Detecting web attacks based on clustering algorithm and multi- branch CNN
Bài báo đề xuất và phát triển mô hình
phát hiện tấn công Web dựa trên kết hợp thuật
toán phân cụm và mạng nơ-ron tích chập (CNN)
đa nhánh. Tập đặc trưng ban đầu được phân cụm
thành các nhóm đặc trưng tương ứng. Mỗi nhóm
đặc trưng được khái quát hóa trong một nhánh
của mạng CNN đa nhánh để tạo thành một vector
đặc trưng thành phần. Các vector đặc trưng thành
phần được ghép lại thành một vector đặc trưng
tổng hợp và đưa vào lớp liên kết đầy đủ để phân
lớp. Sử dụng phương pháp kiểm thử chéo trên mô
hình đề xuất, độ chính xác đạt 98,8%, F1-score đạt
98,8% và tỉ lệ cải tiến độ chính xác là 1,479%.

Trang 1

Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Detecting web attacks based on clustering algorithm and multi- branch CNN", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Detecting web attacks based on clustering algorithm and multi- branch CNN

tion for
94.13% accuracy. Random Forest algorithm with
meaningful research results and good
only NLP-based features gives the best
performance [12], [13].
performance with the 97.98% accuracy rate for
detection of phishing URLs [1]. In [2], the In 2017, multi-branch CNN was proposed by
authors use most of machine learning algorithms Amerini et al to detect double JPEG image
to experiment with phishing detection using compression. It is then further developed in the
hyperlink information and the results show that direction of proposing another feature set for
Logistic Regression algorithm has the highest relatively high accuracy (average between 95% -
accuracy (98.42%). In SQL Injection attack 99%) [14]. In 2019, the research groups
detection, the authors used Naïve Bayes continued to propose branching CNN
algorithm reached 93.3% [3]. In DoS, DDoS architecture for multiple sclerosis lesion
attack detection, the authors [4] uses an SVM segmentation [15], or for myocardial infarction
algorithm based on web log traces. screening from ECG images [16]. Therefore, it is
used effectively in medicine. There are very few
Deep learning is known as a subset of
research results that use this architecture for the
machine learning, with outstanding performance
web attack detection problem [5].
in classification problems. Common deep
learning models have also been used to detect Based on the above survey results, this paper
several types of web attacks with great proposes new methods to Web attack detection
efficiency. Feng et al. (2018) proposed a novel based on the combination of K-means clustering
neural network based on a classification method algorithm and Multi-branch CNN. Our method
for detection of phishing web pages using a will be developed, experimented and evaluated
Monte Carlo algorithm and risk minimization in the following sections.
principle. The CNN model [5] is used to detect
website anomalies based on HTTP requests. The III. IDEA AND THE MATHEMATICAL MODEL
Stacked Auto Encoder (SAE) model [6] is
applied for anomaly detection in web application A. Basic idea
firewall. Some other results such as: DoS attack The key idea of our paper is to use clustering
detection based on Restricted Boltzmann algorithms to split an original feature set into the
Machine [7], detection of code injection attacks
subsets corresponding to clusters; and put them
on hybrid applications using Hybrid Deep
Learning Network (HDLN) between CNN and to branches of a CNN to classify. Each cluster is
LSTM achieves accuracy of over 97.5% [8], etc. put into a branch to generalize features to create
a component feature vector. The component
In addition, there are some studies using a
feature vectors are joined to generate a synthetic
combination of machine learning/deep learning
algorithms to classify attacks on websites with feature vector. This vector is put into a fully
quite good results. An example would be connected layer of CNN to classify. Because the
combining the neural network approach with features in a cluster have the closest metrics, it is
reinforcement learning for phishing attack more efficient to build the component feature
classification (Smadi, Aslam, and Zhang - 2018). vector for each cluster.
32 No 2.CS (12) 2020
Khoa học và Công nghệ trong lĩnh vực An toàn thông tin
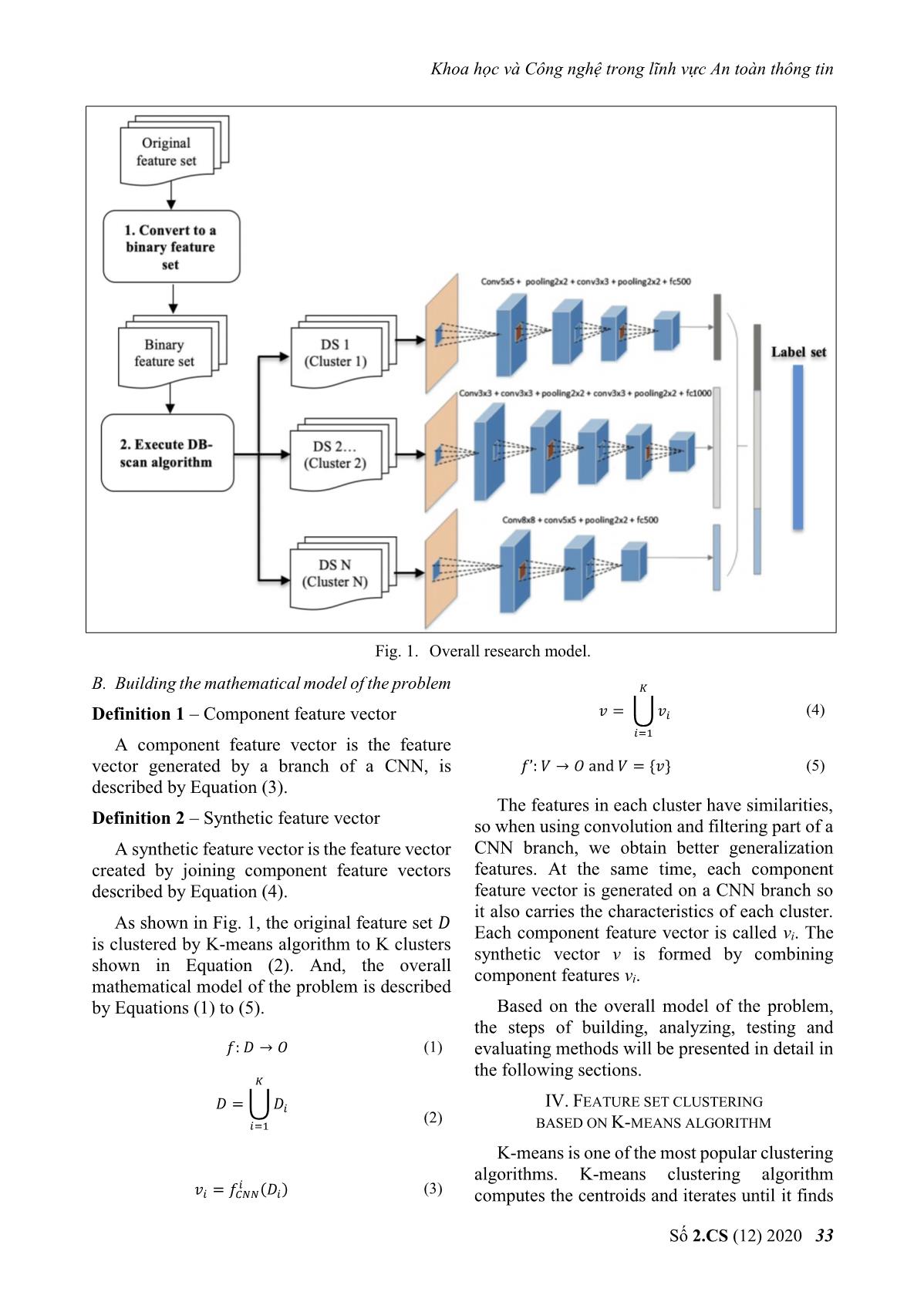
Fig. 1. Overall research model.
B. Building the mathematical model of the problem 퐾
Definition 1 – Component feature vector 푣 = ⋃ 푣푖 (4)
푖=1
A component feature vector is the feature
vector generated by a branch of a CNN, is ’: → and = {푣} (5)
described by Equation (3).
The features in each cluster have similarities,
Definition 2 – Synthetic feature vector so when using convolution and filtering part of a
A synthetic feature vector is the feature vector CNN branch, we obtain better generalization
created by joining component feature vectors features. At the same time, each component
described by Equation (4). feature vector is generated on a CNN branch so
it also carries the characteristics of each cluster.
As shown in Fig. 1, the original feature set
Each component feature vector is called v . The
is clustered by K-means algorithm to K clusters i
synthetic vector v is formed by combining
shown in Equation (2). And, the overall
component features v .
mathematical model of the problem is described i
by Equations (1) to (5). Based on the overall model of the problem,
the steps of building, analyzing, testing and
: → (1) evaluating methods will be presented in detail in
the following sections.
퐾
= ⋃ 푖 IV. FEATURE SET CLUSTERING
(2)
푖=1 BASED ON K-MEANS ALGORITHM
K-means is one of the most popular clustering
algorithms. K-means clustering algorithm
푖 (3)
푣푖 = ( 푖) computes the centroids and iterates until it finds
Số 2.CS (12) 2020 33
Journal of Science and Technology on Information security
optimal centroid. It assumes that the number of V. EVALUATING THE METHOD
clusters is already known. In this paper, we use
In order to evaluate the proposed method, we
K-means algorithm to cluster the original feature
used a K-fold cross-validation method and
set to K subsets of features. K-means algorithm
measures such as Accuracy, Precision, Recall
is described as follows.
and F1-score. These measurements are
K-means algorithm: calculated using Equation (9), (10) and (11).
Input: 푃
푃 푒 푖푠푖표푛 = (9)
A set of features. 푃 + 퐹푃
Number of clusters 퐾. 푃
푅푒 푙푙 = (10)
Output: 퐾 subsets of features 푃 + 퐹
2 ∗ 푃 푒 푖푠푖표푛 ∗ 푅푒 푙푙
Algorithm: 퐹 − 푆 표 푒 = (11)
1 푃 푒 푖푠푖표푛 + 푅푒 푙푙
1 Initialize cluster centroids randomly
where,
(6) TP is the true number of classified
patterns of attack state.
2 Put each point into the cluster which has
FP is the false number of classified
the nearest centroid patterns of attack state.
(7) TN is the true number of classified
patterns of normal state.
Stop if clusters do not change from the
FN is the false number of classified
previous step patterns of normal state.
3 Update centroids VI. EXPERIMENT
A. Experimental model
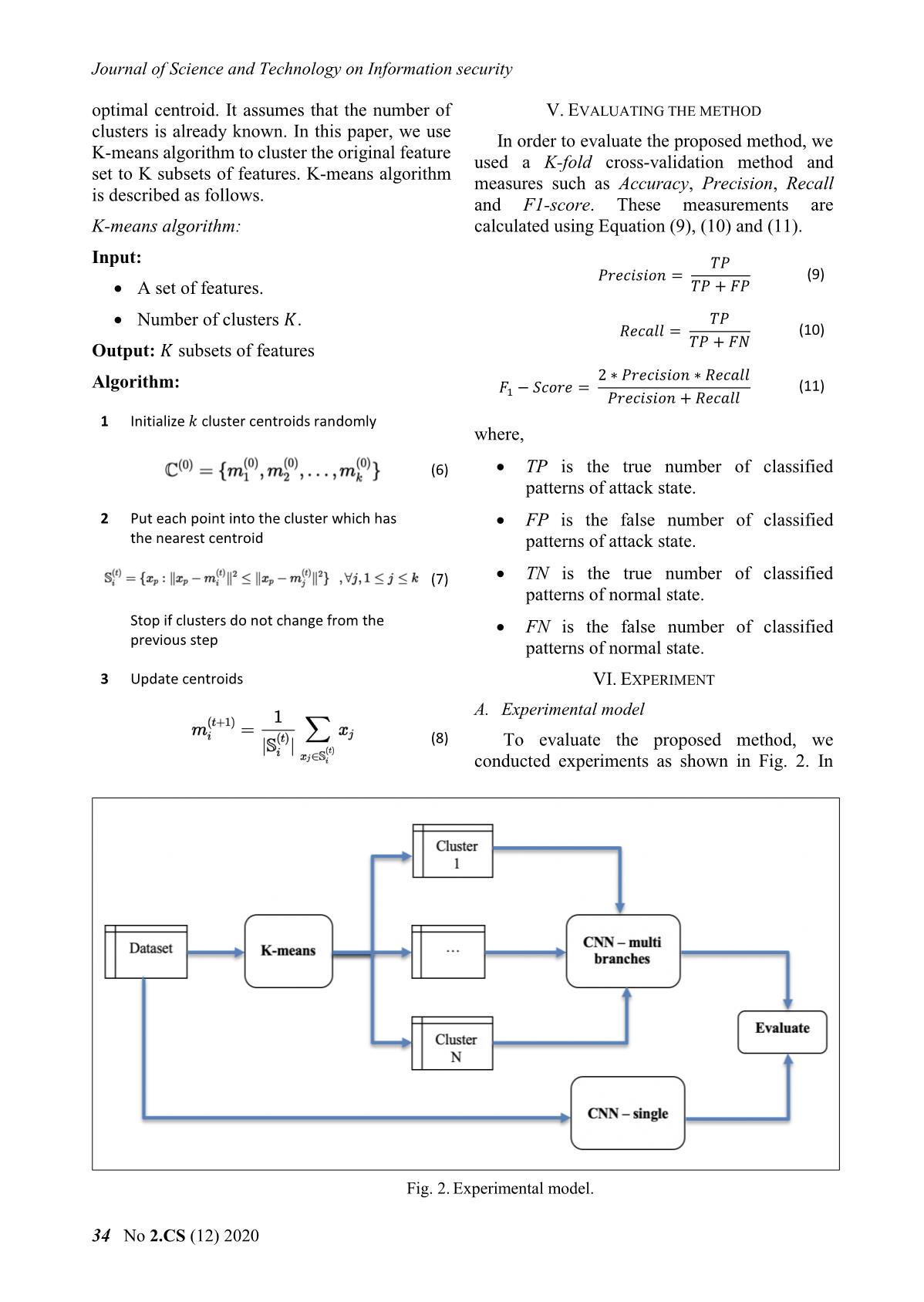
(8) To evaluate the proposed method, we
conducted experiments as shown in Fig. 2. In
Fig. 2. Experimental model.
34 No 2.CS (12) 2020
Khoa học và Công nghệ trong lĩnh vực An toàn thông tin
experiments, an original feature set is clustered binary feature set as shown in Fig. 5. and Fig. 6.
into three clusters; the original feature set is Fig. 5 shows a part of the query string, used as a
passed through a one-branch CNN and each raw feature, having Xpath and XSS labels. Fig. 6
cluster is passed through a branch of a multi- shows some binary features converted by
branch CNN. raw features.
B. Experimental program and data
In this experiment, we installed the web attack
detection program according to CNN in Python
language, using the TensorFlow library. The two
CNN network structures installed in the program
consist of a one-branch CNN and a multi-branch
CNN, described in Fig. 4 and Fig. 3. The multi-
branches have three branches corresponding to
the three clusters, with 585, 835 and 223
elements. To do our experiment, we use the
dataset in [17].
Fig. 5. A part of query string in the original feature set.
Fig. 6. A part of CNN feature set.
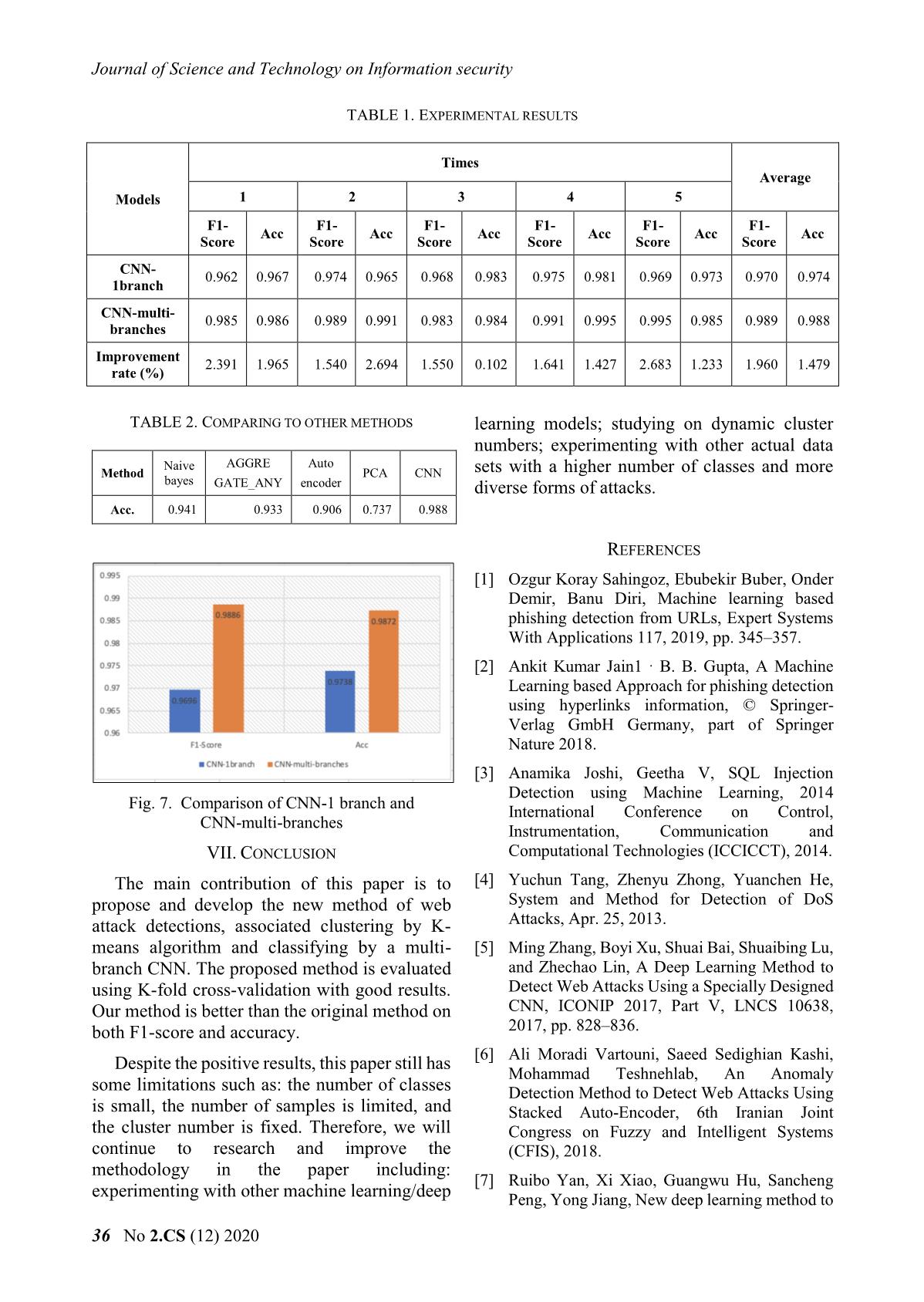
D. Experimental results and evaluation
The accuracy and relevant measurements
when experimenting on the three data sets with
CNN model by the cross-testing method are
Fig. 3. Experimental Structure of
summarized in Table 1. The average
CNN-multi-branches.
improvement rate is 1.479%. Comparing the
improvement level of the proposed method when
experimenting on 3 clusters, it is summarized in
chart form as Fig. 7.
As shown in Table 2, compared with some
machine learning models in the study [18],
including SVM, PCA, etc., the proposed model
has higher accuracy. At the same time, the use of
Fig. 4. Experimental structure of a CNN-1branch. the K-means algorithm to group the features also
improves the accuracy. This is because after
C. Feature conversion clustering, we obtain groups of similar features,
In order to create binary matrices inputted to so the generalization of features in the
a CNN, we convert the original feature set to a convolution layers is more efficient.
Số 2.CS (12) 2020 35
Journal of Science and Technology on Information security
TABLE 1. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Times
Average
Models 1 2 3 4 5
F1- F1- F1- F1- F1- F1-
Acc Acc Acc Acc Acc Acc
Score Score Score Score Score Score
CNN-
0.962 0.967 0.974 0.965 0.968 0.983 0.975 0.981 0.969 0.973 0.970 0.974
1branch
CNN-multi-
0.985 0.986 0.989 0.991 0.983 0.984 0.991 0.995 0.995 0.985 0.989 0.988
branches
Improvement
2.391 1.965 1.540 2.694 1.550 0.102 1.641 1.427 2.683 1.233 1.960 1.479
rate (%)
TABLE 2. COMPARING TO OTHER METHODS learning models; studying on dynamic cluster
numbers; experimenting with other actual data
Naive AGGRE Auto
Method PCA CNN sets with a higher number of classes and more
bayes GATE_ANY encoder diverse forms of attacks.
Acc. 0.941 0.933 0.906 0.737 0.988
REFERENCES
[1] Ozgur Koray Sahingoz, Ebubekir Buber, Onder
Demir, Banu Diri, Machine learning based
phishing detection from URLs, Expert Systems
With Applications 117, 2019, pp. 345–357.
[2] Ankit Kumar Jain1 · B. B. Gupta, A Machine
Learning based Approach for phishing detection
using hyperlinks information, © Springer-
Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer
Nature 2018.
[3] Anamika Joshi, Geetha V, SQL Injection
Detection using Machine Learning, 2014
Fig. 7. Comparison of CNN-1 branch and
International Conference on Control,
CNN-multi-branches
Instrumentation, Communication and
VII. CONCLUSION Computational Technologies (ICCICCT), 2014.
The main contribution of this paper is to [4] Yuchun Tang, Zhenyu Zhong, Yuanchen He,
propose and develop the new method of web System and Method for Detection of DoS
attack detections, associated clustering by K- Attacks, Apr. 25, 2013.
means algorithm and classifying by a multi- [5] Ming Zhang, Boyi Xu, Shuai Bai, Shuaibing Lu,
branch CNN. The proposed method is evaluated and Zhechao Lin, A Deep Learning Method to
using K-fold cross-validation with good results. Detect Web Attacks Using a Specially Designed
Our method is better than the original method on CNN, ICONIP 2017, Part V, LNCS 10638,
both F1-score and accuracy. 2017, pp. 828–836.
Despite the positive results, this paper still has [6] Ali Moradi Vartouni, Saeed Sedighian Kashi,
Mohammad Teshnehlab, An Anomaly
some limitations such as: the number of classes Detection Method to Detect Web Attacks Using
is small, the number of samples is limited, and Stacked Auto-Encoder, 6th Iranian Joint
the cluster number is fixed. Therefore, we will Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Systems
continue to research and improve the (CFIS), 2018.
methodology in the paper including:
[7] Ruibo Yan, Xi Xiao, Guangwu Hu, Sancheng
experimenting with other machine learning/deep Peng, Yong Jiang, New deep learning method to
36 No 2.CS (12) 2020
Khoa học và Công nghệ trong lĩnh vực An toàn thông tin
detect code injection attacks on hybrid [17] Web attack detection dataset:
applications, The Journal of Systems and https://github.com/DuckDuckBug/cnn_waf
Software 137, 2018, pp. 67–77.
[18] Pan Yao, Sun Fangzhou, Teng Zhongwei, White
[8] Yadigar Imamverdiyev, Fargana Abdullayeva, Jules, Schmidt Douglas, Staples Jacob and
Deep Learning Method for Denial of Service Krause Lee, Detecting web attacks with end-to-
Attack Detection Based on Restricted end deep learning. Journal of Internet Services
Boltzmann Machine, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., and Applications, 2019.
Big Data, Volume 6 Number 2, 2018.
[9] Coenen, F., Goulbourne, G. and Leng, P., Tree
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Structures for Mining association Rules, Journal
of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Vol Pham Van Huong
8, No 1, 2003, pp. 25-51. Workplace: Academy of
[10] Asantha Thilina, Shakthi Attanayake, Sacith Cryptography Techniques
Samarakoon, Dahami Nawodya, Lakmal Email: huongpv@actvn.edu.vn
Rupasinghe, Nadith Pathirage, Tharindu Education: Received Bachelor's
Edirisinghe, Kesavan Krishnadeva, Intruder degree in 2005, Master's degree in
Detection Using Deep Learning and Association 2008 and PhD in 2015 in Information
Rule Mining, IEEE International Conference on Technology from University of Engineering and
Computer and Information Technology, 2016. Technology, VNU.
[11] Martin Ester, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Jörg Sander, Recent research direction: IoT, AIoT, embedded
software optimization and big data, deep learning for
and Xiaowei Xu, A density-based algorithm for
information security.
discovering clusters in large spatial databases
with noise, In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM
International Conference on Knowledge Le Thi Hong Van
Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), 1996, pp. Workplace: Academy of
226–231. Cryptography Techniques
[12] Junhao Gan, Yufei Tao, DBSCAN revisited: Email: lthvan@actvn.edu.vn
Mis-Claim, Un-fixability and Approximation, Education: Received Engineer's
SIGMODE 2015. degree in 2009 and Master's degree in
2013 in Information Security from
[13] Erich Schubert, Jorg Sander, Martin Ester, Hans- Academy of Cryptography Techniques.
Peter Kriegel, Xiaowei Xu, DBSCAN Revisited,
Recent research direction: information security,
Revisited: Why and How You Should (Still) Use
cryptography, IoT and application of AI, machine
DBSCAN, ACM Trans. Database Syst. 42, 3, learning for information security.
Article 19, 2017.
[14] 14. Bin Li, Hu Luo, Haoxin Zhang, Shunquan Pham Sy Nguyen
Tan, Zhongzhou Ji, A multi-branch
Workplace: Informatics center, The
convolutional neural network for detecting
Government Office
double JPEG compression, Arxiv, 2017.
Email: phamsynguyen@chinhphu.vn
[15] Shahab Aslani, Michael Dayan, Loredana Education: Received Engineer’s
Storelli, Massimo Filippi, Vittorio Murino, degree in Information Security in
Maria A Rocca, Diego Sona, Multi-branch 2013; received Master’s degree in
Convolutional Neural Network for Multiple Information Security in 2016 from Academy of
Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation, Arxiv, Cryptography Techniques.
April 2019. Recent research direction: web hacking, malware
[16] Pengyi Hao, Xiang Gao, Zhihe Li, Jinglin detection, information security.
Zhang, Fuli Wu, Cong Bai, Multi-branch fusion
network for Myocardial infarction screening
from 12-lead ECG images, Computer Methods
and Programs in Biomedicine 184, 2020.
Số 2.CS (12) 2020 37 File đính kèm:
 detecting_web_attacks_based_on_clustering_algorithm_and_mult.pdf
detecting_web_attacks_based_on_clustering_algorithm_and_mult.pdf

