Customer satisfaction in mobile service quality: Evidence from hanoi and Ho Chi Minh city’s officers
Abstract: This study explores the factors influencing the quality of telecommunication services in
Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. By conducting an online survey of 413 office workers, the results
indicate that among the five components of the perceived quality of telecommunications services,
reliability, assurance, and empathy are Key factors affecting consumer satisfaction in Hanoi and
Ho Chi Minh City. The findings of this research help mobile service providers to understand how
consumers perceive the quality of mobile services. Thus, mobile service providers would
effectively design marketing strategy to improve customer loyalty as well as enter new markets.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Customer satisfaction in mobile service quality: Evidence from hanoi and Ho Chi Minh city’s officers

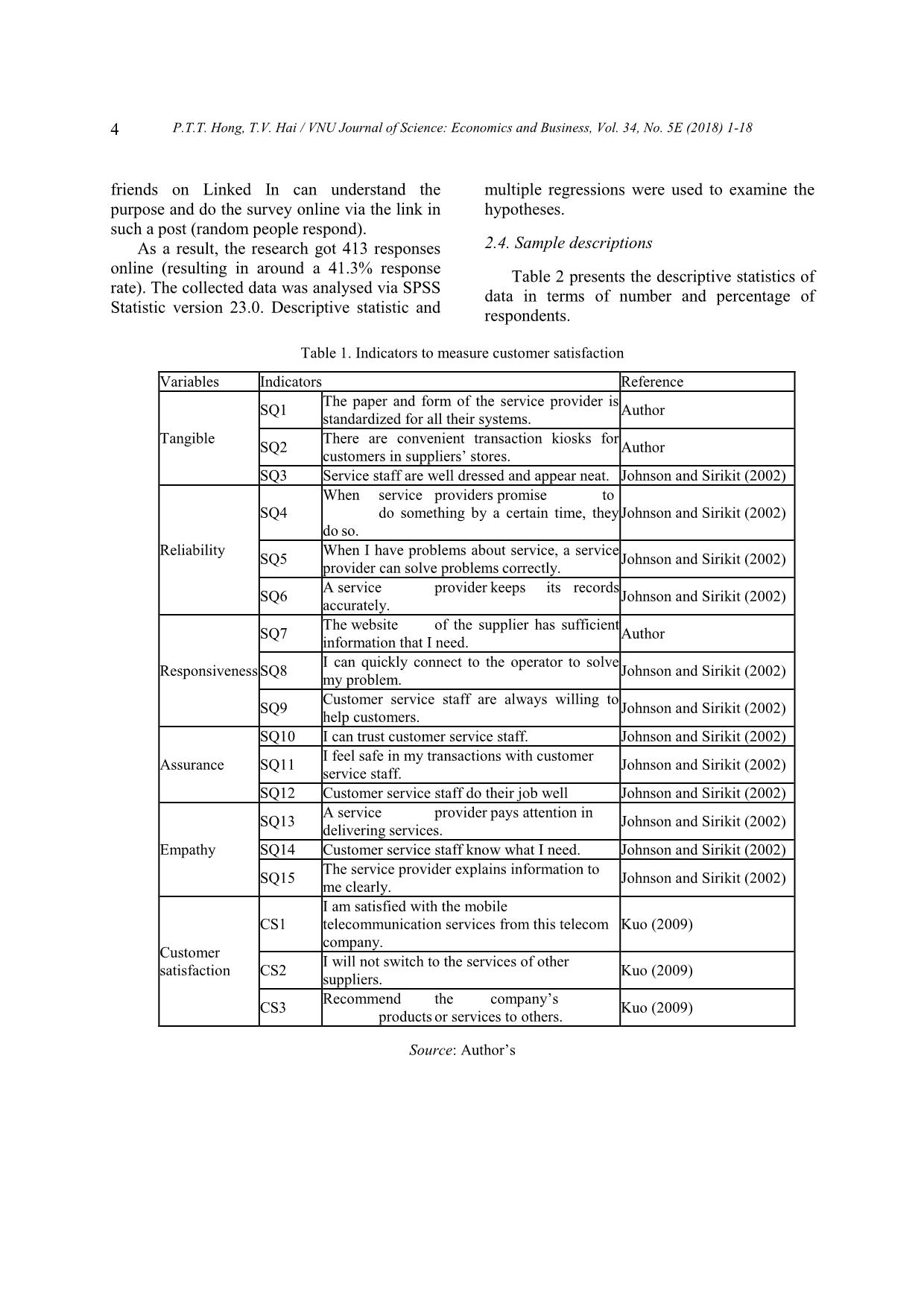
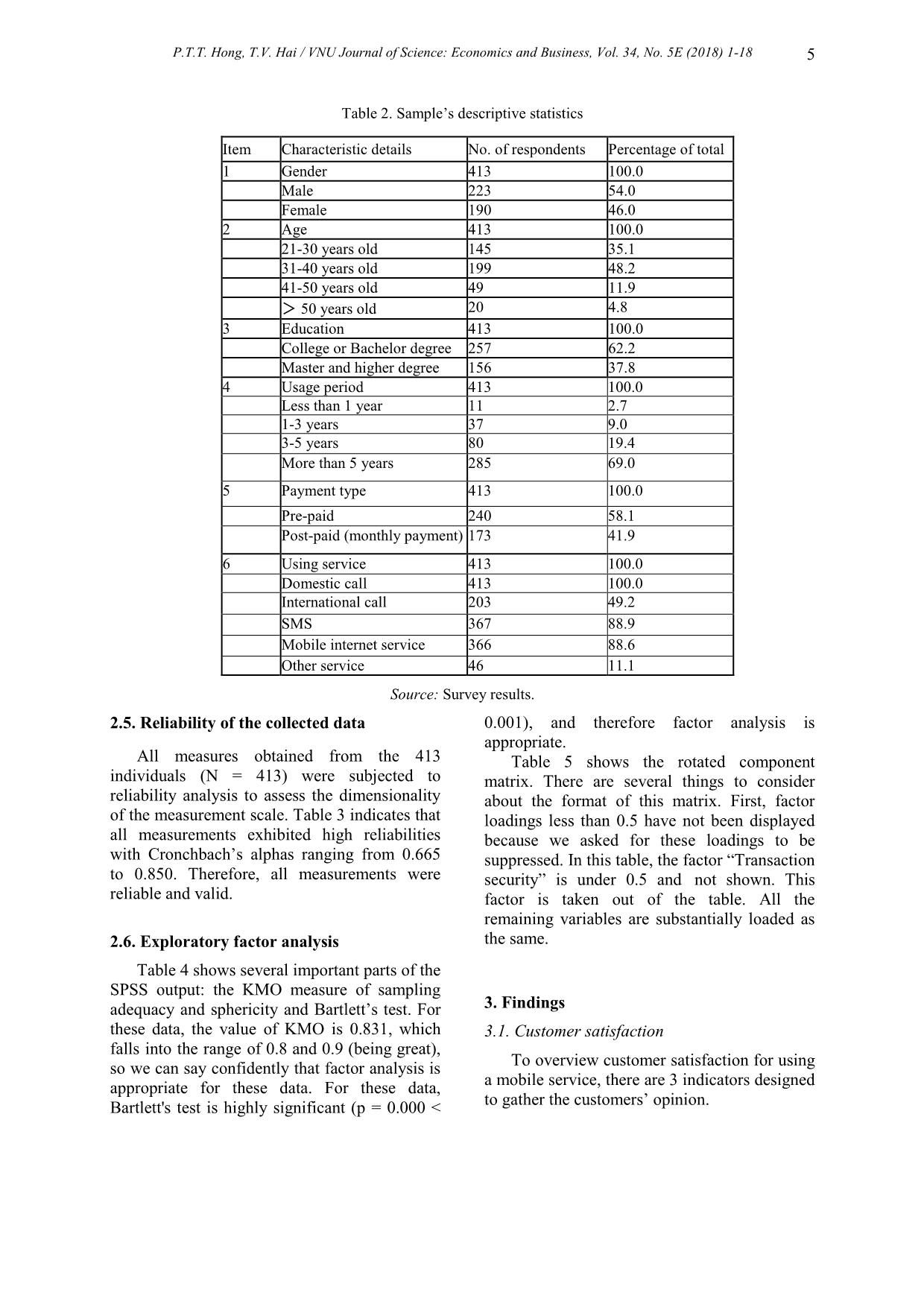
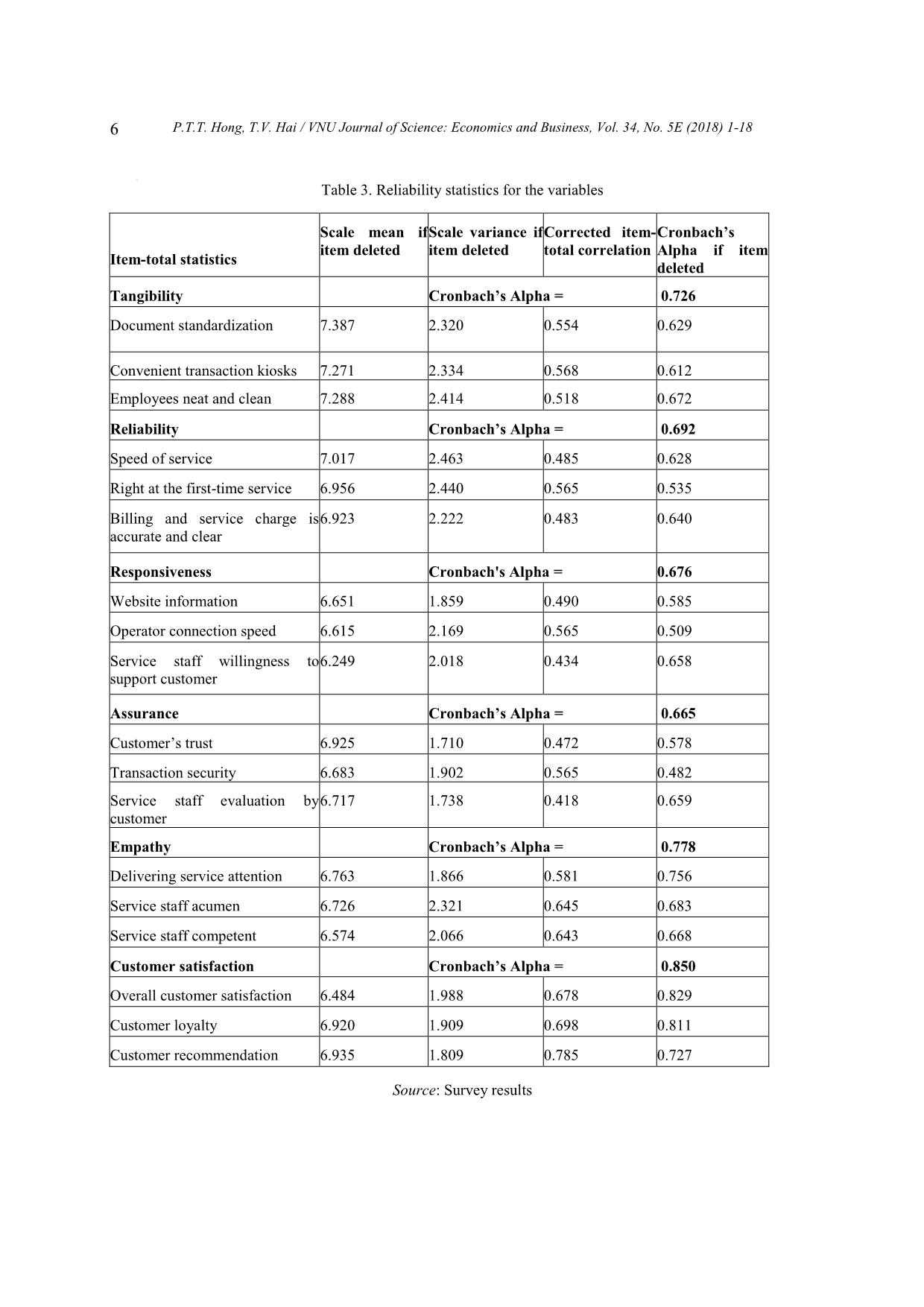
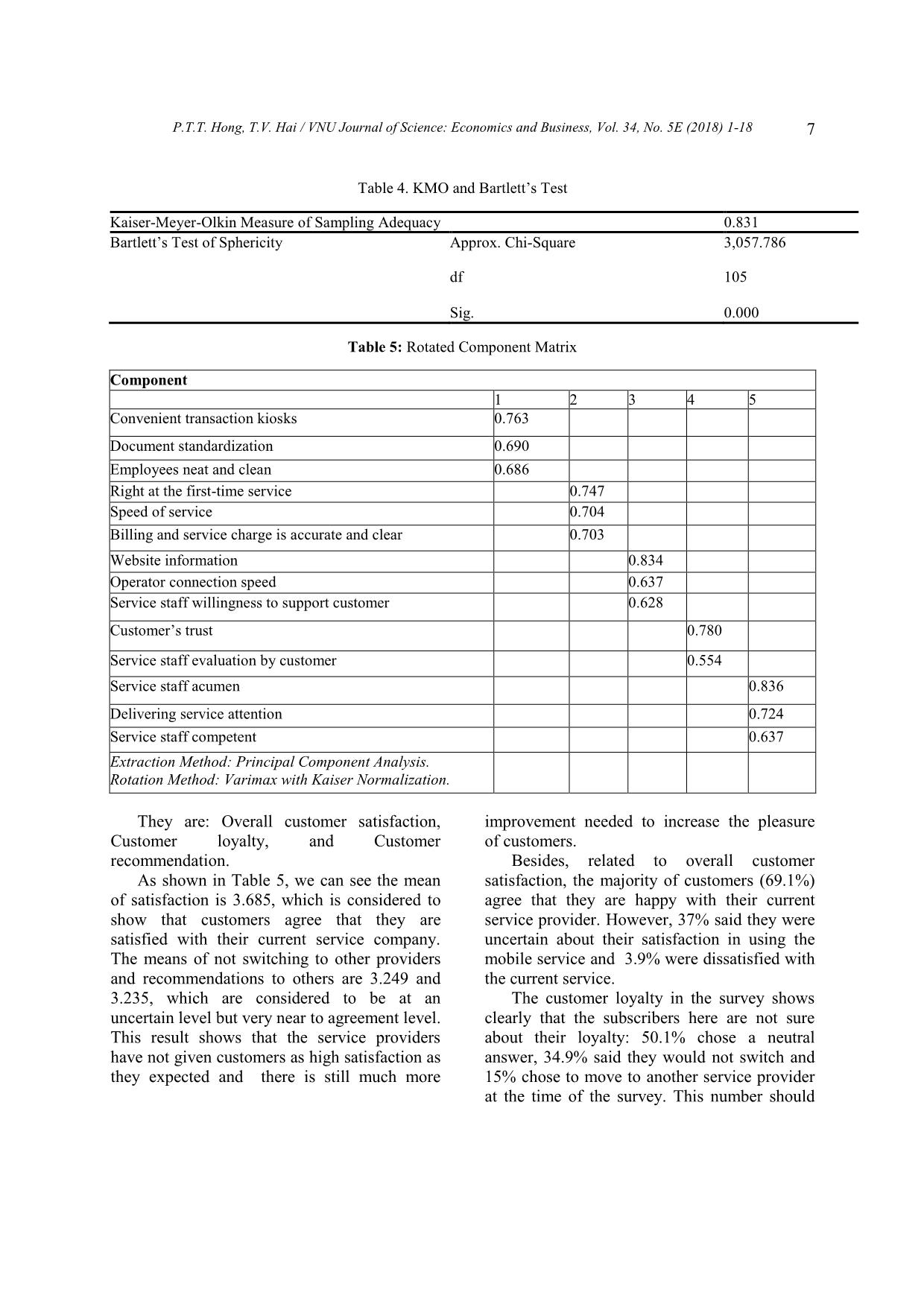
sfaction of customers on the empathy dimension is at an uncertain level. Empathy has a significant influence on customer's satisfaction (α < 0.05, β = 0.333). In the research of Eugenia et al. (2015) [3] and in the research of Aydin et al. (2005) [16] the same result was found. 4.6. Customer satisfaction As the results of data analysis on the level of agreement show, customer satisfaction (Mean=3.390, SD=0.665) was shown at the neutral level. The hypotheses aim to identify the effect of service quality (tangible, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy) on customer satisfaction of customers using mobile telecommunications in 2 cities in Vietnam. According to the result of the hypotheses’ test it shows that there is a relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction. Overall, most customers are satisfied with the current services with a highest average mean score (3.685). On the other hand, loyalty and recommendation nearly got the agreed level. Therefore, we can conclude that customers are satisfied with the telecommunication services in Vietnam, but the satisfaction level is not quite high. Eugenia et al. (2015) has mentioned in her research about the same topic with customer in Taiwan a similar finding [3]. It also agrees with the findings of Torsten and Ilknur (2016) [18]. So, we can see this result is similar with other researches, and we can conclude that the customer satisfaction in using mobile services of people working in offices is not different from that of other people. 5. Conclusions and implications 5.1. Conclusions P.T.T. Hong, T.V. Hai / VNU Journal of Science: Economics and Business, Vol. 34, No. 5E (2018) 1-18 15 From the research, customer satisfaction (Mean = 3.390, SD = 0.665) was shown to be at a slightly satisfied level with the service quality of mobile service providers. Customers of these services, who are working in offices highly appreciate the appearance of the store and staff as well as the Reliability dimensions. Even though customers are quite satisfied with the mobile services in general, they do not have positive perceptions of some dimensions. The most considerable will be for providing personal information and suppliers’ survey conducting. Therefore, the suppliers need to have more specialized campaigns on customer data security and enhancing customer services. The hypothesis of the service quality test shows that these variables have an influence on customer satisfaction. If a product outperforms expectations (positive disconfirmation) post- purchase satisfaction will result [4] [19]. Thus, when customers use the mobile telecommunications service and get better service quality, they will get more satisfaction. Also, there is a significant relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction. But with service quality consisting of five dimensions, the different dimensions have different effects on customer satisfaction. Reliability (β = 0.202), assurance (β = 0.336) and empathy (β = 0.333) have a significant relationship with customer satisfaction; assurance (β = 0.336) is higher than the others, meaning assurance has more impact than the others on customer satisfaction. The significance value of tangible and responsiveness are more than the alpha level (α = 0.05). Therefore, they have no relationship with customer satisfaction at a significant level. Accordingly, the three most important dimensions (reliability, assurance and empathy) in turn give the most satisfaction to customers using telecommunication services. 5.2. Management Implications The analytical results of this study have several implications for researchers and practitioners. Obviously, the ultimate target of mobile service providers is to improve the company performance and increase its market share. However, since Vietnam mobile telecommunication is in the 4G era, mobile service providers must confront a new competitive situation, and different 4G mobile services are provided to customers. For mobile service providers, this research can be used to find out what factors influence customer satisfaction and for marketing strategy planning. In this research, we also found that Reliability, Assurance and Empathy all significantly affect customer satisfaction in using mobile services, but the users here still feel not really satisfied with their current service. Thus, mobile service providers should only focus their investments in these 3 categories to boost performance. Based on the findings of this study, mobile service providers should focus on the Reliability, Assurance and Empathy of service quality. These three dimensions of service quality have a significant relationship with customer satisfaction in using mobile services in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. From that they can make customers sacrifice time and effort in purchasing their mobile services, and how to make customers feel it is worth choosing their company over other mobile service providers. Improve relationship with distribution channels The findings imply that the customer service sector needs to be ameliorated. In the tough competition where service operators hardly hold a proprietary technology in the mobile service market, enhancing customer service is a pivotal strategy to pre-empt customer satisfaction against other competitors. This can help the company not only win more customers but also gain more of the market share. The suppliers here have done a good job in providing reliable services that have satisfied the majority of customers. However, that does not mean that they can stop improving their P.T.T. Hong, T.V. Hai / VNU Journal of Science: Economics and Business, Vol. 34, No. 5E (2018) 1-18 16 service. For example, they should work closely with distribution channels. Distribution channels help suppliers bring products and services closer to customers as well as to receive feedback from customers through the process of using the service. Besides chargeable staff are people who can easily get feedback from customers about the service. That is an effective information channel for companies to offer new business, policy changes or policy adjustments accordingly. Therefore, there should be cooperation between suppliers and distribution channels, so chargeable staff can quickly fix customer complaints. Besides, as good relationships and benefits increase, the selling of mobile sim cards at dealers will be reduced. Professional ethics and working environment socialization It is important to improve the capacity for employees, but suppliers also cannot ignore professional ethics; therefore they need to combine harmoniously to create both special attention on the issuing of sim cards or the collection of telephone charges that can improve the confidence of their customers. There should be an open discussion between the leadership and staff of the company to talk about professional ethics to enhance the consciousness of each person, to exchange ideas and propose strict sanctions if there are deliberate mistakes. Complete customer policy Moreover, even if companies have very nice customers, it will become meaningless if service staff do not follow them closely. Therefore, companies need to implement policies for customer care and their staff must carry these policies out strictly. They need to develop appropriate policies and stimulate participation from both employees and customers. In addition, companies should develop a database of customers that can consolidate information from different departments such as customer information management, customer interaction management, marketing management, product & services management, etc. so that the company has a full picture of all customers. By that system, tellers will easily recognize many potential customers and collaborate with other technical departments in the company to implement marketing activities, sales and provide appropriate services. Therefore, companies will optimize profitability and bring the highest satisfaction to customers. Besides, the system also helps the leadership to consider and evaluate employees’ effectiveness. Enhance customer empathy Customers expect to be given individual attention. Thus, the suppliers should understand specific customers’ desires or requests and respond to them promptly. To achieve that target, the company needs to invest in a large research investigating customers’ demands according to each segment. Each customer group has definite requirements for their desired services; by understanding these desires, the company can provide services accordingly. Employees’ performances should also be monitored to assure that there is no mistake in dealing with each customer’s circumstance. Furthermore, when the company receives any complaints, they need to respond to the customer with precise and satisfactory answers or actions. Those answers or actions should not be equivocal which can cause confusion for customers. Training for employees Company should emphasize more soft skills training for the staff force which deals directly with the customers. Their skills in promotion, communication and negotiation should instil confidence in customers. Employees should flexibly tackle customers’ problems without having them waiting too long and giving an unsatisfactory response. Furthermore, more employees need to be arranged for the customer service sector so that customer’s issues can be tackled in succession and in the shortest time. Even though most customers have been satisfied with the appearance of the store, the simplicity or security of the service, etc. the company should not disregard these factors. P.T.T. Hong, T.V. Hai / VNU Journal of Science: Economics and Business, Vol. 34, No. 5E (2018) 1-18 17 Without their supportive roles, the service quality of the company could have resulted in dissatisfaction. Those dimensions should also have better elaboration to ensure the long-term loyalty of customer to the company. 5.3. Suggestions and recommendations There are some suggestions for future research. First, the culture and regulations are quite different from one country to the other, which is the limitation of the paper. Thus, future researchers may wish to conduct study (1) involving a sufficiently large sample size for the entire country, or (2) including other target groups by geographic location or culture difference factors. Finally, this study used closed-ended questions to examine the factors that influenced customer satisfaction, and the relationships among the variables. Future researchers may wish to use other methods for collecting data. Further studies could be carried out to develop and validate the models by adding external constructs within a more specific context. References [1] Boohene, R., & Agyapong, G., “Analysis of the antecedents of customer loyalty of telecommunication industry in Ghana: The case of Vodafone (Ghana)”, International Business Research, 4 (2011) 1, 229-240. [2] Leelakulthanit, O., & Hongcharu, B., “Factors that impact customers satisfaction: Evidence from the Thailand mobile cellular network industry”, International Journal of Management and Marketing Research, 4 (2011) 2, 67-76. [3] Eugenia Y. Huang, Sheng-Wei Lin, Ya-Chu Fan, “M-S-Qual: Mobile service quality measurement”, Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 14 (2015), 126-142, [4] Omotayo, O., & Abiodun, A., “Service quality, value offer, satisfaction, and loyalty: An empirical relationship in the Nigerian telecom industry”, Contemporary Management Research, 5 (2011) 2, 14-23. [5] Lee, Roy Chun, “Telecommunications in Vietnam”, Chung-Hua Institution for Economic Research (CIER). Chinese Taipei WTO Center, C.20 (2011), p.1. [6] Agarwal, S., M. Erramilli, et al., “Market orientation and performance in service firms: role of innovation”, Journal of Services Marketing 17 (2003) 1, 68-82. [7] Agyapong, G., “The effect of service quality on customer satisfaction in the utility industry: A case of Vodafone (Ghana)”, International Journal of Business and Management, 6 (2011) 5, 203- 210. [8] Yee, R. W. Y., Yeung, A. C. L. & Cheng, T. C. E., “An empirical study of employee loyalty, service quality and firm performance in the service industry”, International Journal of Production Economics, 124 (2010) 1, 109-120. [9] Le The Gioi and Nguyen Minh Duan, “Improving the competitiveness of VMS-MOBIFONE on mobile communication market”, Journal of Science and Technology, University of Da Nang, 2 (2007) 19, 68-72. [10] Dinh Thi Hong Thuy, “Research the factors affecting on the decision for mobile telecommunications of students in Ho Chi Minh City”, Master Thesis, (2008). [11] Le Thi Tuyet Trinh, “Research the customer satisfaction in using Vinaphone mobile service in Binh Dinh province”, Master Thesis, 2012. [12] Bui Van Trinh and Luu Ngoc Mai Anh, “Research the customer satisfaction in using Viettel mobile service in Hai Giang province”, Master Thesis, 2013. [13] Pizam, A., Ellis, T., “Customer satisfaction and its measurement in hospitality enterprises”, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 11 (1999) 7, p. 326-339, [14] A. Parasuraman, Valarie A. Zeithaml, Leonard L. Berry, “A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its Implications for Future Research”, The Journal of Marketing, Vol. 49, No. 4 (1985), pp. 41-50 [15] Cronin Jr, J. J., & Taylor, S. A. “SERVPERF versus SERVQUAL: reconciling performance- based and perceptions-minus-expectations measurement of service quality”. The Journal of Marketing, 58 (1994). 125-131. [16] Aydin, S. and G. Ozer, “National Customer Satisfaction Indices: An Implementation in the P.T.T. Hong, T.V. Hai / VNU Journal of Science: Economics and Business, Vol. 34, No. 5E (2018) 1-18 18 Turkish Mobile Telephone Market”, Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 23 (2005) 5, 486-504. [17] Mishra, R.C and Sandilya, A., Reliability and Quality Management, New Age International Publishers, 2009. [18] Torsten J. Gerpott, Ilknur Bicak, “Telecommunication service choice and use among migrants: The case of German-Turkish consumers”, Computers in Human Behavior, 6 (2016), 584-596, [19] Uddin, M. B., Akhter, B., “Customer satisfaction in mobile phone services in Bangladesh: A survey research”, Management & Marketing X (1) (2012), 20-36.
File đính kèm:
 customer_satisfaction_in_mobile_service_quality_evidence_fro.pdf
customer_satisfaction_in_mobile_service_quality_evidence_fro.pdf

