact that the implanted 67 Fe ions in the present study and Ref. [10] were produced by knockout reactions of an approximately 250 MeV/u cocktail beam on a proton target and by fragmentation of the 60 MeV/u 86 Kr beam on nat Ni target, respectively. As the result, the 67 Fe isomers were fed by these similar mechanisms that was not the case of the 67 Mn -decay experiment in Ref. [11]. Fig. 6. The total isomer-yield gamma energy spectrum of 67 Fe detected by EURICA. From Figure 5 and 6, it is seen that the 387 keV line is visible only in the total isomer-yield gamma spectrum. This is explained that either the particular (p, 2p) and (p, pn) reactions do not feed the isomer which decays to the 387 level or the statistic is not enough. The decay curve was built by gating on 367 keV in the EURICA HPGe array and plotting the time-difference between the HPGe and the final BigRIPS scintillator, see Figure 7. This curve was fitted with an exponential function to get the half-life of the decay. From this we obtained a half-life of T1/2=150(10) µs. Compared to the previous result, the current value is about twice the most recently reported value of 75(21) µs [10]. This discrepancy could be related to the time range in the current experiment, up to 100 µs, while the range was only 45 µs in Ref. [10]. For a long half-life, this leads to a bias of the fitting results for too short time-ranges. Moreover, our statistics are much higher than previous work [10] which also influences the fitting results. LE XUAN CHUNG et al. 53 Fig. 7. Decay curve of the isomer via 367 keV state in 67 Fe. The points with error bar are experimental data. The solid line is the fitting exponential curve. IV. CONCLUSIONS In this paper, the study on the isomeric decay of neutron-rich isotope 67 Fe is reported. The gamma-delayed energy spectra of this isotope were recorded from 68 Co(p, 2p) 67 Fe and 68 Fe(p, pn) 67 Fe channels as well as 238 U fission. The spectra obtained from these first 2 channels clearly show the peak at 367 keV. While the total isomer- yield spectrum clearly presents 2 lines at 367 and 378 keV. The invisibility of 378 keV line was explained either the (p, 2p) and (p, pn) channels did not feed these isomer which decays to ground state via 387 keV gamma emission or the statistics is not enough. The half-life time of the isomer which decays to the 367 keV level was measured to be equal to 150(10) µs, significantly longer than previously measurements. This work is partly supported by VINATOM via the Grant No. ÐTCB.09/17/VKHKTHN. REFERENCES [1]. C. Santamaria et al., Physical Review Letters 115, 192501, 2015. [2]. N. Paul et al., Physical Review Letters 118, 032501, 2017. [3]. R. Taniuchi et al, Nature 569, 53, 2019. [4]. L.X. Chung et al., Physical Review C 92, 034608, 2015. [5]. S. Chen et al., Physical Review Letters 123, 142501, 2019. [6]. A. Navin et al., Physical Review Letters 85, 266, 1999. [7]. J. M. Daugas et al., Physics Letters B 476, 213, 2000. [8]. R. Grzywacz et al., Physics Letters B 355, 437, 1995. [9]. R. Grzywacz et al., Physical Review Letters 81, 766, 1998. [10]. M. Sawicka et al., European Physical Journal A 16, 51, 2003. [11]. J.M. Daugas et al., Physical Review C 83, 054312, 2011. [12]. Phong V. H. et al., Physical Review C 100, 011302(R), 2019. STUDY ON THE ISOMERIC DECAY OF NEUTRON-RICH ISOTOPE 67 FE 54 [13]. D. Pauwels et al., Physical Review C 79, 044309, 2009. [14]. P. Doornenbal and A. Obertelli, RIBF NP- PAC-13, 2013. [15]. N. Fukuda et al., Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 317, 323, 2013. [16]. A. Obertelli et al, The European Physical Journal A 50, 8, 2014. [17]. S. Takeuchi et al., Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 763, 596, 2014. [18]. B. D. Linh et al., Nuclear Science and Technology 7, 08-15, 2017. [19]. N. D. Ton et al., Nuclear Science and Technology 8, 04, 2018. [20]. -A S derstr m et al., Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 317, 649, 2013. [21]. -A S derstr m et al., RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report 51, 2018. INSTRUCTIONS FOR AUTHORS GENERAL INFORMATION Nuclear Science and Technology (NST), an international journal of the Vietnam Atomic Energy Society (VAES) and Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VINATOM), quarterly publishes articles related to theory and application of nuclear science and technology. All papers and technical notes will be refereed. It is understood that the paper has been neither published nor currently submitted for publication elsewhere. The copyright of all published papers and notes will be transferred in VAES. DETAILED FIELDS NST coves all fields of nuclear science and technology for peaceful utilization of nuclear energy and radiation. Authors should choose one of the following fields at the time they submit their manuscript: 1) Nuclear Physics, 2) Nuclear Data, 3) Reactor Physics, 4) Thermal Hydraulics, 5) Nuclear Safety, 6) Nuclear I&C, 7) Nuclear Fuel and Materials, 8) Radioactive Waste Management, 9) Radiation Protection, 10) Radiation Technology, 11) Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture, 12) Nuclear Medicine and Radiotherapy, 13) Nuclear Techniques in Industries, 14) Environment Radioactivity, 15) Isotope Hydrology, 16) Nuclear Analytical Methods, 17) Health Physics, 18) Fusion and Laser Technology. MANUSCRIPT SUBMISSION Manuscript for publication should be submitted to the Editorial Office in triplicate by postal mail. For electronical submission use nuscitech@vinatom.gov.vn. Submission Address Department of Planning, R&D Management Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute, 59 Ly Thuong Kiet Street, Hanoi, Vietnam E-mail: nuscitech@vinatom.gov.vn. MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION Manuscripts must be written in English with adequate margins and indented paragraph. All manuscript must use SI (metric) units in text, figures, and tables. Manuscripts should in general be organized in the following order: title, names of authors and their complete affiliation including zip code, abstract (not exceeding 200 words), keywords (up to 7), introduction, main body of a paper, acknowledgments, references, appendices, table & figure captions, tables and figures. Unnecessary sections may be omitted. Headings: Use I, II, for major headings and A, B, for secondary headings. Mathematical formulas: All mathematical formulas should be clearly written, with special consideration to distinctive legibility of sub-and superscripts. Equation (at least the principal ones) should be numbered consecutively using Arabic numerals in parentheses in the right hand margin. Tables and Figures: Tables should be numbered with Roman numerals. Figures should be numbered consecutively with Arabic numerals in order of their first appearance and have a complete descriptive title. They should be typed on separate sheets. Tables should no repeat data which are available elsewhere in the paper. Figures should be original ink drawing or computer drawn figures in the original and of high quality, ready for direct reproduction. Figures should be referred to in the text as, for example, Fig. 1., or Fig. 2. . Reference: References should be listed at the end of the text and presented as follows: [1] C. Y. Fu et al., Nuclear Data for Science and Technology, S. M. Qaim (Ed.), p. 587 (1991). [2] C. Kalbach, Z. Phys, A283, 401 (1977). [3] S. Shibata, M. Imamura, T. Miyachi and M. Mutou, “Photonuclear spallation reactions in Cu”, Phys. Rev. C 35, 254 (1987). KHOA HỌC VÀ CÔNG NGHỆ HẠT NHÂN Chịu trách nhiệm xuất bản TRẦN HỮU PHÁT Chịu trách nhiệm nội dung TRẦN HỮU PHÁT TRẦN CHÍ THÀNH Trình bày LÊ THÚY MAI In 200 cuốn, khổ 19x26,5cm tại Công ty TNHH Trần Công Địa chỉ: số 12 ngách 155/176 Đường Trường Chinh, Hà Nội Giấy đăng ký kế hoạch xuất bản số: 770/GP-BTTTT cấp ngày 20 tháng 5 năm 2011 In xong và nộp lưu chiểu Quý IV năm 2019 25 000đ
File đính kèm:
 nuclear_science_and_technology_volume_9_number_3_september_2.pdf
nuclear_science_and_technology_volume_9_number_3_september_2.pdf

