Bài giảng Phát triển ứng dụng web - Bài 6: Mô hình MVC trong PHP - Nguyễn Hữu Thể
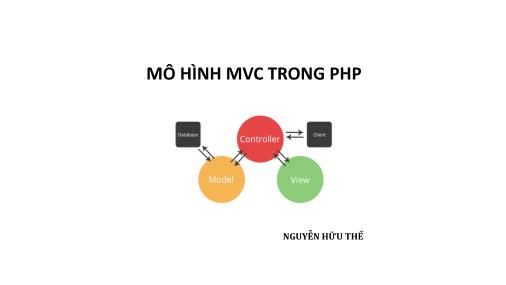
1. Model View Controller (MVC)
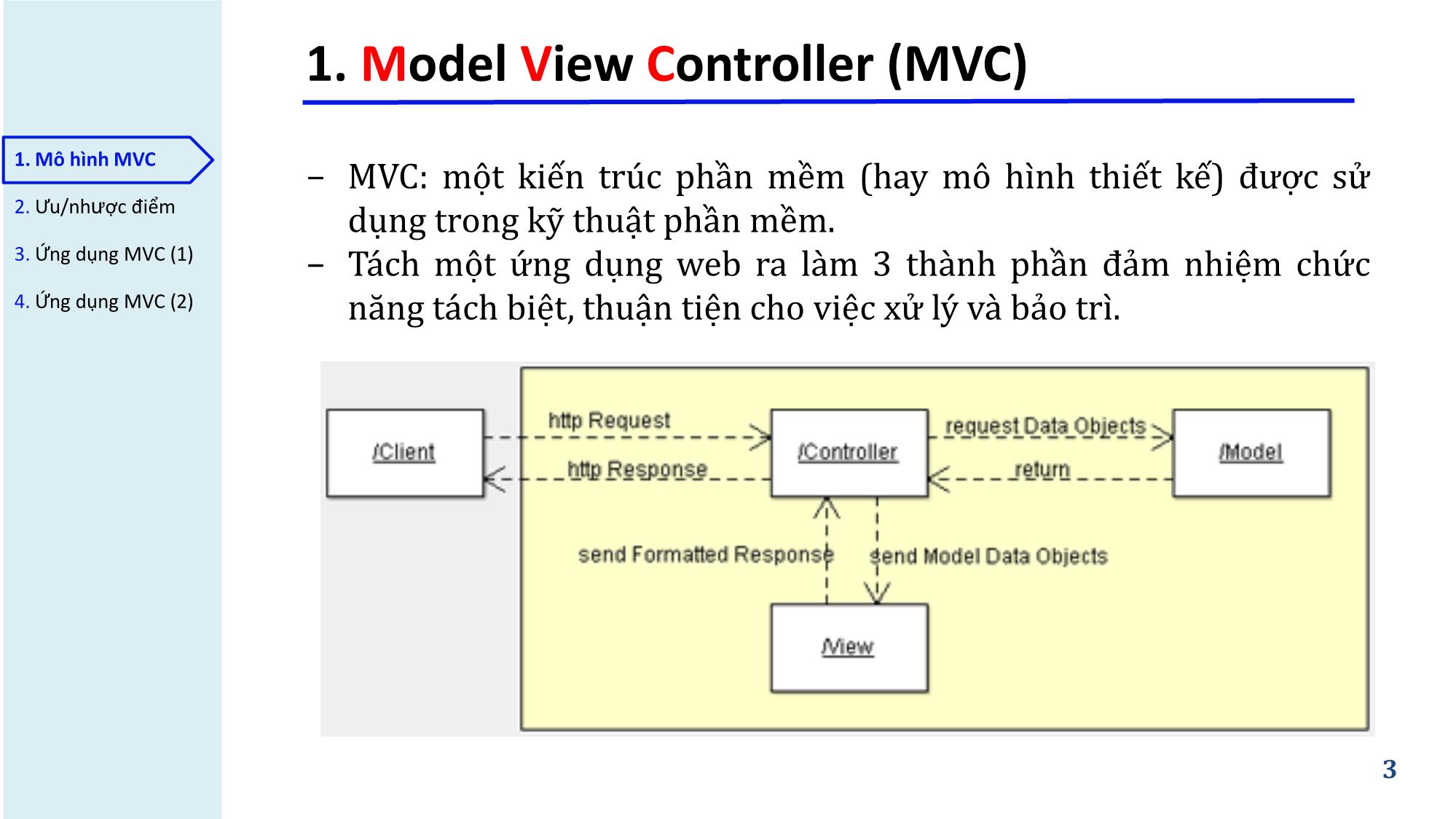
− MVC: một kiến trúc phần mềm (hay mô hình thiết kế) được sử
dụng trong kỹ thuật phần mềm.
− Tách một ứng dụng web ra làm 3 thành phần đảm nhiệm chức
năng tách biệt, thuận tiện cho việc xử lý và bảo trì.
1. Model View Controller (MVC)
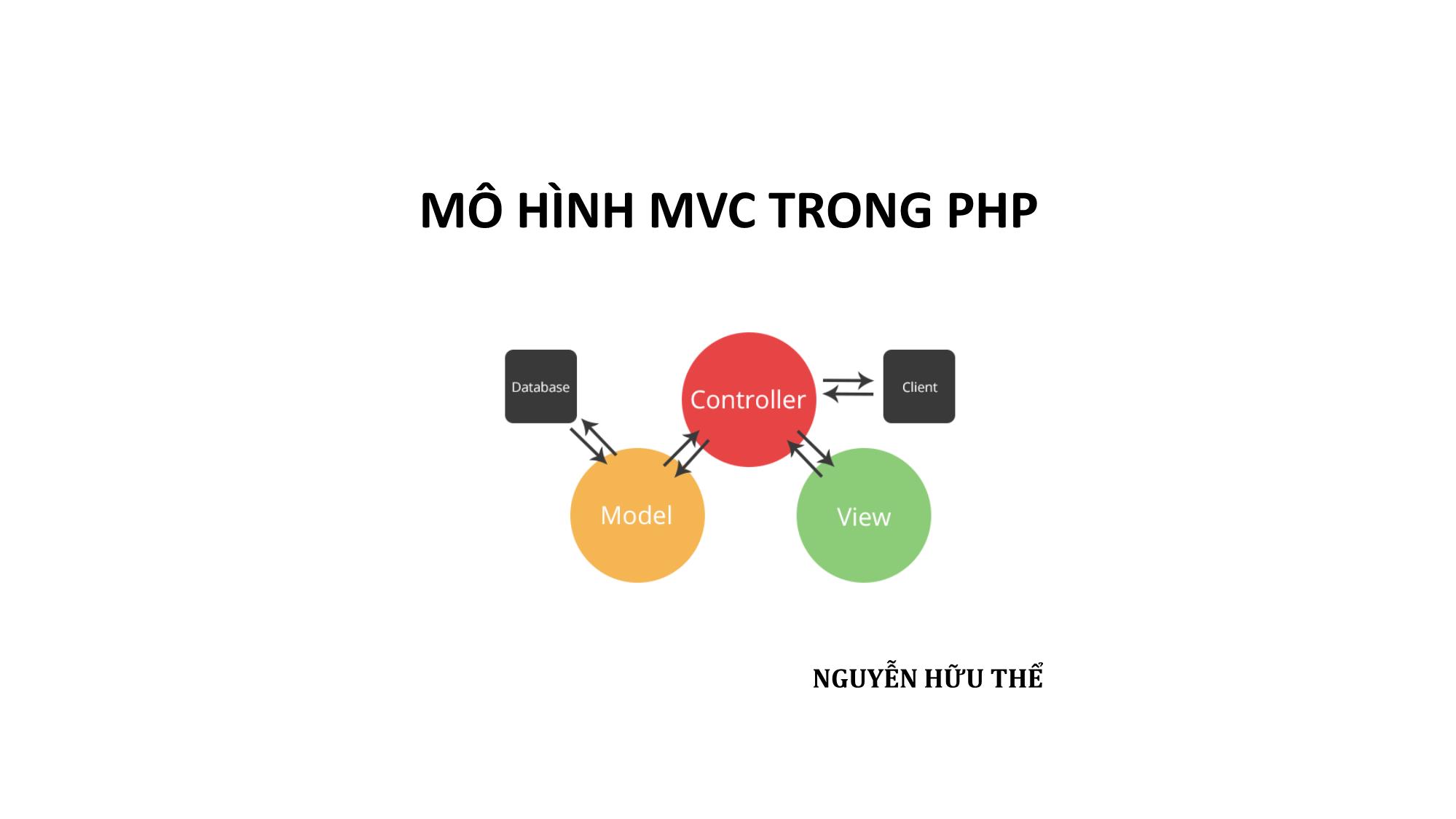
− Model: Quản lý dữ liệu, lưu trữ và truy xuất các dữ liệu từ cơ sở
dữ liệu, các logic xử lý.
− View: Hiển thị dữ liệu đã được truy xuất từ model.
− Controller: Trung gian, giúp cho model và view tương tác với
nhau.
• Controller nhận request từ client.
• Gọi các model để thực hiện các yêu cầu và gửi ra View.
• View sẽ format lại data từ controller gửi ra và trình bày dữ liệu
(HTML).
Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Phát triển ứng dụng web - Bài 6: Mô hình MVC trong PHP - Nguyễn Hữu Thể", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Phát triển ứng dụng web - Bài 6: Mô hình MVC trong PHP - Nguyễn Hữu Thể
MÔ HÌNH MVC TRONG PHP
NGUYỄN HỮU THỂ
03/01/2021 1
Nội dung
❑Mô hình MVC
❑Ưu và nhược điểm của mô hình MVC
❑Phát triển ứng dụng Web theo mô hình MVC
❑Tài liệu tham khảo
2
03/01/2021
1. Model View Controller (MVC)
1. Mô hình MVC
− MVC: một kiến trúc phần mềm (hay mô hình thiết kế) được sử
2. Ưu/nhược điểm dụng trong kỹ thuật phần mềm.
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) − Tách một ứng dụng web ra làm 3 thành phần đảm nhiệm chức
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) năng tách biệt, thuận tiện cho việc xử lý và bảo trì.
3
3 3
1. Model View Controller (MVC)
1. Mô hình MVC − Model: Quản lý dữ liệu, lưu trữ và truy xuất các dữ liệu từ cơ sở
2. Ưu/nhược điểm dữ liệu, các logic xử lý.
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) − View: Hiển thị dữ liệu đã được truy xuất từ model.
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) − Controller: Trung gian, giúp cho model và view tương tác với
nhau.
• Controller nhận request từ client.
• Gọi các model để thực hiện các yêu cầu và gửi ra View.
• View sẽ format lại data từ controller gửi ra và trình bày dữ liệu
(HTML).
4
4 4
2. Ưu và nhược điểm của MVC
1. Mô hình MVC
❖ Ưu điểm:
2. Ưu/nhược điểm
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) − Thể hiện tính chuyên nghiệp trong lập trình, phân tích
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) thiết kế.
− Phát triển ứng dụng theo cấu trúc đơn giản, dễ nâng
cấp, bảo trì, triển khai.
=> Sử dụng phổ biến nhất trong các PHP Framework
❖ Nhược điểm:
− Tốn nhiều thời gian để xây dựng thư viện, cấu trúc.
− Yêu cầu về chuyên môn khá cao, có kiến thức vững về
các mô hình chuẩn.
5
5 5
3. Thiết kế ứng dụng Web theo mô hình MVC
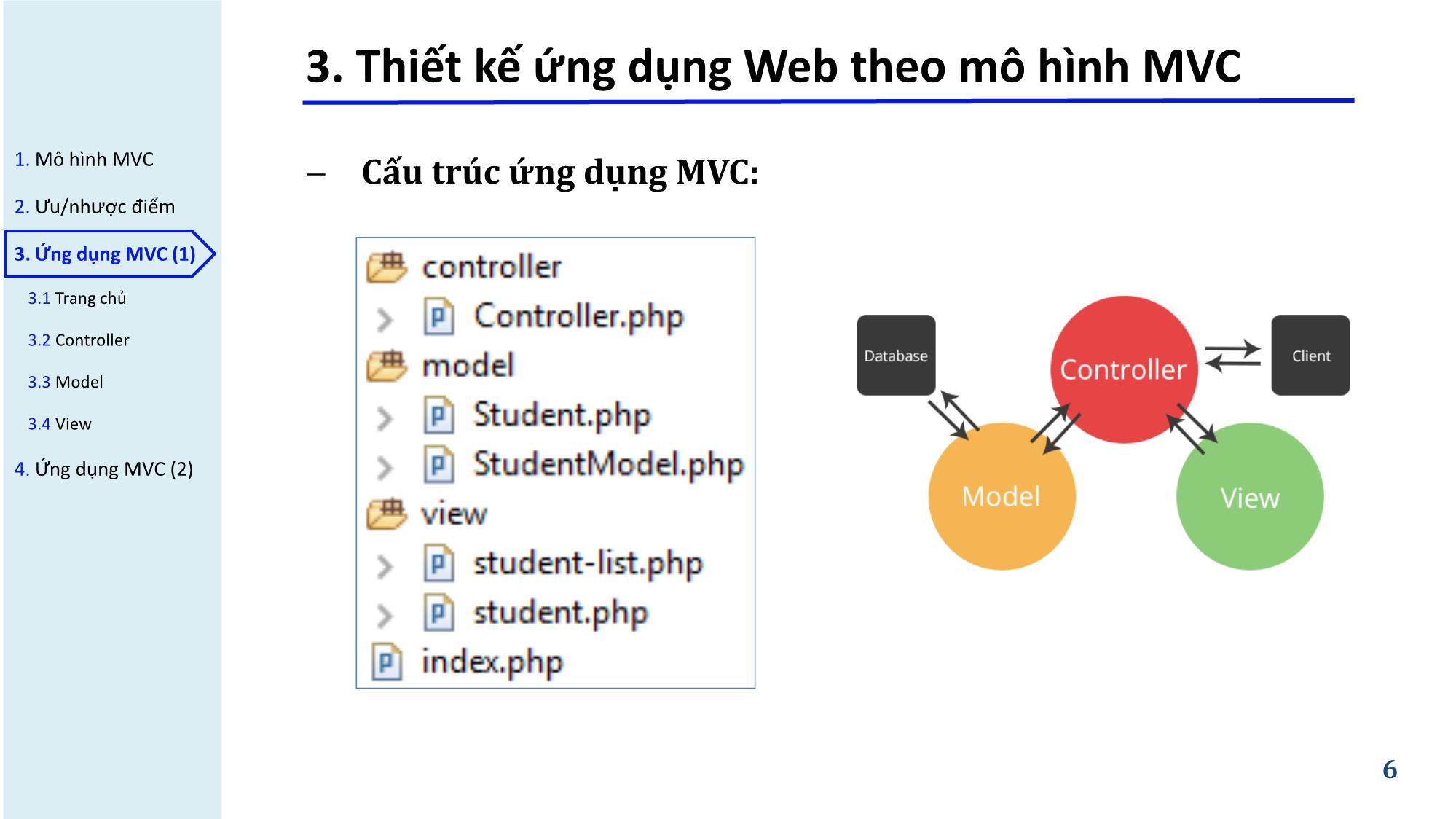
1. Mô hình MVC − Cấu trúc ứng dụng MVC:
2. Ưu/nhược điểm
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
3.1 Trang chủ
3.2 Controller
3.3 Model
3.4 View
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2)
6
6 6
index.php
1. Mô hình MVC − Controller: nơi đầu tiên nhận các yêu cầu (request).
2. Ưu/nhược điểm − Controller được gọi từ file index.php.
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
3.1 Trang chủ
3.2 Controller index.php
3.3 Model
<?php
3.4 View
include_once("controller/Controller.php");
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2)
$controller = new Controller();
$controller->invoke();
7
7 7
<?php
include_once("model/StudentModel.php"); Controller.php
class Controller {
private $modelStudent;
1. Mô hình MVC public function __construct(){
2. Ưu/nhược điểm $this->modelStudent = new StudentModel();
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) }
public function invoke(){
3.1 Trang chủ
if (!isset($_GET['id'])){
3.2 Controller
$students = $this->modelStudent->getStudentList();
3.3 Model include 'view/student-list.php';
3.4 View }
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) else{
$student = $this->modelStudent->getStudent($_GET['id']);
include 'view/student.php';
}
}
}
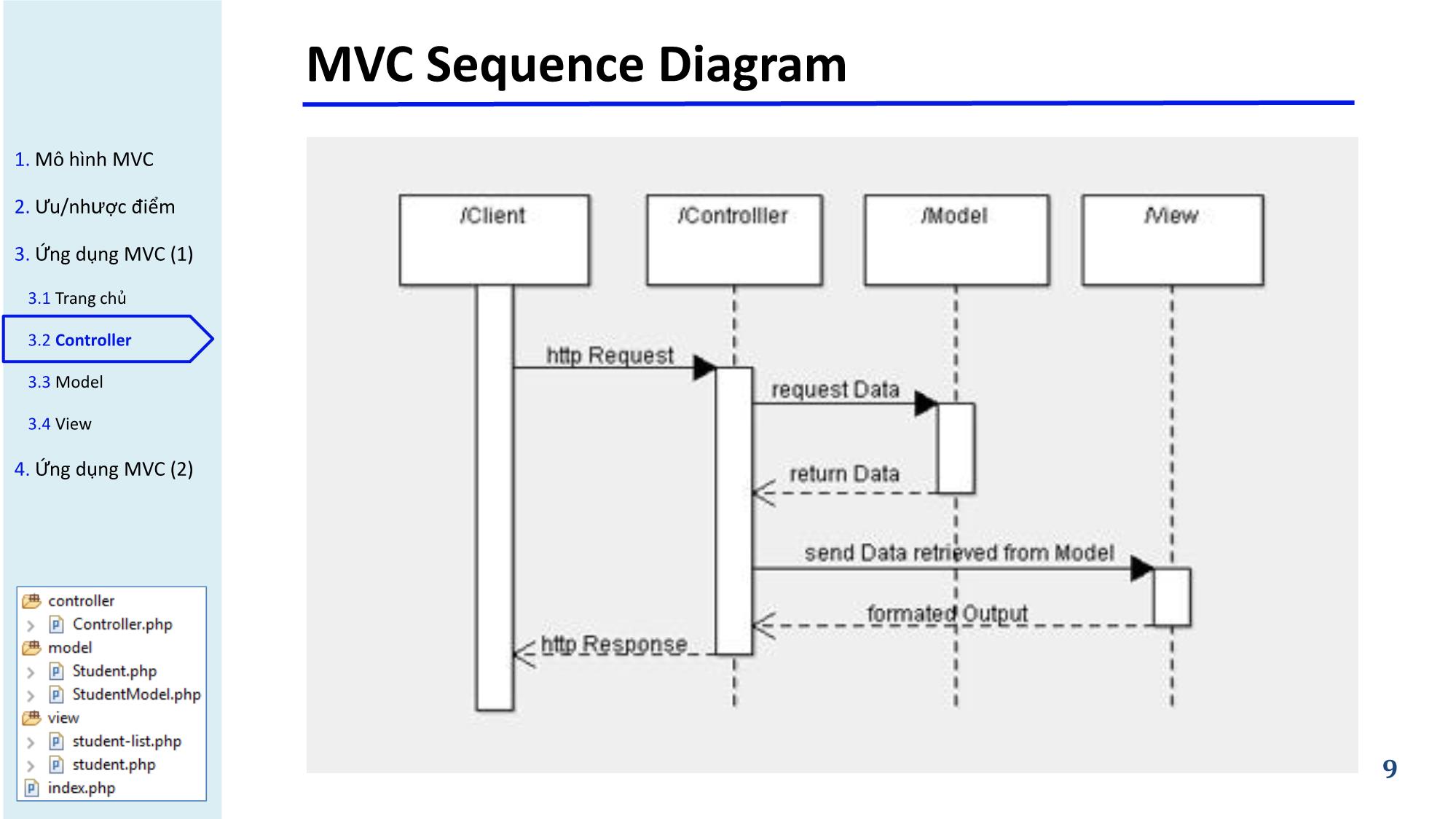
▪ Contructor: gọi và khởi tạo lớp Model.
▪ Invoke: quyết định data nào được phép trả ra từ model => gọi model
8
để lấy dữ liệu => gửi dữ liệu ra view. 8 8
MVC Sequence Diagram
1. Mô hình MVC
2. Ưu/nhược điểm
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
3.1 Trang chủ
3.2 Controller
3.3 Model
3.4 View
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2)
9
9 9
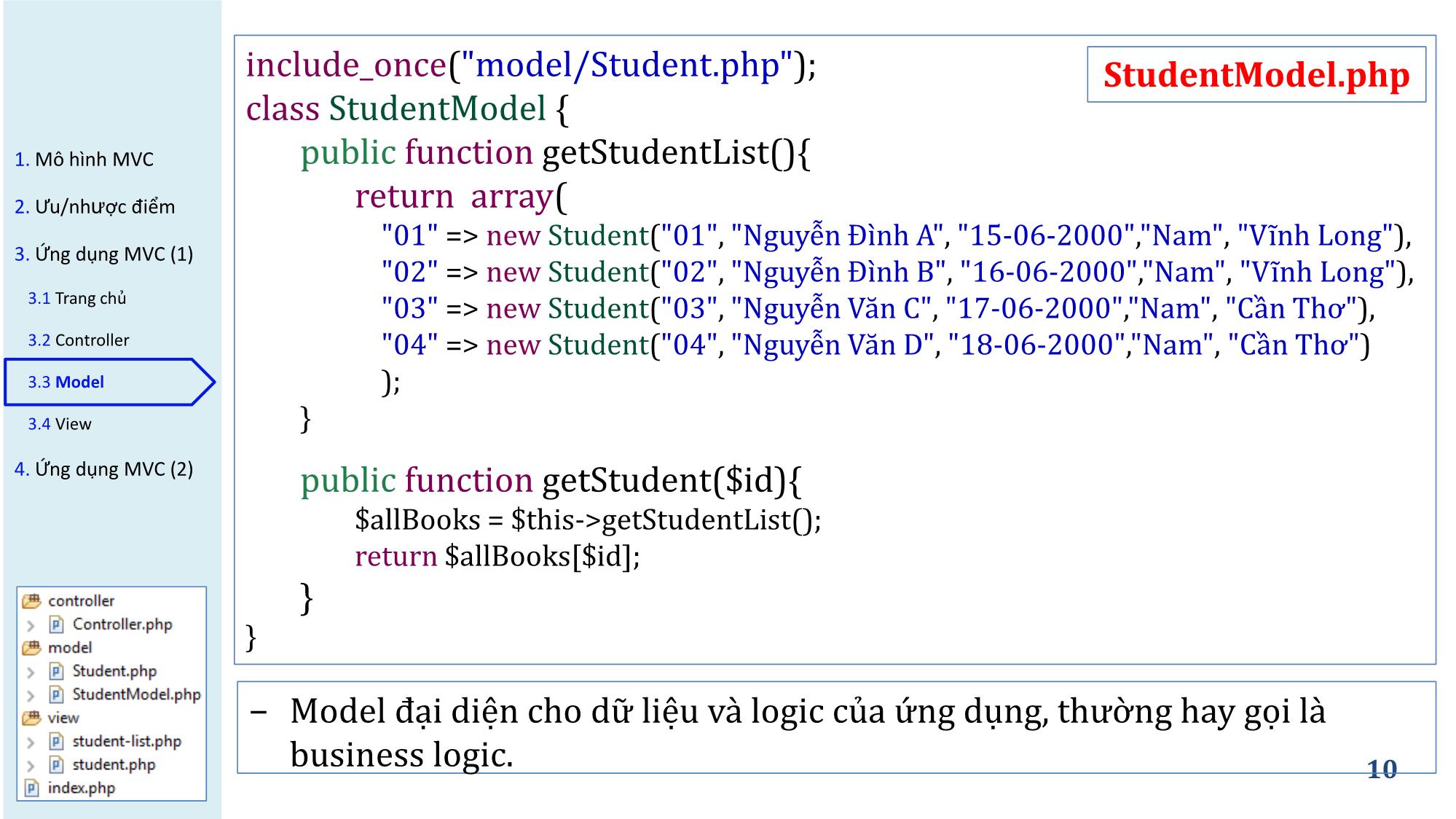
include_once("model/Student.php"); StudentModel.php
class StudentModel {
1. Mô hình MVC public function getStudentList(){
2. Ưu/nhược điểm return array(
"01" => new Student("01", "Nguyễn Đình A", "15-06-2000","Nam", "Vĩnh Long"),
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
"02" => new Student("02", "Nguyễn Đình B", "16-06-2000","Nam", "Vĩnh Long"),
3.1 Trang chủ "03" => new Student("03", "Nguyễn Văn C", "17-06-2000","Nam", "Cần Thơ"),
3.2 Controller "04" => new Student("04", "Nguyễn Văn D", "18-06-2000","Nam", "Cần Thơ")
3.3 Model );
3.4 View }
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) public function getStudent($id){
$allBooks = $this->getStudentList();
return $allBooks[$id];
}
}
− Model đại diện cho dữ liệu và logic của ứng dụng, thường hay gọi là
business logic. 10
10
class Student { Student.php
private $id;
private $name;
private $birthday;
1. Mô hình MVC
private $gender;
2. Ưu/nhược điểm private $address;
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
public function getID(){
3.1 Trang chủ return $this->id;
3.2 Controller }
3.3 Model public function getName(){
return $this->name;
3.4 View
} public function __construct($id, $name,
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) public function getBirthday(){ $birthday, $gender, $address){
return $this->birthday; $this->id = $id;
}
$this->name = $name;
public function getGender(){
return $this->gender; $this->birthday = $birthday;
} $this->gender = $gender;
public function getAddress(){ $this->address = $address;
return $this->address; }
} }
11
11
View
1. Mô hình MVC − View: định đạng lại dữ liệu nhận được từ model.
2. Ưu/nhược điểm − Trình bày nhiều dạng dữ liệu (xml, json, array,).
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
3.1 Trang chủ view/student.php
3.2 Controller
3.3 Model Mã sốgetID()?>
3.4 View Họ và têngetName()?>
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) Ngày sinhgetBirthday()?>
Giới tínhgetGender()?>
Địa chỉgetAddress()?>
12
12 12
view/student-list.php
1. Mô hình MVC Mã sốHọ và tênNgày sinhĐịa chỉ
2. Ưu/nhược điểm <?php
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) foreach ($students as $list => $student){
3.1 Trang chủ echo ‘
getID().'">'.$student->getID().'
3.2 Controller
'.$student->getName().'
3.3 Model
'.$student->getBirthday().'
3.4 View '.$student->getAddress().'
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) ';
}
?>
13
13 13
Demo
1. Mô hình MVC
2. Ưu/nhược điểm
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1)
View: student-list.php
3.1 Trang chủ
3.2 Controller
3.3 Model
3.4 View
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2)
View: student.php
14
14 14
ỨNG DỤNG MVC CÓ DATABASE
1. Mô hình MVC
2. Ưu/nhược điểm ❑ Cấu trúc ứng dụng 1: ❑ Cấu trúc ứng dụng 2:
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) bổ sung database
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2)
4.1 Trang chủ
4.2 Controller
4.3 Model
4.4 View
✓ File Database.php có thể
lưu ở 1 thưc mục khác,
VD: library
15
15 15
Bổ sung lớp Database.php
Chứa phương thức kết nối/ hủy kết nối đến database
class Database {
private $connection;
public function getConnection() {
if (! ($this->connection)) {
$this->connection = mysqli_connect ( 'localhost', 'root', '',
'mvc_student' ) or die ( 'Không thể kết nối CSDL' );
mysqli_set_charset ( $this->connection, 'utf8' );
}
return $this->connection;
}
public function closeConnection() {
if ($this->connection) {
mysqli_close ( $this->connection );
}
}
}
16
16 16
❑ Ứng dụng 1: ❑ Ứng dụng 2:
index.php index.php
<?php <?php
include_once("controller/Controller.php"); include_once("controller/Controller.php");
$controller = new Controller(); $controller = new Controller();
$controller->invoke(); $controller->invoke();
17
17 17
❑ Ứng dụng 1: ❑ Ứng dụng 2:
Controller.php Controller.php
include_once("model/StudentModel.php"); include_once("model/Database.php");
include_once("model/StudentModel.php");
class Controller { class Controller {
private $modelStudent; private $modelStudent;
public function __construct(){ public function __construct(){
$this->modelStudent = new $this->modelStudent = new
StudentModel(); StudentModel((new Database())->getConnection());
} }
public function invoke(){ public function invoke(){
if (!isset($_GET['id'])){ if (!isset($_GET['id'])){
$students = $this->modelStudent- $students = $this->modelStudent-
>getStudentList(); >getStudentList();
include 'view/student-list.php'; include 'view/student-list.php';
} }
else{ else{
$student = $this->modelStudent- $student = $this->modelStudent-
>getStudent($_GET['id']); >getStudent($_GET['id']);
include 'view/student.php'; include 'view/student.php';
} }
} }
} }
18 18
❑ Ứng dụng 1: ❑ Ứng dụng 2:
StudentModel.php StudentModel.php
include_once("model/Student.php"); include_once("model/Student.php");
class StudentModel { class StudentModel {
public function getStudentList(){ private $connection;
public function __construct($db) {
return array(
$this->connection = $db;
"01" => new Student("01", "Nguyễn Đình }
A", "15-06-2000","Nam", "Vĩnh Long"), function getStudentList() {
"02" => new Student("02", "Nguyễn Đình $sql = "Select * from Student";
B", "16-06-2000","Nam", "Vĩnh Long"), $result = mysqli_query ( $this->connection, $sql );
"03" => new Student("03", "Nguyễn Văn C", while ( $row = mysqli_fetch_array ( $result ) ) {
"17-06-2000","Nam", "Cần Thơ"), $data [] = new Student($row["id"],
"04" => new Student("04", "Nguyễn Văn $row["name"],$row["birthday"],$row["gender"],$row["address"]);
D", "18-06-2000","Nam", "Cần Thơ") }
); return $data;
} }
function getStudent($id) {
public function getStudent($id){ $sql = "Select * from Student where id = $id";
$allBooks = $this->getStudentList(); $result = mysqli_query ( $this->connection, $sql );
return $allBooks[$id]; if (mysqli_num_rows ( $result ) > 0) {
} $row = mysqli_fetch_assoc ( $result );
} $student = new Student($row["id"],
$row["name"],$row["birthday"],$row["gender"],$row["address"]);
return $student;
}
return null;
}
} 19
❑ Ứng dụng 1: ❑ Ứng dụng 2:
Student.php Student.php
class Student { class Student {
private $id; private $id;
private $name; private $name;
private $birthday; private $birthday;
private $gender; private $gender;
private $address; private $address;
public function getID(){ public function getID(){
return $this->id; return $this->id;
} }
public function getName(){ public function getName(){
return $this->name; return $this->name;
} }
public function getBirthday(){ public function getBirthday(){
return $this->birthday; return $this->birthday;
} }
public function getGender(){ public function getGender(){
return $this->gender; return $this->gender;
} }
public function getAddress(){ public function getAddress(){
return $this->address; return $this->address;
} }
public function __construct($id, $name, $birthday, $gender, $address){ public function __construct($id, $name, $birthday, $gender, $address){
$this->id = $id; $this->id = $id;
$this->name = $name; $this->name = $name;
$this->birthday = $birthday; $this->birthday = $birthday;
$this->gender = $gender; $this->gender = $gender;
$this->address = $address; $this->address = $address;
} } 20
} } 20
❑ Ứng dụng 1: ❑ Ứng dụng 2:
view/student.php view/student.php
Mã sốgetID()?> Mã sốgetID()?>
Họ và têngetName()?> Họ và têngetName()?>
Ngày sinhgetBirthday()?> Ngày sinh
Giới tínhgetGender()?> getBirthday()))?>
Địa chỉgetAddress()?>
Giới tínhgetGender()?>
Địa chỉgetAddress()?>
21
21 21
❑ Ứng dụng 1: ❑ Ứng dụng 2:
view/student-list.php view/student-list.php
Mã số Mã số
Họ và tên Họ và tên
Ngày sinh Ngày sinh
Địa chỉ Địa chỉ
<?php <?php
foreach ($students as $list => $student){ foreach ($students as $student){
echo echo
'
‘
getID().'">'.$student-
getID().'">'.$student-
>getID().'
>getID().'
'.$student->getName().'
'.$student->getName().' '.date('d-m-Y', strtotime($student->getBirthday())).'
'.$student->getBirthday().' '.$student->getAddress().'
'.$student->getAddress().' ';
'; }
} ?>
?>
22
22 22
Demo
View: student-list.php
View: student.php
23 23
Tài liệu tham khảo
1. Mô hình MVC
1. 5/6/2018.
ư
2. Ưu/nh ợc điểm 2. https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/model-view-controller-MVC, 5/6/2018
3. Ứng dụng MVC (1) 3. https://www.tutorialspoint.com/mvc_framework/mvc_framework_introduction.htm
4. Ứng dụng MVC (2) 4. https://laravel.com/docs, 6/6/2018.
Tài liệu tham khảo 5. https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_table.asp, 6/6/2018.
24
24 24File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_phat_trien_ung_dung_web_bai_6_mo_hinh_mvc_trong_ph.pdf
bai_giang_phat_trien_ung_dung_web_bai_6_mo_hinh_mvc_trong_ph.pdf

