Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành điện tử
What is engineering?
Engineering is a scientific field and job that involves taking out scientific
understanding of the natural world and using it to invent, design and building things
to solve problems and achieve practical goals.
Engineering is the application of science and math to solve problems. Engineers
figure out how things work and find practical uses for scientific discoveries.
Scientists and inventors often get the credit for innovations that advance the human
condition, but it is engineers who are instrumental in making those innovations
available to the world.
New vocabulary:
Engineer(n) (N) Kỹ sư Achieve (v) Thực hiện
Engineering (n) Kỹ thuật Discoveries (v) Khám phá
Scientist(n) Nhà khoa học Instrumental(adj) Góp phần vào
Inventor(n) Người phát minh Involve Liên quan

Trang 1
Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
Trang 9
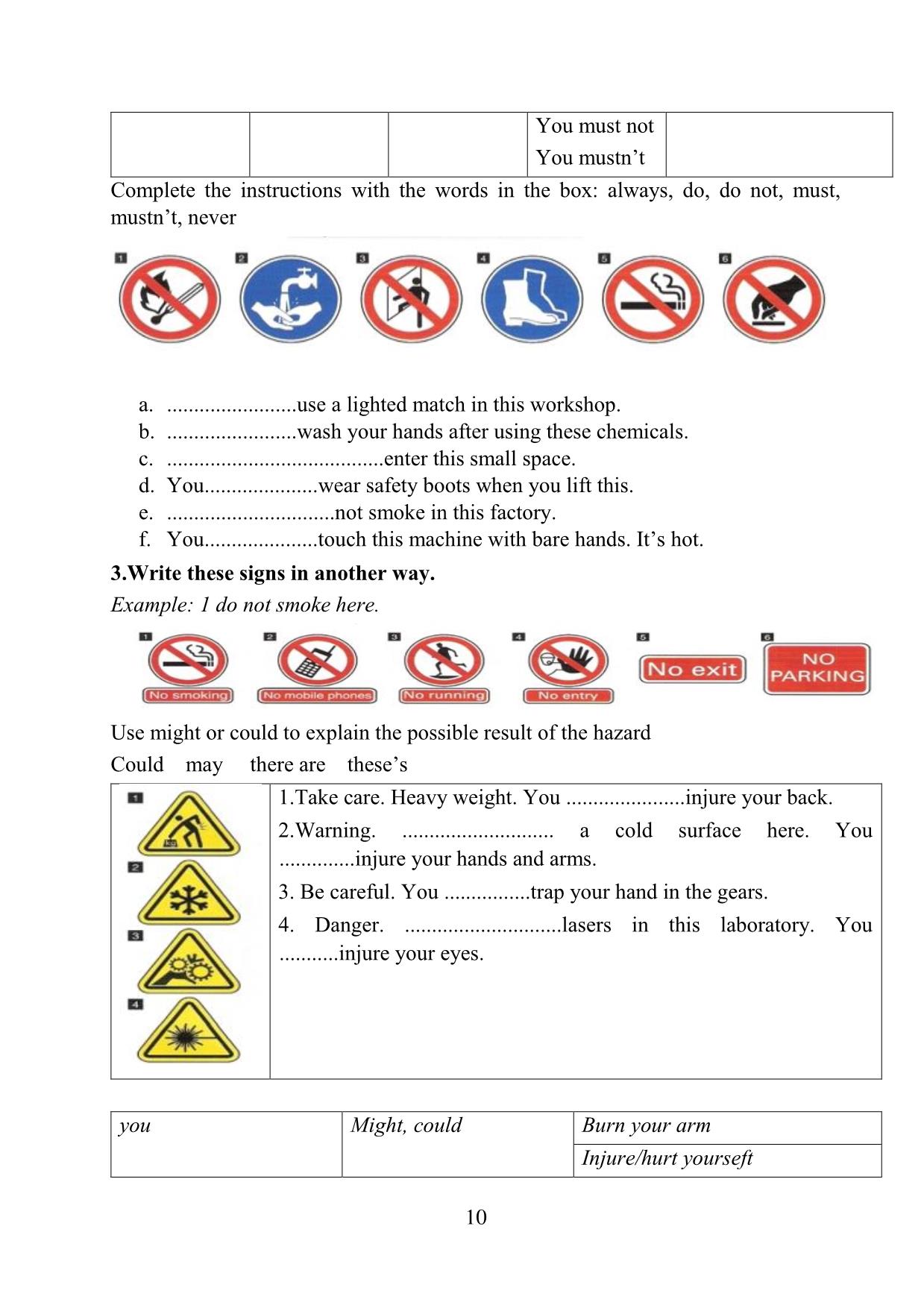
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Giáo trình Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành điện tử

rushes to rub against the commutator. The rubbing creates friction, and the higher the speed, the harder the brushes have to press to maintain good contact. Not only does this friction make the motor noisy, but it also creates an upper limit on the speed and causes the brushes eventually to wear out and to require replacement. The imperfect electric contact also causes electrical noise in the attached circuit. These problems vanish when you turn the motor inside out, putting the permanent magnets on the inside and the coils on the outside thus designing out the need for brushes in a brushless design. However such designs need electronic circuits to control the switching of the electromagnets (the function that is performed in conventional motors by the commutator). .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................................... Wound field DC motor The permanent magnets on the outside (stator) of a DC motor may be replaced by electromagnets. By varying the field current it is possible to alter the speed/torque ratio of the motor. Typically the field winding will be placed in series (series wound) with the armature winding to get a high torque low speed motor, in parallel (shunt wound) with the armature to get a high speed low torque motor, or to have a winding partly in parallel, and partly in series (compound wound) to get the best of both worlds. Further reductions in field current are possible to gain even higher speed but correspondingly lower torque. This technique is ideal for electric traction and many similar applications where its use can eliminate the requirement for a mechanically variable transmission 81 Unit 9 THE MOVING COIL I. Reading and comprehension: 1.Construction and component The essential component of a moving coil meter are a permanent magnet and a moving coil. The magnet is U-shaped or semi-circular and is made of a material such as Alcomax. Each pole terminates in a soft-iron pole piece shaped and positioned as in figure 5.1. Figure 5.1 The moving coil, which gives the instrument its name, is composed of fine copper wire wound on a thin rectangular aluminum former. The former is mounted centrally on hard steel spindles and can rotate around a fixed cylindrical soft-iron core. The core is placed between the pole pieces in such a manner that an annular gap is formed between it and the pole pieces. A pointer is attached to the former and traverses a linear scale. The spindles which bear the moving coil are mounted on jeweled bearing two spiral hair springs are attached to the spindles. They are wound in apposition and are adjusted so that they balance when the pointer is at the zero mark. 82 .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................................... 2.Operation This instrument operates on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, a force is exerted on the conductor which causes it to move. When the meter is inserted in a live circuit, current flows through the control springs into the coil. This sets up a magnetic field around the coil which reacts with the radial magnetic field of the permanent magnet. The reaction produces a torque which tends to rotate the coil. Since the strength of the permanent magnet’s field is uniform, this torque is directly proportional to the current flowing in the coil. As the coil rotates, the control springs tighten thus opposing the motion of the coil. When the deflecting force of the coil is balanced by the controlling force of the springs, the coil comes to rest. The extent of the coil’s movement, and hence the size of the current flowing through the coil, is indicated on the scale by the pointer. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................................... Exercise 1: Describing position Say where the following components are located. Use the expressions you learnt in Unit 1. 1. the pole pieces. 2. the core. 3. the pointer 4. the former. 83 5. the springs. Exercise 2: Describing functions This table describes the function of the component of the meter. The functions are in the wrong order. Write a sentence to describe the function of each component using the methods you learnt in unit 2. note that the springs have two functions. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................................... Now add part 1 of the reading passage a description of the function of these component. Begin like: The function of the moving coil meter is to detect the presence of a direct current. Its essential components Component Function 1. core 2. former 3. spring 4. bearings 5. magnet To provide controlling torque. To reduce friction and wear. To produce a powerful uniform magnetic field. To carry the coil. To serve as leads to carry current to the coil. To produce radial filed lines within the gap. Exercise 3: phrasing Rewrite the following sentences rephrasing the words in italics with expressions from the passage which have similar meaning: 1. The meter is inserted in a circuit with a current flowing through it. 2. The coil is rotated by turning force. 3. The strength of the permanent magnet’s field is always the same. 84 4. The turning force varies directly with the current flowing through the coil. 5. The force which rotates the coil is balanced by the force which restrains the coil II. Use of language: 1. Cause and effects 1 Study this sentence Insulation breakdown leads to short circuit. This sentence contains a cause and effect. We can link a cause and an effect as follow Insulation causes short circuit Breakdown results in Produces Leads to Gives rise to Is the cause of We can also put the effect first Short circuits are caused by insulation breakdown Result from Arise from Are the effect of Are the result of Are the consequence of Are due to cause effect effect cause 85 When a cause has several effects or when an effect has a number of possible causes, we put can or may before the causative expression. Example: Sparking MAY be cause by worn brushes Or: sparking CAN be caused by a worn commutator. Similarly, instead of the cause/effect/result/consequence of, we write one cause/effect/result/consequence of. Example: Worn brushes are ONE cause of sparking A worn commutator is ONE cause of sparking. Now match these cause and effect pairs. Then link them using the expressions given above. Write two sentences for each example, one with the cause first and the other with the effect first. CAUSE EFFECT 1. glare arching across the points 2. eddy currents power losses in transformers 3. excessive heat serious accidents 4. faulty soldering breakdown of the motor 5. sparking discomfort to the eyes 6. failure of a point capacitor damage to semiconductor 7. exceeding the motor rating bad joints 8. faulty earth connections interference in receivers 2. Cause and effect chains Describe this cause and effect chain. Use different expressions for each link Overrunning Excessive Insulation Short Blown a motor heat breakdown circuit fuses Now rewrite your description starting at the end of the chain and working backwards. 86 3. Describing the reception of a signal Put these events, which describe the progress of a signal through a receiver, in sequence with the help of the diagram. Then link the sentences in pairs using time clauses with before and after. a. the signal is again amplified. b. The desired signal is fed to the acceptor circuit. c. The signal is amplified d. The signal is fed to a loudspeaker e. The signal is mixed with a signal from the oscillator to give a standard intermediate frequency f. The signal is rectified by the detector. 3. Short relative clause Study these sentences: 1. A telephone dial consists of small keys 2. those keys has many characters and numbers We can link them using a relative clause: 1+2. A telephone dial consists of small keys having many characters and numbers. A telephone dial consists of small keys WITH many characters and numbers. Sometimes we can reduce a relative clause to an adjective Example: 3. high quality instrument use resistors. 4. the resistors are wire wound. 3+4. high quality instruments use resistors WHICH ARE WIREWOUND high quality instruments use WIREWOUND resistors. Make this paragraph shorter by reducing the relative clauses. Use all the methods of reduction you have learned in this unit. oscillator mixer r Acceptorr Intermediate e detector o r Audio a 87 The telephone is an instrument which enables us to transmit speech via wire (wireless ness). The body of the telephone contains an induction coil, capacitors, resistors, a regulator, which controls the sensitivity of the instrument, and a bell. The handset contains a microphone and a receiver which are enclosed by screwed caps at the ends of the handset. The bell contains a hammer which is operated by a solenoid. The hammer is set between two domes which is eccentrically mounted. The dial is mounted on the face of the telephone. It consists of small keys which have characters and numbers. When those keys are pressed in, it causes spring contacts to open and close a number of times which respond to the number dialed. This transmits pulses down the line causing selectors, which connect the calling line to the line which is called, to operate. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. ............................................................... III. Further- reading: Oscillator The Basics One of the most commonly used oscillators is the pendulum of a clock. If you push on a pendulum to start it swinging, it will oscillate at some frequency -- it will swing back and forth a certain number of times per second. The length of the pendulum is the main thing that controls the frequency. 88 ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................... For something to oscillate, energy needs to move back and forth between two forms. For example, in a pendulum, energy moves between potential energy and kinetic energy. When the pendulum is at one end of its travel, its energy is all potential energy and it is ready to fall. When the pendulum is in the middle of its cycle, all of its potential energy turns into kinetic energy and the pendulum is moving as fast as it can. As the pendulum moves toward the other end of its swing, all the kinetic energy turns back into potential energy. This movement of energy between the two forms is what causes the oscillation. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................... Eventually, any physical oscillator stops moving because of friction. To keep it going, you have to add a little bit of energy on each cycle. In a pendulum clock, the energy that keeps the pendulum moving comes from the spring. The pendulum gets a little push on each stroke to make up for the energy it loses to friction. An electronic oscillator works on the same principle. 89 90 Symbols : general warnings and safety symbols: Danger/ warning/caution/hazard. Specific hazards Flammable Toxic/ poison High voltage Safety equipment or help 91 Emergency exit/fire exit Fire alarm Fire extinguisher Hospital First aid Emergency stop Prohibitons No entry No exit No smoking TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO 1. David Bonamy- Christopher Jacques-Technical English – Students’ book. 2. Eric H.Glendinning John McEwan-Oxford English for Electronics. 3. Giáo trình tiếng anh chuyên ngành điện- Đại Học Hưng Yên. 4. Google – data sheet- internet.
File đính kèm:
 giao_trinh_tieng_anh_chuyen_nganh_dien_tu.pdf
giao_trinh_tieng_anh_chuyen_nganh_dien_tu.pdf

