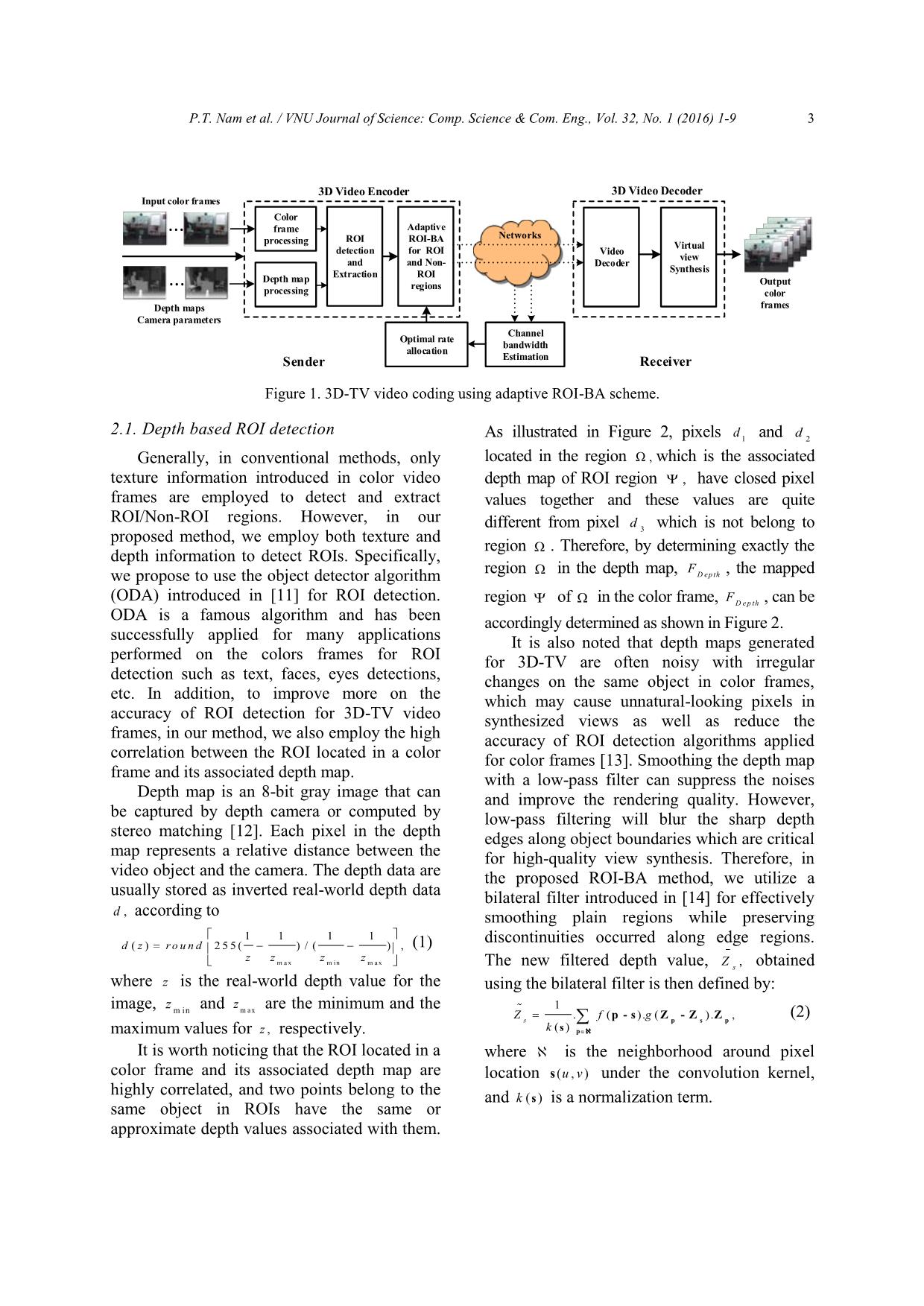
Efficient region-Of-interest based adaptive bit allocation for 3D-TV video transmission over networks
Due to characteristics of human visual system (HVS), people usually focus more on a specific region named
region-of-interest (ROI) of a video frame, rather than watch the whole frame. In addition, ROI-based video
coding can also help to effectively reduce the number of encoding bitrates required for video transmission over
networks, especially for the 3D-TV transmissions. Therefore, in this work, we propose a novel ROI-based bit
allocation (BA) method which can adaptively extract and increase the visual quality of ROI while saving a huge
number of encoding bitrates for video data. In the proposed method, we first detect and extract ROI based on the
depth information obtained from 3D-TV video coding sequences. Then, based on the extracted ROI, a novel BA
scheme is performed to solve the rate-distortion (R-D) optimization problem, in which the higher priority bitrates
are adaptively assigned to ROI while the total encoding bitrates of video frames are kept satisfying all constraints
required by the R-D optimization. Experimental results show that the proposed method provides much better
higher peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) as compared to other conventional BA methods.

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7
Trang 8

Trang 9
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Efficient region-Of-interest based adaptive bit allocation for 3D-TV video transmission over networks

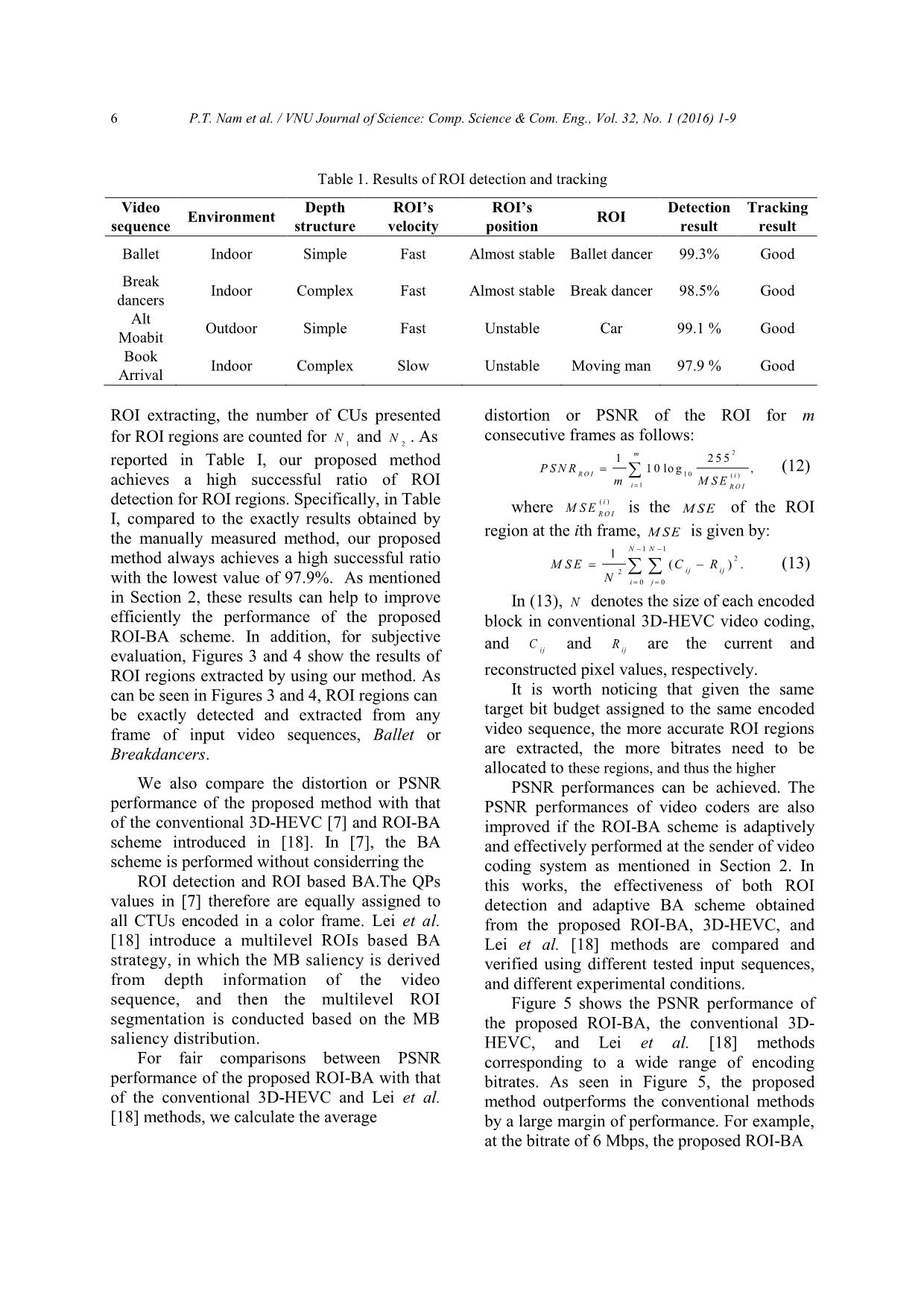
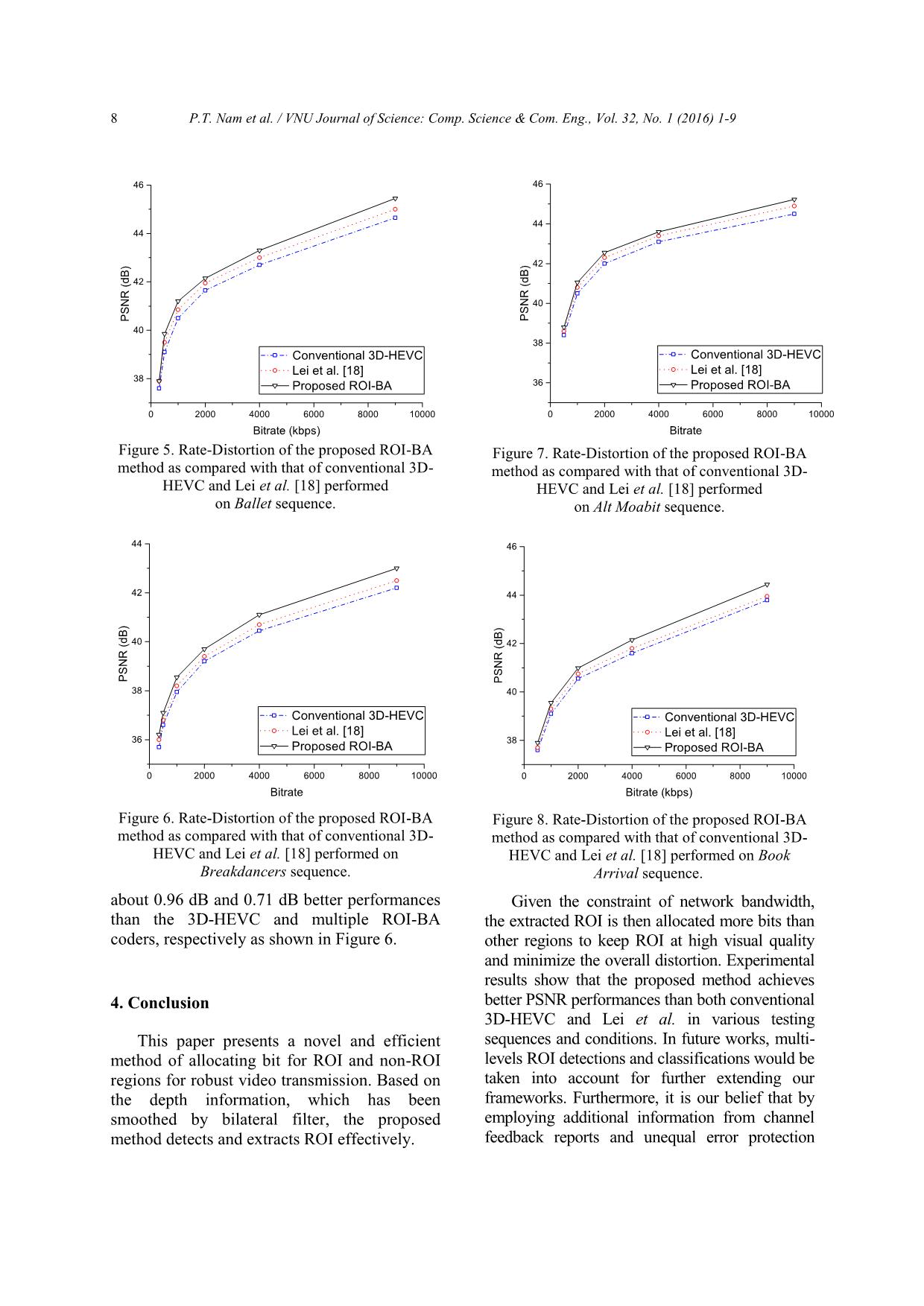
nd non-ROI regions, sequences used in our experiments are Ballet, respectively. Breakdancers, Alt Moabit, and Book Arrival As assumed in (6), the bitrate budget spent with resolution is XGA 1024 768, and each for non-ROI coding region in a color frame is sequence consists of 8/16 color views captured then given by: from different cameras (100 frames per R m ax view). Along with color views are correlative R m ax . nr (8) depth maps generated from stereo. The former .SS r n r two test sequences come from [16] by Similarly, the bitrate budget spent for ROI Microsoft, while the latters are provided by [17] coding region is from Heinrich Hertz Institute. In our m ax m ax m ax .R experiments, the value of is set to 1.3 for Alt RRr .. n r (9) .SSr n r Moabit test sequence and 1.25 for three The proposed ROI-BA scheme is then stated as remaining samples. The first test sequence Ballet contains a dancing-ballet woman and a follows: Given R , the proposed BA finds m ax watching-man in a room. The second, the optimal set of Breakdancers, contains a dancing man and four QPQPQP **, (i 0,1..., S ; j 0,1..., S ), i r,, i nr j r n r other men are watching him in a practicing * * room. The third test sequence, Alt Moabit is a where QP and QP are the optimal QP ri, n r, i traffic scene in Berlin with some cars parked chosen for the ith CTU of ROI and non-ROI down near the pavement while other cars are coding regions, respectively. This optimal set of moving. The final one is Book Arrival with a ** QPQPQPi r,, i, nr j should be derived to man sits in the room before another man minimize the total distortion DQP() at the coming in and they have a talk. i The ROI detection was applied to the receiver of the 3D-TV system (10) monoscopic 2D sequences. Table I shows M in D (,)QPQPr,, i n r i QPQP, results of the proposed ROI detection and r,, i n r i tracking method, which is implemented in subject to RQPR() m a x (10) r, i r several situations with the camera is set up m a x indoor and the location of the camera can be and RQPR()n r, i n r At the sender, the ROI-BA scheme fixed or changeable. In these cases, specific presented in (10) is processed to get the optimal ROIs chosen by users are moving objects. And, bitrates assigned to ROI and non-ROI regions to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed to transmit over networks. The proposed ROI detection method, we utilize a success adaptive ROI-BA scheme takes all possible ratio, which is measured by: NN combinations of QPQPQP , that 12 i r,, i nr j Ps u c c 1, (11) N satisfy the constraints in (10) and chooses the 2 where N and N are the areas of ROI best one that minimizes the total expected 1 2 distortion D . extracted by our proposed method and manually measured method, respectively. After 6 P.T. Nam et al. / VNU Journal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 32, No. 1 (2016) 1-9 Table 1. Results of ROI detection and tracking Video Depth ROI’s ROI’s Detection Tracking Environment ROI sequence structure velocity position result result Ballet Indoor Simple Fast Almost stable Ballet dancer 99.3% Good Break Indoor Complex Fast Almost stable Break dancer 98.5% Good dancers Alt Outdoor Simple Fast Unstable Car 99.1 % Good Moabit Book Indoor Complex Slow Unstable Moving man 97.9 % Good Arrival ROI extracting, the number of CUs presented distortion or PSNR of the ROI for m consecutive frames as follows: for ROI regions are counted for N 1 and N 2 . As 1m 2 5 5 2 reported in Table I, our proposed method PSNR 1 0 lo g , (12) ROI 10 ()i achieves a high successful ratio of ROI mi 1 M S E ROI detection for ROI regions. Specifically, in Table ()i where MSE is the MSE of the ROI I, compared to the exactly results obtained by ROI the manually measured method, our proposed region at the ith frame, is given by: 1 NN 11 method always achieves a high successful ratio MSECR ().2 (13) 2 ij ij with the lowest value of 97.9%. As mentioned N ij 00 in Section 2, these results can help to improve In (13), N denotes the size of each encoded efficiently the performance of the proposed block in conventional 3D-HEVC video coding, ROI-BA scheme. In addition, for subjective and C and R are the current and evaluation, Figures 3 and 4 show the results of ij ij ROI regions extracted by using our method. As reconstructed pixel values, respectively. can be seen in Figures 3 and 4, ROI regions can It is worth noticing that given the same be exactly detected and extracted from any target bit budget assigned to the same encoded frame of input video sequences, Ballet or video sequence, the more accurate ROI regions Breakdancers. are extracted, the more bitrates need to be allocated to these regions, and thus the higher We also compare the distortion or PSNR PSNR performances can be achieved. The performance of the proposed method with that PSNR performances of video coders are also of the conventional 3D-HEVC [7] and ROI-BA improved if the ROI-BA scheme is adaptively scheme introduced in [18]. In [7], the BA and effectively performed at the sender of video scheme is performed without considerring the coding system as mentioned in Section 2. In ROI detection and ROI based BA.The QPs this works, the effectiveness of both ROI values in [7] therefore are equally assigned to detection and adaptive BA scheme obtained all CTUs encoded in a color frame. Lei et al. from the proposed ROI-BA, 3D-HEVC, and [18] introduce a multilevel ROIs based BA Lei et al. [18] methods are compared and strategy, in which the MB saliency is derived verified using different tested input sequences, from depth information of the video and different experimental conditions. sequence, and then the multilevel ROI Figure 5 shows the PSNR performance of segmentation is conducted based on the MB the proposed ROI-BA, the conventional 3D- saliency distribution. HEVC, and Lei et al. [18] methods For fair comparisons between PSNR corresponding to a wide range of encoding performance of the proposed ROI-BA with that bitrates. As seen in Figure 5, the proposed of the conventional 3D-HEVC and Lei et al. method outperforms the conventional methods [18] methods, we calculate the average by a large margin of performance. For example, at the bitrate of 6 Mbps, the proposed ROI-BA P.T. Nam et al. / VNU Journal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 32, No. 1 (2016) 1-9 7 (a) (a) (b) (b) (c) (c) Figure 3. ROI detection performed Figure 4. ROI detection performed on Ballet sequence. on Breakdancers sequence. provides up to 0.84 dB better performance than confirmed from the experimental results of this the conventional 3D-HEVC coder. The method that there are often noisy with irregular proposed method also provides higher PSNR changes on the extracted ROI regions, which performance than the multiple ROI-BA [18] make confusing on the choice of threshold and coder. With the same target bit budget assigned thus reduce the accuracy of ROI detection to the proposed ROI-BA, however the multiple algorithms proposed by this method. ROI-BA coder yields worse performances than Similar results are obtained from the proposed method at all values of bitrates as Breakdancers, Alt Moabit, and Book Arrival shown in Figure 5. The reason lies in the fact sequences as shown in Figures 6-8, that the ROI based BA scheme is not supported respectively. For the Breakdancers sequence in the conventional 3D-HEVC for adaptive BA, where the motion activities are high and and thus, all CTUs are encoded using equal QPs complexity, however, as can be seen in Figure without assigning more bitrates for ROI 6, the proposed method also introduces much regions. In Lei et al. [18] method, low-pass higher PSNR performance than the 3D-HEVC filters are not applied for depth maps to smooth and multiple ROI-BA [18]. More specifically, and suppress noises on the depths. Therefore, as at the rate of 7.5 Mbps, the proposed provides 8 P.T. Nam et al. / VNU Journal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 32, No. 1 (2016) 1-9 46 46 44 44 42 ) ) B B d d 42 ( ( R R N N 40 S S P P 40 38 Conventional 3D-HEVC Conventional 3D-HEVC Lei et al. [18] Lei et al. [18] 38 Proposed ROI-BA 36 Proposed ROI-BA 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 Bitrate (kbps) Bitrate Figure 5. Rate-Distortion of the proposed ROI-BA Figure 7. Rate-Distortion of the proposed ROI-BA method as compared with that of conventional 3D- method as compared with that of conventional 3D- HEVC and Lei et al. [18] performed HEVC and Lei et al. [18] performed on Ballet sequence. on Alt Moabit sequence. 44 46 42 44 ) ) B B d 40 d ( 42 ( R R N N S S P P 38 40 Conventional 3D-HEVC Conventional 3D-HEVC Lei et al. [18] Lei et al. [18] 36 38 Proposed ROI-BA Proposed ROI-BA 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 Bitrate Bitrate (kbps) Figure 6. Rate-Distortion of the proposed ROI-BA Figure 8. Rate-Distortion of the proposed ROI-BA method as compared with that of conventional 3D- method as compared with that of conventional 3D- HEVC and Lei et al. [18] performed on HEVC and Lei et al. [18] performed on Book Breakdancers sequence. Arrival sequence. about 0.96 dB and 0.71 dB better performances Given the constraint of network bandwidth, than the 3D-HEVC and multiple ROI-BA the extracted ROI is then allocated more bits than coders, respectively as shown in Figure 6. other regions to keep ROI at high visual quality and minimize the overall distortion. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves 4. Conclusion better PSNR performances than both conventional 3D-HEVC and Lei et al. in various testing This paper presents a novel and efficient sequences and conditions. In future works, multi- method of allocating bit for ROI and non-ROI levels ROI detections and classifications would be regions for robust video transmission. Based on taken into account for further extending our the depth information, which has been frameworks. Furthermore, it is our belief that by smoothed by bilateral filter, the proposed employing additional information from channel method detects and extracts ROI effectively. feedback reports and unequal error protection P.T. Nam et al. / VNU Journal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 32, No. 1 (2016) 1-9 9 (UEP) scheme applied for ROI regions, the Video Coding, ” IEEE Journal on Selected performance of the proposed ROI-BA method can Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. be more improved to provide an optimal end-to- 1001-1016, Dec. 2013. [8] T. Wiegand, G. Sullivan, G. Bjontegaard, and end rate-distortion optimization. A. Luthra, “Overview of the H.264/AVC video coding standard,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 13, no. 7, pp. 560-576, Jul. Acknowledgement 2003. [9] B. Lee, M. Kim, and T. Nguyen, “A frame-level rate control scheme based on texture and non- This work was supported by the basic texture rate models for high efficiency video research projects in natural science in 2012 of coding,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video the National Foundation for Science & Technol. vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 1–14, Mar. 2014. Technology Development (Nafosted), Vietnam [10] M. Meddeb, M. Cagnazzo, and B. Pesquet- (102.01-2012.36, Coding and communication Popescu, “Region-of-interest-based rate of multiview video plus depth for 3D control scheme for high efficiency video coding,” APSIPA Transactions on Signal Television Systems). and Information Processing, vol. 3, pp. 1-18, Dec. 2014. [11] P. Viola and M. Jones, “Rapid object detection References using a boosted cascade of simple features,” IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. vol. 1, pp. 511- [1] Z. He and S.Mitra, “Optimum bit allocation and 518, 2001. accurate rate control for video coding via ρ- [12] K. Müller, P. Merkle, and T. Wiegand, “3-D domain source modeling,” IEEE Trans. Circuits video representation using depth maps,” Proc. Syst. Video Technol., vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 840- IEEE 99, vol. 4, pp. 643-656, 2011. 849, Oct. 2002. [13] Y. Mori, N. Fukushima, T. Yendo, T. Fujii, and [2] B. Li, H. Li, and L. Li, “Adaptive bit allocation M. Tanimoto, “View generation with 3D for R-lambda model rate control in HM,” JCT- warping using depth information for FTV,” Sig VC M0036, 13th Meeting of Joint Processing: Image Comm. vol. 24, no. 1-2, pp. Collaborative Team on Video Coding of 65-72, 2009. ITU-T SG1 6WP3 and ISO/IEC JTC1/SC [14] C. Tomasi and R. Manduchi, “Bilateral filtering 29/WG11, Incheon, Kr, 2013. for gray and color images,” Proceedings of [3] A. Borji and L. Itti, “State-of-the-art in visual IEEE international conference computer vision, attention modeling,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. pp 839-846, 1998. Machine Intell., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 185–207, [15] Test Model 6 of 3D-HEVC and MV-HEVC. Jan. 2013. Available: [4] R.A. Khan, A. Meyer, H. Konik, and S. Bouakaz, “Exploring human visual system: h/high-efficiency-video-coding/test-model-6- Study to aid the development of automatic 3d-hevc-and-mv-hevc. facial expression recognition framework,” [16] C. L. Zitnick, S. B. Kang, M. Uyttendaele, S. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Winder, and R. Szeliski, “High quality video Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, view interpolation using a layered pp. 49–54, 2012. representation,” ACM Transactions on Graphics [5] H. Hu, B. Li, W. Lin, W. Li, and M. -T. Sun, (TOG), vol. 23, pp. 600-608, 2004. “Region-based rate control for H.264/AVC for [17] I. Feldmann, M. Mueller, F. Zilly, R. low bit-rate applications,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Tanger, K. Mueller, A. Smolic, P. Kauff, Syst. Video Technol., vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 1564– and T. Wiegand, “HHI test material for 3D 1576, Oct. 2012. video” ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11, vol. [6] X. Yang, W. Lin, Z. Lu, X. Lin, S. Rahardja, E. 15413 Apr. 2008. Ong, and S. Yao, “Rate control for video phone [18] J. Lei, M. Wu, K. Feng, C. Hu, and C. Hou, using local perceptual cues,” IEEE Trans. “Multilevel region of interest guided bit Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 15, no. 4, allocation for multiview video coding,” pp. 496-507, Apr. 2005. International Journal for Light and Electron [7] G. J. Sullivan, J. M. Boyce, Y. Chen, J.-R. Optics, vol. 125, no. 1, pp. 39-43, Jan. 2014. Ohm, C. A. Segall, and A. Vetro, “Standardized Extensions of High Efficiency
File đính kèm:
 efficient_region_of_interest_based_adaptive_bit_allocation_f.pdf
efficient_region_of_interest_based_adaptive_bit_allocation_f.pdf

