Study on application of ann - based mpc controllers for load-frequency control of an interconnected hydropower plant
Currently, in Vietnam electricity market, hydropower plants still
account for a large proportion approximately 38%. Thus, study on control problems
of the hydropower plants plays an extremely important role. Load – frequency
control is one of the most significant control problems. Major objectives of such a
control strategy are to focus on maintaining the system frequency at a nominal
value (50Hz in Vietnam) and the tie-line power interchange at a scheduled value.
This guarantees the stability of multi-area interconnected hydropower systems
against load changes in particular and the national power networks in general. This
paper proposes an artificial neural network (ANN)-based model predictive control
(MPC) for the LFC of an interconnected hydropower system. This control strategy
in co-operation with an optimization mechanism– tuned gains has become a
workable solution for the LFC. Together with numerical simulation results obtained
in this study, there is enough evidence to affirm the applicability of the ANN-based
MPC-type LFC controller proposed in dealing with the LFC problem of a multiarea interconnected hydropower system.

Trang 1
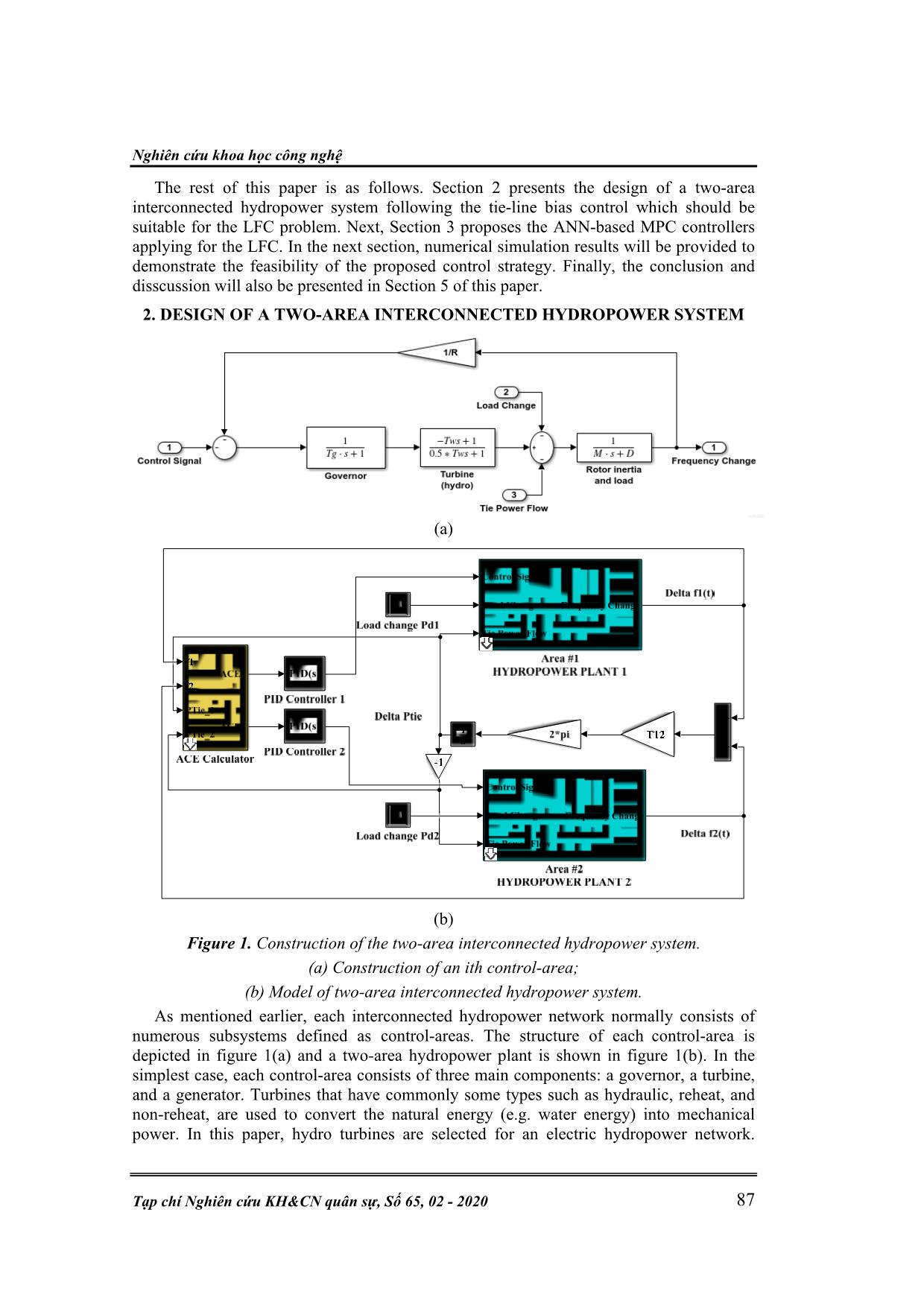
Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Study on application of ann - based mpc controllers for load-frequency control of an interconnected hydropower plant

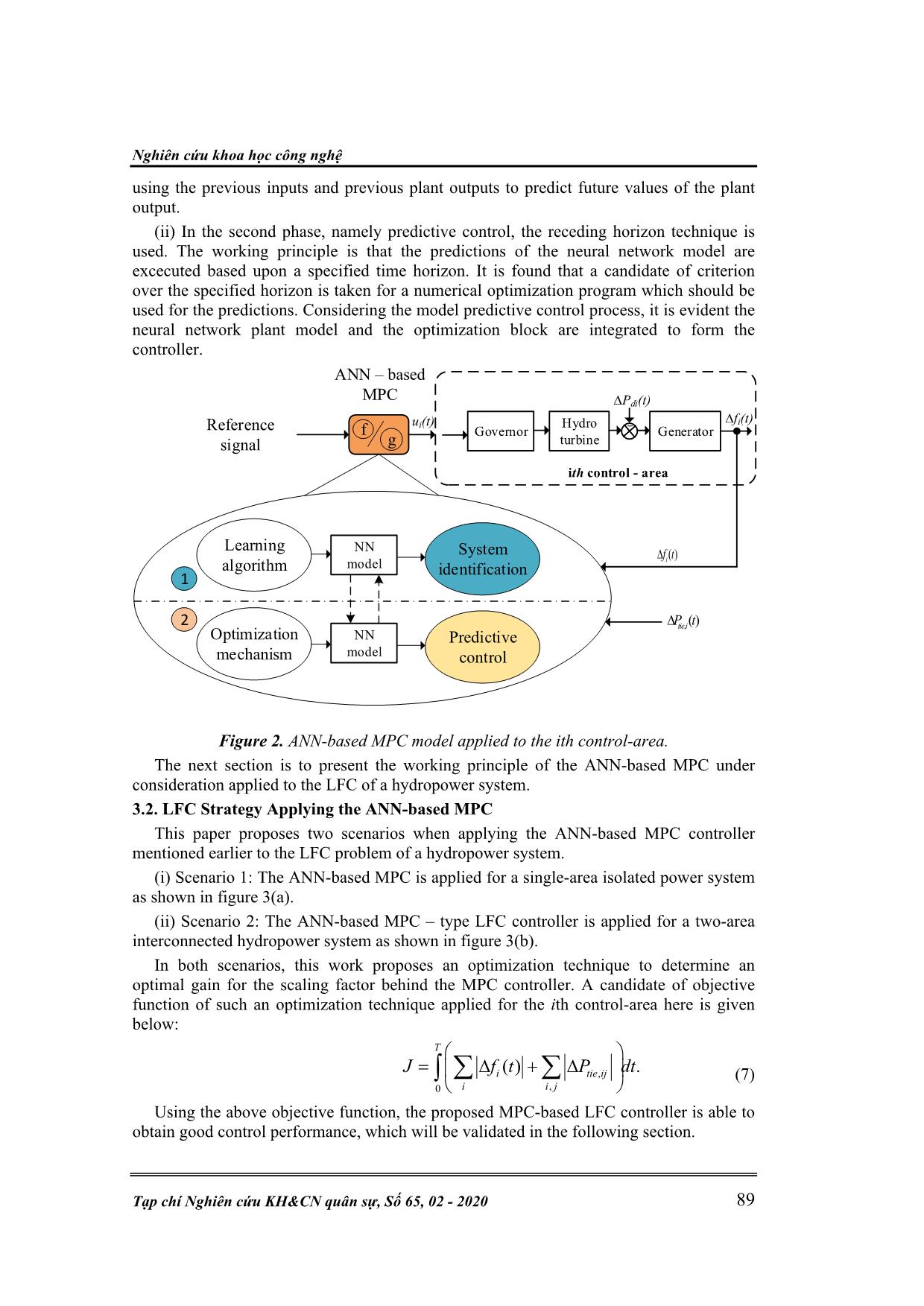
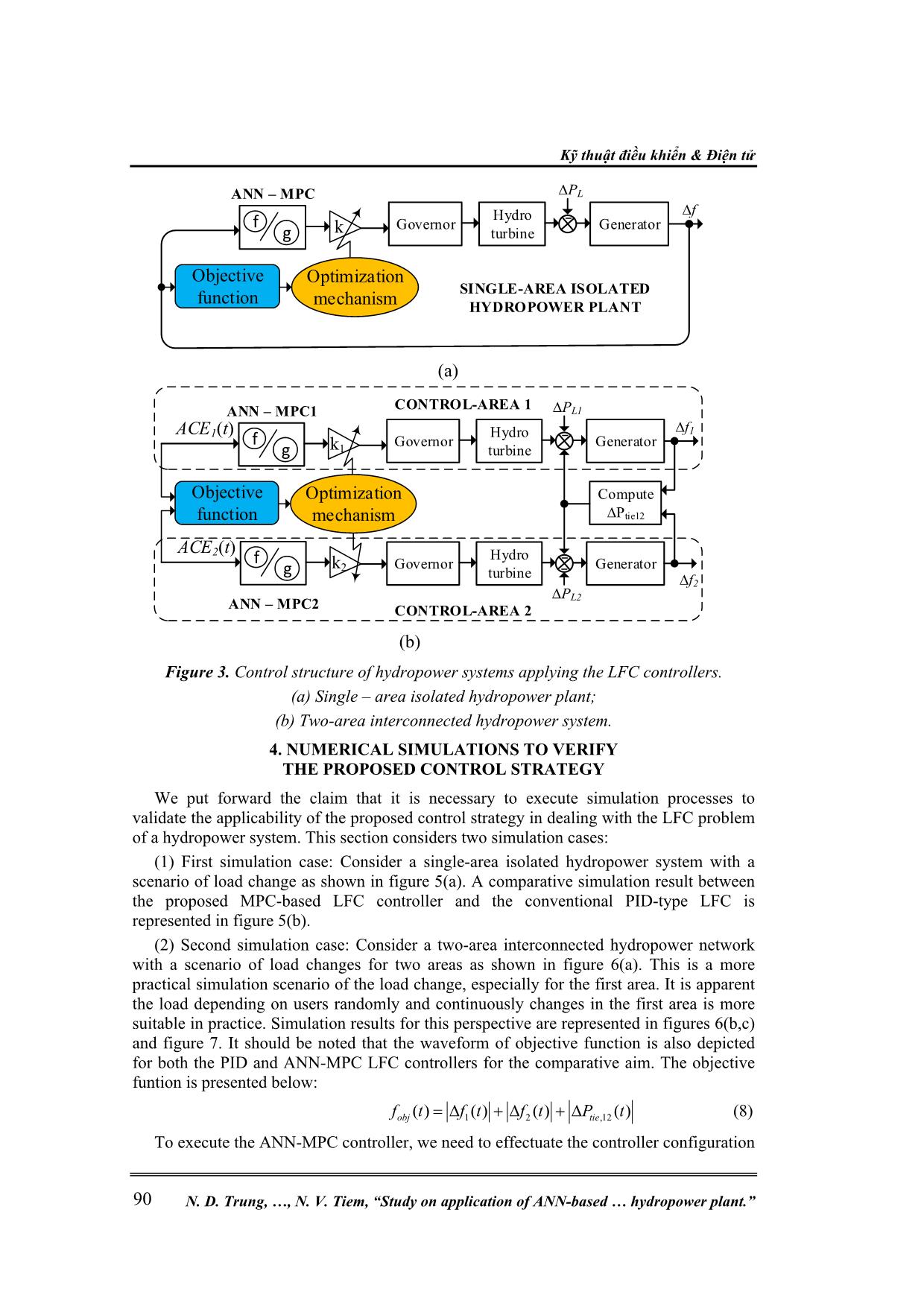
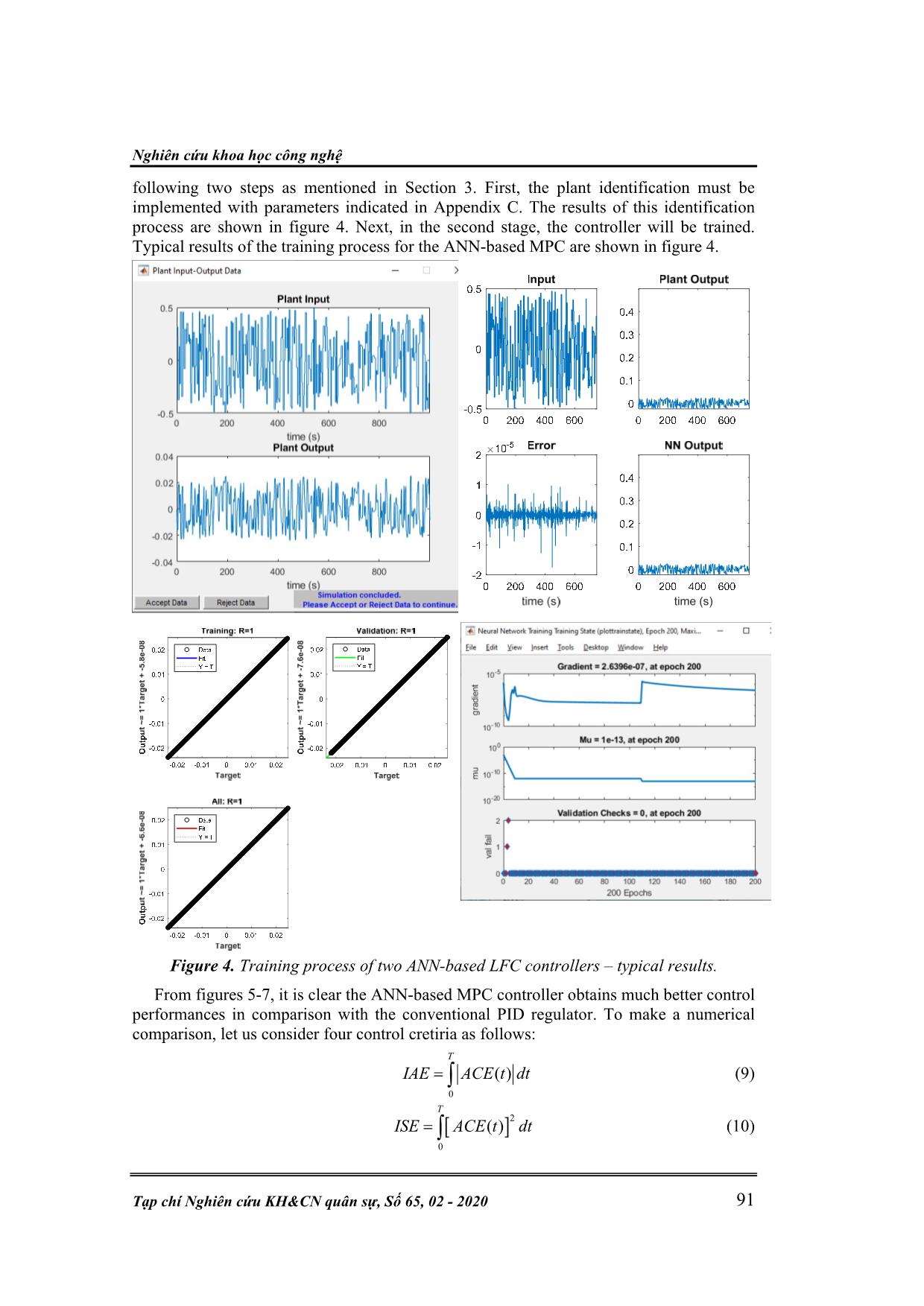
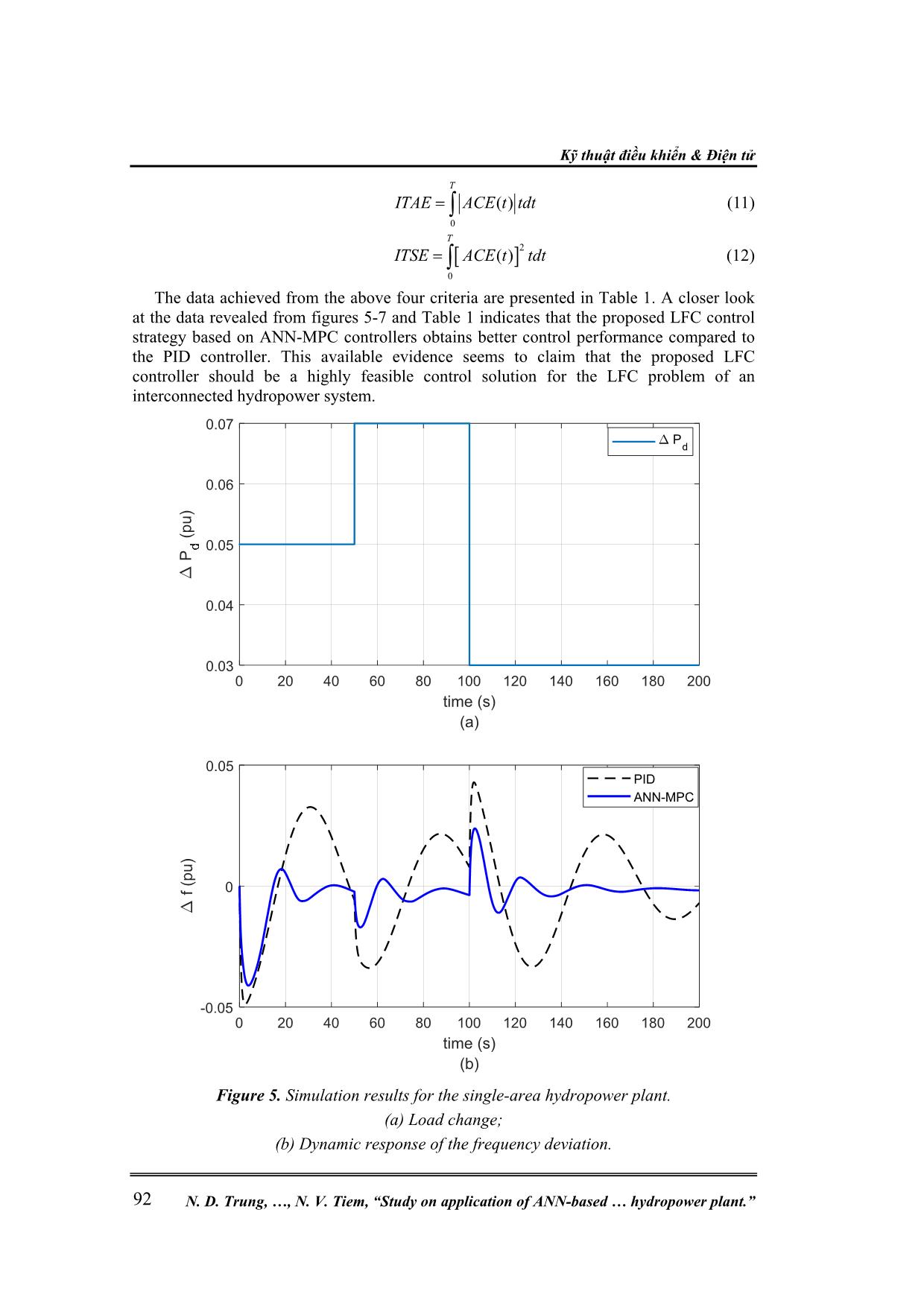
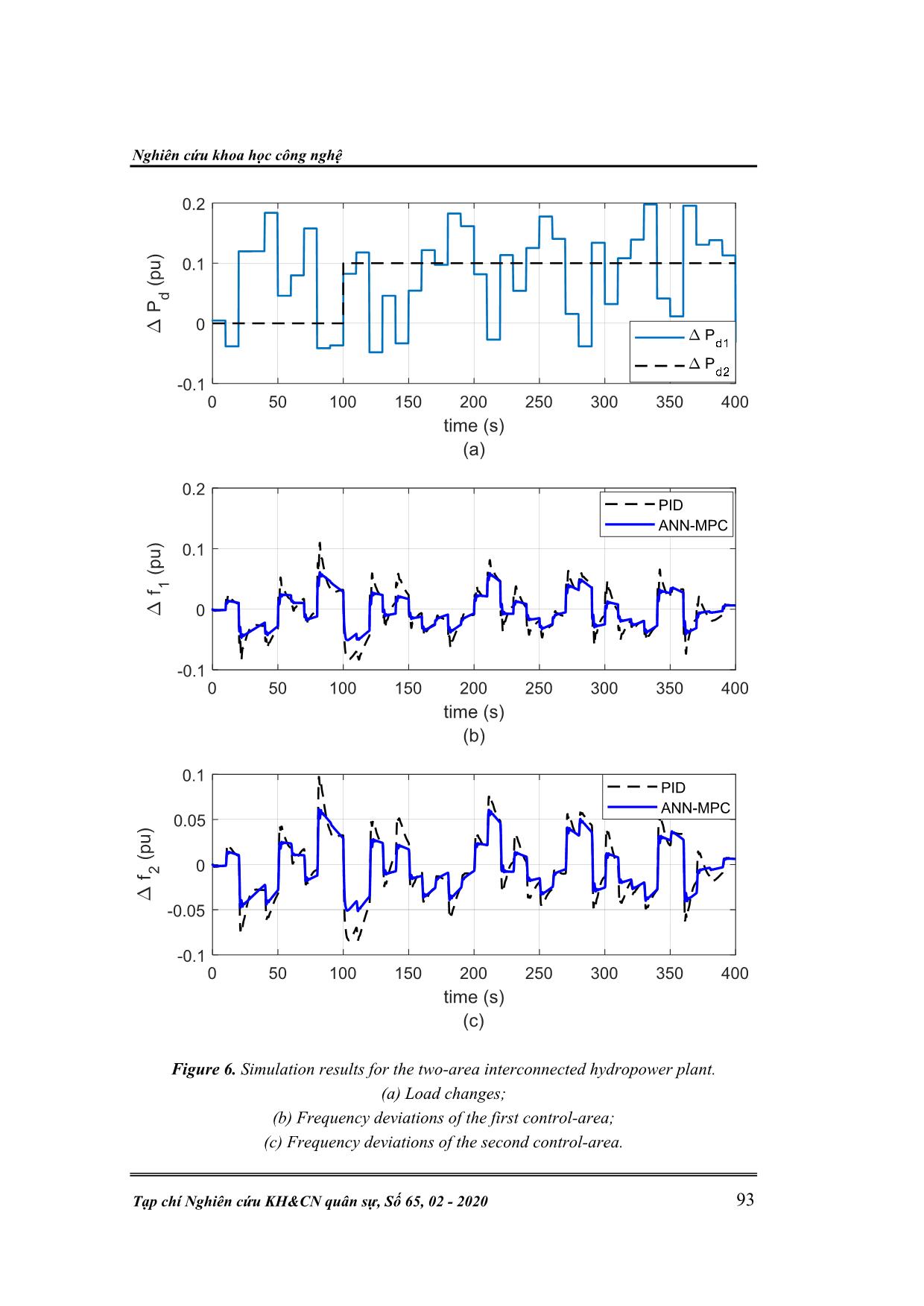
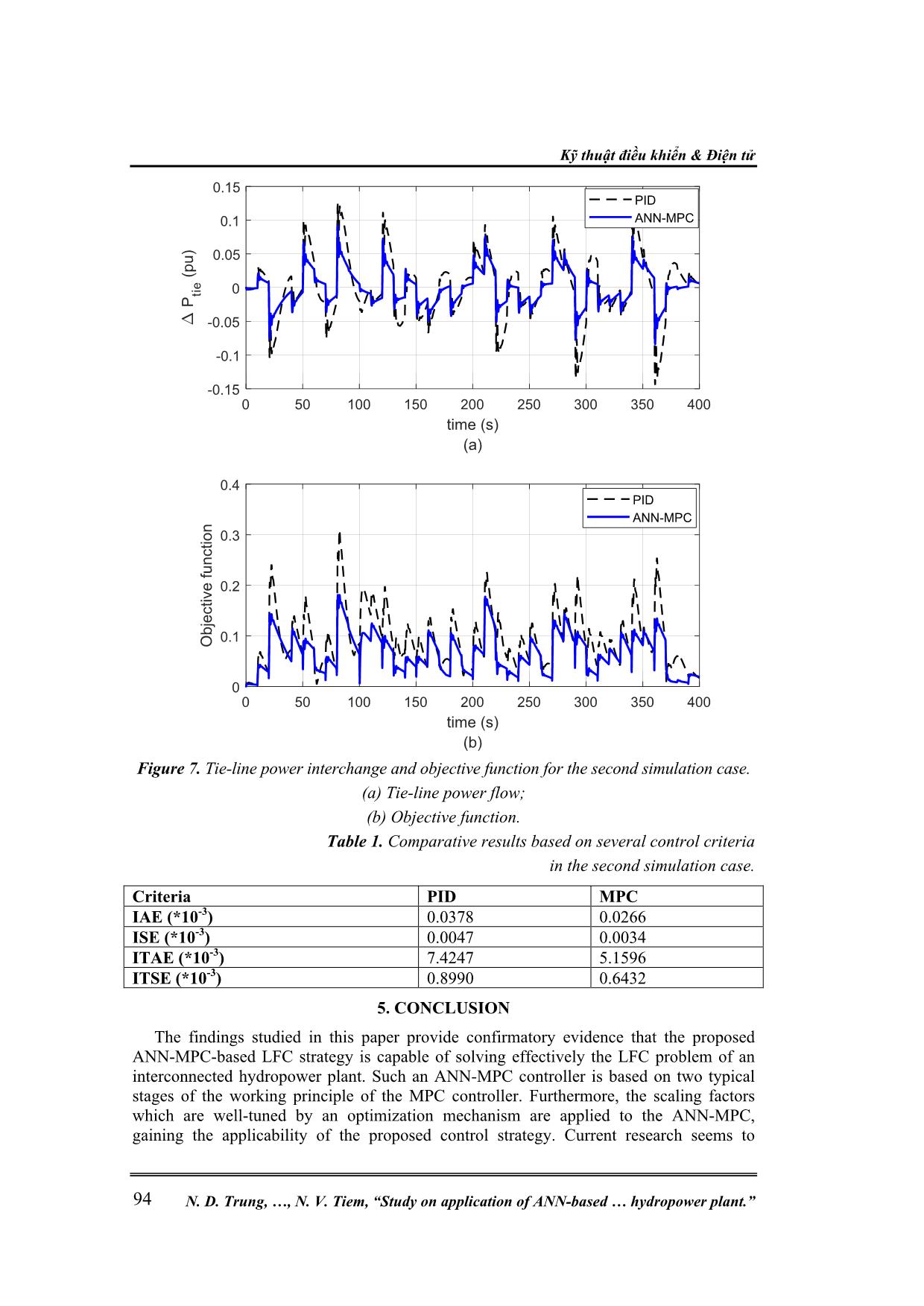
( ), ( ), ( ) T t t tie tiex t f t f t P t P t X t X t P t P t (3) u(t) is the input signal vector, 1 2 ( ) ( ) ( ) u t u t u t (4) D is the load disturbance vector, ,1 ,2 ( ) ( ) d d P t D P t (5) Matrices of A, B, and F are corresponding to the matrices of state, input, and load disturbance. The output vector, y(t), is given as 1 2 ,12( ) ( ), ( ), T tiey t f t f t P (6) and C denotes an identity matrix. The model mentioned above can be used efficiently in control solutions of the LFC. In this paper, both a single-area isolated and multi-area interconnected hydropower system models will be applied to validate the effectiveness of the proposed LFC strategies. 3. ANN – BASED MPC FOR LFC 3.1. An overview of ANN – based MPC In this section, we put forward the claim that artificial neural network (ANN) technique with its fast development recently has motivated researchers to apply for various control problems, including the LFC issue [9-11]. Model predictive control (MPC) is one of the most advanced control strategies which has been in use in the process industries. The application of the MPC in power system has been gained recently. Typically, the MPC, when integrated with the ANN, acts based on two phases: (i) In the first phase, the control plant under consideration should be indentified by training a neural network. It means that such a neural network needs to be trained to represent the dynamics of the control plant. Typically, the neural network uses a training signal which can be calculated from the error between the plant output and the neural network output. It is evident the neural network can be trainned offline in batch mode, Nghiên cứu khoa học công nghệ Tạp chí Nghiên cứu KH&CN quân sự, Số 65, 02 - 2020 89 using the previous inputs and previous plant outputs to predict future values of the plant output. (ii) In the second phase, namely predictive control, the receding horizon technique is used. The working principle is that the predictions of the neural network model are excecuted based upon a specified time horizon. It is found that a candidate of criterion over the specified horizon is taken for a numerical optimization program which should be used for the predictions. Considering the model predictive control process, it is evident the neural network plant model and the optimization block are integrated to form the controller. Governor Hydro turbine Generator ∆Pdi(t) ∆fi(t) ith control - area f g NN model System identification NN model Predictive control Learning algorithm Optimization mechanism , ( )tie iP t ( )if t Reference signal ui(t) 1 2 ANN – based MPC Figure 2. ANN-based MPC model applied to the ith control-area. The next section is to present the working principle of the ANN-based MPC under consideration applied to the LFC of a hydropower system. 3.2. LFC Strategy Applying the ANN-based MPC This paper proposes two scenarios when applying the ANN-based MPC controller mentioned earlier to the LFC problem of a hydropower system. (i) Scenario 1: The ANN-based MPC is applied for a single-area isolated power system as shown in figure 3(a). (ii) Scenario 2: The ANN-based MPC – type LFC controller is applied for a two-area interconnected hydropower system as shown in figure 3(b). In both scenarios, this work proposes an optimization technique to determine an optimal gain for the scaling factor behind the MPC controller. A candidate of objective function of such an optimization technique applied for the ith control-area here is given below: , ,0 ( ) . T i tie ij i i j J f t P dt (7) Using the above objective function, the proposed MPC-based LFC controller is able to obtain good control performance, which will be validated in the following section. Kỹ thuật điều khiển & Điện tử N. D. Trung, , N. V. Tiem, “Study on application of ANN-based hydropower plant.” 90 Governor Hydro turbine Generator ∆PL ∆f SINGLE-AREA ISOLATED HYDROPOWER PLANT ANN – MPC f g k Optimization mechanism Objective function (a) Governor Hydro turbine Generator ∆PL1 Compute ∆Ptie12 Governor Hydro turbine Generator ∆PL2 ACE1(t) ∆f1 ∆f2 CONTROL-AREA 1 CONTROL-AREA 2 ANN – MPC1 f g k1 ACE2(t) ANN – MPC2 f g k2 Optimization mechanism Objective function (b) Figure 3. Control structure of hydropower systems applying the LFC controllers. (a) Single – area isolated hydropower plant; (b) Two-area interconnected hydropower system. 4. NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS TO VERIFY THE PROPOSED CONTROL STRATEGY We put forward the claim that it is necessary to execute simulation processes to validate the applicability of the proposed control strategy in dealing with the LFC problem of a hydropower system. This section considers two simulation cases: (1) First simulation case: Consider a single-area isolated hydropower system with a scenario of load change as shown in figure 5(a). A comparative simulation result between the proposed MPC-based LFC controller and the conventional PID-type LFC is represented in figure 5(b). (2) Second simulation case: Consider a two-area interconnected hydropower network with a scenario of load changes for two areas as shown in figure 6(a). This is a more practical simulation scenario of the load change, especially for the first area. It is apparent the load depending on users randomly and continuously changes in the first area is more suitable in practice. Simulation results for this perspective are represented in figures 6(b,c) and figure 7. It should be noted that the waveform of objective function is also depicted for both the PID and ANN-MPC LFC controllers for the comparative aim. The objective funtion is presented below: 1 2 ,12( ) ( ) ( ) ( )obj tief t f t f t P t (8) To execute the ANN-MPC controller, we need to effectuate the controller configuration Nghiên cứu khoa học công nghệ Tạp chí Nghiên cứu KH&CN quân sự, Số 65, 02 - 2020 91 following two steps as mentioned in Section 3. First, the plant identification must be implemented with parameters indicated in Appendix C. The results of this identification process are shown in figure 4. Next, in the second stage, the controller will be trained. Typical results of the training process for the ANN-based MPC are shown in figure 4. Figure 4. Training process of two ANN-based LFC controllers – typical results. From figures 5-7, it is clear the ANN-based MPC controller obtains much better control performances in comparison with the conventional PID regulator. To make a numerical comparison, let us consider four control cretiria as follows: 0 ( ) T IAE ACE t dt (9) 2 0 ( ) T ISE ACE t dt (10) Kỹ thuật điều khiển & Điện tử N. D. Trung, , N. V. Tiem, “Study on application of ANN-based hydropower plant.” 92 0 ( ) T ITAE ACE t tdt (11) 2 0 ( ) T ITSE ACE t tdt (12) The data achieved from the above four criteria are presented in Table 1. A closer look at the data revealed from figures 5-7 and Table 1 indicates that the proposed LFC control strategy based on ANN-MPC controllers obtains better control performance compared to the PID controller. This available evidence seems to claim that the proposed LFC controller should be a highly feasible control solution for the LFC problem of an interconnected hydropower system. Figure 5. Simulation results for the single-area hydropower plant. (a) Load change; (b) Dynamic response of the frequency deviation. P d PID ANN-MPC Nghiên cứu khoa học công nghệ Tạp chí Nghiên cứu KH&CN quân sự, Số 65, 02 - 2020 93 Figure 6. Simulation results for the two-area interconnected hydropower plant. (a) Load changes; (b) Frequency deviations of the first control-area; (c) Frequency deviations of the second control-area. Kỹ thuật điều khiển & Điện tử N. D. Trung, , N. V. Tiem, “Study on application of ANN-based hydropower plant.” 94 Figure 7. Tie-line power interchange and objective function for the second simulation case. (a) Tie-line power flow; (b) Objective function. Table 1. Comparative results based on several control criteria in the second simulation case. 5. CONCLUSION The findings studied in this paper provide confirmatory evidence that the proposed ANN-MPC-based LFC strategy is capable of solving effectively the LFC problem of an interconnected hydropower plant. Such an ANN-MPC controller is based on two typical stages of the working principle of the MPC controller. Furthermore, the scaling factors which are well-tuned by an optimization mechanism are applied to the ANN-MPC, gaining the applicability of the proposed control strategy. Current research seems to ti e PID ANN-MPC PID ANN-MPC Criteria PID MPC IAE (*10-3) 0.0378 0.0266 ISE (*10-3) 0.0047 0.0034 ITAE (*10-3) 7.4247 5.1596 ITSE (*10-3) 0.8990 0.6432 Nghiên cứu khoa học công nghệ Tạp chí Nghiên cứu KH&CN quân sự, Số 65, 02 - 2020 95 validate the view that the LFC strategies are still to be improved in order to achieve better control performance, especially for looking a feasible LFC solution of a multi-area interconnected power system. Complicated large-scale electric power grids in co-operation with renewable energy sources should be significant control plants inspired by this study. APPENDICES Appendix A Nomenclature fn nominal frequency, fn = 50Hz f real frequency of the network, Hz tieP tie line power flow, p.u. ∆f1,2 (t) frequency deviations of the first and second areas, in time domain, p.u. ∆F1,2 (s) frequency deviations of the first and second areas, in Laplace domain, p.u. 1,2 ( )ACE t Area control error, in time domain 1 2( ), ( )u t u t control signal for the first and the second areas 1,2dP load changes in the first and the second areas, p.u. ,12tieP tie-line power flow deviation, p.u. ,g iT time constant of governor, s ,w iT time constant of hydro turbine unit, s Di load damping factor, p.u. MW/Hz Mi generator inertia constant, p.u. Tij tie-line time constant, sec Bi frequency bias factor, MW/p.u.Hz Ri speed regulation constant, Hz/MW ,g iG transfer function of the governor unit ,t iG transfer function of the hydro turbine unit ,PiG transfer function of the rotor inertia and load (power system) Appendix B Two-area interconnected power system parameters: 1 2 48.7g gT T s ; 1 2 1w wT T s 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 120.513; 0.6; 1; 2.4; 0.0707;r rT T M M D D R R T Two simulation cases: Case 1: load change appears with three magnitutes of 0.05pu, 0.07pu and 0.03pu at three respective step times of 0s, 50s and 100s. Case 2: ∆PD1 is a uniform random number function generates uniformly distributed random numbers over an interval of [-0.05; 0.2] and a sample time of 10s. Kỹ thuật điều khiển & Điện tử N. D. Trung, , N. V. Tiem, “Study on application of ANN-based hydropower plant.” 96 ∆PD2 is a step function with a step time of 100s and the final value of 0.1pu. Appendix C Parameters to execute the ANN-based MPC are shown below: REFERENCES [1]. Kundur P. “Power system stability and control”. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill, 1994. [2]. Shashi KP, Soumya RM, Nand K. “A literature survey on load-frequency control for conventional and distribution generation power systems”. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2013; 25: 318-334. [3]. R. C. Dorf and R. H. Bishop, “Modern Control Systems”, Pearson Prentice Hall, 2008. [4]. R. Verma, S. Pal and S. Sathans, “Intelligent Automatic Generation Control of Two- Area Hydrothermal Power System Using ANN and Fuzzy Logic,” In: 2013 International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), pp. 552-556, 6-8 April 2013. Nghiên cứu khoa học công nghệ Tạp chí Nghiên cứu KH&CN quân sự, Số 65, 02 - 2020 97 [5]. Hykin S. “Neural network”. USA: Mac Miller, 1994. [6]. Mohammad T. and Keigo W. “Intelligent Control Based on Flexible Neural Networks”. Springer, 1999. [7]. Norgaard M., Poulsen N. K., Hansen L. K., Ravn O. “Neural Networks for Modelling and Control of Dynamic Systems”. Springer, 2003. [8]. Ławryńczuk M. “Neural Networks in Model Predictive Control”. In: Nguyen N.T., Szczerbicki E. (eds) Intelligent Systems for Knowledge Management. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 252. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009. [9]. Han, Hong-Gui & Zhang, Lu & Hou, Ying & Qiao, Jun-Fei. “Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Based on a Self-Organizing Recurrent Neural Network”. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, 2015. 27. 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2465174. [10]. Steven S. P. K., Aditya T., Bhushan G., Philip L. “A Deep Learning Architecture for Predictive Control”. IFAC PapersOnline 51-18, 2018, pp. 512 – 517. [11]. James B. R., David Q. M. and Moritz M. D. “Model Predictive Control: Theory, Computation and Design”, 2nd Edition, Nob Hill Publishing, LLC, 2019. TÓM TẮT NGHIÊN CỨU ỨNG DỤNG ĐIỀU KHIỂN DỰ BÁO DỰA TRÊN TRÍ TUỆ NHÂN TẠO CHO BÀI TOÁN ĐIỀU KHIỂN TẦN SỐ - PHỤ TẢI NHÀ MÁY THỦY ĐIỆN ĐA KẾT NỐI Trong thị trường điện Việt Nam hiện nay, thủy điện vẫn chiếm một tỷ trọng lớn (khoảng 38%). Do đó, việc nghiên cứu các vấn đề điều khiển trong nhà máy thủy điện có ý nghĩa vô cùng lớn. Chiến lược điều khiển tần số-phụ tải là một trong số những bài toán điều khiển đặc biệt quan tâm. Mục tiêu chính của bài toán điều khiển này khi phụ tải lưới điện thay đổi liên tục và ngẫu nhiên là kiểm soát tần số lưới điện xung quanh giá trị danh định (ở Việt Nam là 50Hz) và công suất thực trao đổi trên đường dây cân bằng với công suất đã lên lịch trình trước. Việc này đảm bảo sự ổn định của hệ thống các nhà máy thủy điện đa kết nối nói riêng và hệ thống điện quốc gia nói chung. Bài báo này đề xuất một giải pháp điều khiển dự báo dựa trên mạng trí tuệ nhân tạo cho bài toán điều khiển tần số - phụ tải của nhà máy thủy điện. Chiến lược điều khiển này kết hợp với các hệ số chỉnh định có được từ một thuật toán tối ưu đã trở thành một giải pháp khả thi cho bài toán điều khiển tần số - phụ tải. Cùng với các kết quả mô phỏng số đã đạt được trong nghiên cứu này, ta có thể khẳng định tính khả thi của việc ứng dụng giải pháp điều khiển dự báo dựa trên mạng trí tuệ nhân tạo đã đề xuất cho bài điều khiển tần số - phụ tải của một hệ thống thủy điện đa kết nối. Từ khóa: ANN; MPC; LFC; Hệ thống thủy điện đa kết nối; Thay đổi phụ tải; Độ lệch tần số lưới; Công suất trao đổi. Received date, 10th December, 2019 Revised manuscript, 10th January, 2020 Published, 12th February, 2020 Author affiliations: 1 Electric Power University; 2 National Center for Technological Progress; 3 University of Transport and Communications. *Corresponding author: trungnd@epu.edu.vn.
File đính kèm:
 study_on_application_of_ann_based_mpc_controllers_for_load_f.pdf
study_on_application_of_ann_based_mpc_controllers_for_load_f.pdf

