Bài giảng Lý thuyết mật mã - Chương 3: Hệ mật DES - Đỗ Trọng Tuấn
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric-key block
cipher published by the National Institute of Standards and
Technology (NIST).
In 1973, NIST published a request for proposals for a
national symmetric-key cryptosystem. A proposal from
IBM, a modification of a project called Lucifer, was
accepted as DES. DES was published in the Federal
Register in March 1975 as a draft of the Federal
Information Processing Standard (FIPS).
Thám mã hệ mật DES
Let’s try the first weak key to encrypt a block two times. After
two encryptions with the same key the original plaintext block is
created. Note that we have used the encryption algorithm two
times, not one encryption followed by another decryption.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7
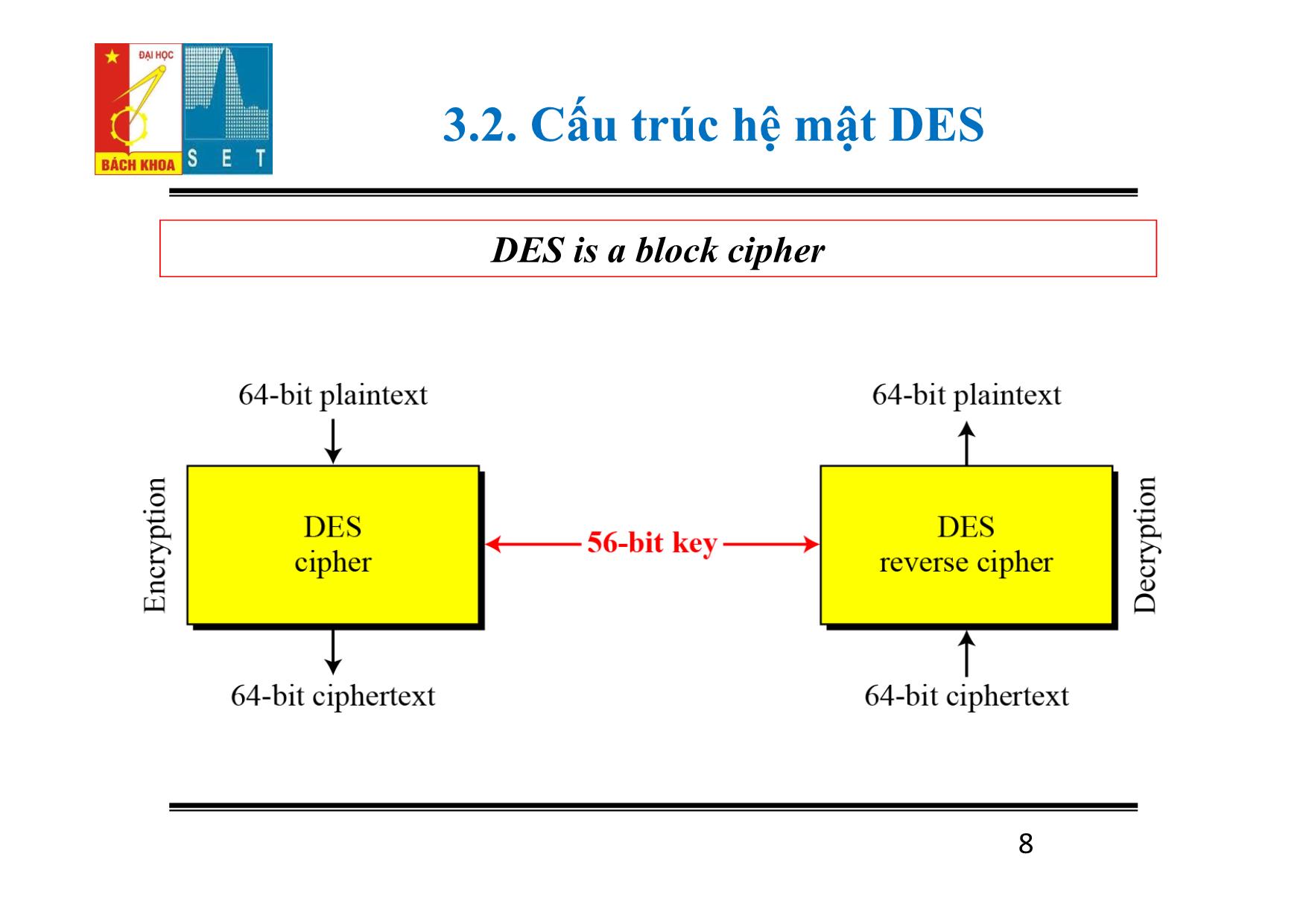
Trang 8
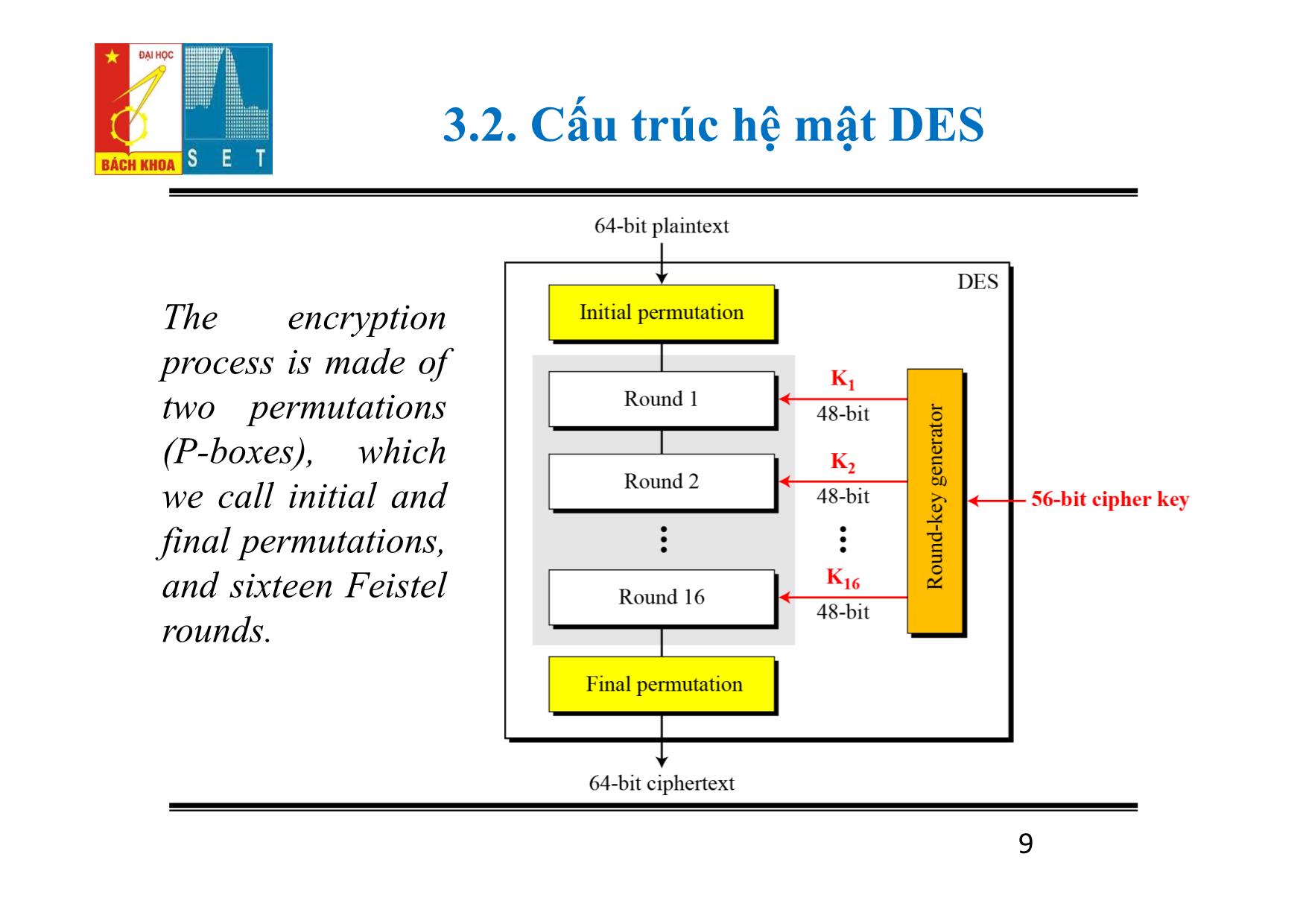
Trang 9
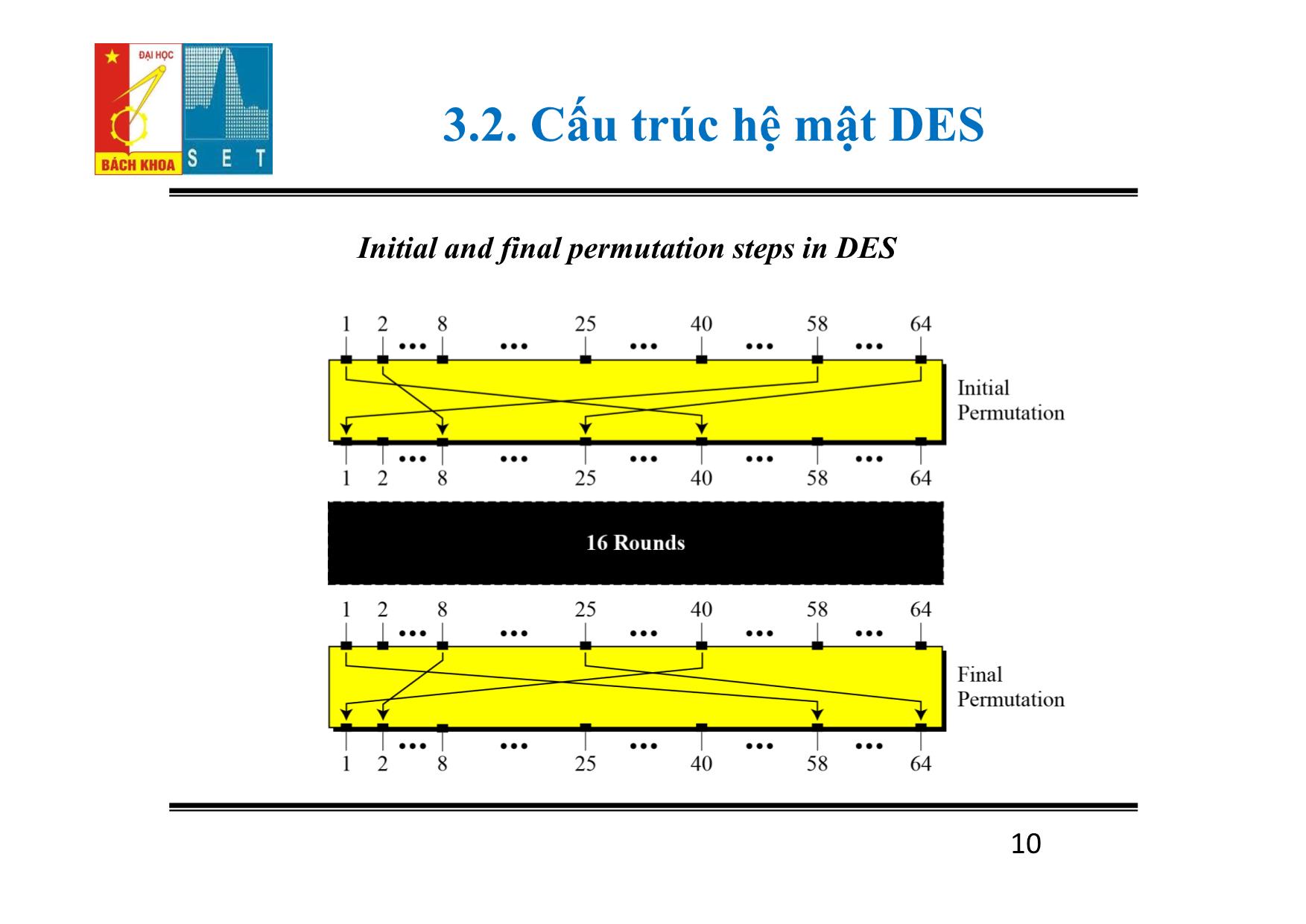
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Lý thuyết mật mã - Chương 3: Hệ mật DES - Đỗ Trọng Tuấn

TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC BÁCH KHOA HÀ NỘI VIỆN ĐIỆN TỬ - VIỄN THÔNG BỘ MÔN ĐIỆN TỬ HÀNG KHÔNG VŨ TRỤ Môn học: LÝ THUYẾT MẬT Mà Giảng viên: PGS.TS. Đỗ Trọng Tuấn Email: dotrongtuan@gmail.com 4/27/2016 1 Mục tiêu học phần Cung cấp kiến thức cơ bản về mật mã đảm bảo an toàn và bảo mật thông tin: Các phương pháp mật mã khóa đối xứng; Phương pháp mật mã khóa công khai; Các hệ mật dòng và vấn đề tạo dãy giả ngẫu nhiên; Lược đồ chữ ký số Elgamal và chuẩn chữ ký số ECDSA; Độ phức tạp xử lý và độ phức tạp dữ liệu của một tấn công cụ thể vào hệ thống mật mã; Đặc trưng an toàn của phương thức mã hóa; Thám mã tuyến tính, thám mã vi sai và các vấn đề về xây dựng hệ mã bảo mật cho các ứng dụng. 2 Nội Dung 1. Chương 1. Tổng quan 2. Chương 2. Mật mã khóa đối xứng 3. Chương 3. Hệ mật DES 4. Chương 4. Hàm băm và chữ ký số 5. Chương 5. Dãy giả ngẫu nhiên và hệ mật dòng 6. Chương 6. Kỹ thuật quản lý khóa 4/27/2016 3 Tài liệu tham khảo 1. A. J. Menezes, P. C. Van Oorschot, S. A. Vanstone, Handbook of applied cryptography, CRC Press 1998. 2. B. Schneier, Applied Cryptography. John Wiley Press 1996. 3. M. R. A. Huth, Secure Communicating Systems, Cambridge University Press 2001. 4. W. Stallings, Network Security Essentials, Applications and Standards, Prentice Hall. 2000. 4 Nhiệm vụ của Sinh viên 1. Chấp hành nội quy lớp học 2. Thực hiện đầy đủ bài tập 3. Nắm vững ngôn ngữ lập trình Matlab 5 Chương 3. Hệ mật DES 3.1. Giới thiệu sơ lược hệ mật DES 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 6 3.1. Sơ lược hệ mật DES The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric-key block cipher published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). In 1973, NIST published a request for proposals for a national symmetric-key cryptosystem. A proposal from IBM, a modification of a project called Lucifer, was accepted as DES. DES was published in the Federal Register in March 1975 as a draft of the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS). 7 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES DES is a block cipher 8 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES The encryption process is made of two permutations (P-boxes), which we call initial and final permutations, and sixteen Feistel rounds. 9 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Initial and final permutation steps in DES 10 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Initial and final permutation steps in DES 11 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Ví dụ Find the output of the final permutation box when the input is given in hexadecimal as: 12 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES The initial and final permutations are straight P-boxes that are inverses of each other. They have no cryptography significance in DES. 13 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES DES uses 16 rounds. Each round of DES is a Feistel cipher. 14 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES DES Function The heart of DES is the DES function. The DES function applies a 48-bit key to the rightmost 32 bits to produce a 32-bit output. 15 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Since RI−1 is a 32-bit input and KI is a 48-bit key. It needs to expand RI−1 to 48 bits. Expansion P-box 16 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES DES uses this table to define this P-box 17 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Whitener (XOR) After the expansion permutation, DES uses the XOR operation on the expanded right section and the round key. • Note that: • Both the right section and the key are 48-bits in length. • The round key is used only in this operation. 18 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES S-Boxes The S-boxes do the real mixing (confusion). DES uses 8 S-boxes, each with a 6-bit input and a 4-bit output. 19 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES 20 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES S-box 1 S-box 2 21 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES S-box 3 S-box 4 22 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES S-box 5 S-box 6 23 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES S-box 7 S-box 8 24 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Straight Permutation 25 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Using mixers and swappers, we can create the cipher and reverse cipher, each having 16 rounds. First Approach To achieve this goal, one approach is to make the last round (round 16) different from the others; it has only a mixer and no swapper. In the first approach, there is no swapper in the last round. 26 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Using mixers and swappers, we can create the cipher and reverse cipher, each having 16 rounds. 27 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Key Generation The round-key generator creates sixteen 48-bit keys out of a 56-bit cipher key. 28 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES 29 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES 30 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Key-compression table 31 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES Ví dụ We choose a random plaintext block and a random key, and determine what the ciphertext block would be (all in hexadecimal): 32 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES 33 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES 34 3.2. Cấu trúc hệ mật DES At the destination, Bob can decipher the ciphertext received from Alice using the same key. 35 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES Two desired properties of a block cipher are the avalanche effect and the completeness. Completeness effect Completeness effect means that each bit of the ciphertext needs to depend on many bits on the plaintext. 36 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES During the last few years critics have found some weaknesses in DES. Weaknesses in Cipher Design 1. Weaknesses in S-boxes 2. Weaknesses in P-boxes 3. Weaknesses in Key 37 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 38 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 39 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES Trong 2�� trường hợp khóa K có 4 khóa có độ an toàn rất kém đó là các khóa toàn 0 hoặc 1 40 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 41 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES Let’s try the first weak key to encrypt a block two times. After two encryptions with the same key the original plaintext block is created. Note that we have used the encryption algorithm two times, not one encryption followed by another decryption. Weak key should be avoided 42 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 43 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 44 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES A pair of semi-weak keys in encryption and decryption 45 3.3. Thám mã hệ mật DES 46
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_ly_thuyet_mat_ma_chuong_3_he_mat_des_do_trong_tuan.pdf
bai_giang_ly_thuyet_mat_ma_chuong_3_he_mat_des_do_trong_tuan.pdf

