Bài giảng Macroeconomics - Chapter 2: Supply and demand - Nguyễn Thùy Dung
MARKET AND COMPETITION
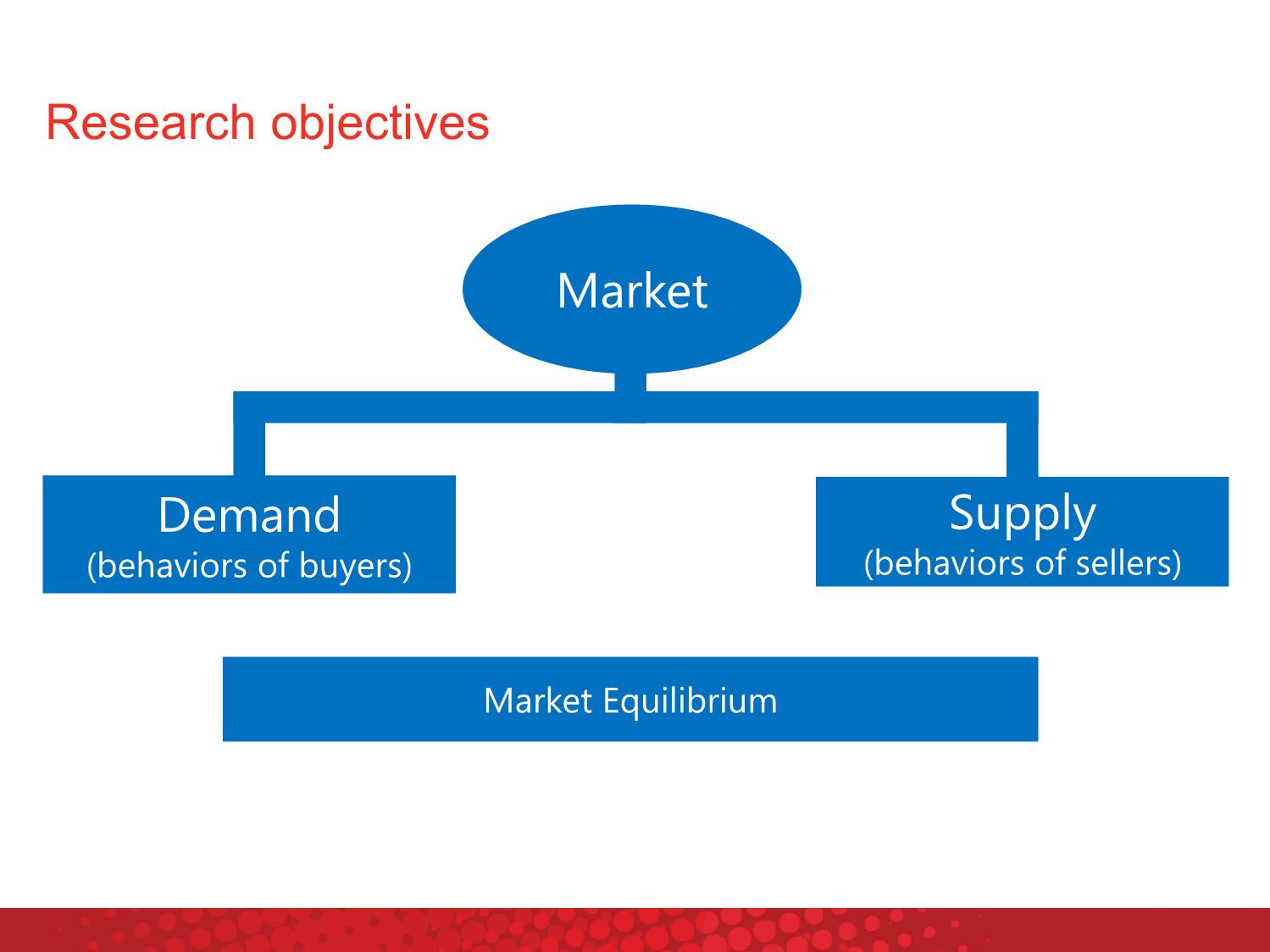
Market and Competition
▪ Competitive market: a market with many buyers
and sellers and each of them has a negligible
effect on market price.
▪ A perfectly competitive market must have 2
characteristics:
(1) All goods exactly the same
(2) Buyers & sellers so numerous that no one
can affect market price – each is a “price taker”
▪ In this chapter, we assume markets are perfectly
competitive.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6
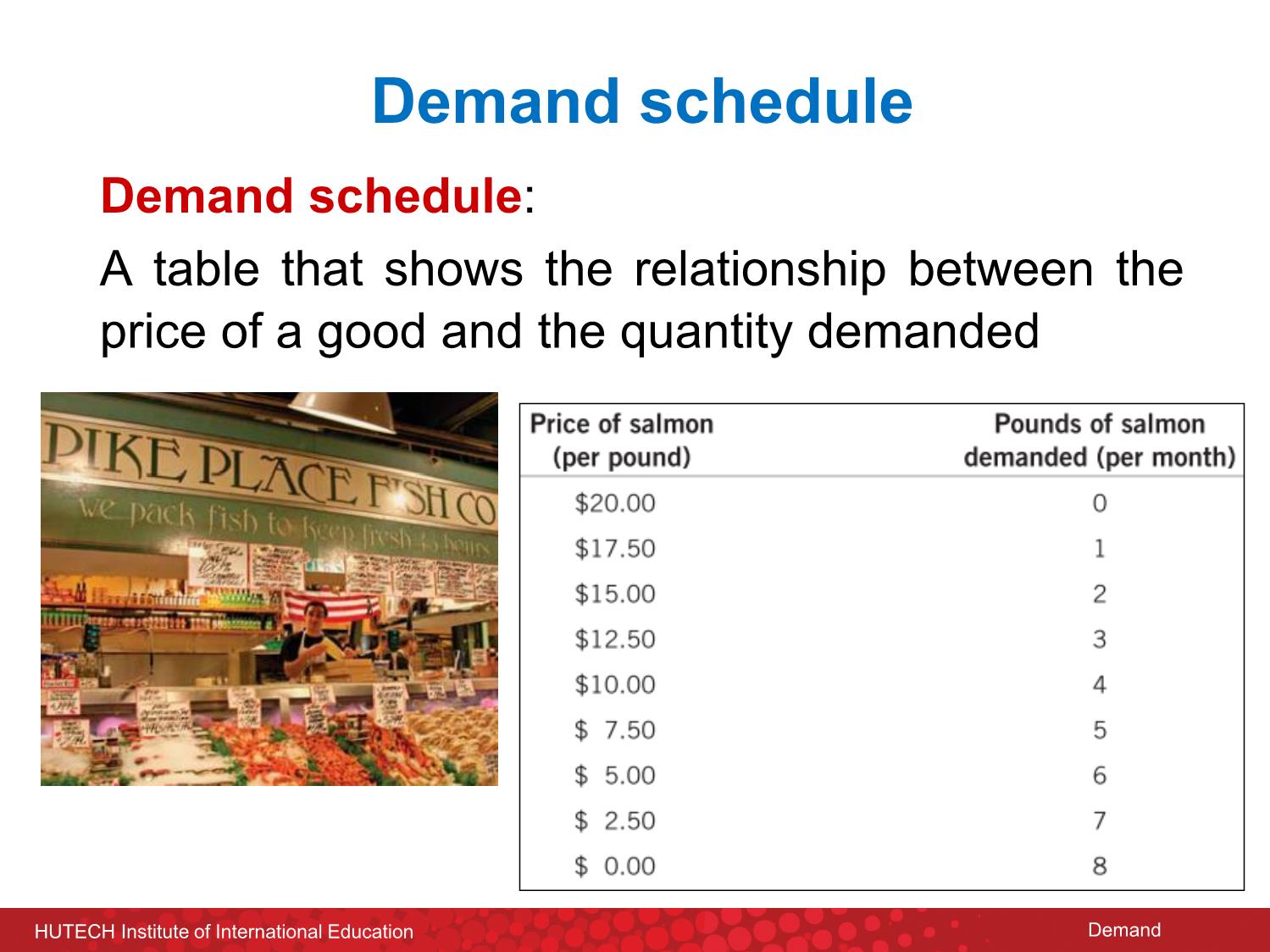
Trang 7
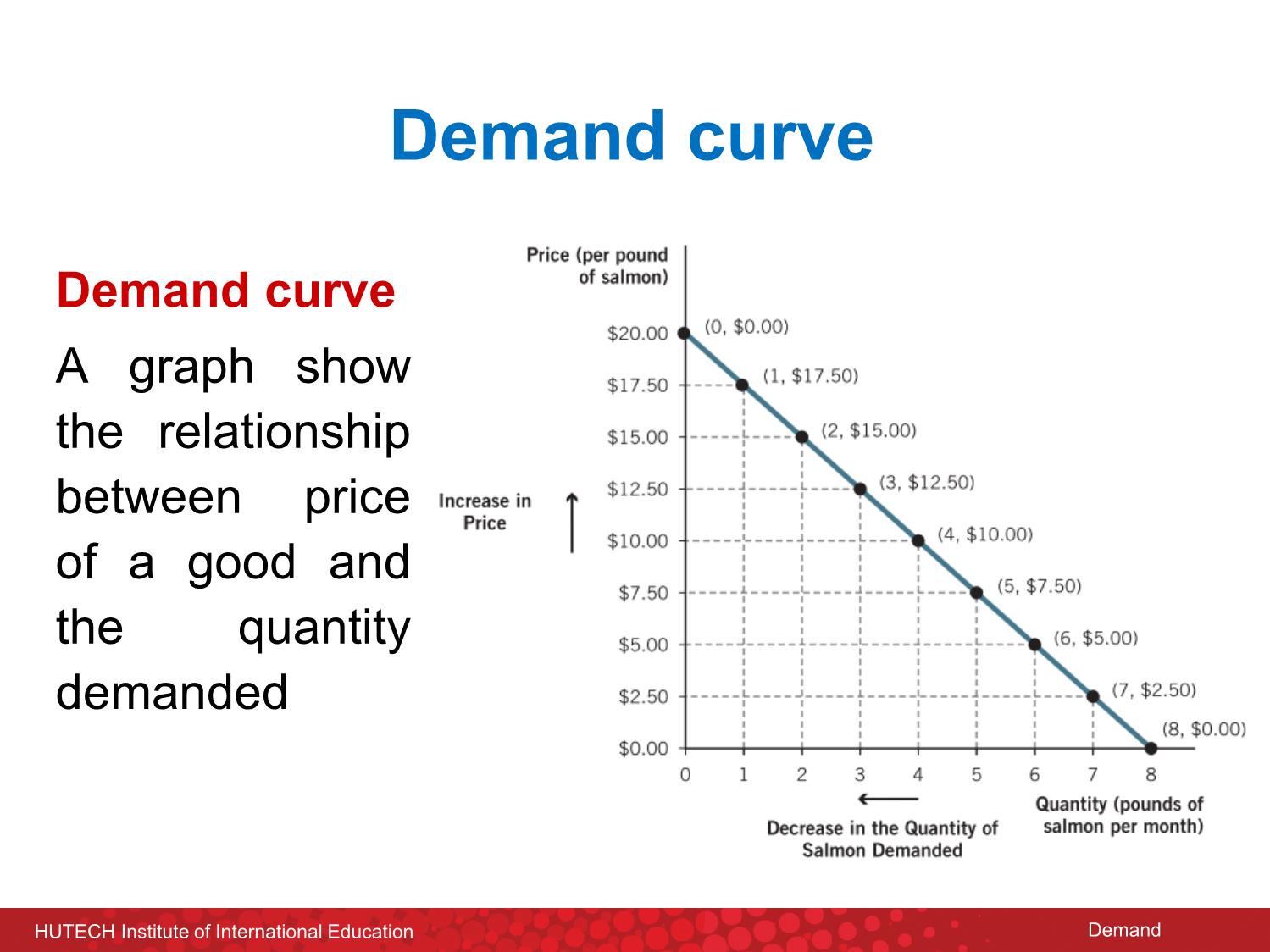
Trang 8
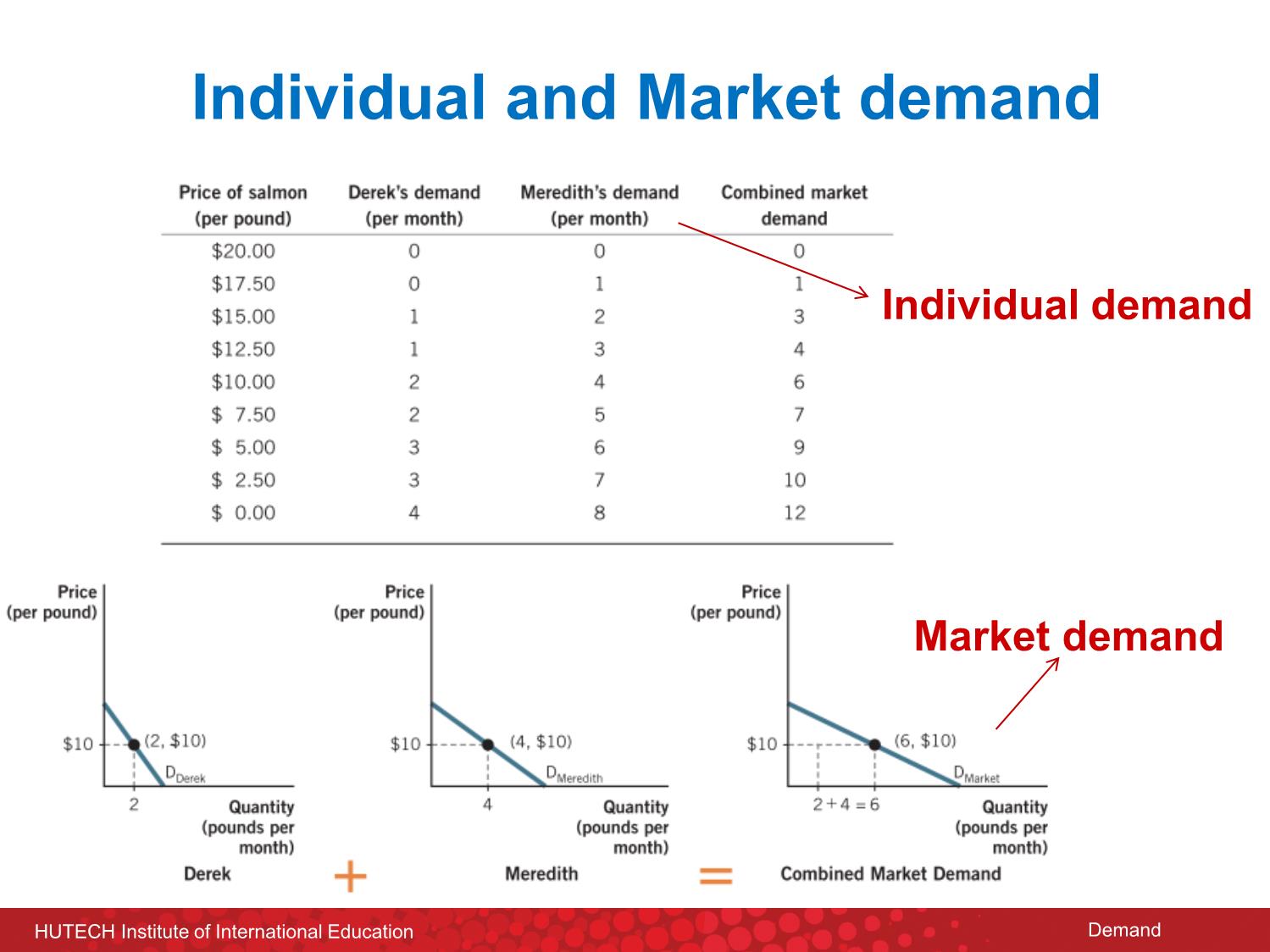
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Macroeconomics - Chapter 2: Supply and demand - Nguyễn Thùy Dung", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Macroeconomics - Chapter 2: Supply and demand - Nguyễn Thùy Dung

ECO107 MICROECONOMICS Lecturer: MSc. Nguyen Thuy Dung Faculty of Accounting, Banking and Finance www.hutech.edu.vn/quocte HUTECH Institute of International Education Supply and Demand Market and Competition Demand Equilibrium TOPIC 2 Supply 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 HUTECH Institute of International Education What is a market? 2.1 MARKET AND COMPETITION Market and Competition A market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or services Research objectives Market Demand (behaviors of buyers) Supply (behaviors of sellers) Market Equilibrium HUTECH Institute of International Education MARKET AND COMPETITION Market and Competition ▪ Competitive market: a market with many buyers and sellers and each of them has a negligible effect on market price. ▪ A perfectly competitive market must have 2 characteristics: (1) All goods exactly the same (2) Buyers & sellers so numerous that no one can affect market price – each is a “price taker” ▪ In this chapter, we assume markets are perfectly competitive. HUTECH Institute of International Education DEMAND Demand ▪ The quantity demanded of any good is the amount of the good that buyers are willing and able to purchase. ▪ Law of demand: the claim that the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises if other things being equal Quantity Price DemandQ P D Quantity demandedQD 2.2 HUTECH Institute of International Education Demand schedule Demand Demand schedule: A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded HUTECH Institute of International Education Demand curve Demand Demand curve A graph show the relationship between price of a good and the quantity demanded HUTECH Institute of International Education Individual and Market demand Demand Individual demand Market demand HUTECH Institute of International Education Demand curve Demand Assume there’re only Kate and Charlie in the market demand of milk. Each month, Kate buys 6 cans of milk with the price of $1 each; buy 4 cans with $1.5 each. Charlie buys 4 cans of milk with the price of $1 each, buy 2 cans with $1.5 each. Which point will be on the market demand curve of milk? A. Q = 2; P = 1,5 B. Q = 4; P = 2,5 C. Q = 10; P = 1 D. Q = 16; P = 2,5 Movement along curve Cause by price Shift in curve Cause by other factors Factors affect Demand HUTECH Institute of International Education Shift in Demand curve Demand P0 Price 0 Q0 Q1 D0 D1 QuantityQ2 Decrease Increase A change in demand can be represented by a shift in the position of the demand curve. A change in demand results from a change in one or more of determinants of demand, other than the price of the goods. D2 HUTECH Institute of International Education Demand With normal goodsIncome Demand law Price of goods With inferior goods Shift in Demand curve Causes a movement along the D curve HUTECH Institute of International Education Demand Price of related goods Shift in Demand curve ❑Substitutes 2 goods, an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other ❑Complements 2 goods, an increase in the price of one leads to an decrease in the demand for the other HUTECH Institute of International Education Demand Shift in Demand curve ❑ Tastes – Change in tastes → changes the demand ❑ Expectations - about the future (income, prices) – Affect current demand ❑ Number of buyers – increase – Market demand will increases HUTECH Institute of International Education SUPPLY Supply ▪ The quantity supplied of any good is the amount of the good that sellers are willing and able to sell ▪ Law of supply: the claim that the quantity supplied of a good rises when the price of the good rises if other things being equal Quantity Price SupplyQ P S Quantity suppliedQS 2.3 HUTECH Institute of International Education Supply schedule Supply Supply schedule: A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied HUTECH Institute of International Education Supply curve Supply A graph show the relationship between price of a good and the quantity supplied HUTECH Institute of International Education Individual and Market supply Supply Individual supply Market Supply HUTECH Institute of International Education Shift in Supply curve Supply Price 0 S0 S1 Quantity Increase Decrease S2 A change in supply results from a change in one or more of determinants of supply, other than the price of the goods. A change in supply can be represented by a shift in the position of the supply curve. HUTECH Institute of International Education Supply curve Shifter Supply Technology HUTECH Institute of International Education Supply curve Shifter Supply HUTECH Institute of International Education Market equilibrium Market equilibrium At $2.00, the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied! Demand Schedule Supply Schedule 2.4 HUTECH Institute of International Education Market equilibrium Market equilibrium HUTECH Institute of International Education Market equilibrium Market equilibrium ▪Equilibrium - a situation in which the market price has reached the level at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded ▪Equilibrium price - the price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded ▪Equilibrium quantity - the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the equilibrium price HUTECH Institute of International Education Markets not in equilibrium Market equilibrium Surplus A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded HUTECH Institute of International Education Markets not in equilibrium Market equilibrium Shortage A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied HUTECH Institute of International Education Market equilibrium To determine the effects of any event, 1. Decide whether event shifts S curve, D curve, or both. 2. Decide in which direction curve shifts. 3. Use supply-demand diagram to see how the shift changes eq’m P and Q. 3 steps to analyze change in equilibrium HUTECH Institute of International Education 3 steps to analyzing change in equilibrium Market equilibrium EXAMPLE: The Market for Hybrid Cars - A Shift in Demand - A Shift in Supply HUTECH Institute of International Education QUICK CHECK Movie tickets and DVDs are substitutes. If the price of DVDs increases, what happens in the market for movie tickets? The supply curve shifts to the left. The supply curve shifts to the right. The demand curve shifts to the left. The demand curve shifts to the right.
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_macroeconomics_chapter_2_supply_and_demand_nguyen.pdf
bai_giang_macroeconomics_chapter_2_supply_and_demand_nguyen.pdf

