Bài giảng Phát triển ứng dụng web - Bài 2: PHP nâng cao - Nguyễn Hữu Thể
Nội dung
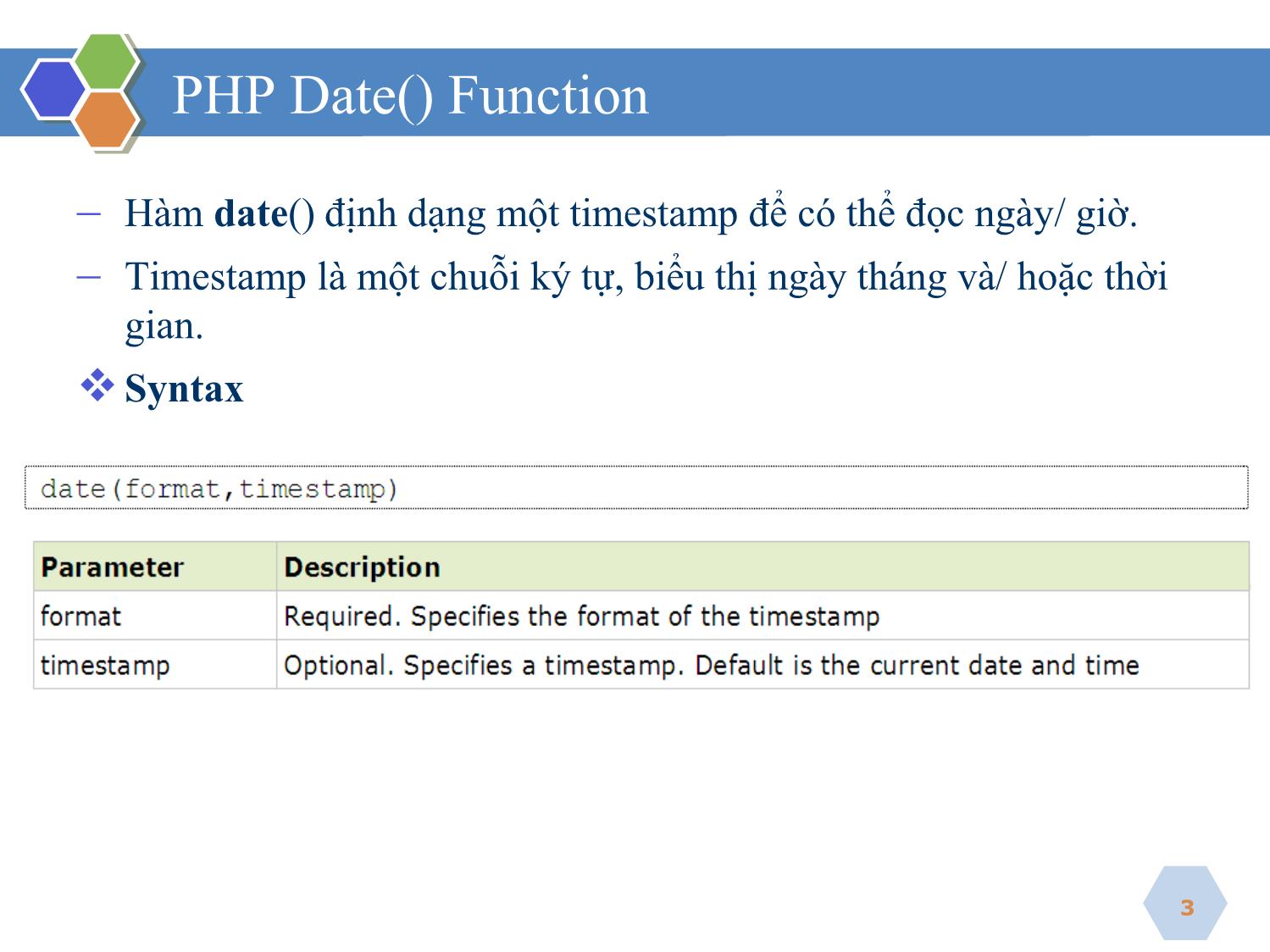
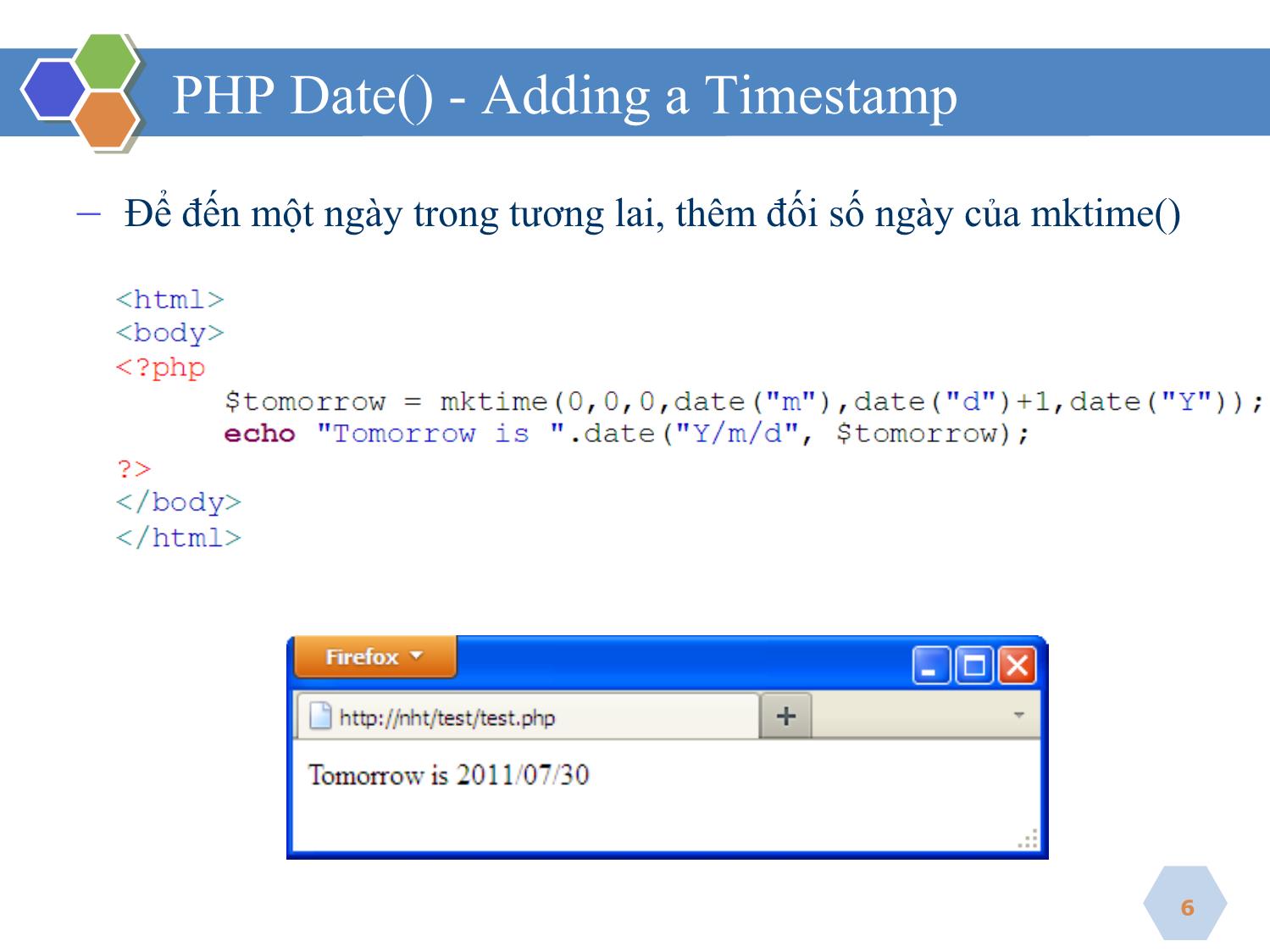
▪ PHP Date() Function
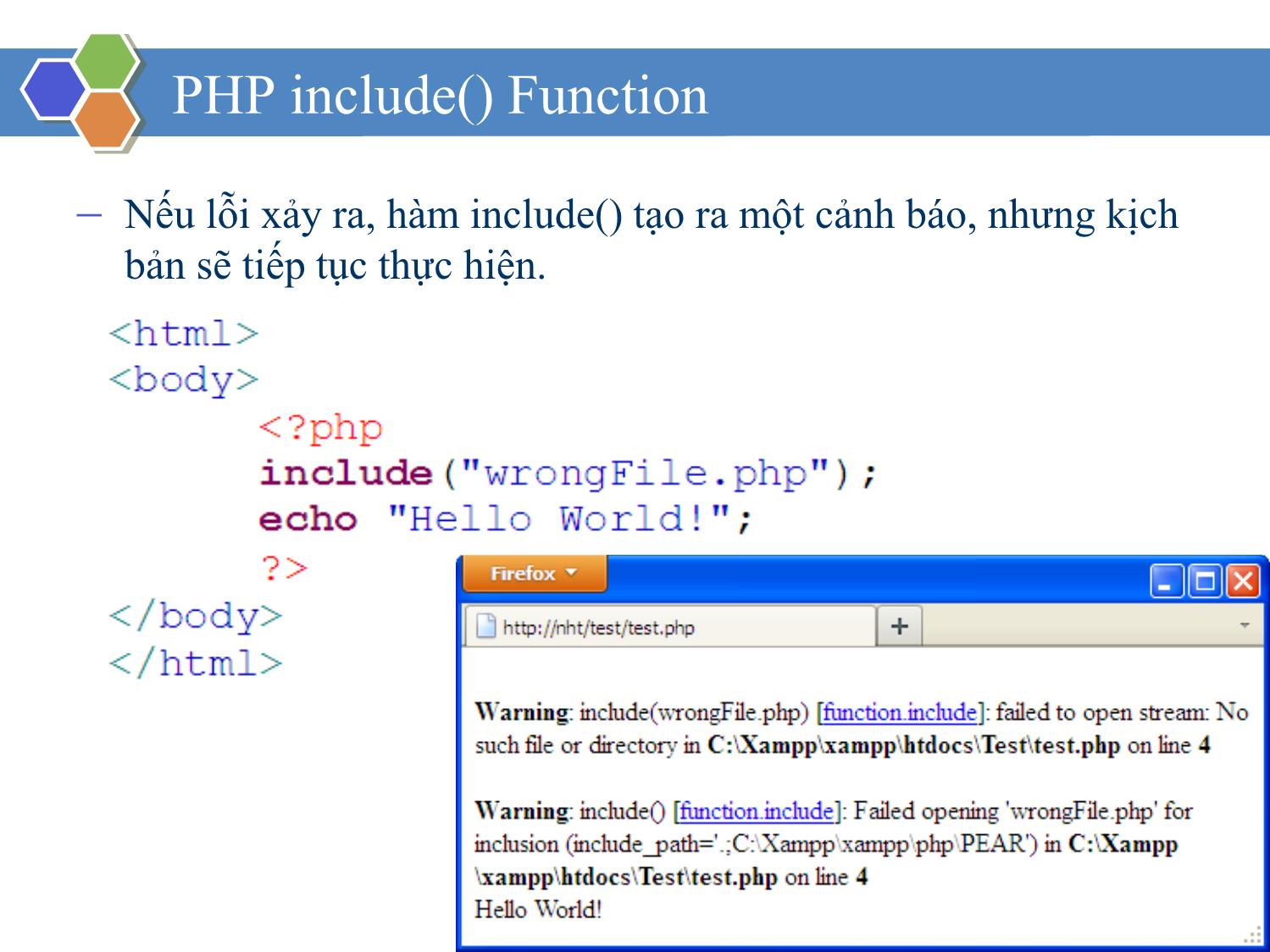
▪ PHP Include File
▪ PHP File Handling
▪ PHP File Upload
▪ PHP Cookies
▪ PHP Sessions
▪ PHP Sending E-mails
▪ PHP Error Handling
▪ PHP Exception Handling

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Phát triển ứng dụng web - Bài 2: PHP nâng cao - Nguyễn Hữu Thể", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Phát triển ứng dụng web - Bài 2: PHP nâng cao - Nguyễn Hữu Thể

trữ, hoặc thay đổi các thiết lập cho một phiên
người dùng.
− Có tác dụng cho tất cả các trang trong một ứng dụng.
− Lưu trữ thông tin người dùng trên server
− Thông tin session là tạm thời và sẽ bị xóa sau khi người dùng rời
khỏi trang web.
− Session tạo ra một id duy nhất (UID) cho mỗi client.
− UID được lưu trữ trong một cookie hoặc là gửi kèm trong URL.
34
Starting a PHP Session
− Hàm session_start(): khởi động session.
<?php Lưu ý: hàm
// Start the session session_start() cần đặt
session_start(); trước thẻ
?>
<?php
// Set session variables
$_SESSION["favcolor"] = "green";
$_SESSION["favanimal"] = "cat";
echo "Session variables are set.";
?>
Session variables are set.
35
Storing a Session Variable
− $_SESSION: lưu trữ biến session
36
Destroying a Session
− Xóa dữ liệu session, sử dụng unset() hoặc session_destroy().
− Hàm unset(): giải phóng bộ nhớ biến session
− Hàm session_destroy()
− Lưu ý: hàm session_destroy() sẽ thiết lập lại session và sẽ mất tất
cả dữ liệu session đã được lưu trữ.
37
Destroying a Session
<?php
session_start();
?>
<?php
// remove all session variables
session_unset();
// destroy the session
session_destroy();
?>
38
PHP Filters
− Validating data = Determine if the data is in proper form.
− Sanitizing data = Remove any illegal character from the data.
❖Why Use Filters?
− Many web applications receive external input. External
input/data can be:
▪ User input from a form
▪ Cookies
▪ Web services data
▪ Server variables
▪ Database query results
39
PHP Filters - PHP filter_var() Function
− The filter_var() function both validate and sanitize data.
− The filter_var() function filters a single variable with a
specified filter. It takes two pieces of data:
▪ The variable you want to check
▪ The type of check to use
EX: Sanitize a String: Remove all HTML tags from a string
<?php
$str = "Hello World!";
$newstr = filter_var($str, FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
echo $newstr; Hello World!
?>
40
PHP Filters - PHP filter_var() Function
❖Validate an Integer
− If $int is an integer, the output of the code below will be:
"Integer is valid".
− If $int is not an integer, the output will be: "Integer is not
valid"
<?php
$int = 100;
if (!filter_var($int, FILTER_VALIDATE_INT) === false) {
echo("Integer is valid");
} else {
echo("Integer is not valid");
}
?> Integer is valid
41
PHP Filters - PHP filter_var() Function
❖Validate an IP Address
− Check if the variable $ip is a valid IP address
<?php
$ip = "127.0.0.1";
if (!filter_var($ip, FILTER_VALIDATE_IP) === false)
{
echo("$ip is a valid IP address");
} else {
echo("$ip is not a valid IP address");
}
?>
127.0.0.1 is a valid IP address 42
PHP Filters - PHP filter_var() Function
❖Sanitize and Validate an Email Address
− Remove all illegal characters from the $email variable, then
check if it is a valid email address
<?php
$email = “nguyenvana@example.com";
// Remove all illegal characters from email
$email = filter_var($email, FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL);
// Validate e-mail
if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL) === false) {
echo("$email is a valid email address");
} else {
echo("$email is not a valid email address");
}
?> 43
PHP Filters - PHP filter_var() Function
❖Sanitize and Validate a URL
− Remove all illegal characters from a URL, then check if $url is
a valid URL:
<?php
$url = "https://www.google.com";
// Remove all illegal characters from a url
$url = filter_var($url, FILTER_SANITIZE_URL);
// Validate url
if (!filter_var($url, FILTER_VALIDATE_URL) === false) {
echo("$url is a valid URL");
} else {
echo("$url is not a valid URL");
}
?> 44
PHP Sending E-mails
❖ The PHP mail() Function
− Hàm mail() được sử dụng để gửi email.
❖ Configuration: php.ini
Name Default Description Changeable
mail.add_x_he "0" Add X-PHP-Originating-Script that will include UID of the PHP_INI_PERDIR
ader script followed by the filename. For PHP 5.3.0 and above
mail.log NULL The path to a log file that will log all mail() calls. Log include PHP_INI_PERDIR
full path of script, line number, To address and headers. For PHP
5.3.0 and above
SMTP "localhost" Windows only: The DNS name or IP address of the SMTP server PHP_INI_ALL
smtp_port "25" Windows only: The SMTP port number. For PHP 4.3.0 and PHP_INI_ALL
above
sendmail_from NULL Windows only: Specifies the "from" address to be used when PHP_INI_ALL
sending mail from mail()
sendmail_path "/usr/sbin/s Specifies where the sendmail program can be found. This PHP_INI_SYSTEM
endmail -t directive works also under Windows. If set, SMTP, smtp_port
-i" and sendmail_from are ignored 45
PHP Sending E-mails
46
PHP Simple E-Mail
− Sử dụng hàm mail() để gửi một email văn bản.
47
PHP Mail Form
− Tạo một form phản hồi ý kiến (feedback) trên trang web.
48
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
PHP 5 String Functions
Function Description
addcslashes() Returns a string with backslashes in front of the specified characters
addslashes() Returns a string with backslashes in front of predefined characters
bin2hex() Converts a string of ASCII characters to hexadecimal values
chop() Removes whitespace or other characters from the right end of a string
chr() Returns a character from a specified ASCII value
chunk_split() Splits a string into a series of smaller parts
convert_cyr_string() Converts a string from one Cyrillic character-set to another
convert_uudecode() Decodes a uuencoded string
convert_uuencode() Encodes a string using the uuencode algorithm
count_chars() Returns information about characters used in a string
crc32() Calculates a 32-bit CRC for a string
crypt() One-way string hashing
echo() Outputs one or more strings
explode() Breaks a string into an array
fprintf() Writes a formatted string to a specified output stream
get_html_translation_table() Returns the translation table used by htmlspecialchars() and
htmlentities() 49
PHP 5 String Functions (2)
Function Description
hebrev() Converts Hebrew text to visual text
hebrevc() Converts Hebrew text to visual text and new lines (\n) into
hex2bin() Converts a string of hexadecimal values to ASCII characters
html_entity_decode() Converts HTML entities to characters
htmlentities() Converts characters to HTML entities
htmlspecialchars_decode() Converts some predefined HTML entities to characters
htmlspecialchars() Converts some predefined characters to HTML entities
implode() Returns a string from the elements of an array
join() Alias of implode()
lcfirst() Converts the first character of a string to lowercase
levenshtein() Returns the Levenshtein distance between two strings
localeconv() Returns locale numeric and monetary formatting information
ltrim() Removes whitespace or other characters from the left side of a string
md5() Calculates the MD5 hash of a string
md5_file() Calculates the MD5 hash of a file 50
PHP 5 String Functions (3)
Function Description
metaphone() Calculates the metaphone key of a string
money_format() Returns a string formatted as a currency string
nl_langinfo() Returns specific local information
nl2br() Inserts HTML line breaks in front of each newline in a string
number_format() Formats a number with grouped thousands
ord() Returns the ASCII value of the first character of a string
parse_str() Parses a query string into variables
print() Outputs one or more strings
printf() Outputs a formatted string
quoted_printable_decode() Converts a quoted-printable string to an 8-bit string
quoted_printable_encode() Converts an 8-bit string to a quoted printable string
quotemeta() Quotes meta characters
rtrim() Removes whitespace or other characters from the right side of a string
setlocale() Sets locale information
sha1() Calculates the SHA-1 hash of a string
sha1_file() Calculates the SHA-1 hash of a file
51
PHP 5 String Functions (4)
Function Description
similar_text() Calculates the similarity between two strings
soundex() Calculates the soundex key of a string
sprintf() Writes a formatted string to a variable
sscanf() Parses input from a string according to a format
str_getcsv() Parses a CSV string into an array
str_ireplace() Replaces some characters in a string (case-insensitive)
str_pad() Pads a string to a new length
str_repeat() Repeats a string a specified number of times
str_replace() Replaces some characters in a string (case-sensitive)
str_rot13() Performs the ROT13 encoding on a string
str_shuffle() Randomly shuffles all characters in a string
str_split() Splits a string into an array
str_word_count() Count the number of words in a string
strcasecmp() Compares two strings (case-insensitive)
strchr() Finds the first occurrence of a string inside another string (alias of strstr())
strcmp() Compares two strings (case-sensitive)
strcoll() Compares two strings (locale based string comparison)
strcspn() Returns the number of characters found in a string before any part of some
specified characters are found 52
PHP 5 String Functions (5)
Function Description
strip_tags() Strips HTML and PHP tags from a string
stripcslashes() Unquotes a string quoted with addcslashes()
stripslashes() Unquotes a string quoted with addslashes()
stripos() Returns the position of the first occurrence of a string inside another
string (case-insensitive)
stristr() Finds the first occurrence of a string inside another string (case-
insensitive)
strlen() Returns the length of a string
strnatcasecmp() Compares two strings using a "natural order" algorithm (case-
insensitive)
strnatcmp() Compares two strings using a "natural order" algorithm (case-
sensitive)
strncasecmp() String comparison of the first n characters (case-insensitive)
strncmp() String comparison of the first n characters (case-sensitive)
strpbrk() Searches a string for any of a set of characters
strpos() Returns the position of the first occurrence of a string inside another
string (case-sensitive) 53
PHP 5 String Functions (6)
Function Description
strrchr() Finds the last occurrence of a string inside another string
strrev() Reverses a string
strripos() Finds the position of the last occurrence of a string inside another
string (case-insensitive)
strrpos() Finds the position of the last occurrence of a string inside another
string (case-sensitive)
strspn() Returns the number of characters found in a string that contains
only characters from a specified charlist
strstr() Finds the first occurrence of a string inside another string (case-
sensitive)
strtok() Splits a string into smaller strings
strtolower() Converts a string to lowercase letters
strtoupper() Converts a string to uppercase letters
strtr() Translates certain characters in a string
substr() Returns a part of a string
substr_compare() Compares two strings from a specified start position (binary safe
and optionally case-sensitive)
54
PHP 5 String Functions (7)
Function Description
substr_count() Counts the number of times a substring occurs in a string
substr_replace() Replaces a part of a string with another string
trim() Removes whitespace or other characters from both sides of a
string
ucfirst() Converts the first character of a string to uppercase
ucwords() Converts the first character of each word in a string to
uppercase
vfprintf() Writes a formatted string to a specified output stream
vprintf() Outputs a formatted string
vsprintf() Writes a formatted string to a variable
wordwrap() Wraps a string to a given number of characters
55
PHP Error Handling
− Ba phương pháp xử lý lỗi:
▪ Function “die()”
▪ Custom Error Handler
▪ Error Report levels
56
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Error Handling: Using the die() function
− Mở file văn bản:
− Nếu file không tồn tại, thông báo lỗi như sau:
57
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Error Handling: Using the die() function
− Để tránh nhận thông báo lỗi như trên, nên kiểm tra file tồn tại
trước khi truy cập
− Nếu file không tồn tại, thông báo lỗi như sau:
58
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Error Handling: Creating a Custom Error Handler
− Tạo ra một hàm và gọi nó khi có lỗi xảy ra trong PHP.
❖ Syntax
error_function(error_level, error_message, error_file, error_line,
error_context)
59
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Error Handling: Creating a Custom Error Handler
error_function(error_level, error_message, error_file, error_line,
error_context)
60
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Error Handling: Error Report levels
− Các kiễu báo lỗi:
61
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Error Handling: Error Report levels
− Tạo ra một hàm xử lý lỗi
62
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Set Error Handler
− Xử lý lỗi mặc định cho PHP được xây dựng trong error handler.
set_error_handler("customError");
− Example: kiểm tra biến đầu ra có tồn tại không
− Output:
63
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Trigger an Error
− Hàm trigger_error(): kích hoạt lỗi khi dữ liệu nhập không hợp lệ.
− Output
64
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Trigger an Error
− Các kiểu lỗi có thể:
▪ E_USER_ERROR - Tạo run-time error. Lỗi không thể phục hồi
thì các kịch bản phải dừng lại
▪ E_USER_WARNING - Tạo run-time warning. Kịch bản thực thi
không phải dừng lại
▪ E_USER_NOTICE - Tạo run-time notice. Ghi chú các khi tìm
thấy lỗi
65
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Trigger an Error
− Output
66
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
PHP Exception Handling
− Trường hợp ngoại lệ được sử dụng để thay đổi luồng mặc định
của một kịch bản nếu một lỗi nào đó xảy ra
− Các trường hợp có thể xảy ra khi một ngoại lệ được kích hoạt:
▪ Trạng thái code hiện tại được lưu trữ
▪ Code thực thi sẽ chuyển sang một hàm xử lý ngoại lệ
▪ Tùy thuộc vào tình huống xử lý, sau đó có thể:
• Tiếp tục thực hiện,
• Chấm dứt việc thực hiện kịch bản
• Hoặc tiếp tục kịch bản từ một vị trí khác trong code
67
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Basic Use of Exceptions
− Khi một ngoại lệ được ném ra, các code bên dưới nó sẽ không
được thực thi, và PHP sẽ cố gắng tìm "catch" phù hợp.
− Nếu không bắt ngoại lệ => hiện thông báo "Uncaught Exception"
68
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Try, throw and catch
− Mã lệnh thích hợp xử lý ngoại lệ bao gồm:
▪ Try - sử dụng ngoại lệ trong khối "try". Nếu trường hợp ngoại lệ
không kích hoạt, mã lệnh sẽ tiếp tục. Nếu trường hợp ngoại lệ
xuất hiện, ngoại lệ là "throw"
▪ Throw - Đây là cách kích hoạt ngoại lệ. Mỗi "throw" phải có ít
nhất một "catch"
▪ Catch - Một khối "catch" lấy một ngoại lệ và tạo ra một đối
tượng có chứa các thông tin ngoại lệ
69
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Try, throw and catch
70
Lập trình ứng dụng mạng
Creating a Custom Exception Class
− Tạo class với các hàm có thể được gọi khi một ngoại lệ xảy ra.
71
Lập trình ứng dụng mạngFile đính kèm:
 bai_giang_phat_trien_ung_dung_web_bai_2_php_nang_cao_nguyen.pdf
bai_giang_phat_trien_ung_dung_web_bai_2_php_nang_cao_nguyen.pdf

